Notification Settings
Last updated on:
In this page
Overview
This page outlines how to configure notification settings for sending reports and alerts via email and SMS.
You can customize these settings to align with your organization's communication preferences. Scheduled and automatically generated reports are distributed through email, and alerts can be sent through both email and SMS channels.
You can configure the email and SMS settings to align with your organization's notification preferences.
Prerequisite
Ensure that the SMS gateway or modem server is reachable and that valid credentials and connection parameters are configured.
Email settings
To configure or change email settings,
- Navigate to Settings > System Settings > Notification Settings > Mail Settings.
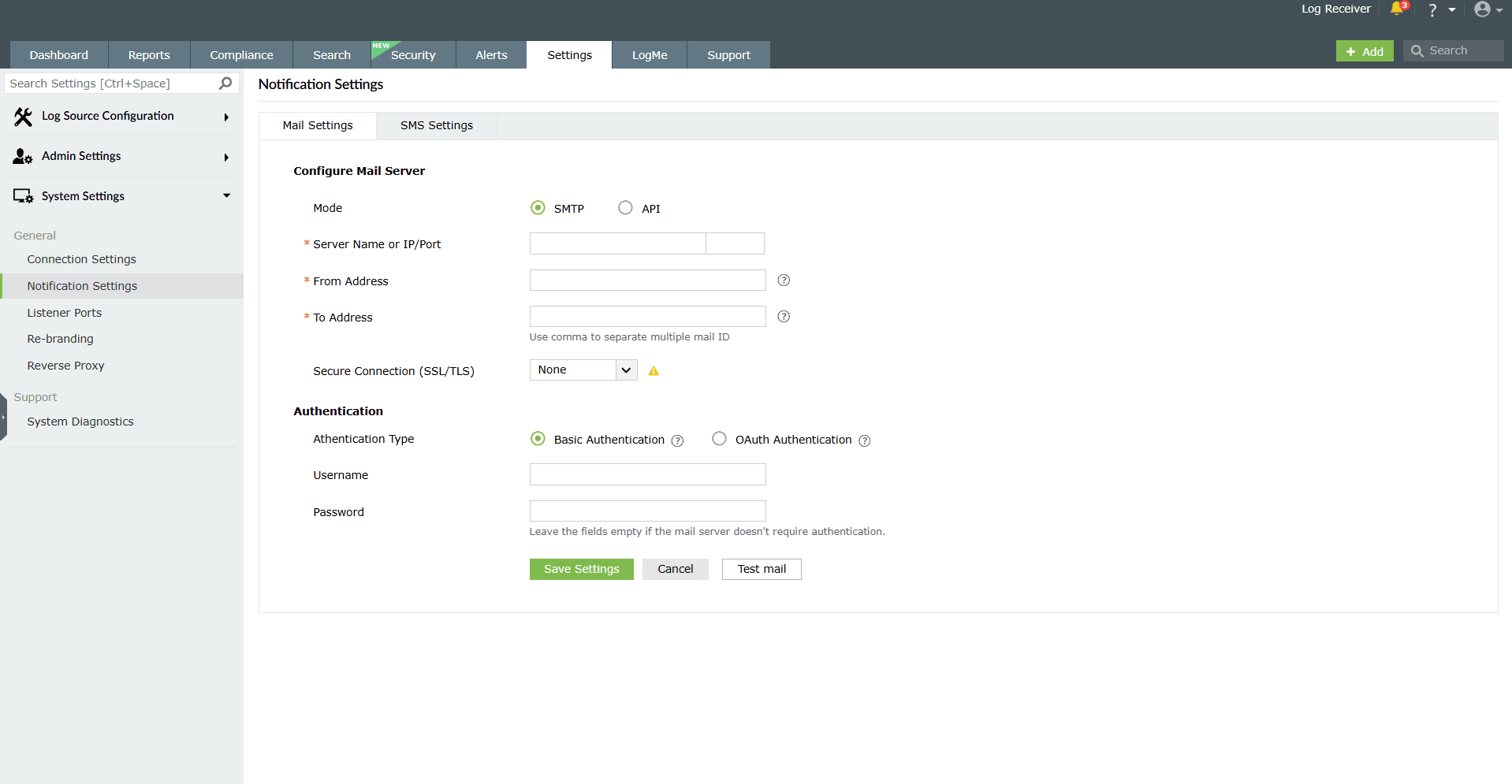
Image 1: Mail server settings configuration
The product console provides two modes of mail server configuration:
SMTP
This method allows you to create and authenticate a mail server via Basic or OAuth authentication.
To configure an SMTP mail server,
- In the choice of Mode, select SMTP.
- Enter your mail server's Server Name or IP, and Port Number in the respective fields.
- In the From Address field, enter the email address that will be used to send out notifications, alerts, etc., from the product console.
- In the To Address field, enter your email address to receive notifications for the emails sent from the product console.
- Select the connection security type from the available options: SSL, TLS, or None.
- Select the authentication type from the options provided:
- Basic authentication
- OAuth authentication
Basic authentication
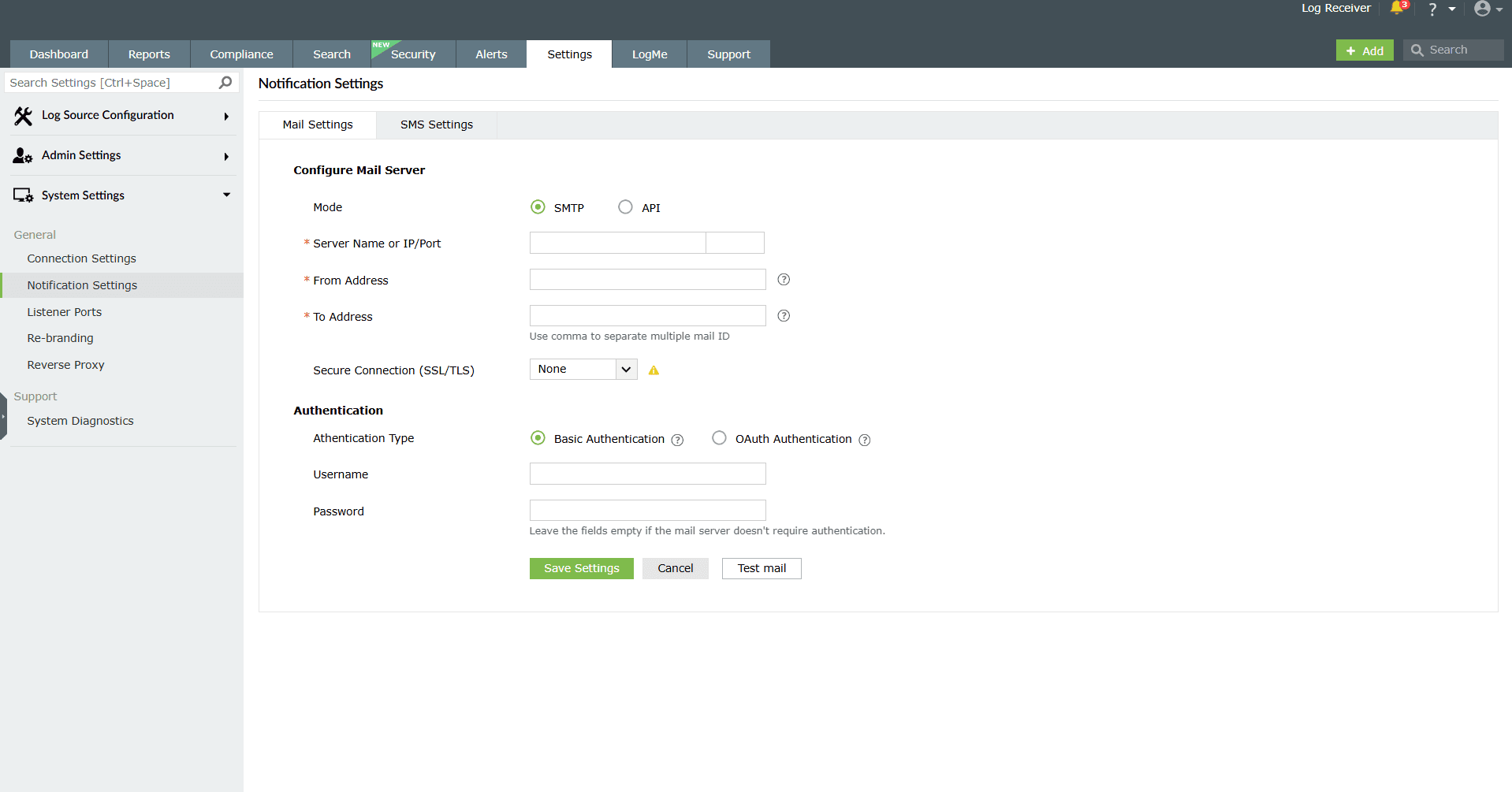
Image 3: Basic authentication method - Enter the Username and Password to access the mail server.
- If your mail server does not require authentication, leave the fields empty.
OAuth authentication
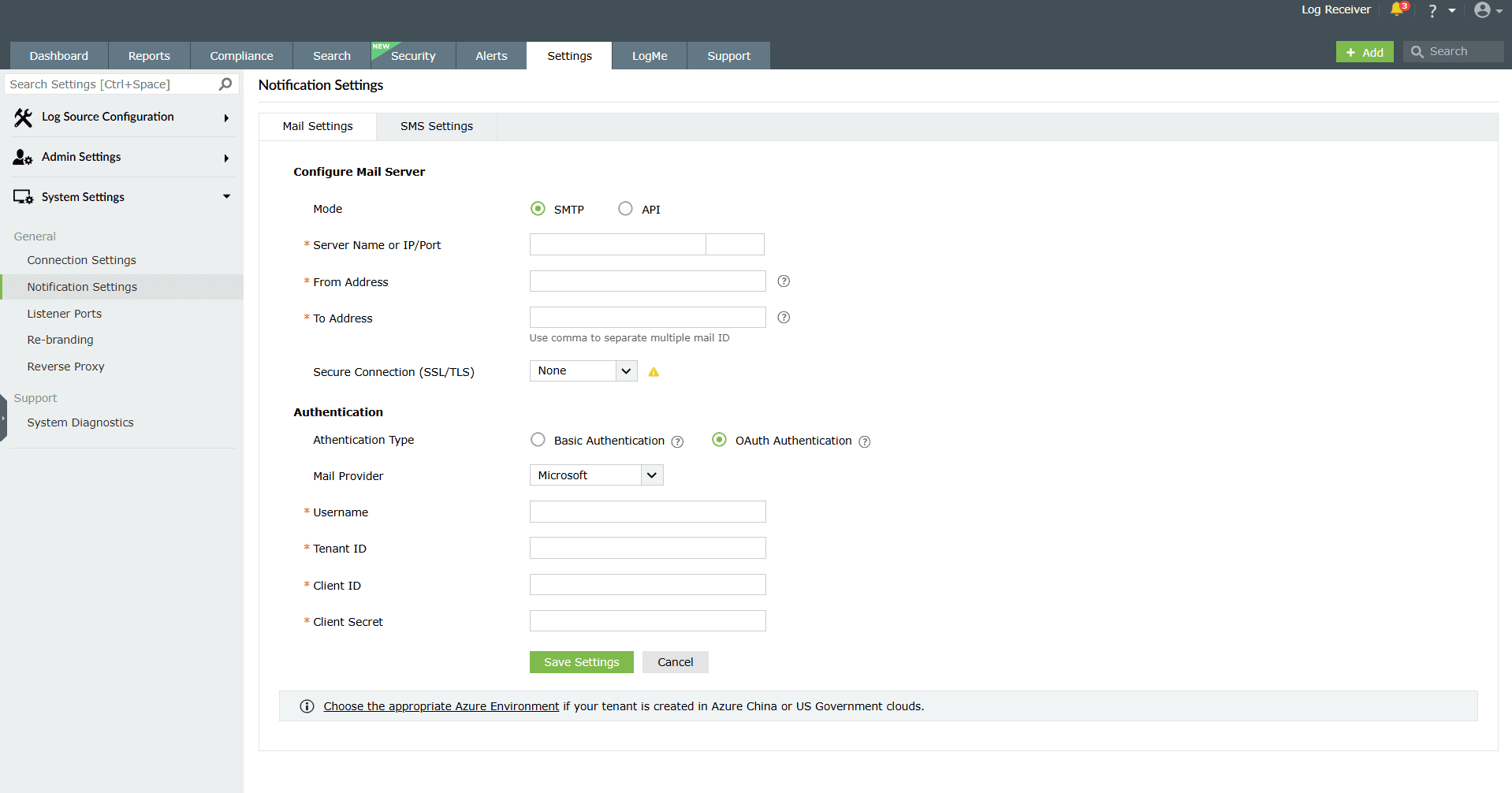
Image 4: OAuth authentication method - Select your mail provider from the available options: Microsoft or Google.
- If your mail provider is Microsoft, provide the Username, Tenant ID, Client ID, and Client Secret in the respective fields. In the product, the Azure Cloud is considered the default Azure environment. You can modify the Azure environment setting by clicking the Choose the appropriate Azure environment link.
NOTE To learn how to find your Azure Tenant ID, Client ID, and Client Secret, refer to the Steps to find your Azure Tenant ID, Client ID, and Client Secret for SMTP mail server configuration section below. - If you have selected Basic Authentication in step 6, you can have Log360 send a test email by clicking the Test Mail button.
- Click Save Settings to save your mail server configuration.
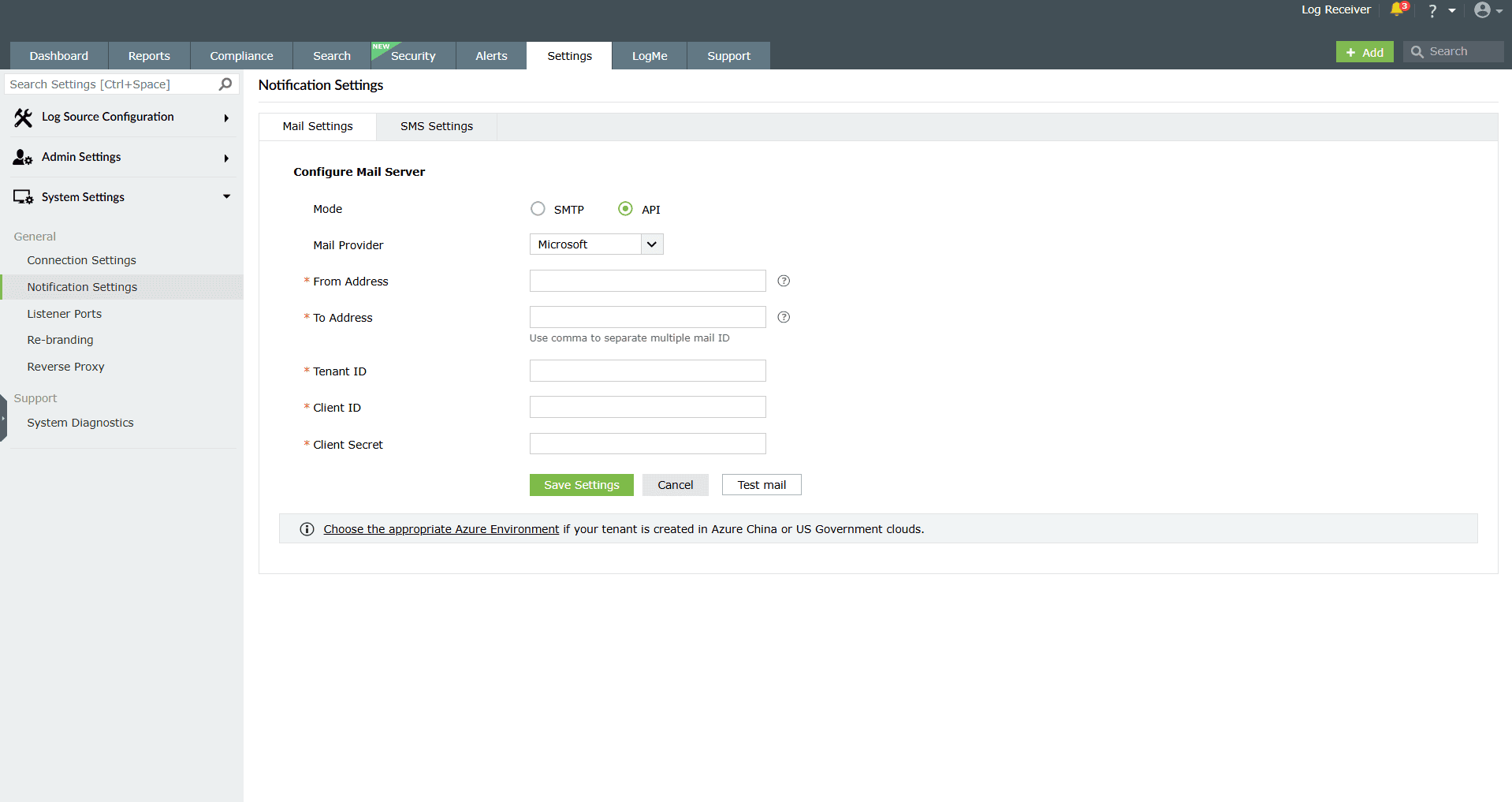
Image 5: Mail settings configuration through API
Steps to find your Azure Tenant ID, Client ID, and Client Secret for SMTP mail server configuration
- Log in to portal.azure.com.
- Under Azure services, click App registrations → New registration.
