Red Hat Linux Patches
How to update Red Hat Linux patches using Patch Manager Plus?
With a software patching tool like Patch Manager Plus you no longer have to follow the tedious process of patching Linux systems manually which involves numerous steps. Using Patch Manager Plus, you can install patches in several ways. This document covers the different aspects of patch management and the methods of installing patches using this Linux patching tool.
How to install patches of Red Hat Linux manually?
To install patches manually first log into the Patch Manager Plus console and then follow the steps given below:
- Click on the Deployment tab -> Manual Deployment.
- Select Install/Uninstall Patch and choose your desired platform (Windows /Mac /Linux). As you are going to install Red Hat Linux patches, select Linux.
- Give a suitable Name and Description to the configuration you are creating to install patch.
- The next step is to add the patches that you wish to install on your Linux systems. Click on Add Patches and you can see a window which pops up. Here, you will be able to see that there is a separate section for the patches missing in your network. You have options to filter them based on the type of application or the type of patch update as in security/ non-security patches. After selecting the patches that you wish to install, click on OK. By doing so you are enhancing the endpoint security of your network.
- You can schedule when you wish to install the patches.This step is optional. For example, there is a scenario where the User does not want the installation to happen on business days. So in this case the User can click on the Install After checkbox and give a suitable Date and Time after which the patch updates will get installed. The User can click on the next checkbox Do not apply this configuration after the time specified below and give the Expiry Date and Expiry Time after which the patch installation task is aborted.
- You can configure the Deployment Settings by applying a Deployment Policy which suits your enterprise. For example, if you want to install patches only during the weekends you can choose the Weekend Policy. You can also create a policy of your own by clicking on Create/Modify Policy. Using this option you can customize your deployment by installing patches at your preferred date and time.
- The next step is to define your target computers. The computers that you specify here are the systems that you want to install patches. You can specify your target computers either based on Remote Office or Domain. You can select multiple targets by clicking on the add button '+'. After specifying the Remote Office or Domain you can further filter the computers based on a variety of categories such as Domain, IP Address, IP Range, Operating System, etc. So the patch updates will be installed in these computers. Also note that you can exclude computers based on the above mentioned categories. For example, there is a critical server in your network and installing patches on that particular server will cause downtime. So it is better to exclude that server from deployment by specifying the its IP Address under Exclude Target.
- Following that you have the Execution Settings. This step is optional. Once you click on the checkbox Retry this configuration on failed targets, the patches will be redeployed on the failed targets for the specified number of times. You can also configure the Execution Settings to retry this deployment during startup/ refresh.
- To receive notifications on the updates of this Configuration, select the checkbox Enable Notification and fill in your E-mail address. You can also configure the notification settings so that you receive notifications during regular intervals.
- Finally click on Deploy/ Deploy Immediately to install patches to your Linux systems.
How to install patches of Red Hat Linux automatically?
The entire process of patching Red Hat Linux can be automated using Patch Manager Plus. Automate Patch Deployment automates the entire process right from scanning the systems for missing patches, to downloading them from the Red hat Linux site (vendor site), up to deploying the patch updates in your systems. To install patches automatically first log into the Patch Manager Plus console and follow the steps given below:
- Click on the Deployment tab -> Automate Patch Deployment.
- Click on Automate Task and choose your desired platform: Windows/ Mac/ Linux. As you are going to install patches for your Linux systems select Linux.
- There are four stages of creating an APD task.
- Select Applications: You can select the Linux and third-party Updates that you want to install based on their severities.
- Choose Deployment Policy: You can apply any deployment policy listed there or you can create a policy of your own - whichever suits your business needs.
- Define Target: You can select your target computers either by choosing their Domain or the Remote Office. This deployment policy will be applied to the specified target computer.
- Configure Notifications: If you wish to receive emails on the latest happenings of this automated deployment task, you can click on the checkbox to enable notifications via e-mail.
- Once you click on Save your APD task is created.
To know more about all the options in the APD task you can refer to this document on Automated Patch Deployment.
