Restoring Data in an MS SQL Server
In the event of a disaster or data loss, restoring backed-up data to the PAM360 database is critical to ensure business continuity. PAM360 provides dedicated scripts and guidelines for restoring data securely. The restoration process ensures that all encrypted data is retrieved and reloaded into the PAM360 database, helping organizations quickly resume normal operations.
This document outlines the step-by-step procedure for restoring data in an MS SQL Server database for PAM360.
Best Practice
PAM360 leverages MS SQL Server's encryption mechanism to secure its data. The encryption master key is stored in the <PAM360-Installation-Directory>/conf folder as masterkey.key. For enhanced security, it is recommended to move this key to a secure location during the MS SQL installation and use it when performing disaster recovery.
Data Restoration Procedure
- Install a new instance of PAM360 with MS SQL Server as the backend database. This new instance will be used to restore the backup. Ensure the MS SQL Server instance is configured with SSL. Refer to the section 3 under MS SQL configuration for SSL setup details.
- Copy the PAM360 backup file from the original SQL Server. By default, the backup file is located in the <MSSQL-Installation-Directory>/Backup folder and follows this naming format: pam360backup_pam360version_backupdate-time.bak (For example, pam360backup_4500_110721-1159.bak). Click here to learn more about taking backups of your PAM360 data. The backups taken from the MS SQL database will be stored as a .bak file in the host, where the SQL server is running.
- On the machine where the backup will be restored (another instance of SQL Server), launch Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio and connect to the Database Engine.
- Right-click on Databases and the click Restore Database from the menu.
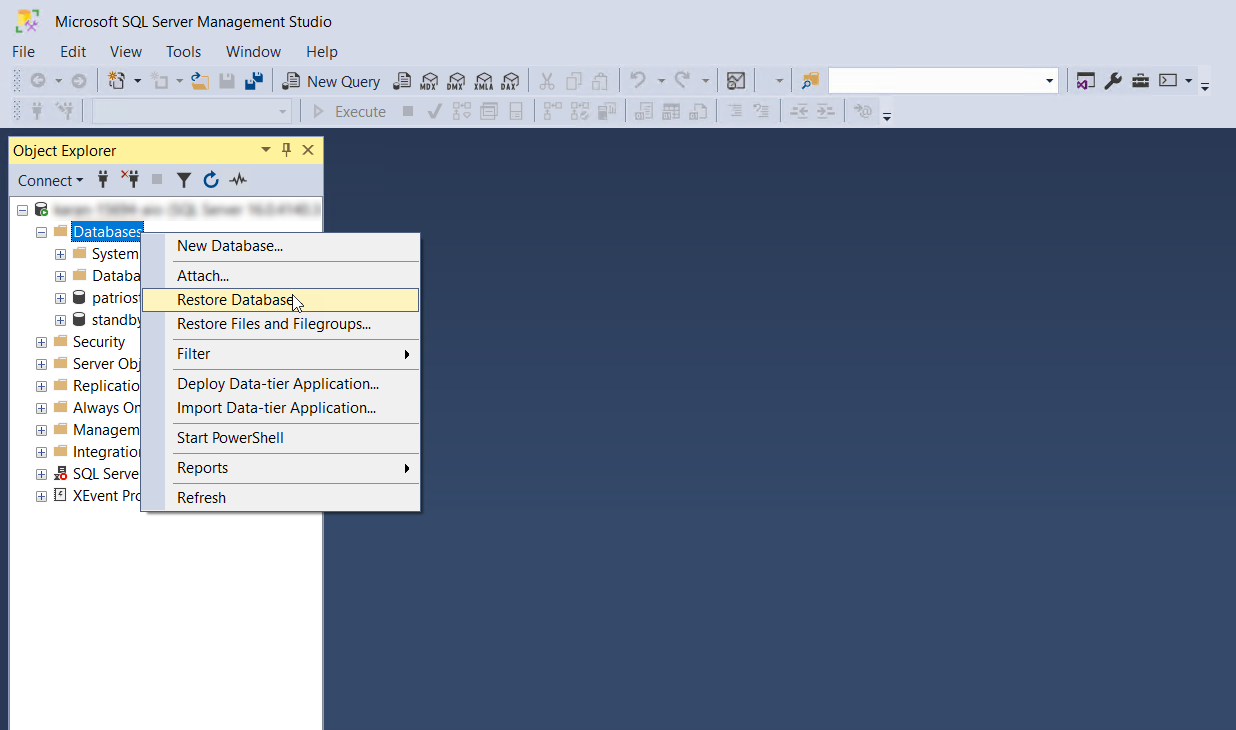
- In the Restore Database window, select Device under the Source, and click the [...] button to browse and select the PAM360 backup file.