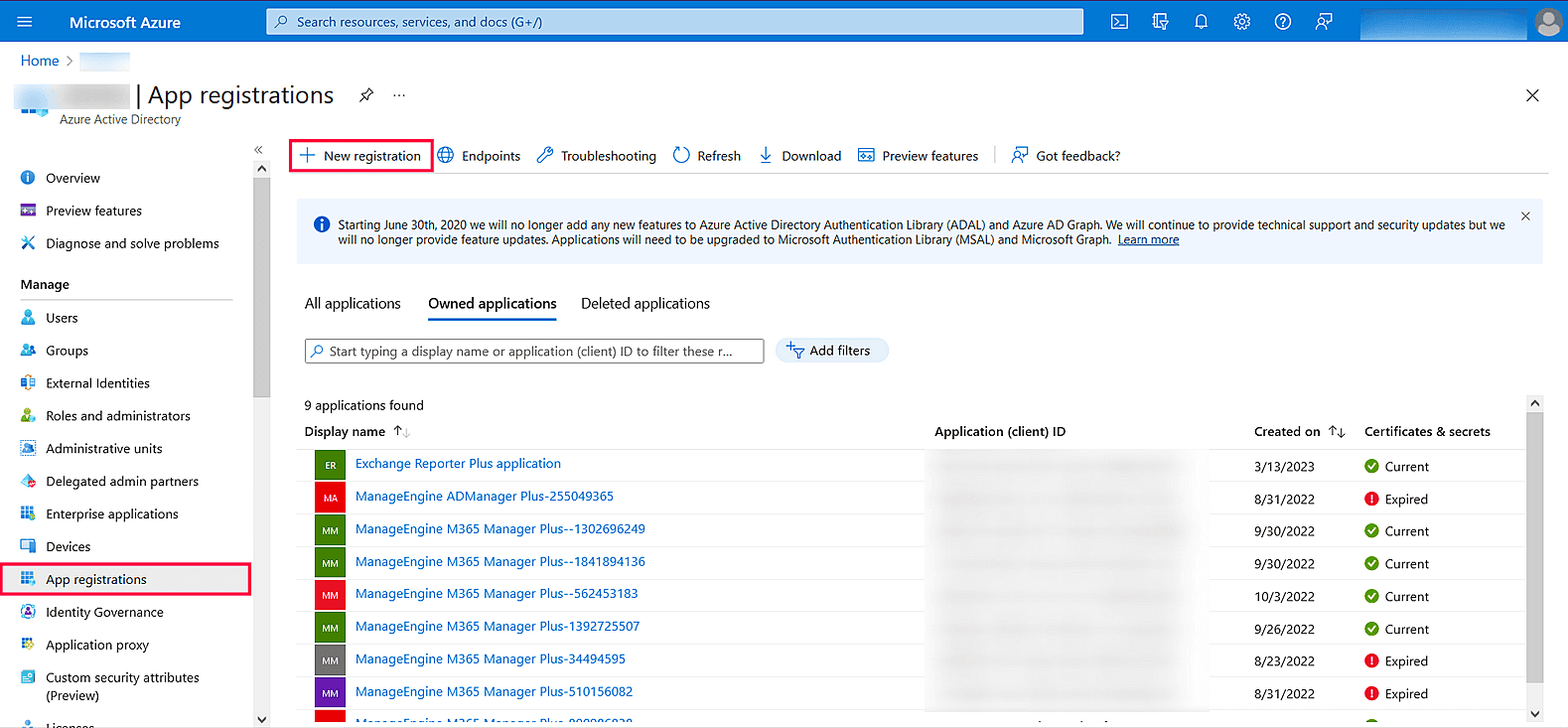
Image 6: New registration in Azure services - Provide a Name of your choice and select the Supported account types. (Leave it as default.)
- In the Redirect URI field, select web & paste the following OAuth link: https://identitymanager.manageengine.com/api/public/v1/oauth/redirect (or) You can also add the localhost redirect API in the following syntax:
- protocol://localhost:port_number/context_if_any/RestAPI/WC/OAuthSetting
- For example, http://localhost:8095/event/RestAPI/WC/OAuthSetting. If you have only added localhost as the redirect URI, you must access the product using localhost to configure mail server.
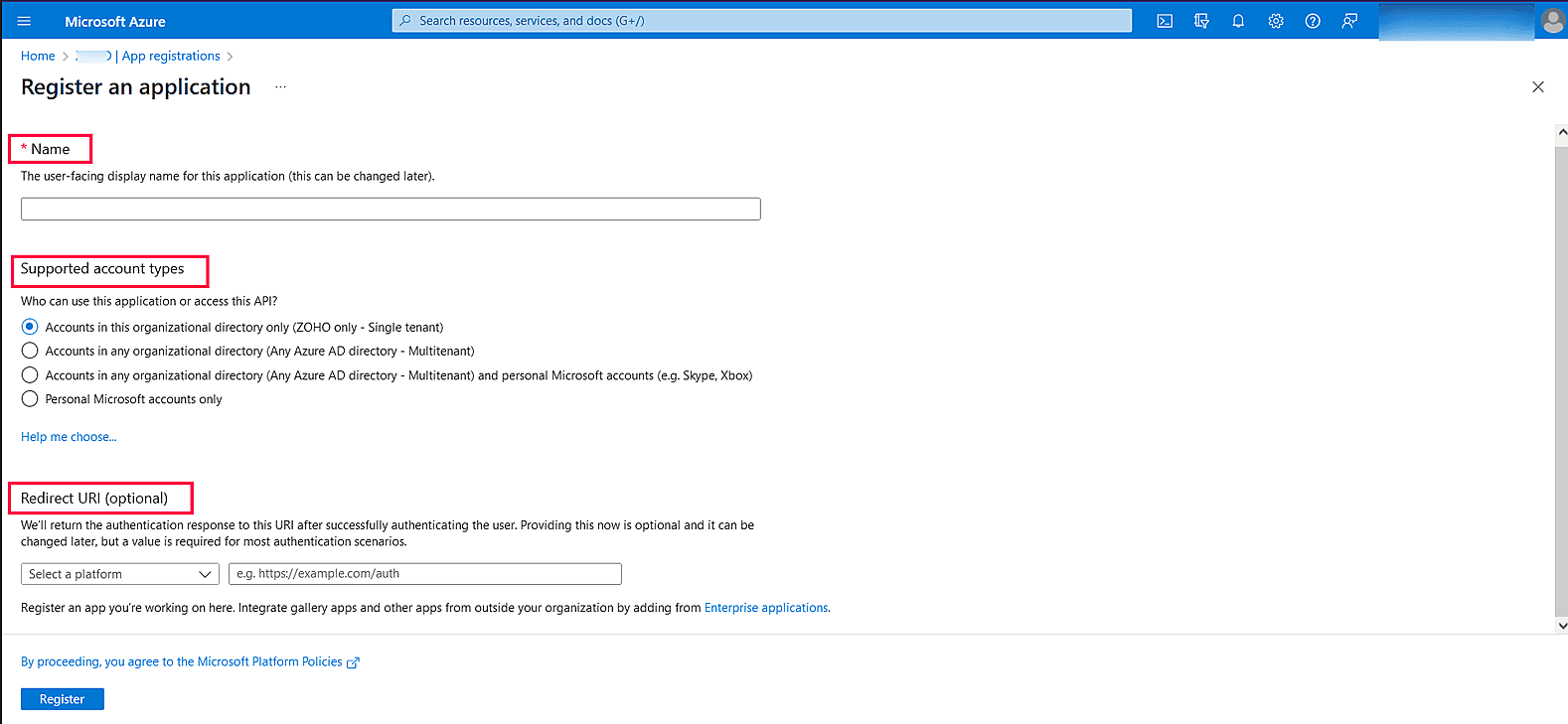
Image 7: Register an application in Azure services - On the next page, you will find the application details. Copy the Client ID & Tenant ID.
- From the left pane, click Certificates & secrets → New client secret.
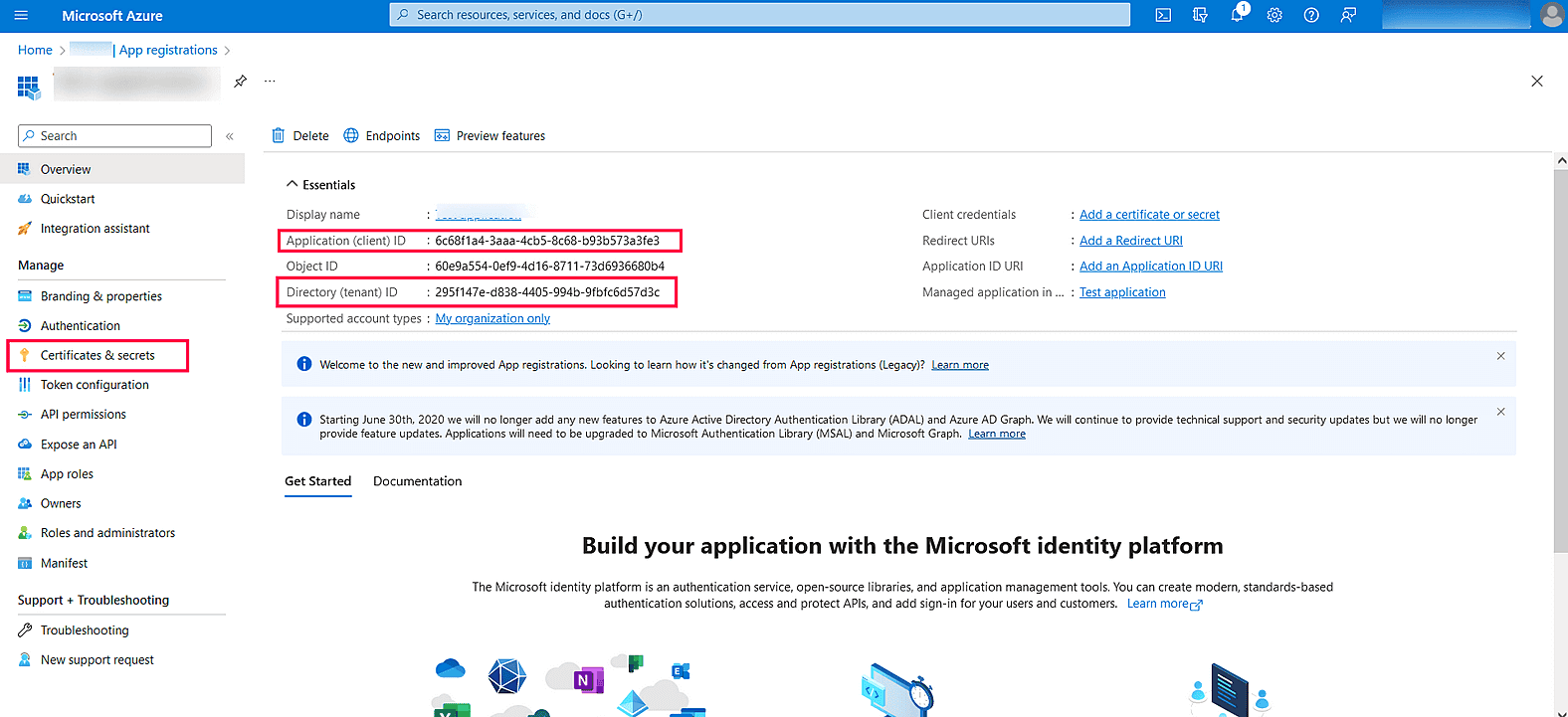
Image 8: New client secret in Azure services - Provide a Description for the client secret, and in the Expires field, choose the validity of the client secret and click Add.
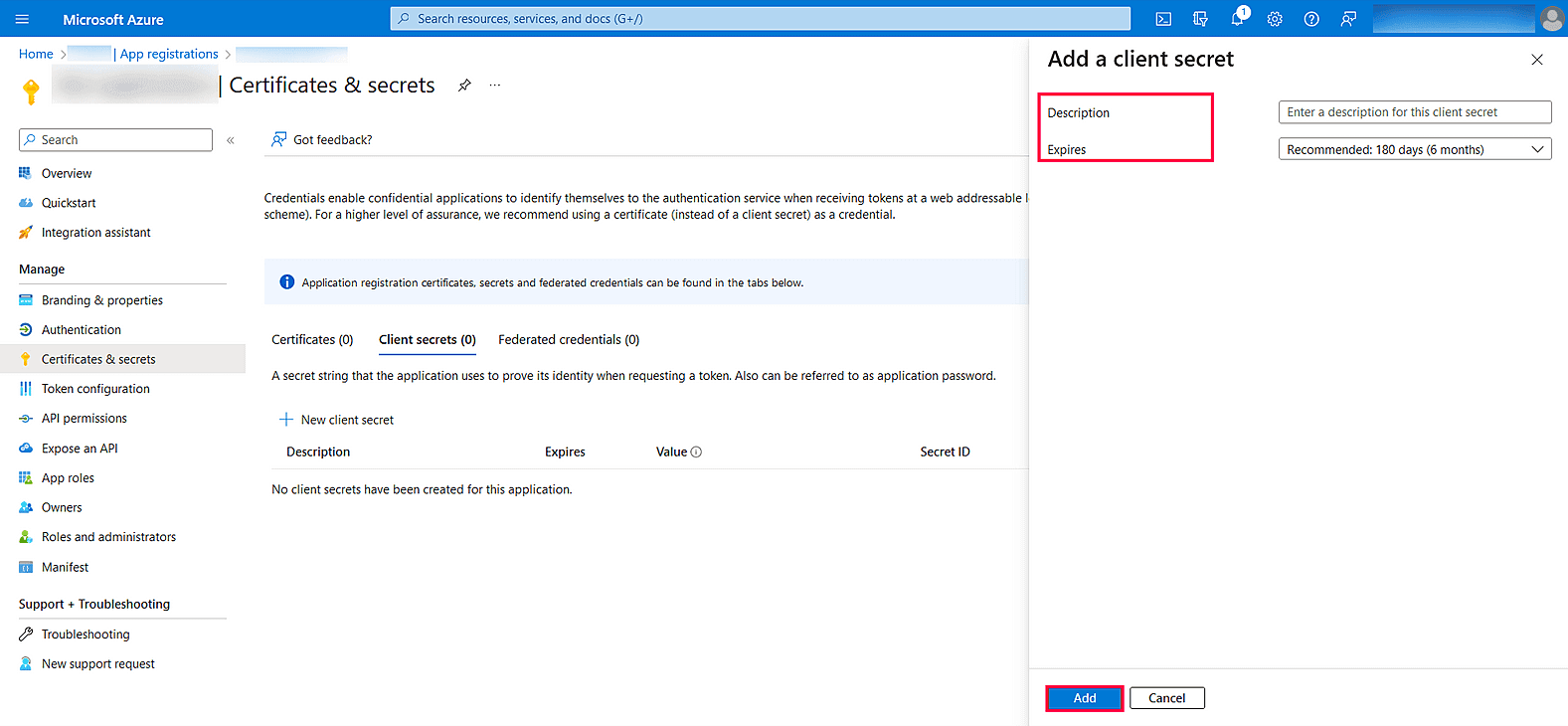
Image 9: New client secret in Azure services - The client secret will be generated. Copy the string displayed under Value.
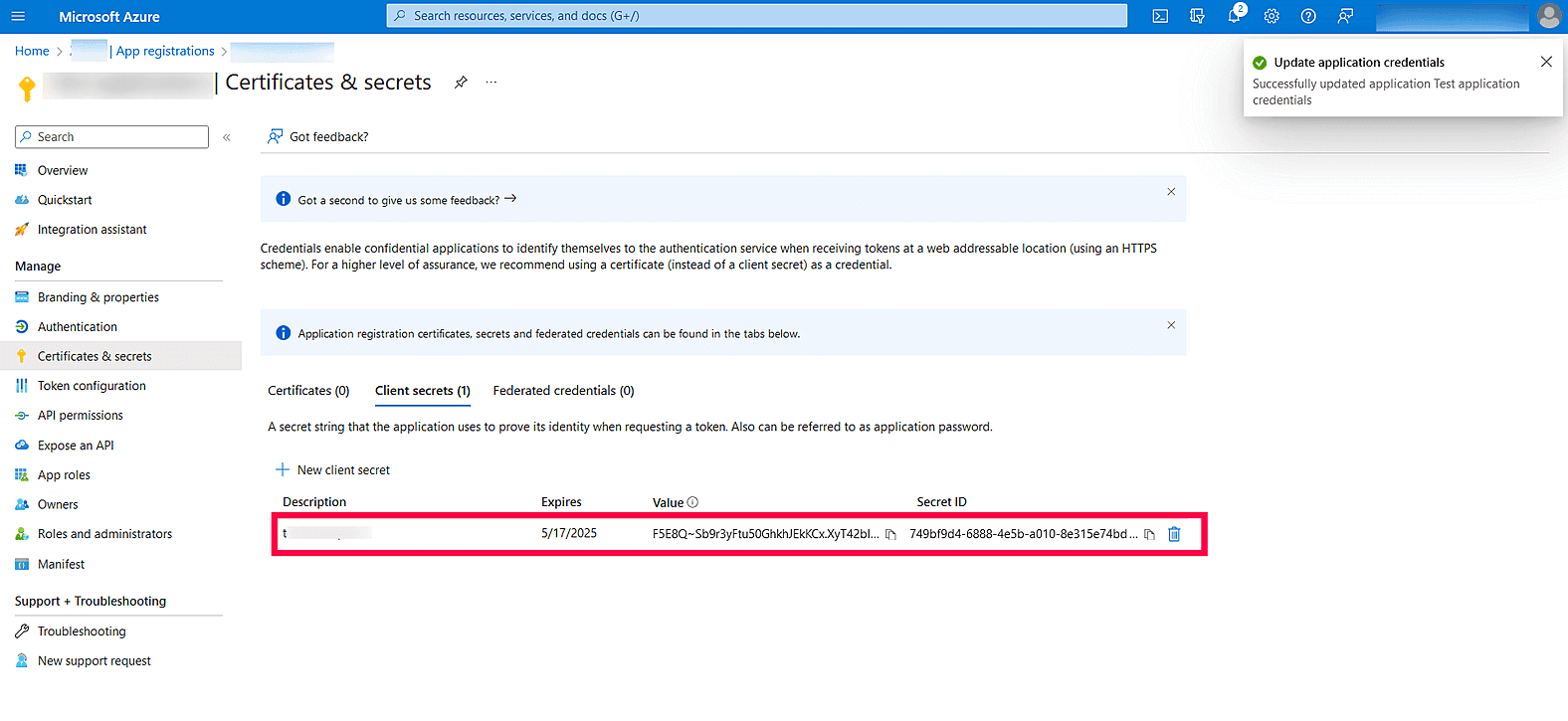
Image 10: The generated client secret in Azure services - Click Save setting and complete the authorization prompt.
Steps to find your Google Workspace Client ID, and Client Secret for SMTP mail server configuration
- Log in to console.developers.google.com.
- In the dashboard, select any existing project or click New Project from the project dropdown list.
