What is business email compromise?
Business email compromise (BEC), a sophisticated cyberthreat, occurs when a bad actor gains access to an employee's work email account to trick someone into transferring money or to acquire sensitive data. This type of attack often involves impersonating a trusted individual within the organization, such as a CEO or vendor, and using social engineering techniques to manipulate employees into compliance.
How does a business email compromise work?
Business email compromise attack is a well-structured and planned campaign often targeting specific users of a company. In a BEC attack, adversaries pretend to be someone from within the organization who is at the top of the hierarchy or those with a lot of corporate clout to fast-track a transaction of large proportions.
Unlike standard phishing emails, BEC emails are carefully crafted to individuals within targeted organizations. The email will contain personal details or references that imitate an executive from intensive research to make the recipient believe that it is legitimate.
Since this attack often targets someone with a prominent stature in the organization, this type of cyberattack is also known as whaling and involves a series of steps to launch a successful attack.
Here is a breakdown of the steps involved:
How does a business email compromise work?
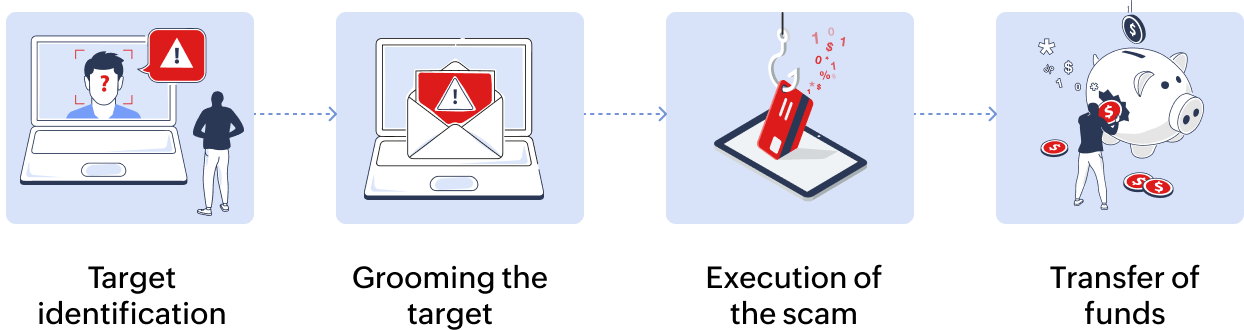
- Target identification Attackers gather information about the organization, its employees, and its structure using social media and company websites to identify key individuals with access to capital or sensitive information.
- Grooming the target Attackers reach out to the target pretending to be a trusted colleague or vendor using spear-phishing techniques.
- Execution of the scam Send emails requesting urgent wire transfers or payments or confidential business information, often citing time-sensitive business needs.
- Transfer of funds Victims receive detailed instructions for transferring funds to the attacker's account. Attackers may follow up to confirm receipt of funds or encourage further transactions.
Characteristics of business email compromise attacks
BEC attacks are particularly dangerous because they often do not involve malware or malicious links, making them harder for traditional email security systems to detect. Instead, these attacks rely heavily on social engineering tactics. Key characteristics include:
- Impersonation techniques: Attackers frequently use spoofed email addresses or lookalike domains (for example, using "zOhO.com" instead of "zoho.com") to trick recipients into believing they are communicating with legitimate contacts.
- Crafted messages that resonate: Emails are crafted based on information gathered during the targeting phase, making them appear credible and relevant.
- Inciting a sense of urgency: Many BEC emails create a sense of urgency, prompting quick responses without proper verification.
Types of business email compromise
The FBI classifies business email compromise into five major types of scams , each employing different tactics to deceive organizations. Here is a summary of these classifications:
- CEO fraud: Attackers impersonate a company executive, often the CEO, and send emails to employees, particularly in finance, requesting urgent wire transfers or sensitive information. This tactic exploits the perceived authority of high-ranking officials to bypass normal verification processes.
- Bogus invoice schemes: Cybercriminals impersonate legitimate vendors or suppliers, sending fake invoices that request payment into accounts controlled by the attackers. This often involves altering existing invoices to redirect payments.
- Account compromise: An attacker gains unauthorized access to an employee's email account, primarily through phishing techniques. The compromised account is then used to request payments from vendors or customers, often changing payment details to benefit the fraudster.