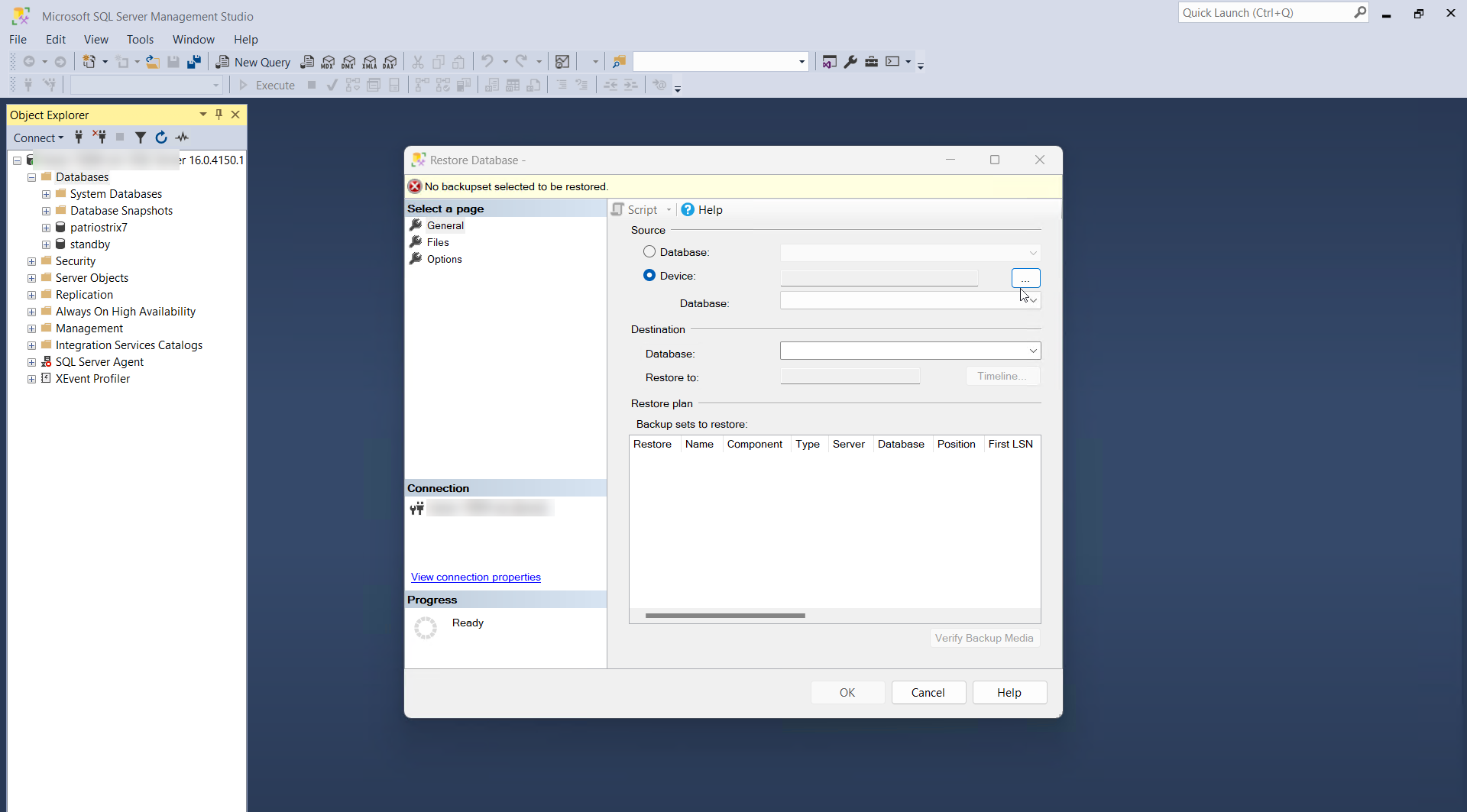
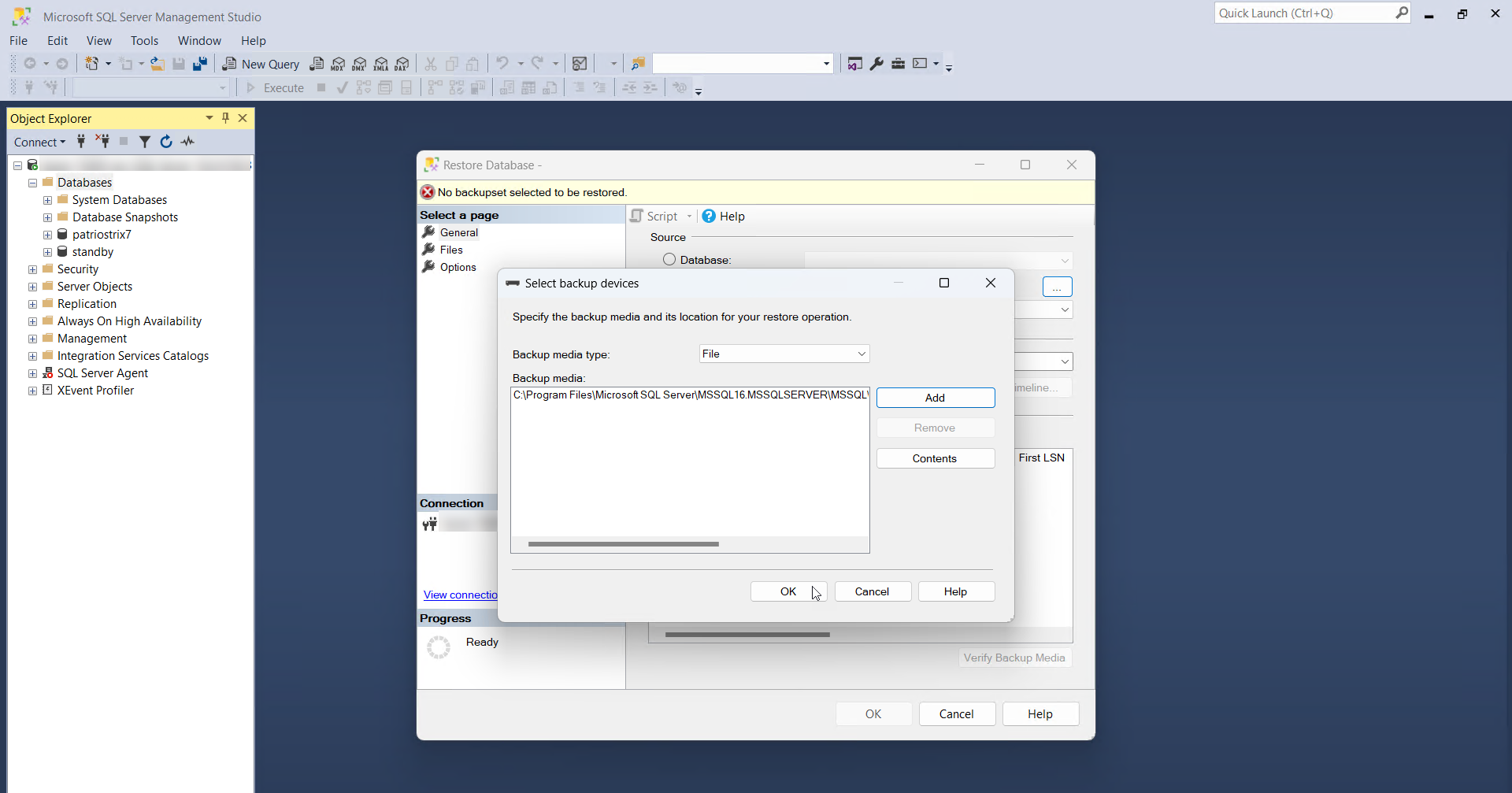
- In the Select backup devices pop-up, choose File as the Backup media type and click Add.
- In the Locate Backup File window, select the PAM360 backup file and click OK.
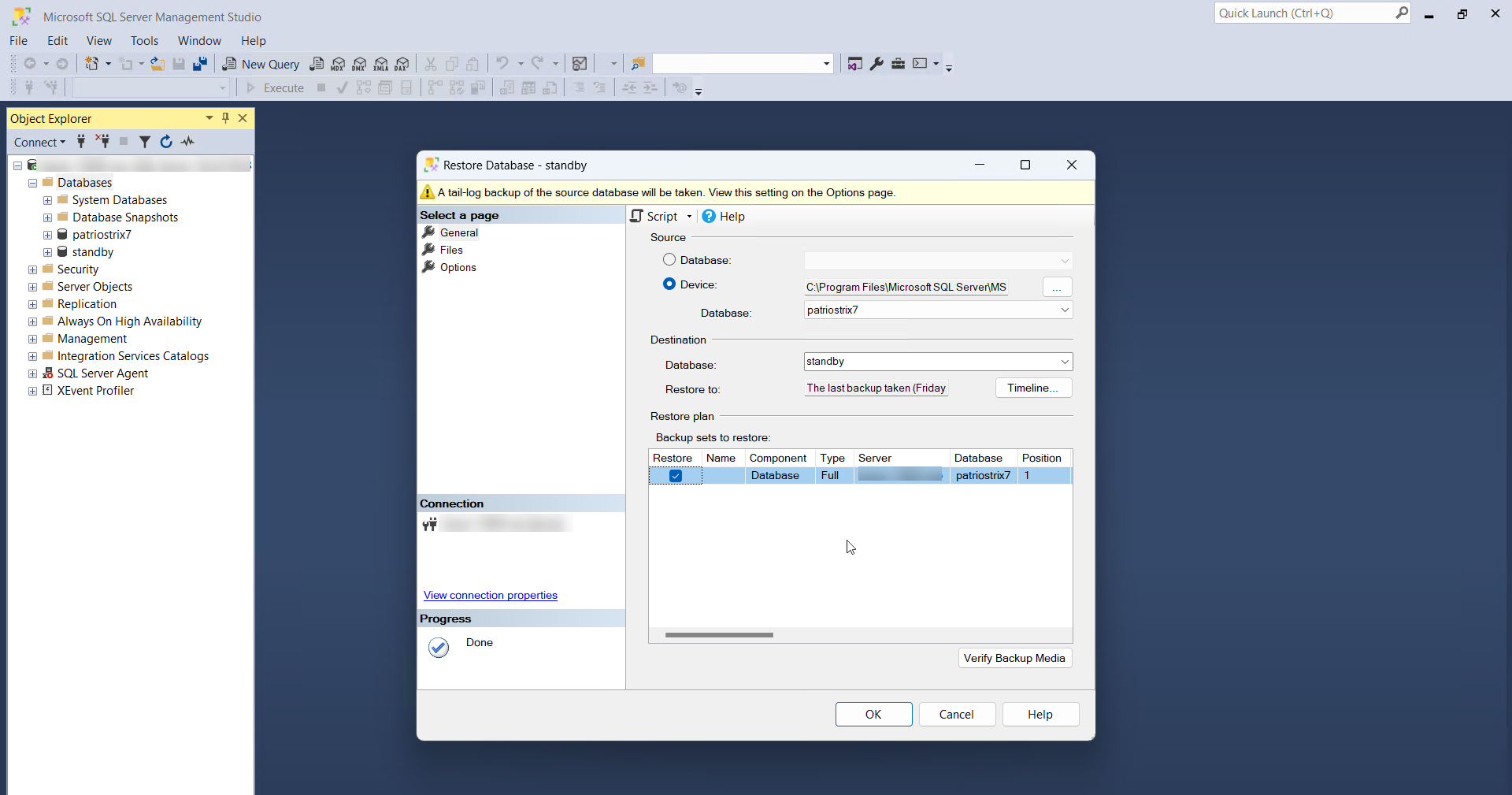
- In the Restore Database window, specify the target database in the Database filed under Destination. Under Backup sets to restore, choose the appropriate Restore column and click OK. Upon completion, a status window will confirm the successful restoration.
- Now, restore the master key. By default, the encryption master key is stored in the <PAM360-Installation-Directory>/conf directory as masterkey.key. If the file was moved to a secure location, retrieve it and copy the password from the masterkey.key file.
- Connect to the SQL Server where the backup has been restored. Open Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio, connect to the Database Engine , and execute the following queries to decrypt the data. Executing these queries will decrypt the data in the database.For example:
use <name_of the restored_database>;