NOTE If you are selecting an existing project, skip to step 10.
Image 11: New project in Google workspace 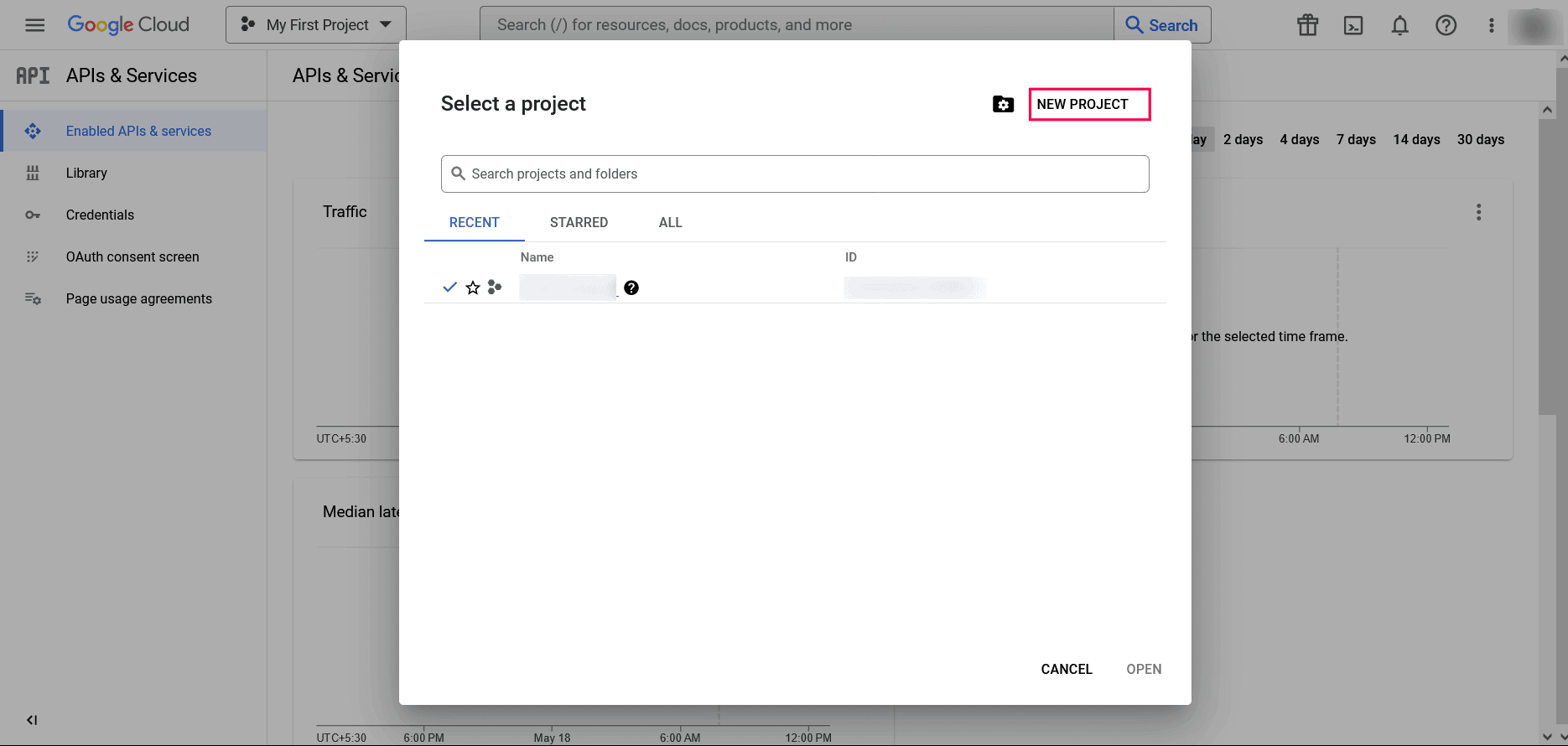
Image 12: New project in Google workspace - Enter the Project Name. In the Location field, click BROWSE and select the parent organization. Click CREATE.
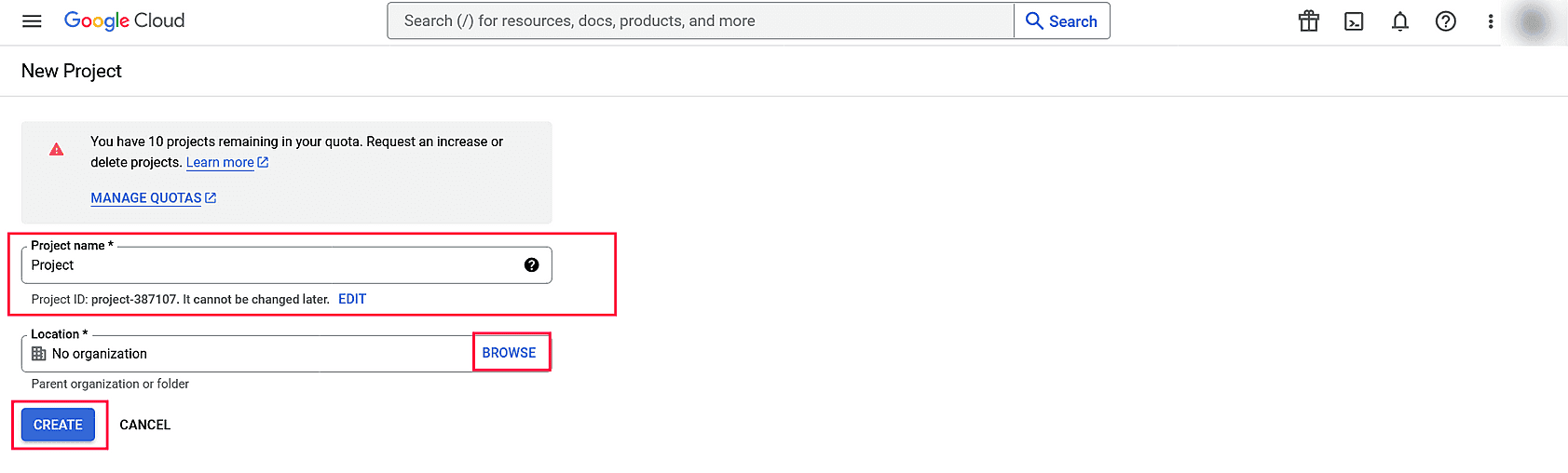
- Once the project has been created, click SELECT PROJECT from the notification prompt.
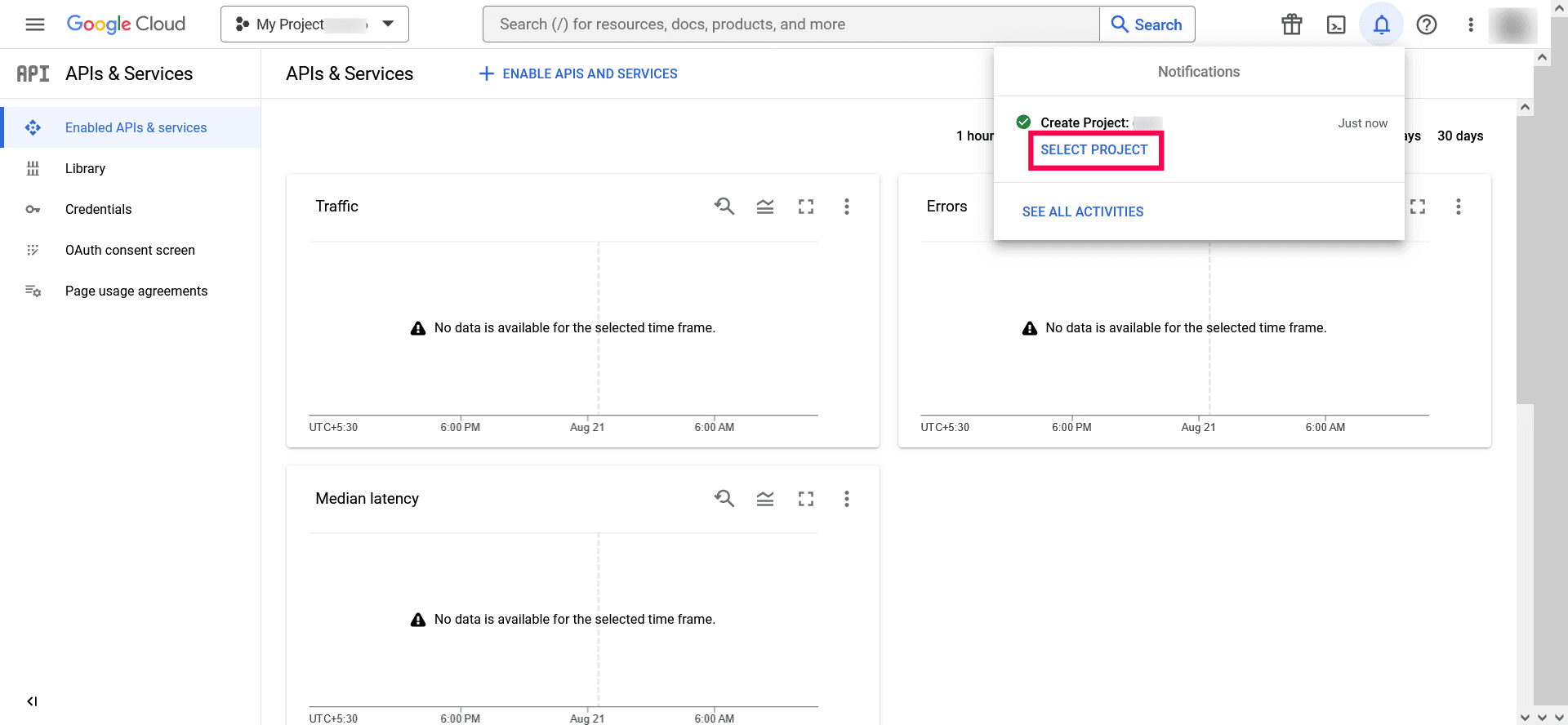
Image 13: Selecting project in Google workspace - In the left pane of the displayed project details page, go to APIs & services → Library.
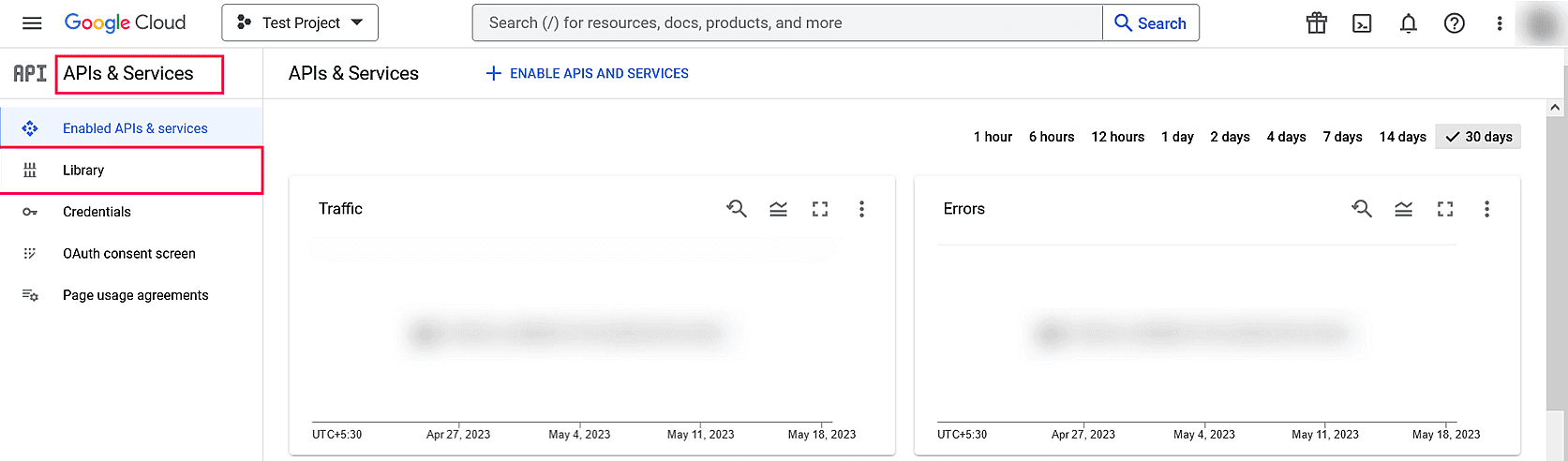
- From the available list of APIs, select Gmail API and click Enable. You can use the search option to find the API quickly.
- In the left pane, click the OAuth consent screen and choose the User Type. If you don't have a Google Workspace account, choose External.
- Click CREATE.
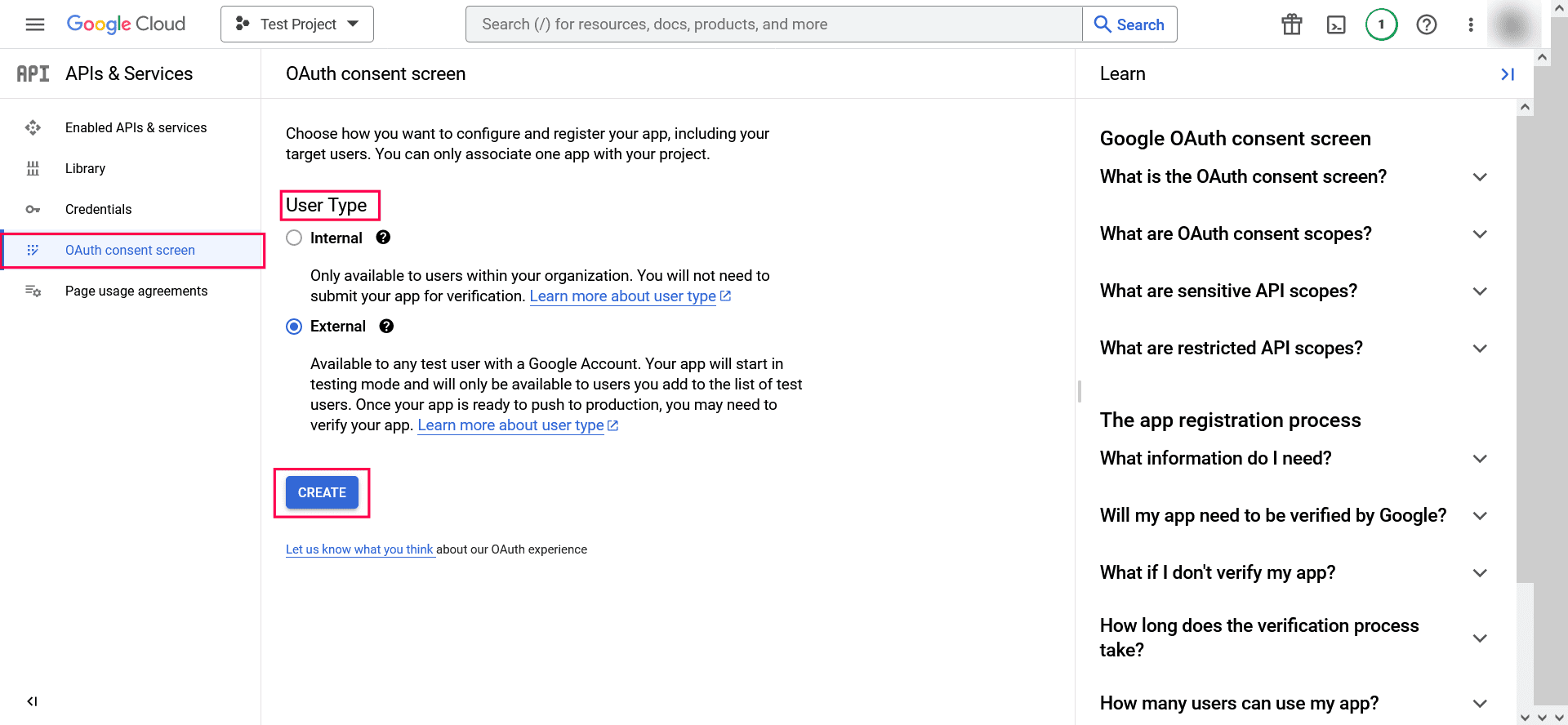
Image 14: Selecting project in Google workspace - In the Edit App Registration screen, provide the Application Name, Application Logo, and the email address of your help desk, developer information, and click Save and Continue.
- In the Scopes screen, click Add or Remove Scopes, choose Gmail API (https://mail.google.com/), and click Update.
- Click Save and Continue.
- In the Test Users screen, add a test user and click Save and Continue.