- Attorney impersonation: Scammers pose as legal representatives, requesting confidential information or funds under the guise of legal urgency. These requests are often made late in the day to make it seem time-sensitive to catch employees off guard.
- Data theft: Attackers target HR departments by impersonating trusted figures and requesting sensitive employee information. This data can be used for further attacks or sold on the dark web.
Who do BEC attacks usually target?
Business email compromise attacks target various roles within organizations, primarily focusing on individuals who have access to sensitive information or financial resources. Here is a detailed list of individuals who are likely to be targeted by these attacks and the reasoning behind it:
| Role | Reason for being targeted |
|---|---|
| Executives (for example, CEO, CFO) | Executives are often authorized to approve large transactions and make critical financial decisions, making them prime targets for scams that seek immediate compliance. |
| Accounts payable staff | Accounts payable staff handle sensitive payment information and transactions, making them susceptible to scams involving fake invoices or unauthorized payment requests. |
| Finance personnel | Individuals in finance roles have access to banking details and payment methods, making them attractive targets for BEC scams that aim to redirect funds or gather sensitive financial information. |
| Human resources staff | HR personnel manage employee records that contain sensitive personal information, such as Social Security numbers and tax statements. Attackers may impersonate executives to gain access to this data for identity theft or fraud. |
| Legal counsel | Legal professionals are involved in contracts and legal transactions that can be manipulated for scams. |
| New employees | New hires may lack familiarity with company protocols and communication styles, making them easier targets for attackers. |
What makes executives prime targets for BEC attacks?
Executives are particularly vulnerable to business email compromise attacks due to several key factors.
- The high-profile positions of an organization's executives make them prime targets for attackers who often impersonate them to exploit their authority and
- Attackers conduct extensive research on executives, leveraging publicly available information to craft convincing emails that appear legitimate. This impersonation is effective because employees might feel compelled to comply with requests from someone in a senior role without verifying the authenticity of the communication.
- Executives typically have access to sensitive information and financial resources, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals seeking to execute fraudulent transactions or steal confidential data.
- The sense of urgency in BEC communications further intensifies this vulnerability, as busy executives might overlook oddities while trying to respond quickly.
- Many executives might not receive adequate cybersecurity training, leaving them less prepared to recognize phishing attempts or suspicious requests, which increases their susceptibility to these sophisticated scams.
Best practices to protect your business from BEC attacks
To mitigate the risk of falling victim to BEC scams, organizations should implement a combination of the mentioned practices:
- Email authentication protocols: Utilize protocols such as Sender Policy Framework (SPF), DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM), and Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance (DMARC) to verify the authenticity of incoming emails and prevent spoofing.
- Multi-factor Authentication: Enforce MFA across all email accounts. This adds an additional layer of security beyond passwords, making unauthorized access significantly more difficult.
- Secure payment processes: Implement strict financial controls for authorizing wire transfers and sensitive transactions. Consider using secure payment platforms that require additional verification steps for payment changes.
- Security awareness training: Conduct regular training sessions to educate employees about recognizing phishing attempts and suspicious emails. Simulating BEC scenarios can help reinforce these lessons.
- Timely software updates: Keep all software, including email servers and antivirus programs, up-to-date to protect against vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
- Employing email security gateways: ESGs analyze incoming and outgoing email traffic for signs of malicious activity. They utilize spam filters, antivirus scanning, and behavioral analytics to detect and block phishing attempts, including BEC attacks.
To fortify cybersecurity defenses, organizations can implement additional layers of security using tools like SIEM and UEBA. These tools facilitate continuous monitoring of network entities and events, improving the detection of IoCs and enabling effective incident response workflows.
How to prevent business email compromise with ManageEngine Log360
ManageEngine Log360 is a comprehensive SIEM solution that offers various features to help organizations defend against cyberattacks, including BEC attacks.
Log360 integrates with open-source threat intelligence feeds, such as STIX/TAXII, which provide real-time data on known phishing domains, malicious IP addresses, and stolen credentials. This integration enriches log data with actionable threat intelligence, enabling security teams to correlate user activity with current threat landscapes.