Architecture and Workflow for Red Hat patching:
This section explains the processes involved in patching Red Hat systems. You can also refer to the architecture diagram below for more details.
1. Cache creation
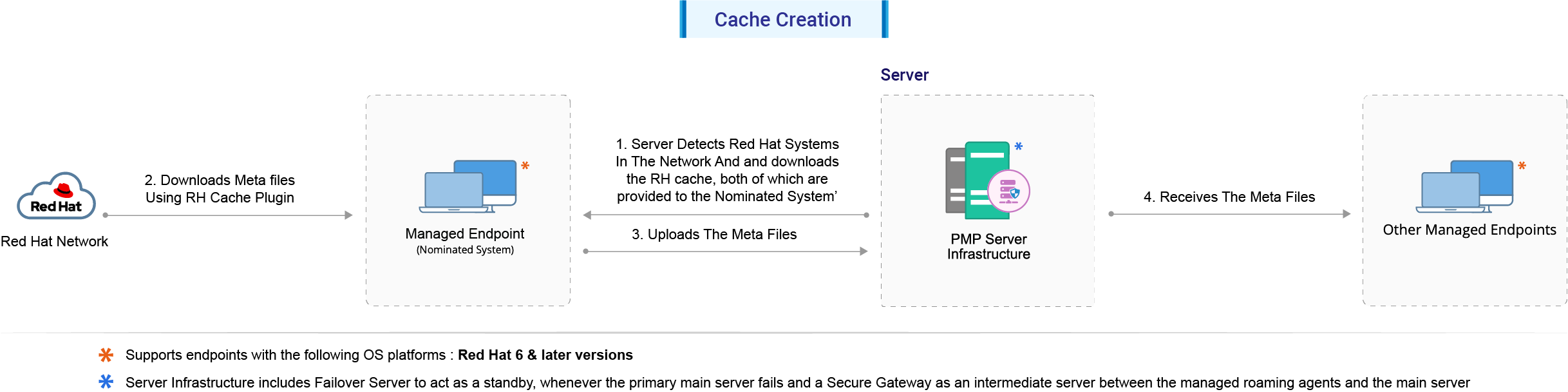
Steps involved in the process of Cache creation:
- The Patch Manager Plus server detects the available Red Hat versions and architecture in all the systems in your network.
- The Nominated System (for servers) downloads the RH Cache Plugin from the server. The Plugin will reside on the Nominated System.
- The RH Cache Plugin in the Nominated System downloads required meta files for all the other systems in the network (servers) from the Red Hat portal, using the YUM tool.
- The downloaded files are then uploaded to the server.
- All the other systems residing in the network receive the data from the server. Each system uses the meta data to detect it's missing patches and dependencies.
Note: The above steps refer to servers. However, the same steps are applicable for Workstations and Desktops as well.
2. Scan and Deployment
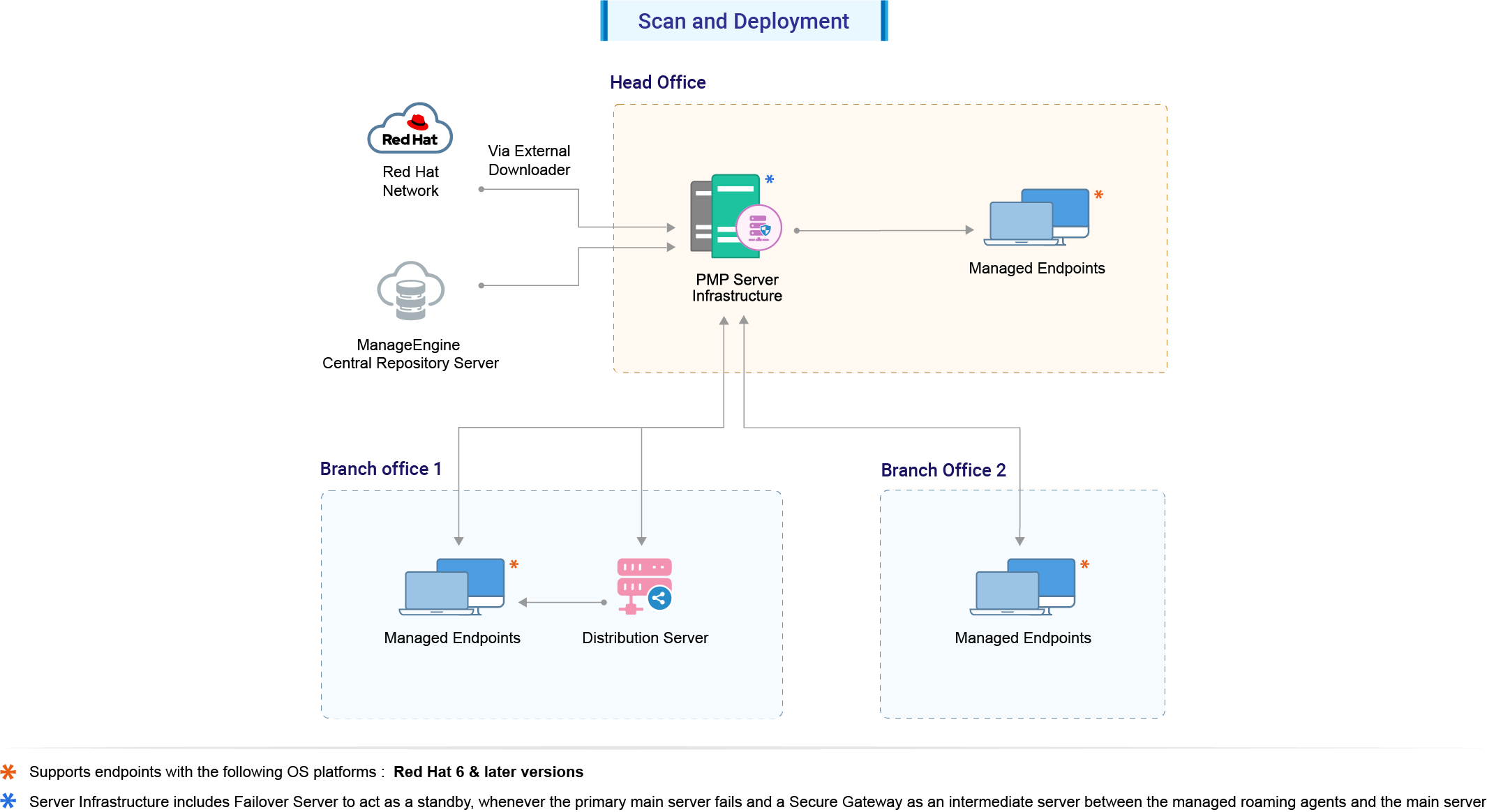
Steps involved in the process of scanning and patch deployment:
- The Central Server syncs the External Download Tool and supported patches information from ManageEngine's central Patch Repository.
- The server initiates the scan on all the Red Hat systems and detects the missing patches.
- The External Download Tool downloads the patches and dependencies from the Red Hat portal using the account credentials provided.
- a) The downloaded files are replicated from the Central server to the Distribution Server(s). The remote office agents download the files from the Distribution Server.
b) Other agents download the files from the Central Server.
- Once patches are downloaded and available, deployment is carried out.
Source:
The Patch Manager Plus server collects the patch information from this site and stores it in cache. This cache will contain all the patch bulletins of Red Hat Linux. The system which you have nominated will download this RH Cache Plugin. The bulletins are downloaded from this source.
Domain:
This is the domain from where Red Hat Linux patches are downloaded.
The RH Cache Plugin present in the Nominated System will download all the patches from the above-mentioned domain using the YUM tool. For Enterprise OS management, the patches are downloaded from this domain.
The downloaded files are sent to the Patch Manager Plus server which connects to the External Download Tool and the online patch database and scans all the systems in your network. The External Download Tool downloads all the patches from the Red Hat portal. Now, every system in the network will download this file from the Server and using this the missing patches are deployed.
For the complete list of supported Linux operating systems,refer here. If you are using other Linux flavors, you can add them to our product roadmap.