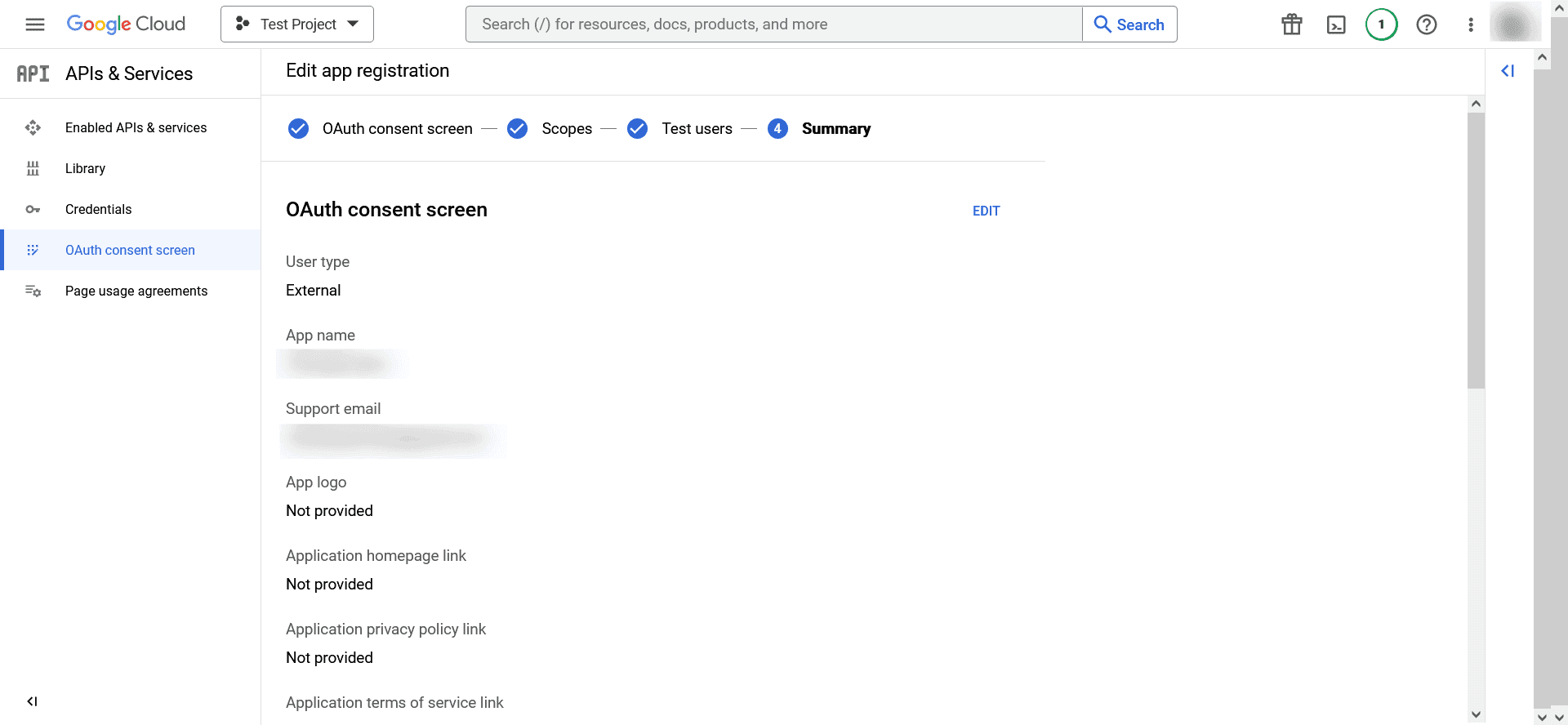
Image 15: Adding test user in Google workspace - In the left pane, click Credentials → CREATE CREDENTIALS → OAuth client ID.
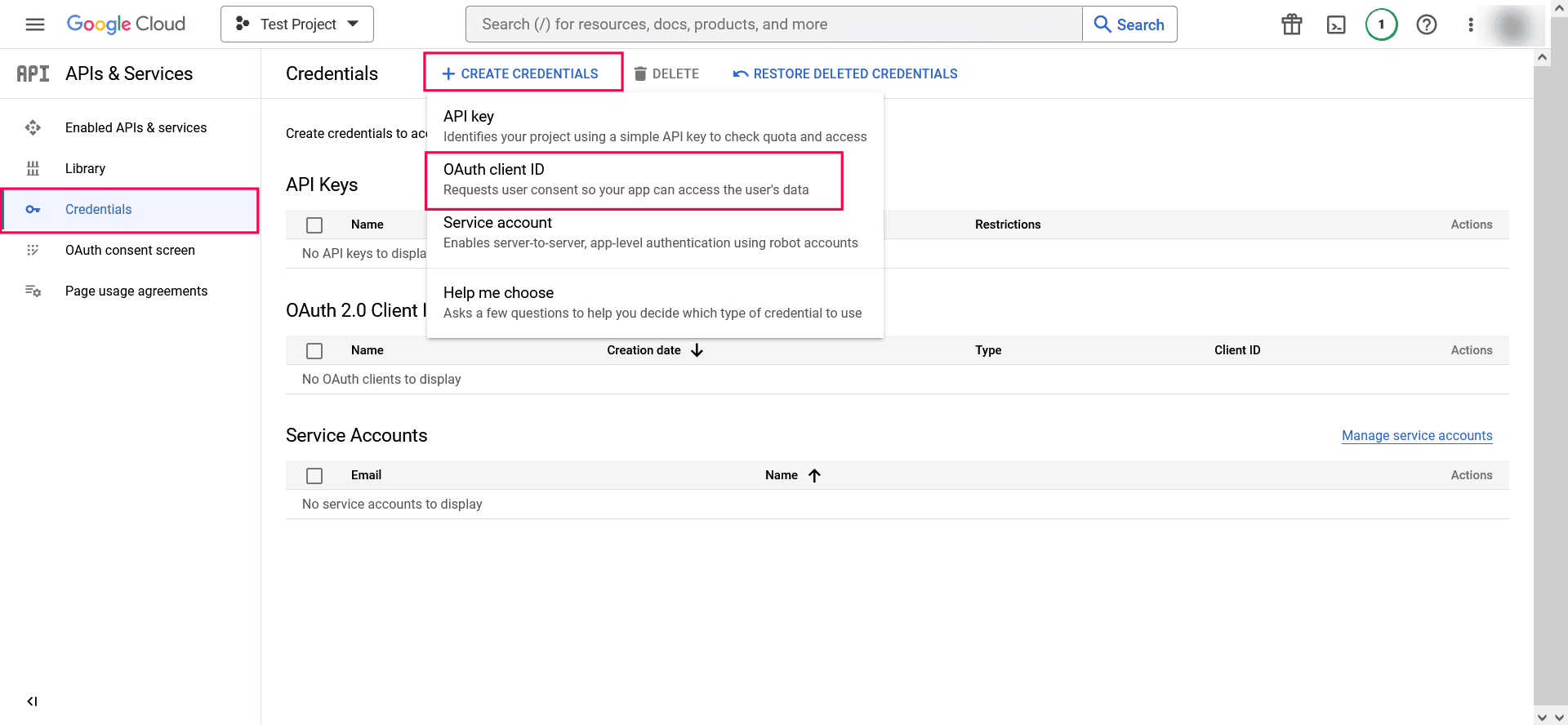
Image 16: Create credentials in Google workspace - Select the application type as Web Application. Provide a name of your choice.
- In the Authorized Redirect URIs, paste the following OAuth link:
https://identitymanager.manageengine.com/api/public/v1/oauth/redirect (or)
You can also add localhost redirect API in the following pattern:
protocol://localhost:port_number/context_if_any/RestAPI/WC/OAuthSetting
For example: http://localhost:8365/RestAPI/WC/OAuthSetting
NOTE If you have only added localhost as the redirect URI, you must access the product using localhost to configure the mail server. - Click CREATE.
- Click DOWNLOAD JSON to download the file containing the authorization server details. Copy the Client ID and Client secret displayed on the screen.
- You can now paste the copied client ID and client secret in their respective fields while configuring OAuth authentication for your mail server.
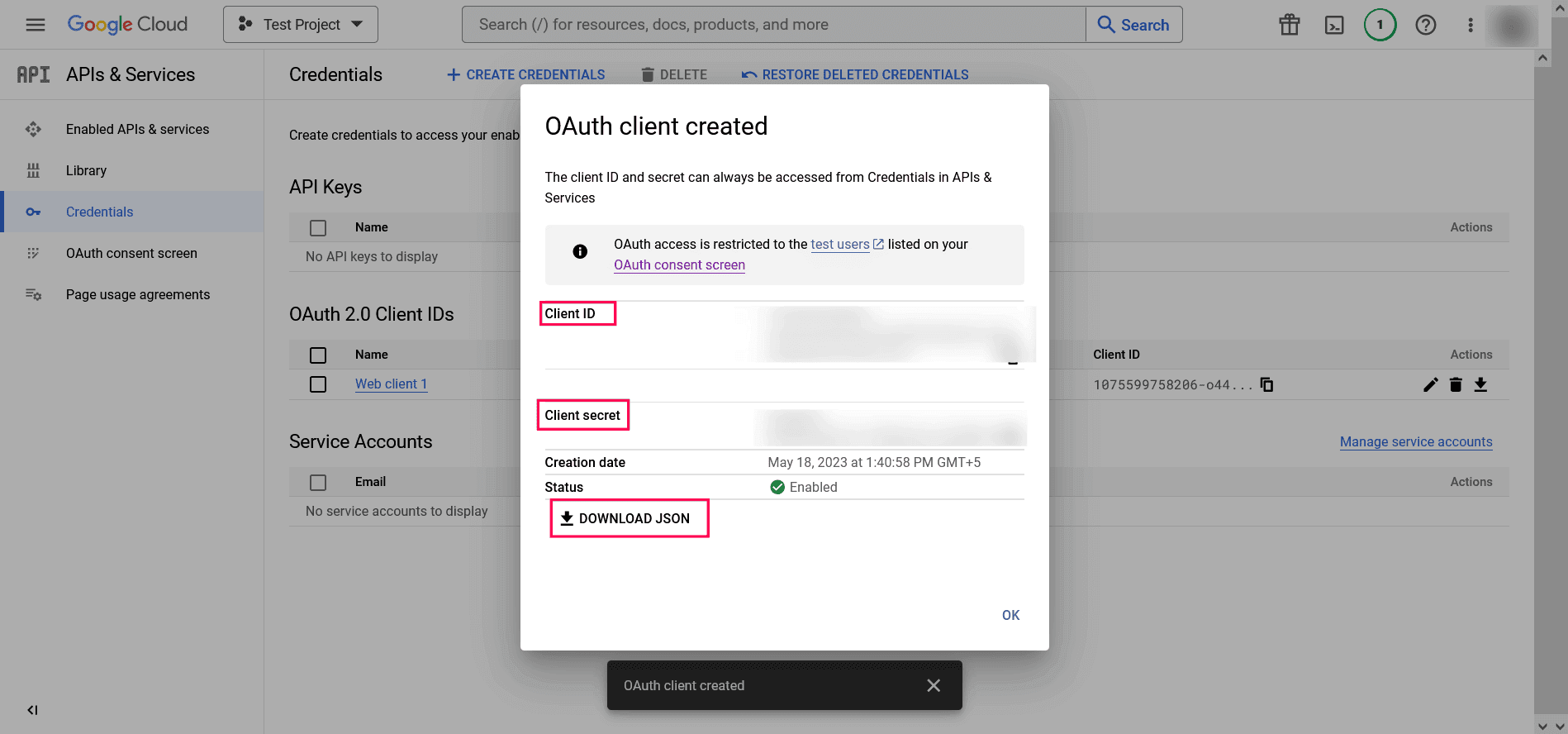
Image 17: OAuth client creation in Google workspace
API
This method allows you to create and authenticate a mail server via your mail provider’s API.
- In the Mode field, select API.
- Select your mail provider from the available options: Microsoft or Google.
- In the From Address field, enter the email address that will be used to send out notifications, alerts, etc., from the product console.
- In the To Address field, enter your email address to receive notifications for the emails sent from the product console.
- If your mail provider is Microsoft, provide the Tenant ID, Client ID, and Client Secret in the respective fields. In the product console, the Azure Cloud is considered the default Azure environment. You can modify the Azure environment setting by clicking the Choose the appropriate Azure environment link.
NOTE To learn how to find your Google Tenant ID, Client ID, and Client Secret, refer to the Steps to find your Google Workspace Client ID, and Client Secret for SMTP mail server configuration section below.
- If your mail provider is Google, upload the JSON private key file.
NOTE To learn how to get your JSON private key file, refer to the Steps to download JSON private key for API mail server configuration section below.
- Click Save settings.
Steps to find your Azure Tenant ID, Client ID, and Client Secret for API mail server configuration
- Log in to portal.azure.com.
- Under Azure services, click App registrations → New registration.
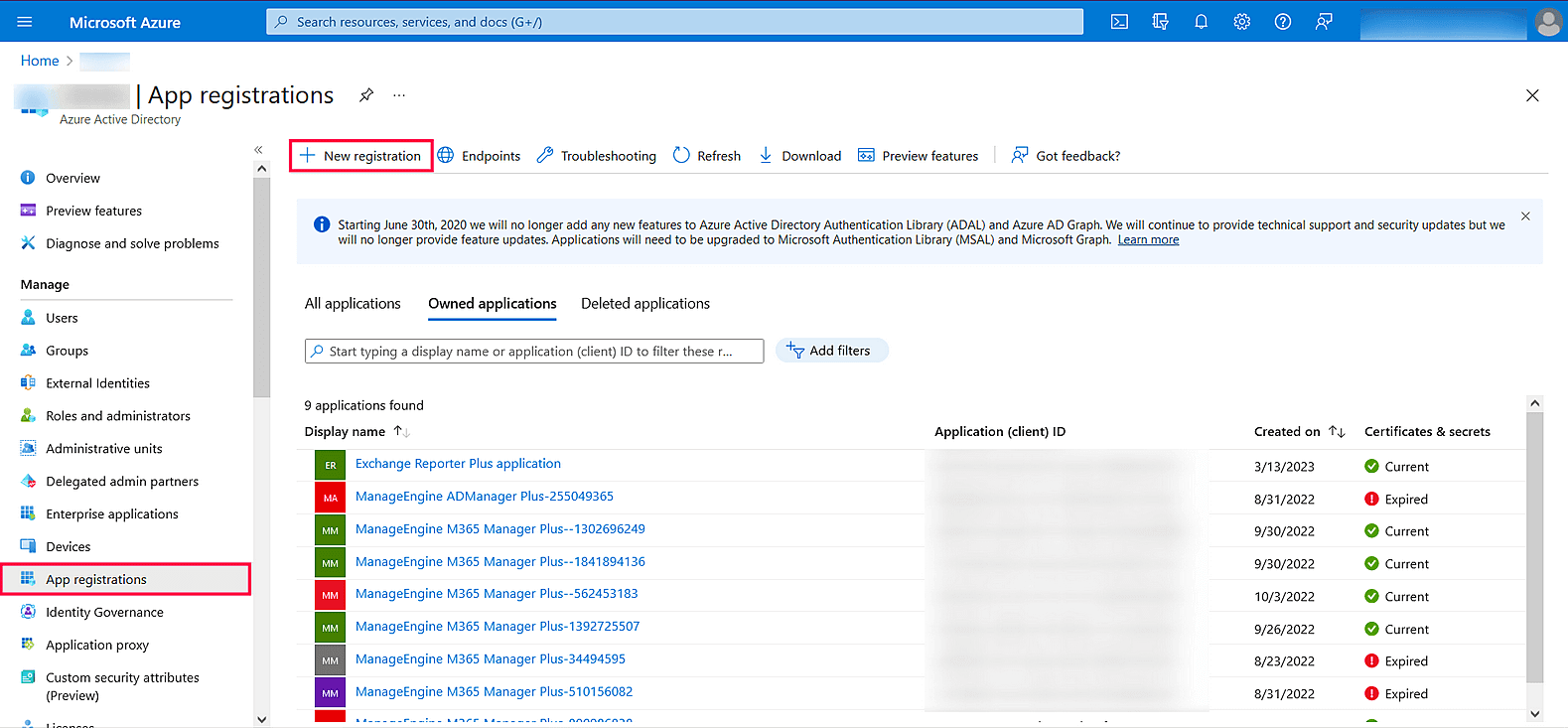
Image 18: New registration in Azure services - Provide a Name of your choice and choose the Supported account types. (If you’re unsure about the supported account types, select Accounts in the organizational directory only).
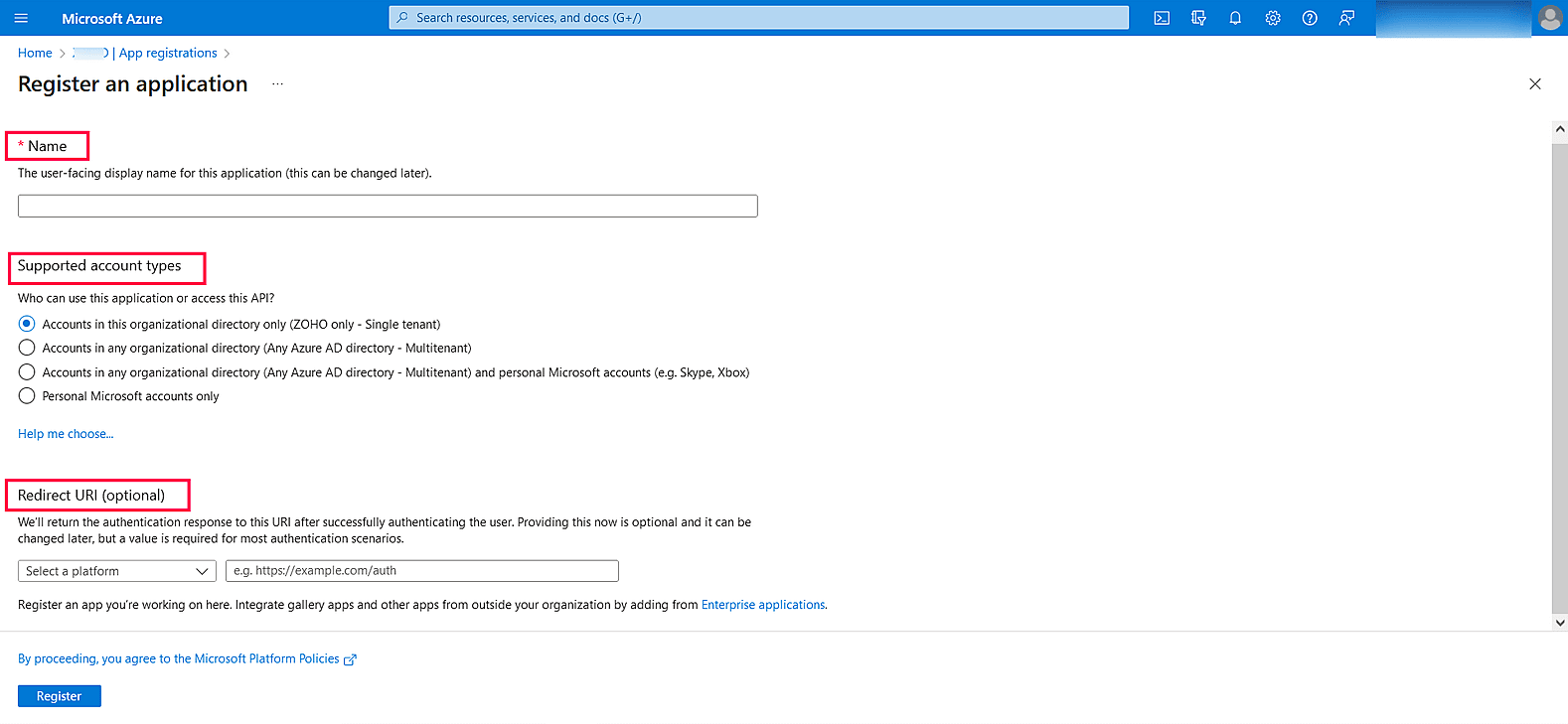
Image 19: Register an application in Azure services - In the left pane, click API Permission → Add a permission.