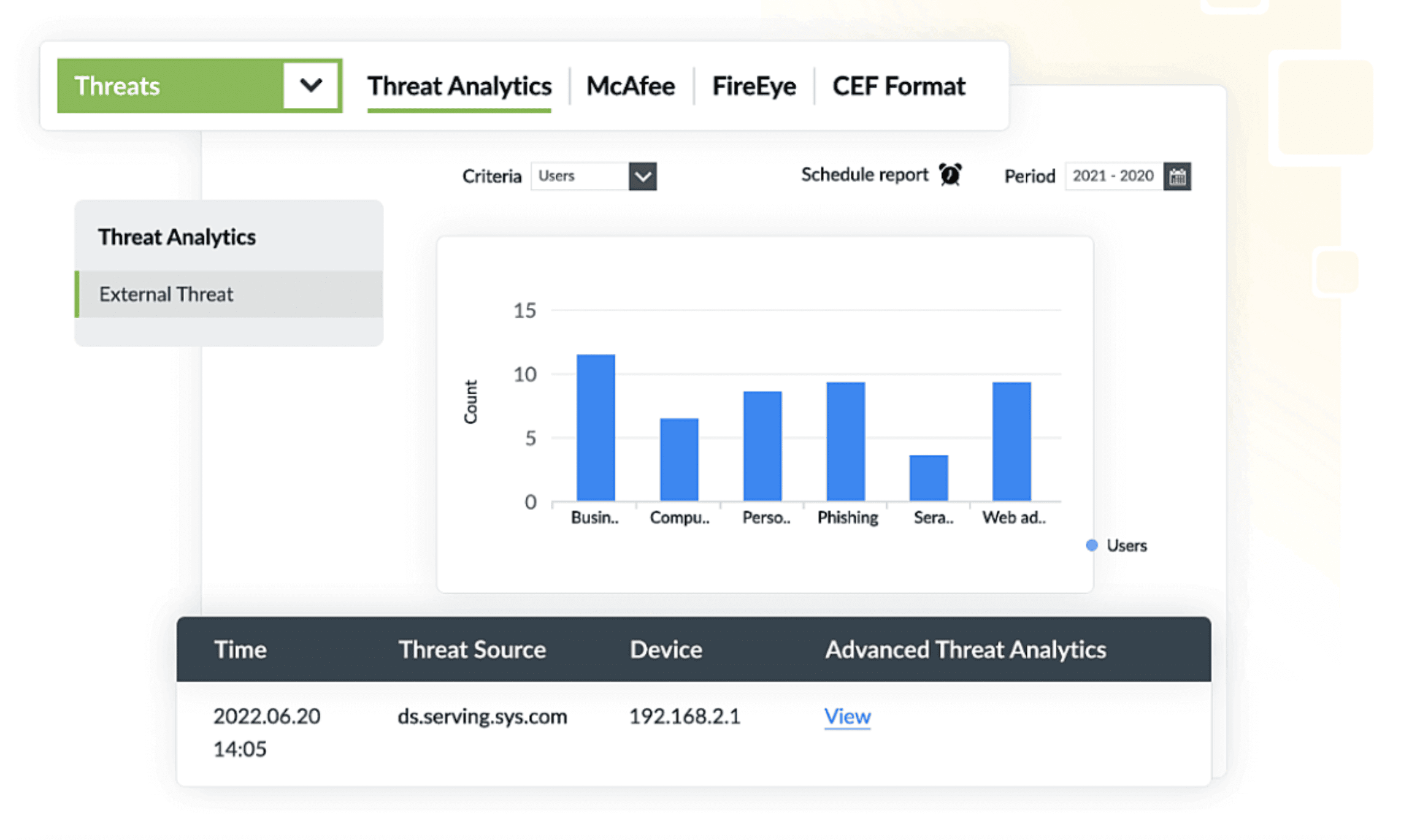
Log360 also employs machine learning to analyze user behavior patterns and identify anomalies. This solution flags unusual activities, such as sudden changes in access patterns or attempts to access unauthorized resources. By detecting these potential IoCs, organizations can respond swiftly to possible social engineering threats before they escalate.