OPEN MASTER KEY DECRYPTION BY PASSWORD = ' master_key_password';
alter master key regenerate with encryption by password = 'master_key_password';
use passtrix;
OPEN MASTER KEY DECRYPTION BY PASSWORD = 'secret';
alter master key regenerate with encryption by password = 'secret'; - Navigate to <PAM360-Installation-Directory>/conf folder and edit the manage_key.conf file to specify the location of the pam360_key.key (the encryption master key). PAM360 requires this key to be accessible when starting up. Once the server starts successfully, the key file is no longer needed, and the device storing the key can be taken offline.
Caution
From PAM360 build 8000 onwards, it is mandatory to retain the pam360_key.key file in the file path specified in the manage_key.conf file for a seamless operation. PAM360 continuously accesses this file to ensure uninterrupted operation. If the pam360_key.key file is not available in the specified path, the service may not startup or certain features such as database backup will not function.
Caution
- Perform the database restore using the same account that PAM360 uses to connect to the database. If a different account is used for restoration, execute the additional queries below to grant the necessary permissions for the PAM360 account to read the master key:
GRANT VIEW DEFINITION ON CERTIFICATE::PMP_CERT TO [user]
GRANT VIEW DEFINITION ON SYMMETRIC KEY::PMP_SYM_KEY TO [user]
Here, [user] refers to the account used by PAM360 to connect to the SQL database. You can find the account's name in the JDBC URL in <PAM360-Installation-Directory>/conf/database_params.conf file, unless the account uses Windows authentication.GRANT CONTROL ON CERTIFICATE::PMP_CERT TO [user]
- Verify the correct names of the CERTIFICATE and SYMMETRIC KEY using the following queries:
select * from sys.certificates
select * from sys.symmetric_keys
- Perform the database restore using the same account that PAM360 uses to connect to the database. If a different account is used for restoration, execute the additional queries below to grant the necessary permissions for the PAM360 account to read the master key:
By following these steps, you can restore your PAM360 data from an MS SQL Server backup and ensure business continuity.