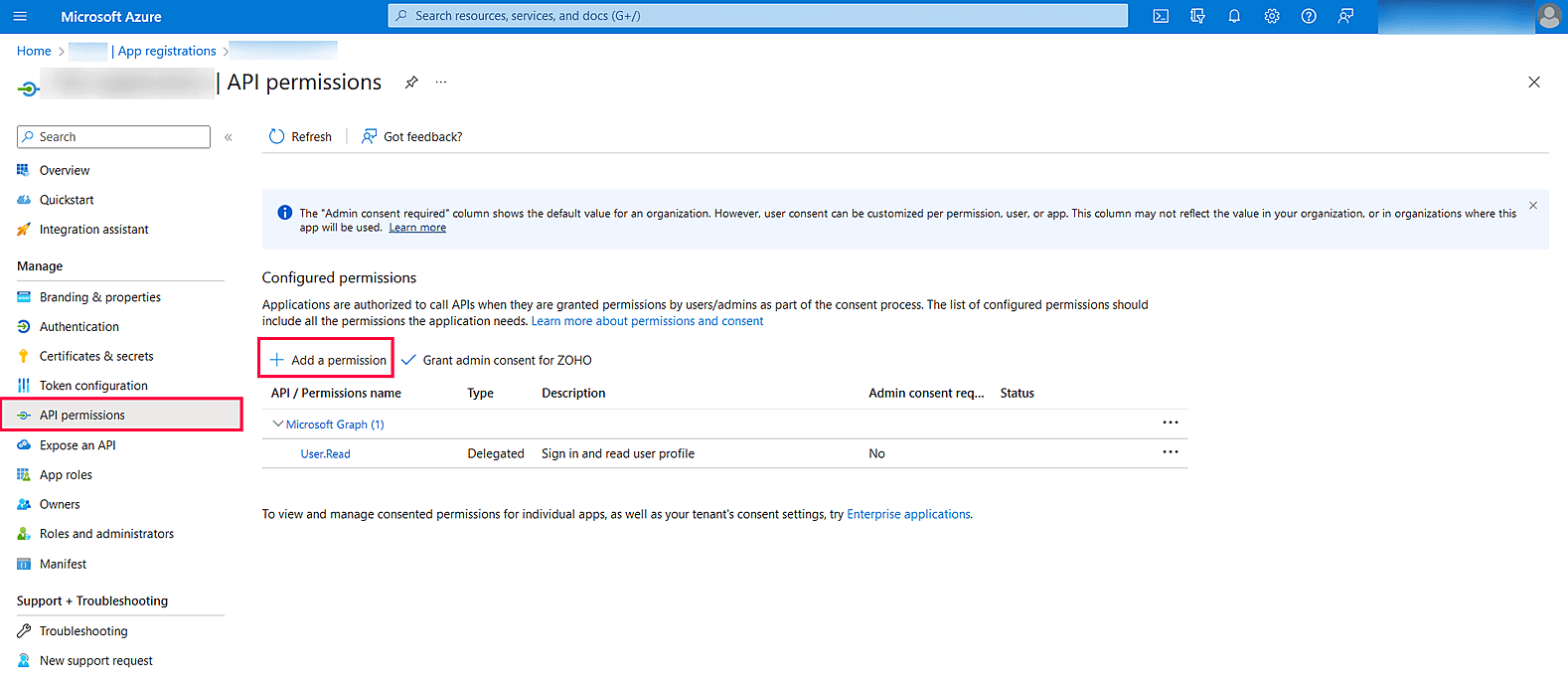
Image 20: Add a permission in Azure services - Click Microsoft Graph → Application permission.
- Search Mail and select the permission Mail.Send and click Add Permission.
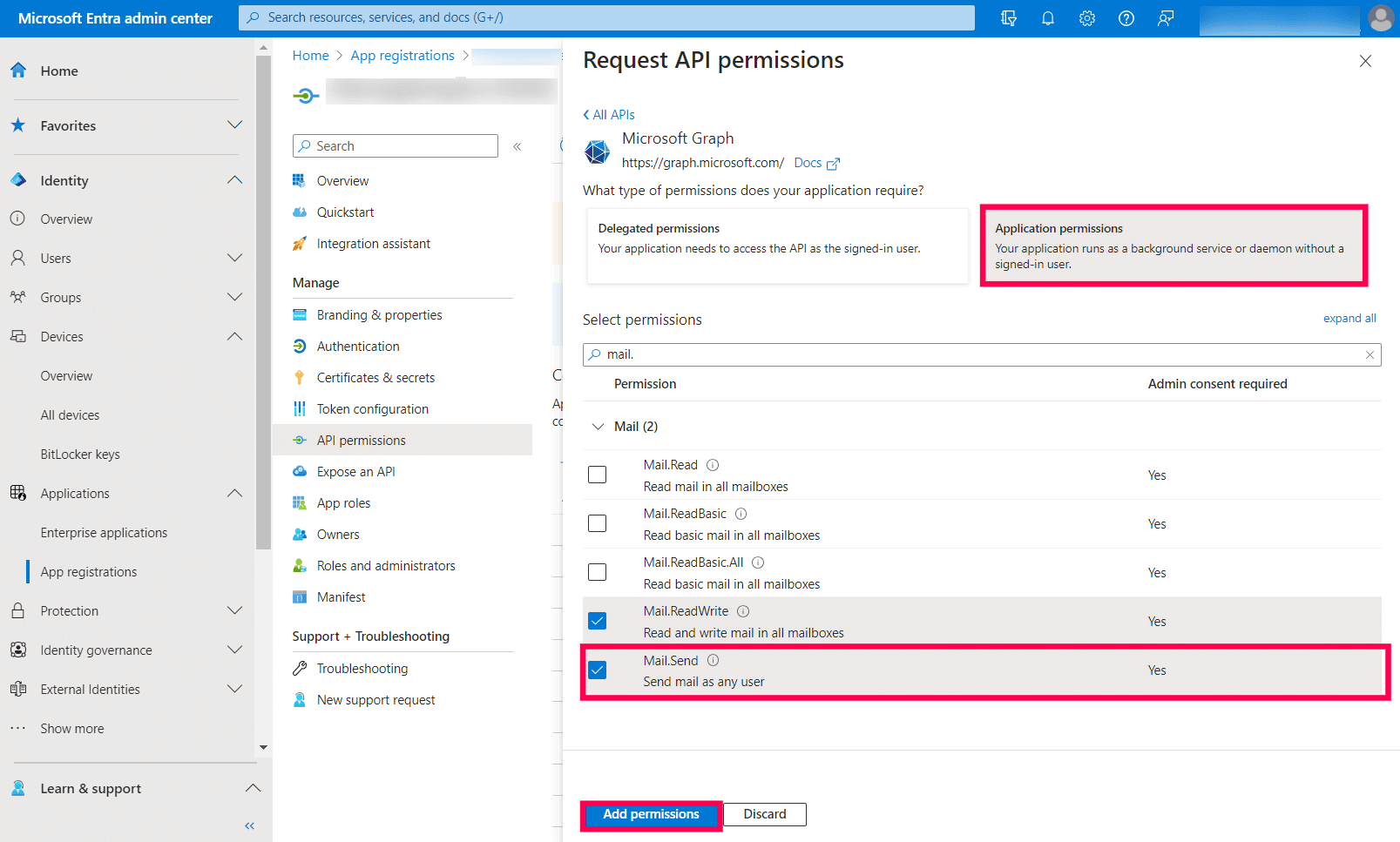
Image 21: Add a permission in Azure services - Click Grant admin consent.
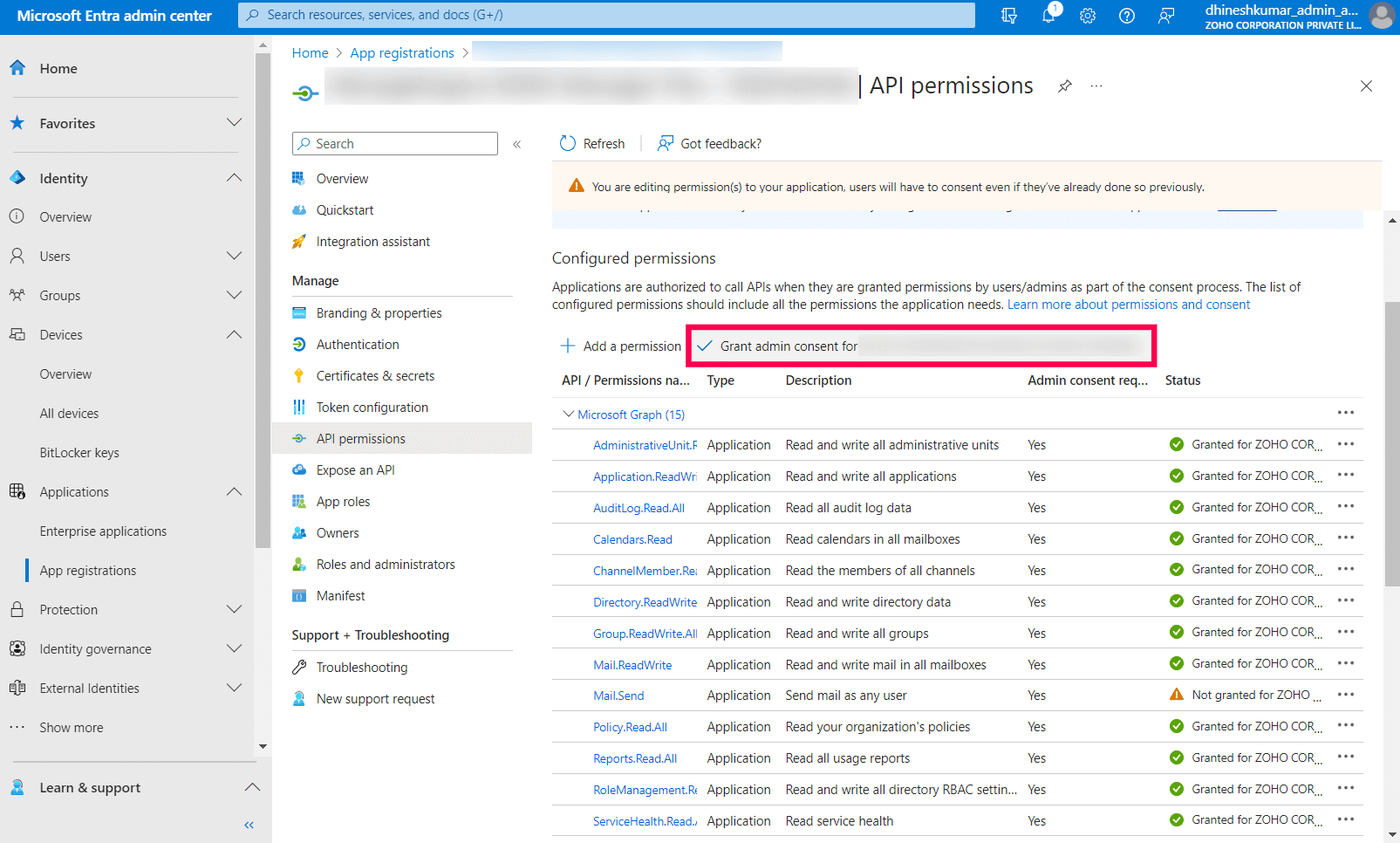
Image 22: Grant admin consent in Azure services - Copy the Client ID & Tenant ID displayed.
- In the left pane, click Certificates & secrets → New client secret.
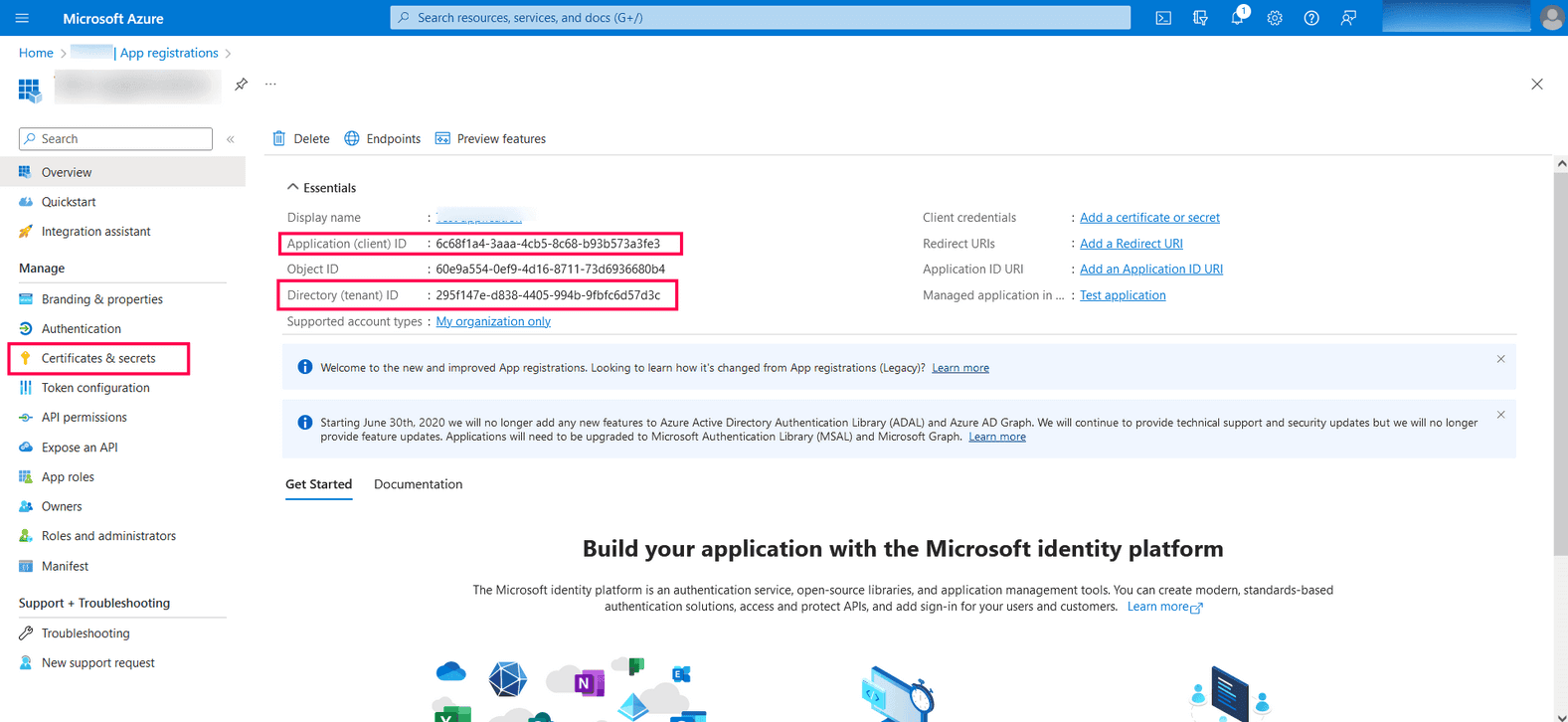
Image 23: Grant admin consent in Azure services - Provide a Description for the client secret. In the Expires field, choose the validity of the client secret and click Add.
- The client secret will be generated. Copy the string displayed under Value.
Steps to download JSON private key for API mail server configuration
- Expand the left sidebar and click IAM & Admin.
- Open the Service Accounts page.
- In the dashboard, select any existing project or click New Project from the project dropdown list.
NOTE If you are selecting an existing project, skip to step 13.
- Click CREATE PROJECT.
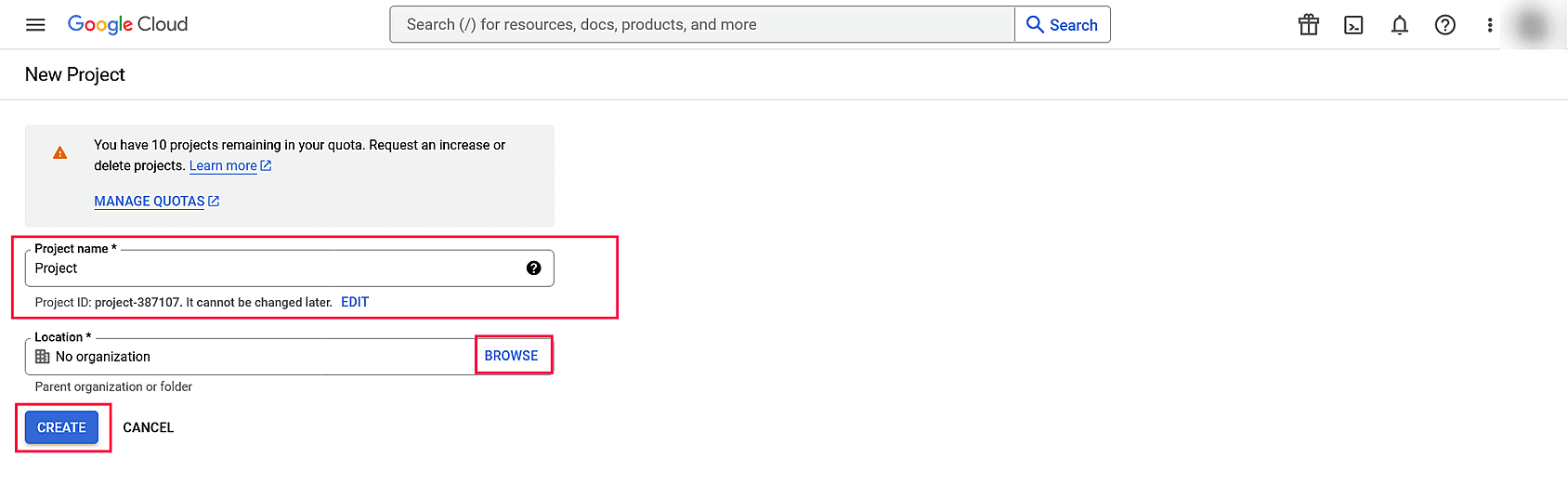
- Enter the Project name and Location. Click CREATE.