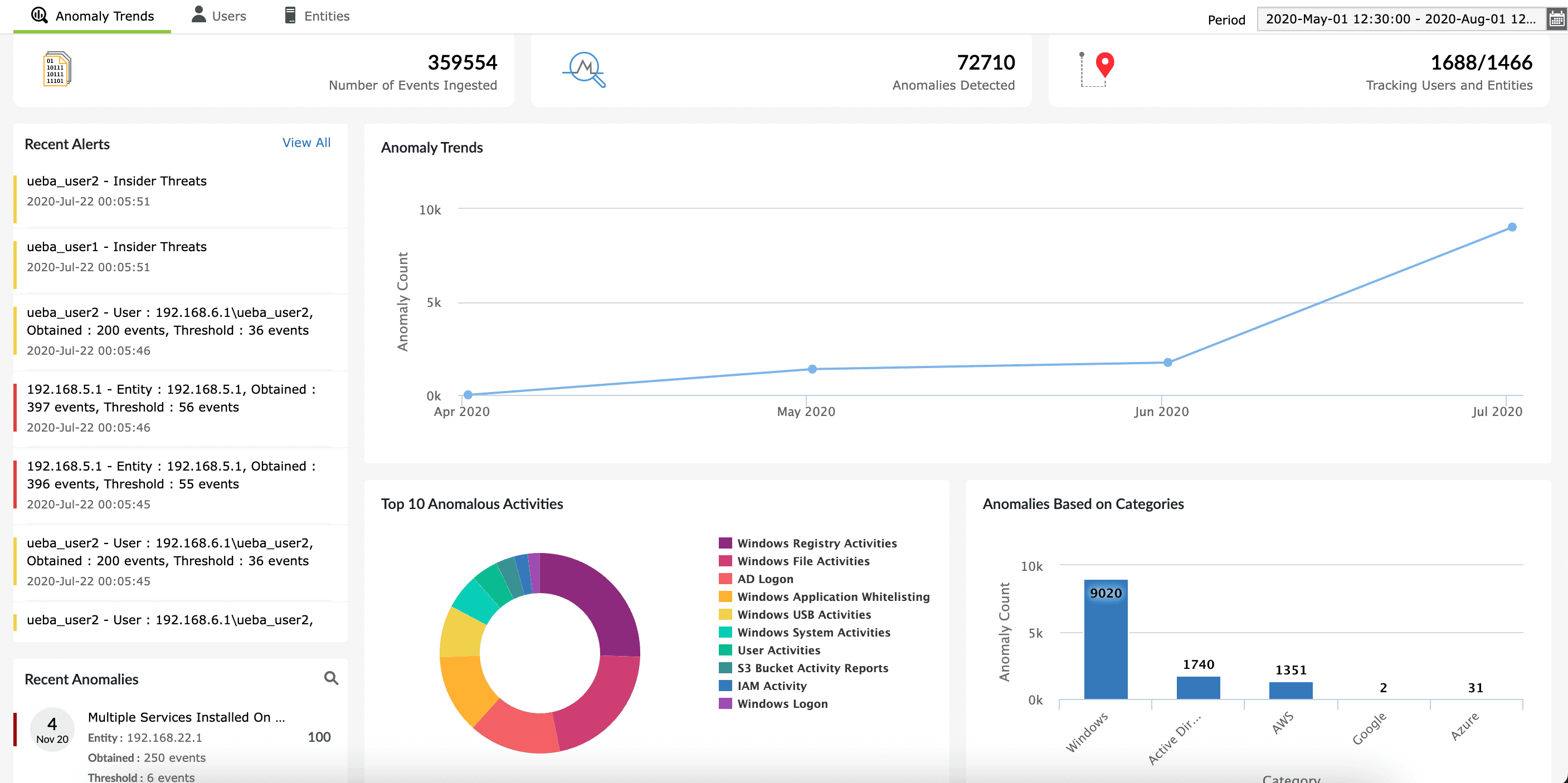
Log360 sends real-time alerts for suspicious activities detected within the network. Organizations can set up custom alerts based on specific criteria related to social engineering tactics, ensuring that security teams are promptly informed of potential threats. This immediate notification allows for quick action to prevent BEC attacks from succeeding.