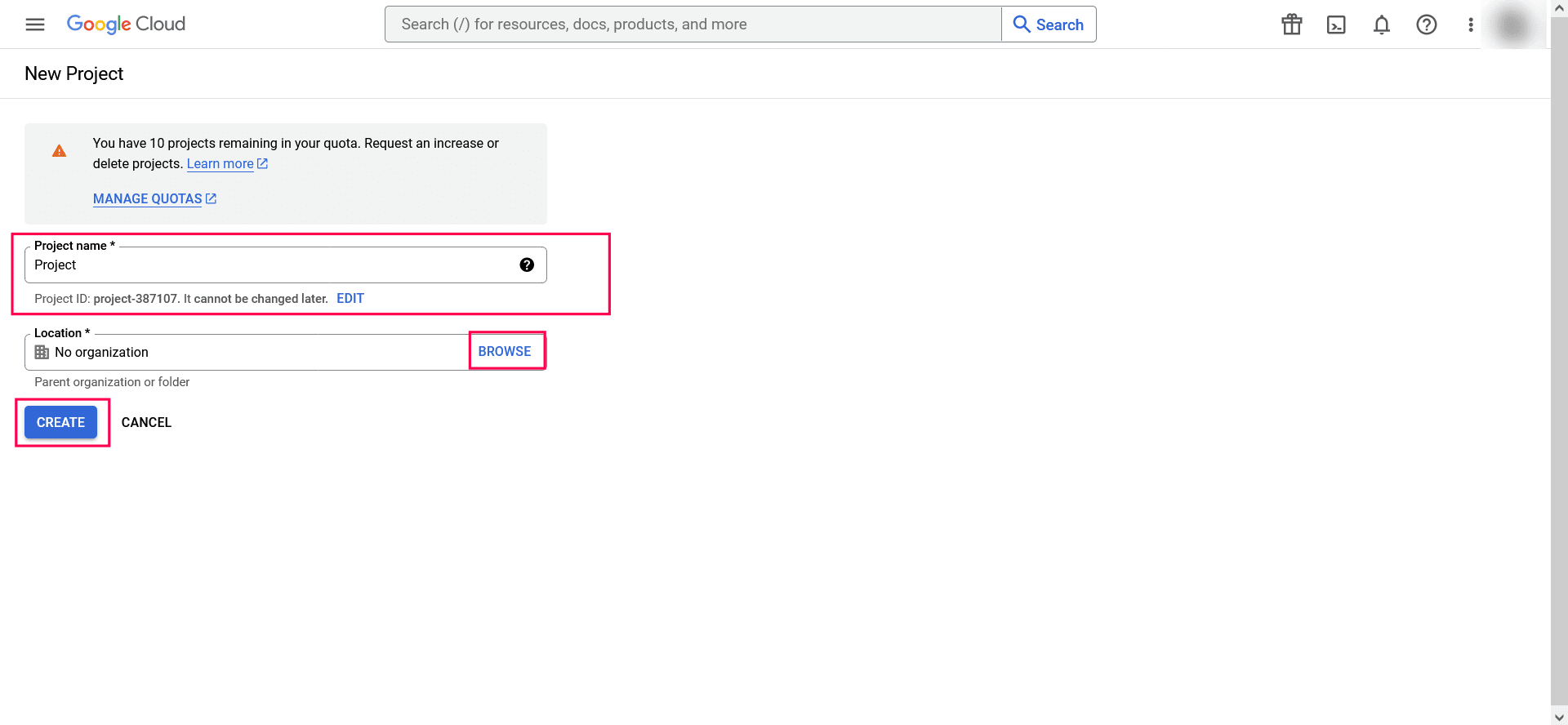
Image 24: Create new project in Google workspace - Click + CREATE SERVICE ACCOUNT button from the top navigation bar.
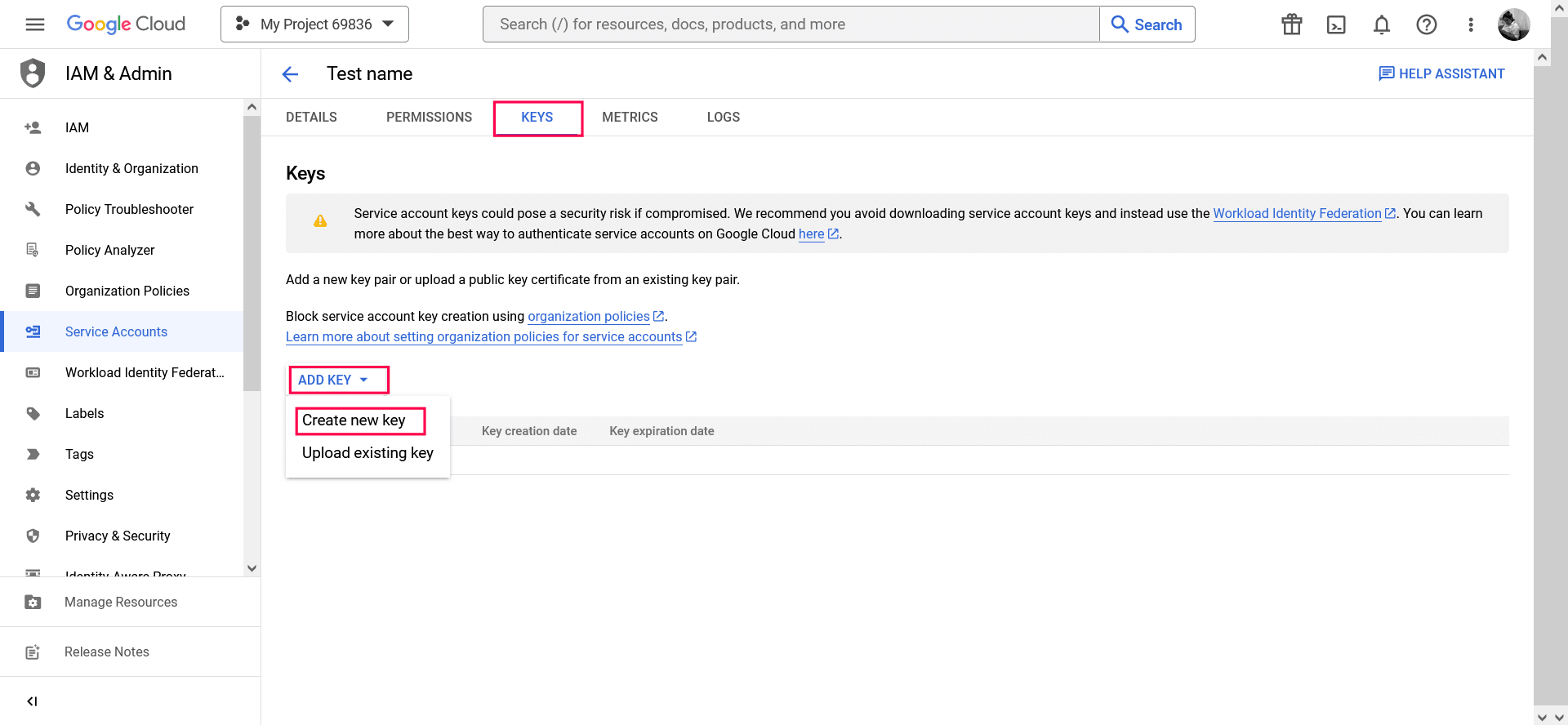
Image 25: Create new key in Google workspace - Under Service account details, type a Service account name, Service account ID, and Service account description, then click CREATE AND CONTINUE.
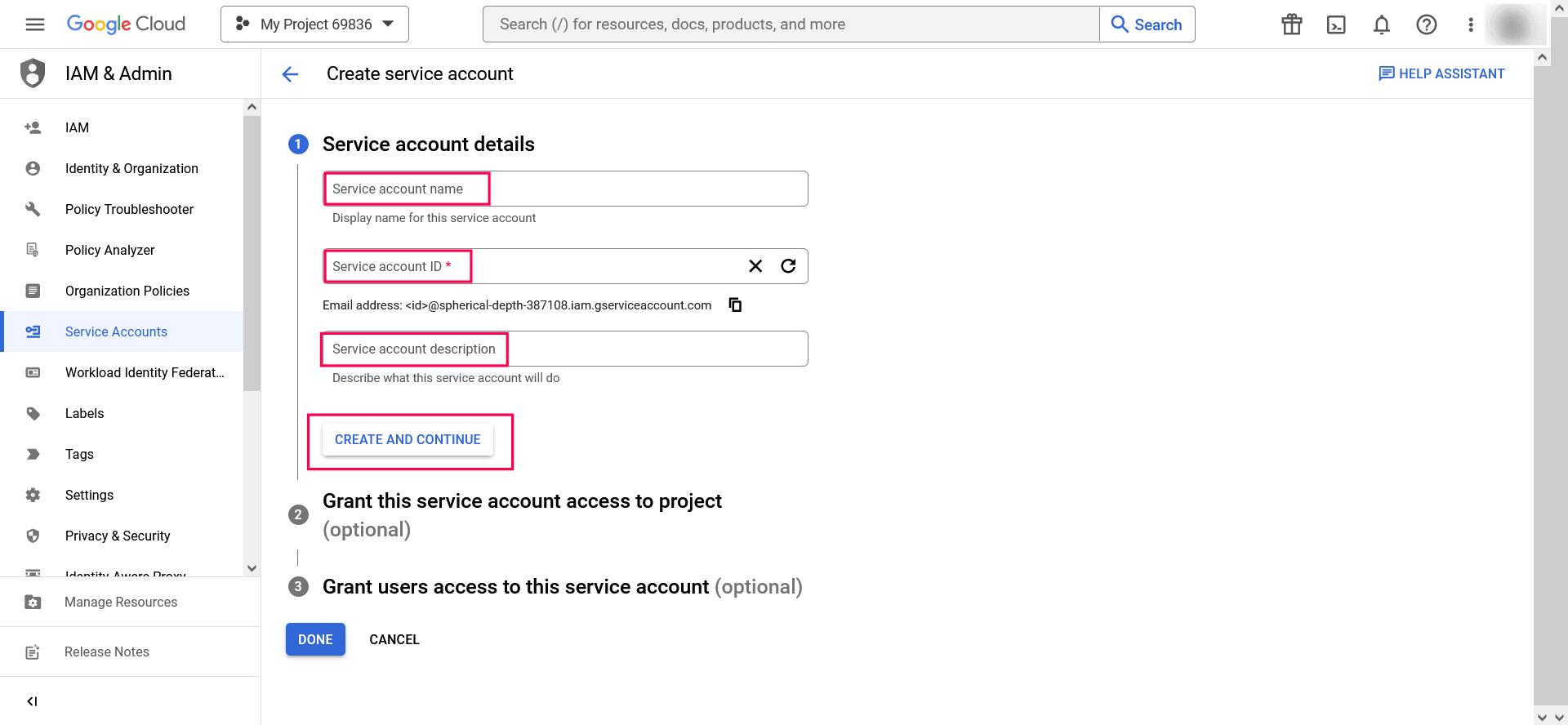
Image 26: Create service account in Google workspace - If required, you can also select the IAM roles to be granted to the service account using the Grant this service account access to project option.
- Click Save.
- If required, you can add the users or groups that are allowed to use and manage the service account.
- Click Done.
- Click the email address for the service account you created.
- Click the KEYS tab.
- In the ADD KEY dropdown list, select Create new key.
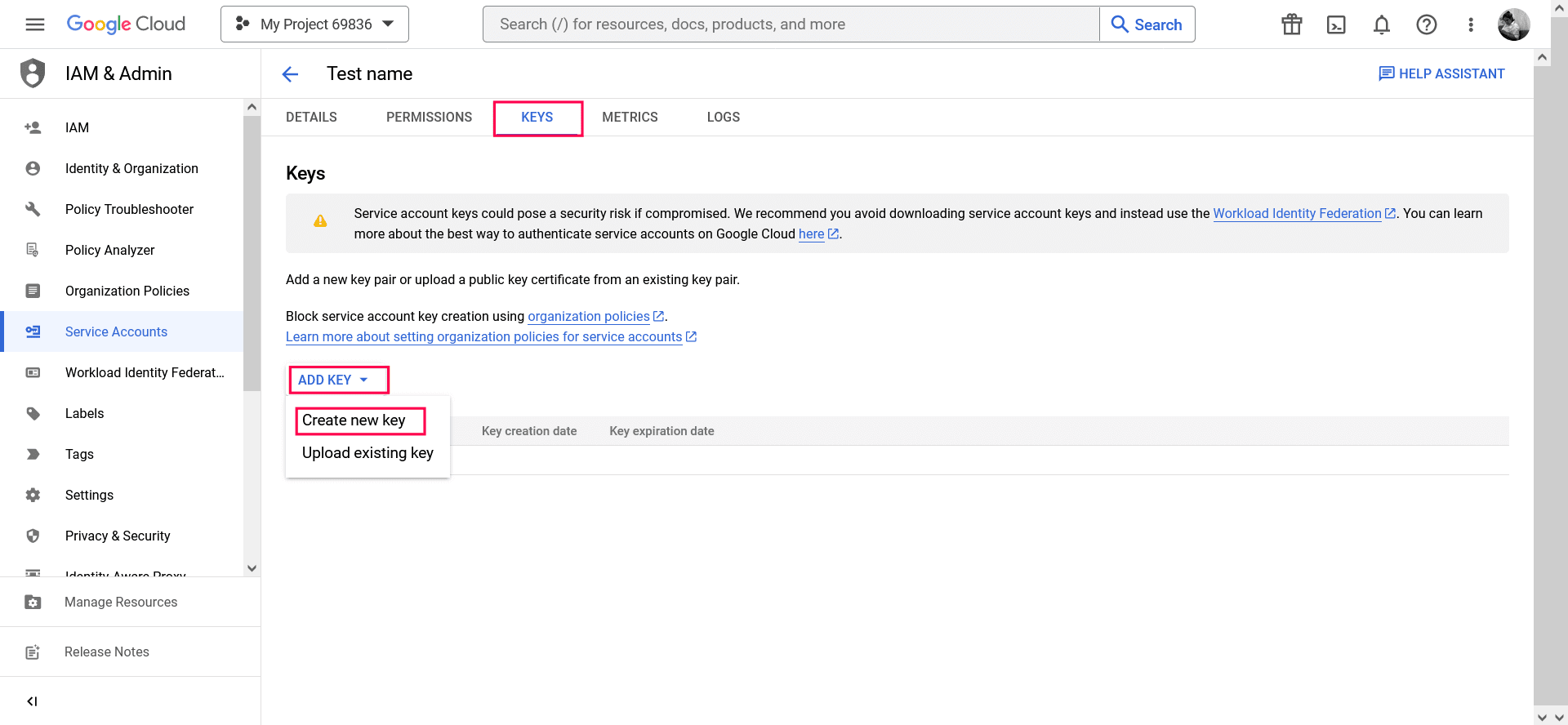
Image 27: Create new key in Google workspace - Select key type as JSON.
- Click Create.
Your new public and private key pair will be generated and downloaded to your machine. Please keep the private key safe as this will be the only copy, and you cannot generate the same private key again.
Once you have downloaded the JSON private key, you'll have to enable Gmail API service and provide domain-wide authority to the service account.
Enable Gmail API service
- Log in to console.cloud.google.com.
- Select the project you created from the dropdown menu.
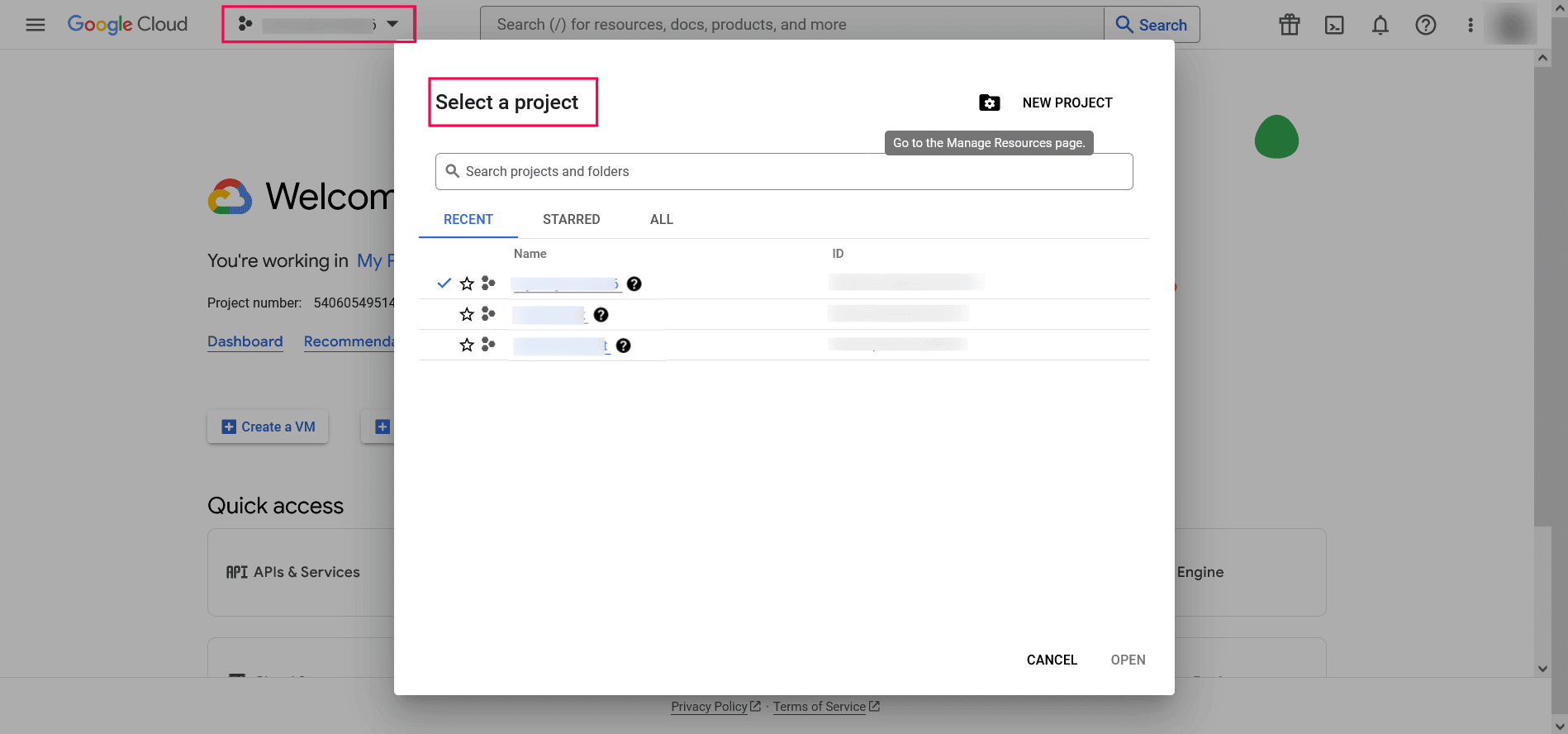
Image 28: Select the project you created in Google workspace - Click APIs & Services and choose + ENABLE APIS AND SERVICES.