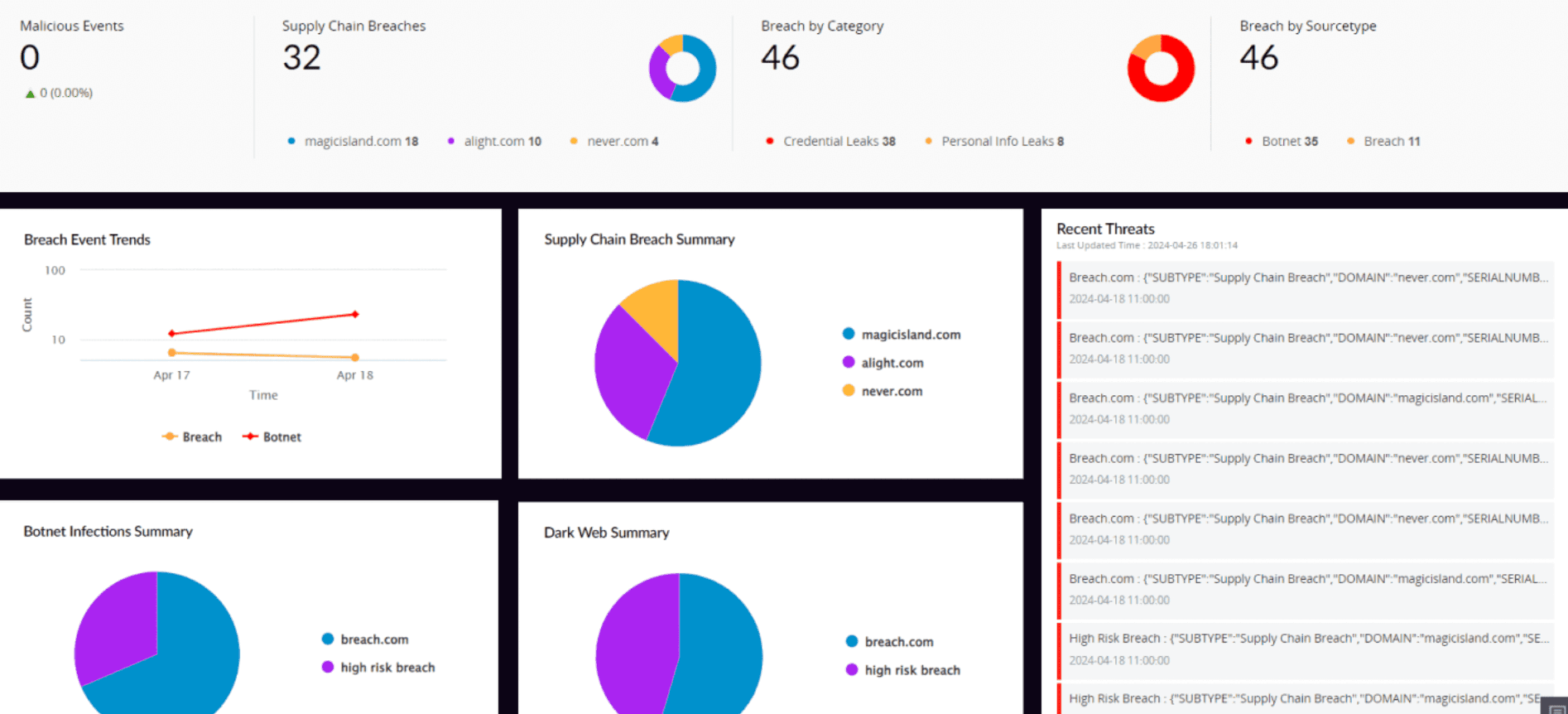
Log360 provides dark web monitoring capability that scours the concealed part of the internet for the exposure of PIIs, such as credentials, Social Security numbers, credit card numbers, email addresses, and domain names, creating a unified view of potential vulnerabilities that can be exploited by threat actors.
The platform provides instant notifications whenever compromised data is found in the illicit data market. This real-time alert system empowers security teams to respond swiftly to potential threats, reducing the window of opportunity for attackers to exploit leaked credentials.
With Log360's comprehensive features that safeguard against dark web threats, security teams gain valuable insights into compromised business emails in the dark web instantly, enabling them to quickly devise incident response strategies to suppress attacks before they cause problems.
What's next?
Try our 30-day free trial to explore the powerful features of Log360 to defend against advanced forms of cyberattacks.
- What is business email compromise?
- How does a business email compromise work?
- Characteristics of business email compromise attacks
- Types of business email compromise
- Who do BEC attacks usually target?
- What makes executives prime targets for BEC attacks?
- Best practices to protect your business from BEC attacks
- How to prevent business email compromise with ManageEngine Log360