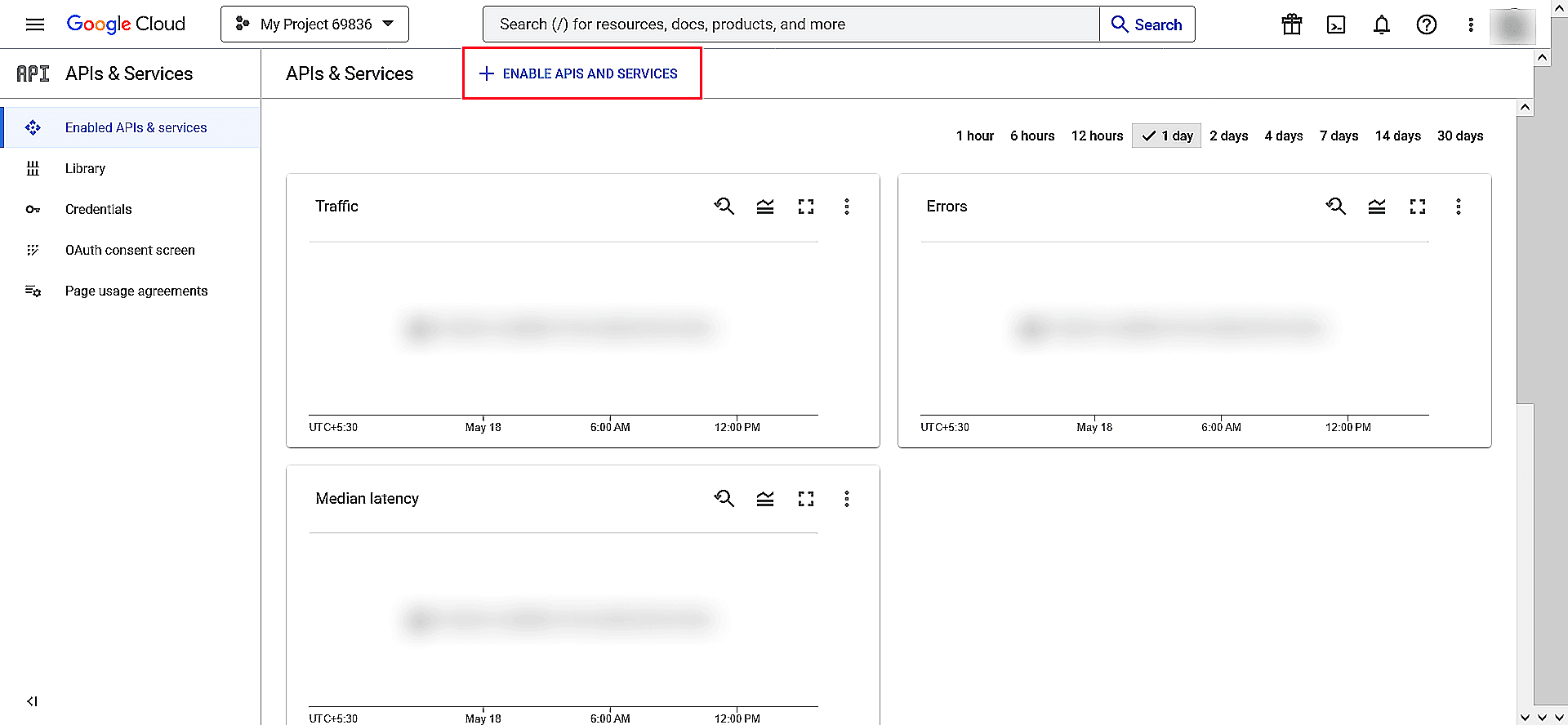
Image 29: Enabling API in Google workspace - Select Gmail API and click Enable.
Delegating domain-wide authority to the service account
- Log in to the Google Workspace domain's Admin console as a super administrator.
- Navigate to Main menu → Security → Access and data control → API controls.
- In the Domain wide delegation pane, select MANAGE DOMAIN WIDE DELEGATION.
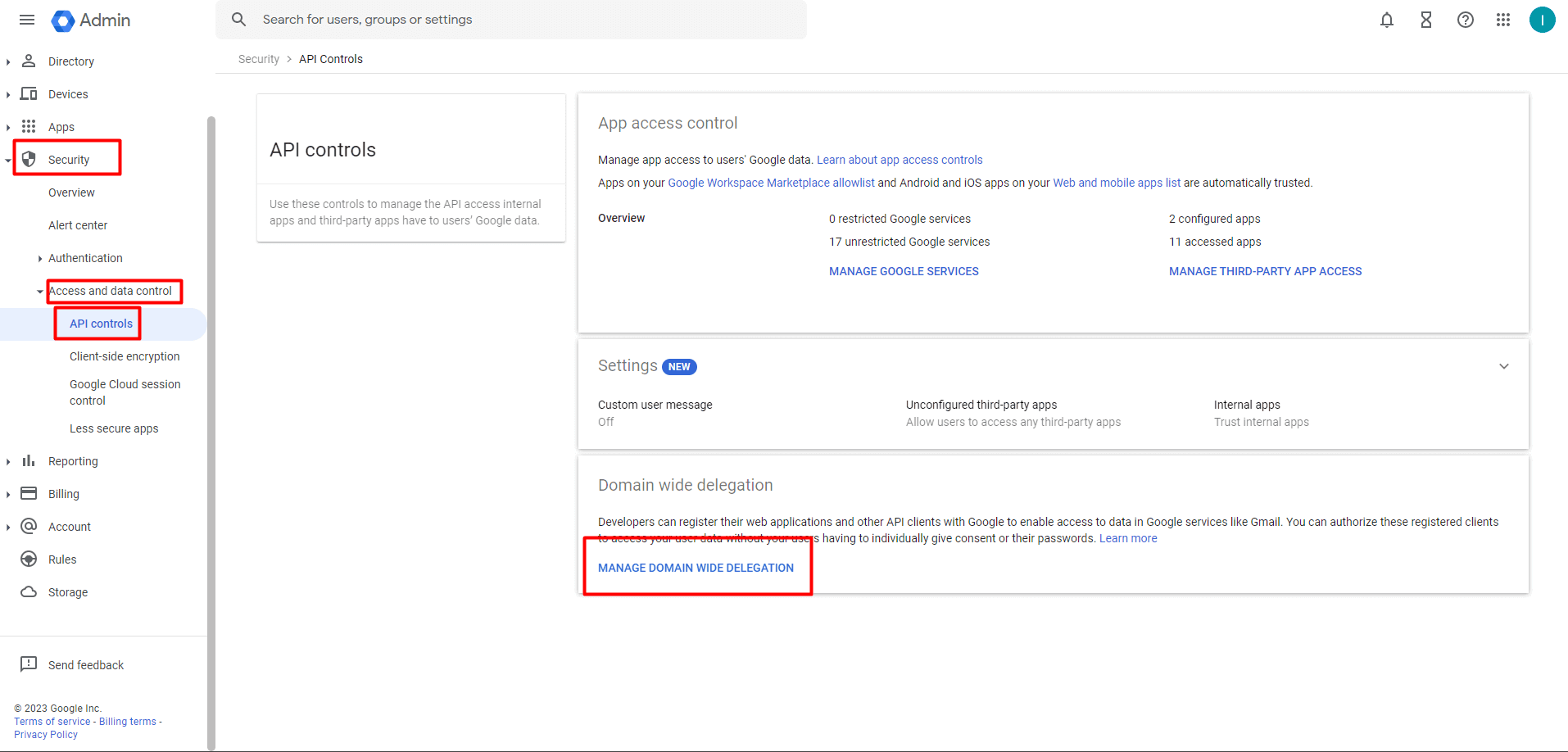
Image 30: Manage domain wide delegation in Google workspace - Click Add new.
- In the Client ID field, enter the service account's client ID. You can find your service account's client ID on the Service accounts page.
- In the OAuth scopes (comma-delimited) field, enter Google Mail API's URI: (https://mail.google.com). You can also list other scopes that your application should be granted access to, by using commas as a delimiter to separate them.
- Click Authorize.
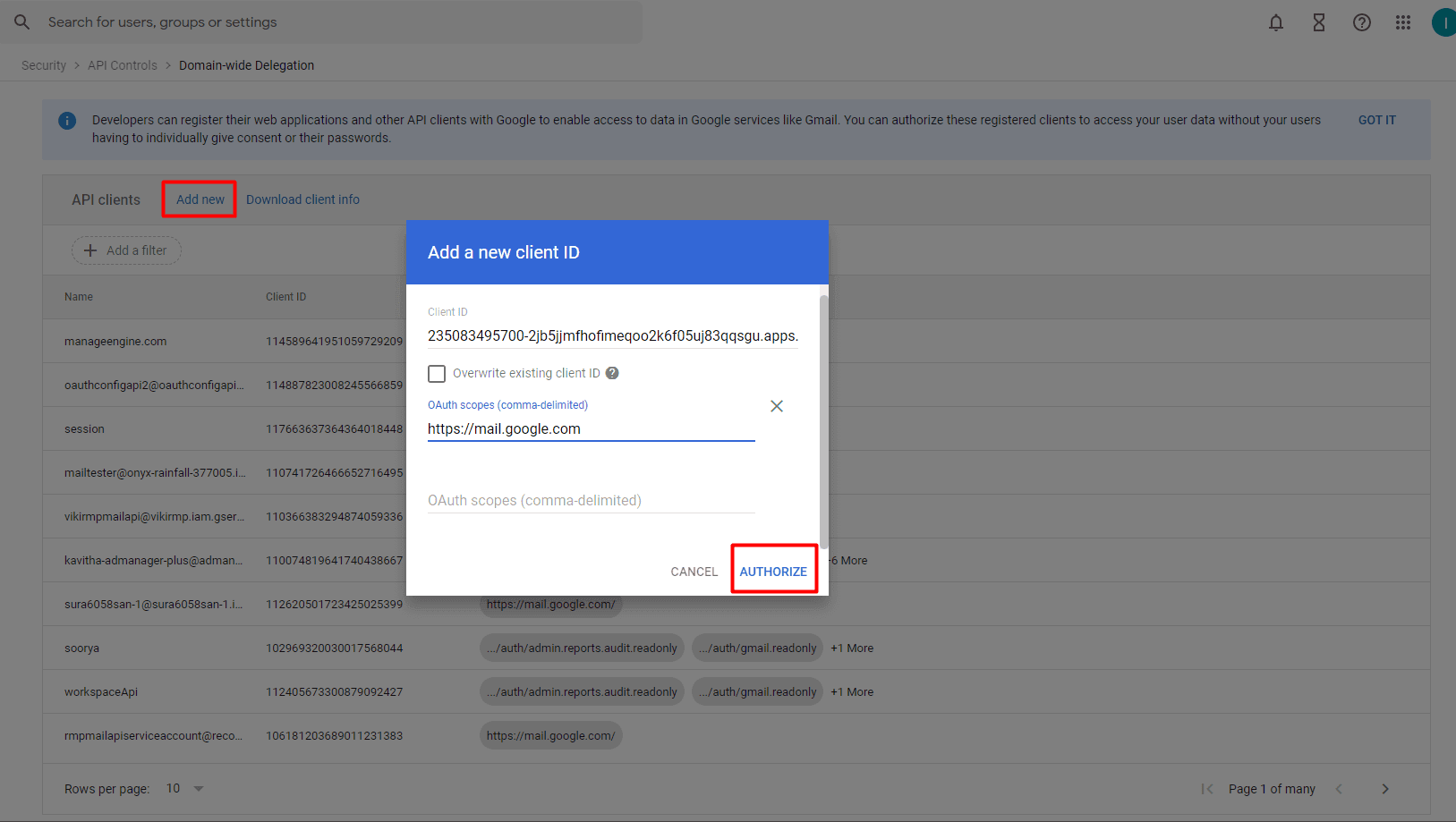
Image 31: Add a new client ID in Google workspace
Your application now has the authority to make API calls as users in your domain (to impersonate users). When you prepare to make authorized API calls, specify the user to impersonate as.
SMS Settings
To configure or change SMS settings,
- Navigate to Settings > System Settings > Notification Settings > SMS Settings.
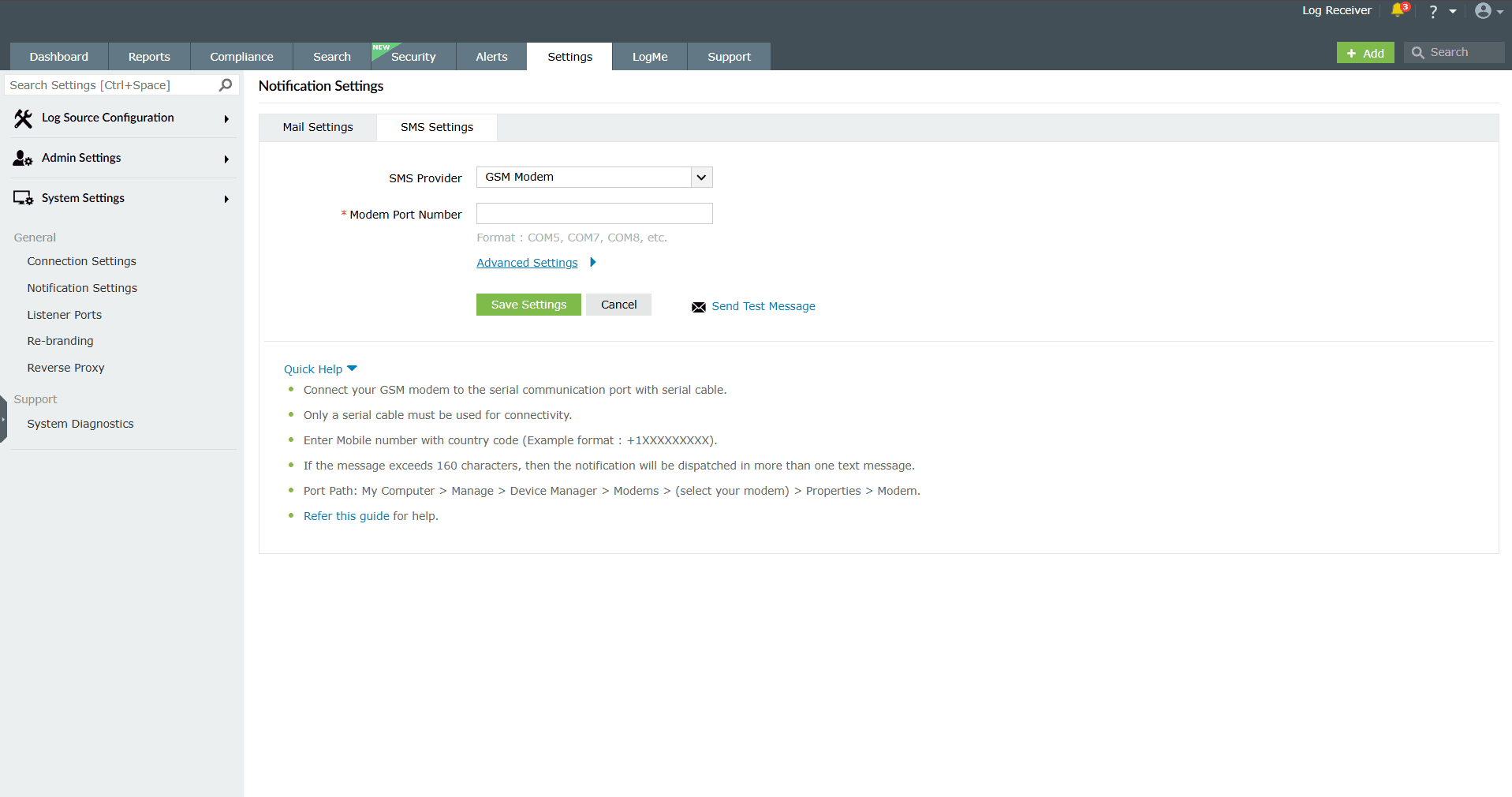
Image 32: SMS settings configuration - For sending SMS alerts, you can configure the product console to use a GSM modem or a custom SMS gateway of your own.
GSM Modem Configuration
To configure a GSM modem,
- Go to Settings > System Settings > Notification Settings > SMS Settings.
- In the SMS Provider drop-down field, select GSM Modem.
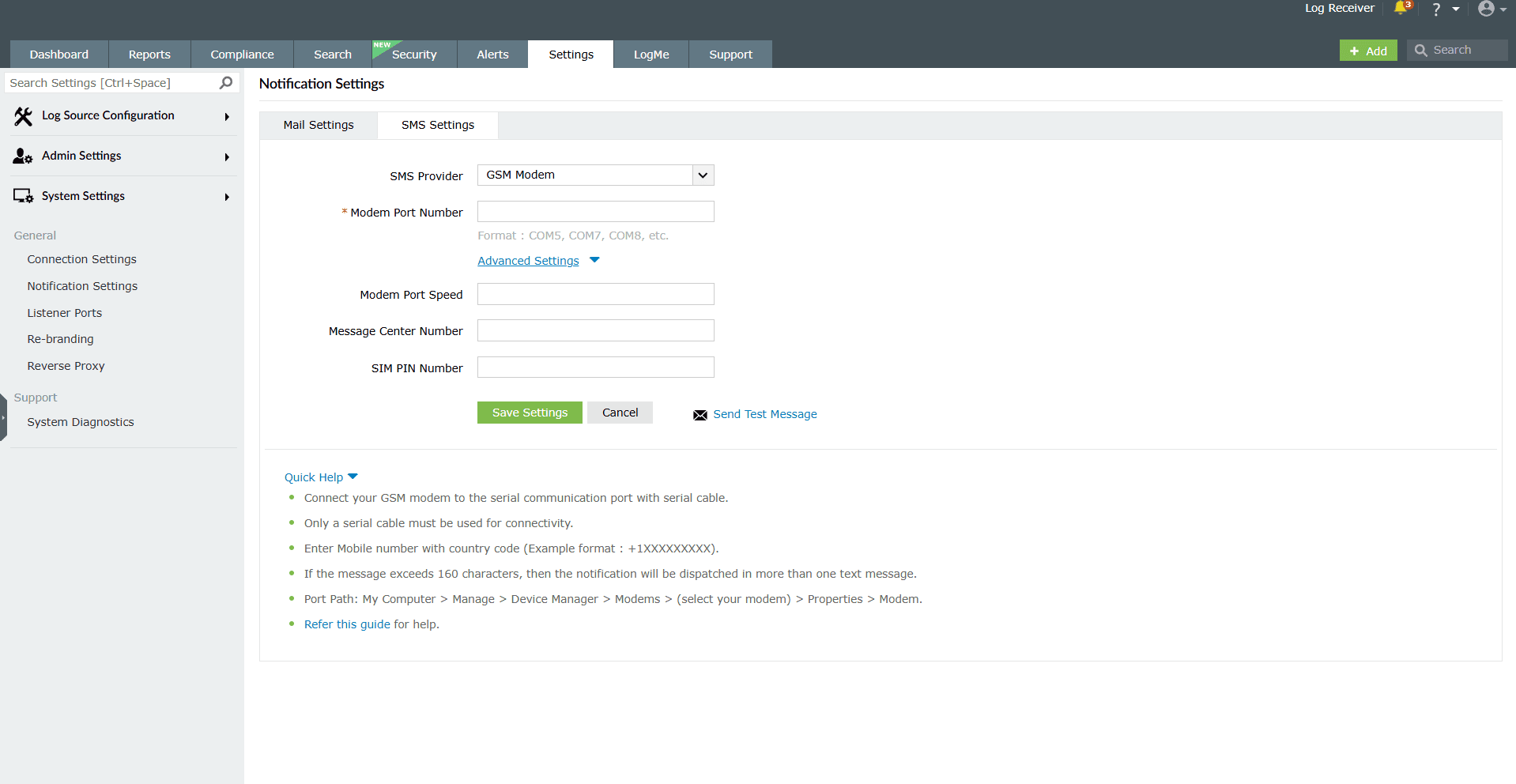
Image 33: GSM modem configuration in SMS settings - In Modem Port Number, enter the hardware port of the product server machine to which the SMS hardware component provided by the telecom service provider is connected.
- Click Save Settings to complete configuration.
- If the SMS settings are not configured here, the product console prompts you to configure SMS settings at the Alert Profile Creation screen.
Steps involved in configuring the modem port and modem speed:
- Connect your GSM Modem to the serial communication port.
- Only a serial cable must be used for connectivity.
- The port number for Windows devices will be comX. For example, COM7 or COM8.
- Enter the port number to which the modem is connected. For example, COM1.
Requirements for establishing SMS server connection:
- The modem/mobile must have GSM functionality with a provision to insert a SIM card.
- It should support 7-bit (GSM default alphabet), 8-bit, and Unicode (UCS2) encoding.
- Ensure that the GSM modem configured with the product console is not used by any other application.
- If you experience any issue in sending SMS notifications through the GSM modem, please restart the product console and try again.
- Matching these criteria will allow the product console to support your modem/mobile phone.
Custom SMS Gateway Configuration
You can configure you own custom SMS gateway, provided the gateway which is based on HTTP, SMTP or SMPP.
HTTP-based SMS Provider:
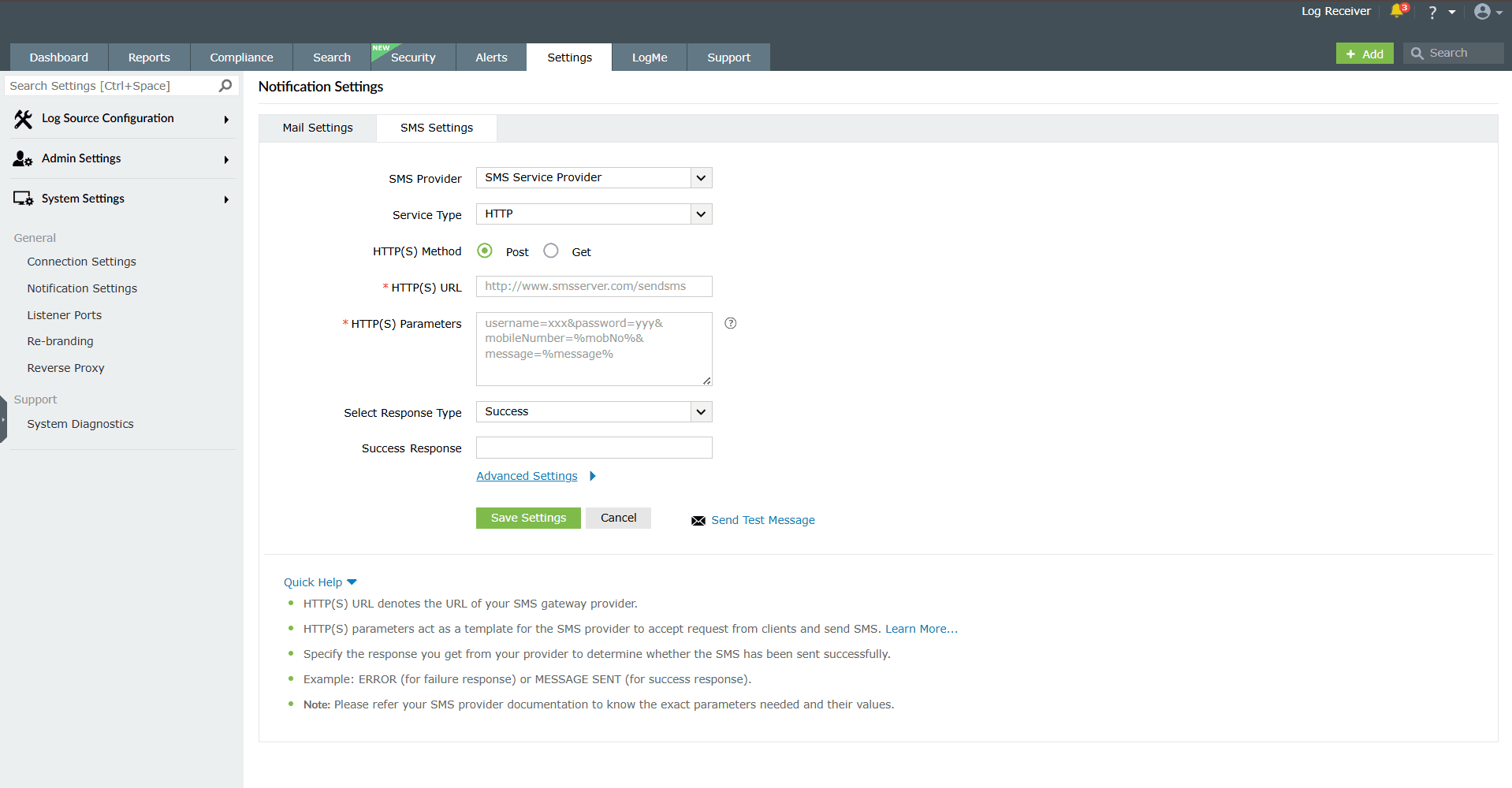
- Navigate to Settings > System Settings > Notification Settings > SMS Settings.
- In the SMS Provider drop-down field, select SMS Service Provider.
- In the Service Type drop-down field, select HTTP.
- In the HTTP(S) Method field, select whether you want to use the Post or Get method for sending SMS.
- POST: Sends the message data in the request body. This method is commonly used when you need to transmit sensitive or large amounts of data securely.
- GET: Sends the message data as URL parameters. This method is typically used for simple requests where parameters can be included directly in the URL.
- In the HTTP(S) URL field, enter the URL of your SMS gateway provider.
- In the HTTP(S) Parameters field, enter the HTTP parameters specific to your SMS provider.
Example format userName=xxx&password=yyy&mobileNumber=%mobNo&message=%message%
Where,
- userName = the parameter which is used to denote the API authentication username
- xxx = API authentication username
- password = the parameter which is used to denote the API authentication password
- yyy = API authentication password
- mobileNumber = recipient parameter
- %mobNo% = this macro denotes the user's mobile number
- message = message parameter
- %message% = this macro denotes the SMS message content
More HTTP Parameters - If you SMS provider requires more parameters like unicode and apiID, include them as well using the '&' sign
- Specify the response you get from your provider to determine the success of sending the SMS.
- Click Advanced Settings and enter the HTTP request headers specific to your SMS provider.
- Select the check box Convert Message into Unicode to send SMS in Unicode format.
- Click Save Settings to complete configuration.
SMTP-based SMS Provider:
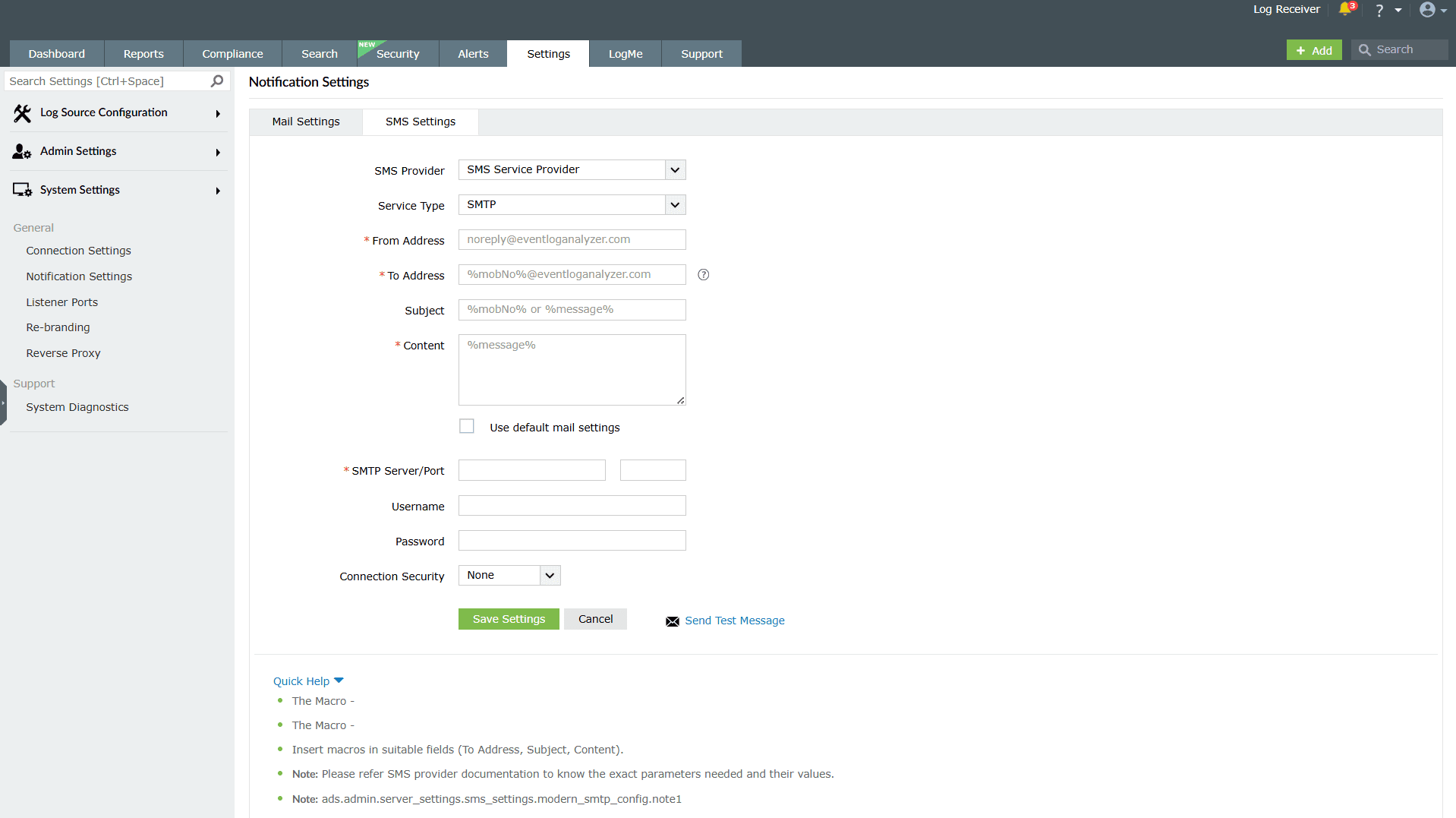
- Navigate to Settings > System Settings > Notification Settings > SMS Settings.
- In the SMS Provider drop-down field, select SMS Service Provider.
- In the Service Type drop-down field, select SMTP.
- In the From Address field, enter an email address from which you want to send the SMS. For example, noreply@eventloganalyzer.com
- In the To Address field, enter the %mobNo% macro followed by the email of your provider. For example: your SMS provider to know the exact values.
- In the Subject field, enter either the mobile number or message, which is based on your SMS provider.
- In the Content field, enter appropriate data, which varies based on the SMS provider.
- In the SMTP Server/Port field, enter the name or IP address of the SMTP Server and its port number.
- Enter appropriate credentials for the SMTP server in the Username and Password fields.
- Choose a Connection Security if you wish to configure. You can choose either SSL or TLS from the drop-down available.
- Click Save Settings to complete configuration.
SMPP-based SMS Provider:
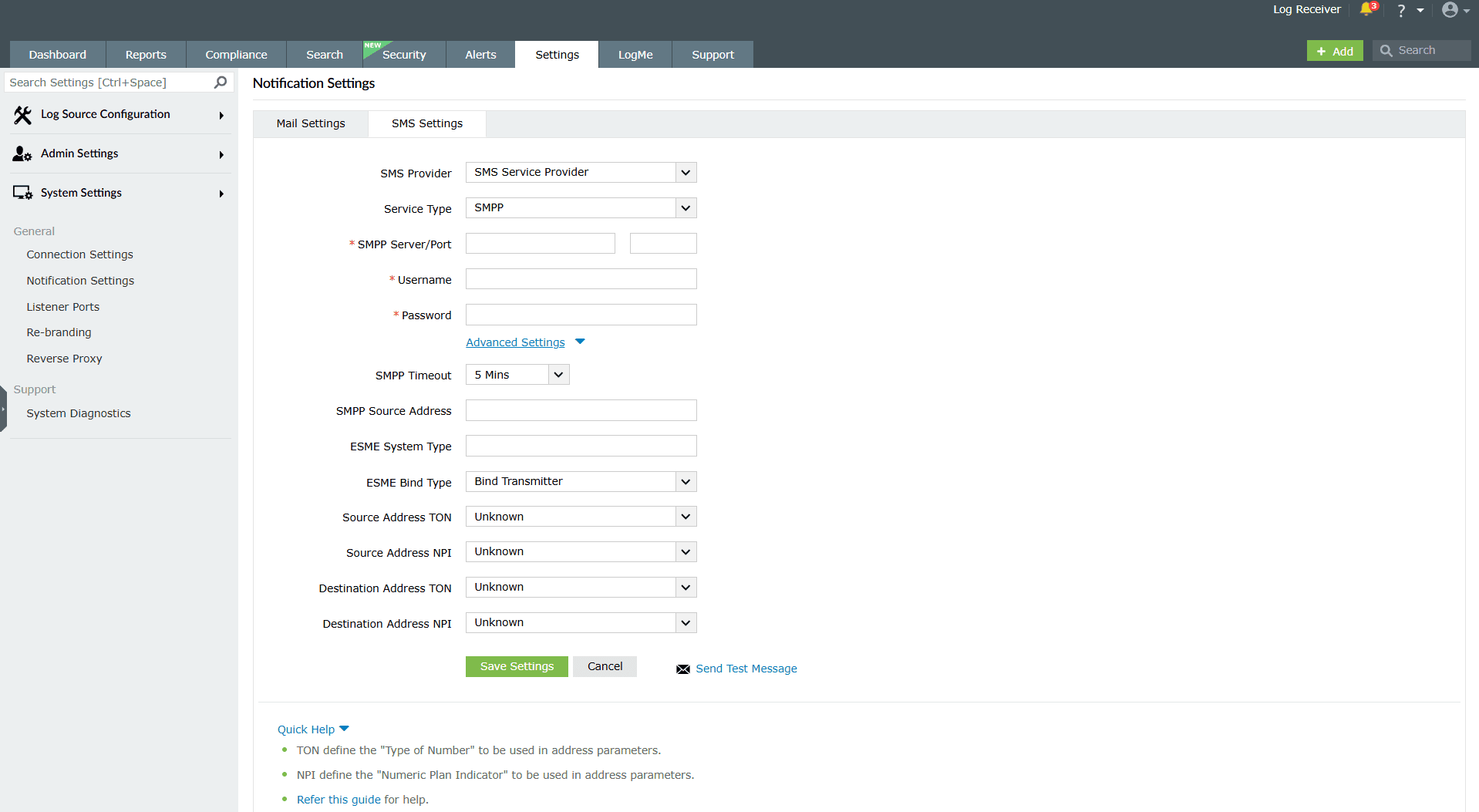
- Navigate to Settings > System Settings > Notification Settings > SMS Settings.
- In the SMS Provider drop-down field, select SMS Service Provider.
- In the Service Type drop-down field, select SMTP.
- In the SMPP Server/Port field, enter the name or IP address of the SMPP Server and its port number.
- Enter appropriate credentials for the SMPP server in the Username and Password fields.
- Click Advanced Settings and in the SMPP Source Address field, enter the appropriate IP address.
- Select the type of number (TON) and numeric plan indicator (NPI) of the source address.
- Select the type of number (TON) and numeric plan indicator (NPI) of the destination address.
- Click Save Settings to complete configuration.
Read also
This page explained how to configure mail and SMS notifications for alerts and reports. To learn more about related configurations, see the following pages: