PAM360 Basic Implementation and Best Practices
Before managing your critical resources and privileged accounts, it is essential to properly set up your PAM360 account. The setup process involves several key steps: configuring the mail server, upgrading your account with the procured license key, managing the encryption key, onboarding users, and enhancing security with two-factor authentication. Let's explore each of these steps in detail to ensure your PAM360 account is configured correctly and securely.
- Licensing
- Managing the PAM360 Encryption Key
- Rotating the PAM360 Encryption Key
- Updating the PAM360 Web Server Certificate
- Setting up the Mail Server
- Adding the Users
- Adding the Resources
- Setting up Disaster Recovery
1. Licensing
The crucial step before configuring the PAM360 application is to update the license key in your PAM360 account. This step unlocks the complete functionality of the software. Store the purchased license file locally on your computer for easy access before beginning this process.
- Click on the profile icon at the top right corner of your PAM360 interface and select the License option. This action will open a pop-up window displaying your current license details.
- Click on the Browse option within the License pop-up window, locate the license file on your computer, and select it.
- Click Open to upload the selected license file.
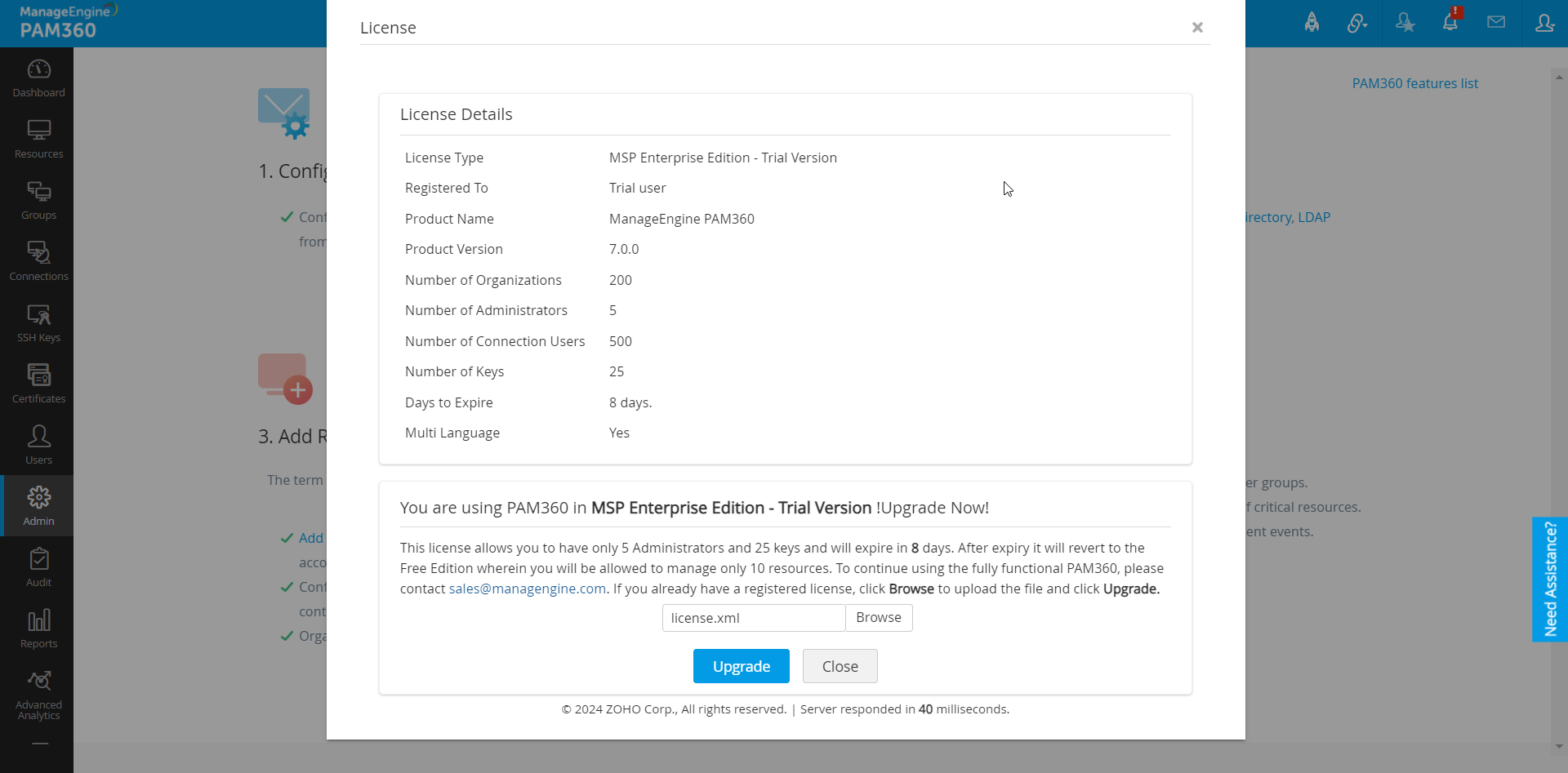
- Finally, click the Upgrade icon within the License window to complete the process.
- Close the PAM360 web client and restart the PAM360 service.
2. Managing PAM360 Encryption Key
PAM360 employs AES-256 encryption to secure passwords and other sensitive information in its password database. The encryption key used is auto-generated and unique for each installation. By default, this key is stored in a file named pam360_key.key within the <PAM360 Installation Directory>/conf folder of the installation directory. However, for production instances, PAM360 mandates that the encryption key not be stored within its installation folder to prevent the encryption key and the encrypted data in both live and backed-up databases from residing together.
We strongly recommend relocating this encryption key to an external location outside the machine where PAM360 is installed, such as another machine or an external drive. You can specify the full path of the folder where you wish to move the pam360_key.key file, manually transfer the file to that location and remove any references within the PAM360 server installation folder. The path can be a mapped network drive or an external USB (hard drive/thumb drive) device.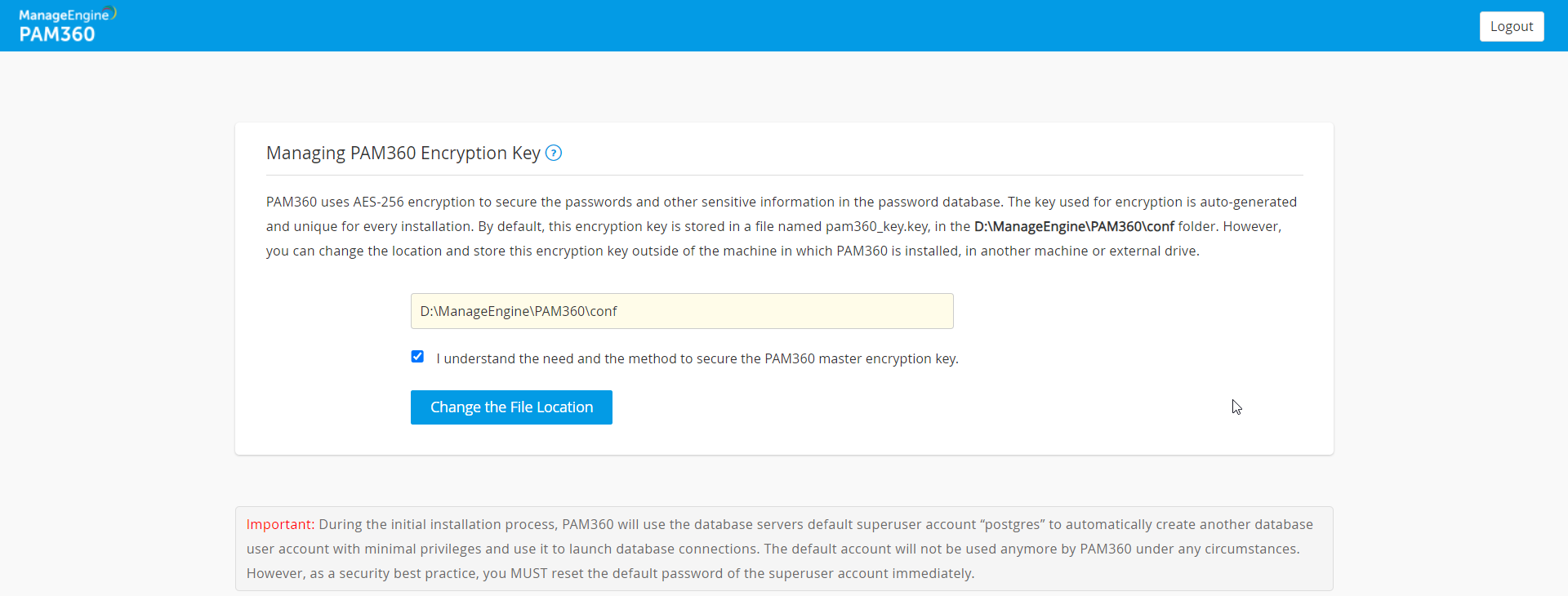
PAM360 will record the location of the pam360_key.key in a configuration file named manage_key.conf, located in the <PAM360 Installation Directory>/conf folder. You can also directly edit this file to change the key file location. After configuring the folder location, move the pam360_key.key file there and ensure the file or the key value is not stored anywhere within the PAM360 installation folder.
PAM360 requires the conf path to be accessible with the necessary permissions to read the pam360_key.key file during startup. Once the startup is complete, access to the file is no longer needed, and the device containing the file can be taken offline.
Caution
From PAM360 build 8000 onwards, it is mandatory to retain the pam360_key.key file in the file path specified in the manage_key.conf file for a seamless operation. PAM360 continuously accesses this file to ensure uninterrupted operation. If the pam360_key.key file is not available in the specified path, the service may not startup or certain features such as database backup will not function.
Best Practices
- Always ensure robust protection for the encryption key with multiple layers of security, such as using Windows File Encryption and stringent access controls. Since only the PAM360 application requires access to this key, it is imperative that no other software, script, or individual can access it under any circumstances.
- It is crucial to securely back up the pam360_key.key file independently. You will need this key to recover PAM360 backups. If the key is misplaced or lost, PAM360 will not start.
- Additionally, if you store the database_params.conf file in a different location, you must copy it back to the original location (i.e., <PAM360 Installation Folder>/conf/) before performing any application upgrades.
3. Rotating the PAM360 Encryption Key
The PAM360 encryption key plays a critical role in protecting the privileged credentials and other sensitive information stored in the database. Over time, prolonged use of the same encryption key increases the risk of compromise. To minimize this risk, organizations are required to rotate the encryption key periodically, in accordance with established security best practices and relevant regulatory requirements. PAM360 offers a secure and streamlined mechanism to rotate the encryption key without impacting data integrity.
3.1 How Does the Key Rotation Process Work?
Once the key rotation process is initiated, PAM360 first identifies the existing encryption key in the pam360_key.key file, located in the path specified in the manage_key.conf file. The key rotation process continues only if the existing key file is present in the location specified. PAM360 creates a database backup before rotating the encryption key to prevent any data loss in the event of unexpected failures.
During the key rotation process, all stored passwords and sensitive data are decrypted using the existing key and then re-encrypted using the newly generated encryption key. The new encryption key is written to the 'pam360_key.key' file located within the specified location. If an error occurs while generating or writing the new encryption key, the key rotation process is aborted to maintain data integrity.
3.2 Steps to Rotate the PAM360 Encryption Key
Caution
Before proceeding with the encryption key rotation, ensure the following:
- The pam360_key.key file is available in the path specified in the manage_key.conf file located within the <PAM360-Installation-Directory>\conf folder.
- High availability and replication status are active in environments configured with high availability setup.
- PAM360 has read and write permissions for accessing the pam360_key.key file.
- No critical administrative operations are in progress.
Follow these steps to rotate the PAM360 encryption key:
- Stop the PAM360 service.
- Navigate to the <PAM360-Installation-Directory>/bin folder, open the command prompt, and execute the following command based on your operating system:
Windows:
RotateKey.bat
Linux:
Upon execution, the encryption key will be rotated successfully, and a confirmation message will be displayed on the screen.sh RotateKey.sh
- Now, start the PAM360 service.
Follow these steps to rotate the PAM360 encryption key in environments configured with the high-availability setup:
- Stop the PAM360 service on the primary server and ensure that the PAM360 service is running on the secondary server.
- Navigate to the <PAM360-Installation-Directory>/bin folder on the primary server, open the command prompt, and execute the following command based on your operating system:
Windows:
RotateKey.bat
Linux:
Upon execution, the encryption key will be rotated successfully, and a confirmation message will be displayed on the screen.sh RotateKey.sh
- If the pam360_key.key file is not stored in a shared location accessible by both the primary and secondary servers, but at different locations in your environment, then copy the pam360_key.key file from the primary server and place it in the location specified in manage_key.conf file on the secondary server.
- Start the PAM360 service on both the primary and secondary servers.
Follow these steps to rotate the PAM360 encryption key in environments configured with the application scaling setup:
- Stop the PAM360 service on the main node and all sub nodes.
- Navigate to the <PAM360-Installation-Directory>/bin folder on the main node, open the command prompt, and execute the following command based on your operating system:
Windows:
RotateKey.bat
Linux:
Upon execution, the encryption key will be rotated successfully, and a confirmation message will be displayed on the screen.sh RotateKey.sh
- Now, start the PAM360 service on the main node. Upon successful startup, follow these steps:
- Copy the value of the password parameter in the database_params.conf file on the main node and replace the corresponding value on each sub-node.
- If the configured backend database in your environment is PostgreSQL, copy and replace the value of the new_superuser_pass parameter on the main node to each sub-node.
- If the configured backend database is MSSQL, copy the masterkey.key file within the conf folder on the main node to each sub node.
- Copy and replace the value of the keystorePass entry within the server.xml file on the main node to each sub node.
- Copy the pam360_key.key file from the location specified in the manage_key.conf file on the main node to each sub-node.
- Start the PAM360 service on all sub nodes.
Additional Detail
In PAM360 builds before 8000, the duration of the encryption key rotation process may vary depending on the number of managed passwords and other system parameters. The process typically takes a few minutes to complete. A confirmation message is displayed once the key rotation is complete.
4. Updating PAM360 Web Server Certificates from Web Console
To update the PAM360 web server certificate from the web console, follow these steps:
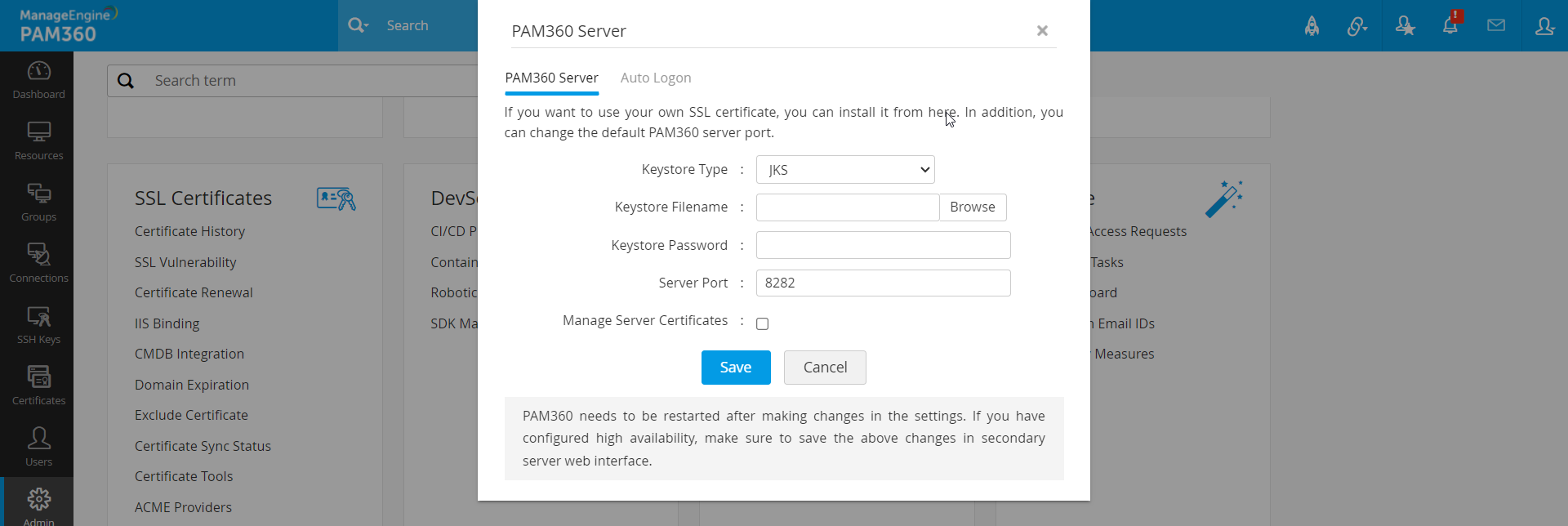
- Navigate to Admin >> Server Settings >> PAM360 Server.
- On the PAM360 Server page that opens, install your keystore file belonging to the SSL certificate and/or change the default PAM360 server port.
- To update your SSL certificate, select the type of the keystore file (JKS, PKCS12, or PKCS11) from the Keystore type drop-down menu.
- Browse for the keystore file on your system and upload it in the Keystore Filename field.
- Enter the password for your keystore file in the Keystore Password field.
- If you want to change the default PAM360 server port, enter the new port number in the Server Port field.
- Click Save and restart PAM360 after saving the changes.
5. Configuring Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
Setting up the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) server is essential for delivering important messages to users. PAM360 uses email to notify users about their account details, such as username, password, and the URL to access the PAM360 application. Therefore, it is crucial to configure the SMTP server before onboarding users. PAM360 offers the following options:
- Existing SMTP mail server in your organization
- Microsoft Exchange Online
Caution
If you choose Microsoft Exchange Online as the mail server, OAuth 2.0 authentication is required for all email communications sent from the product.
Refer to the Mail Server Settings documentation to know more about the configuration and setup.
6. Adding Users into PAM360
Best Practice
Ensure you change the password of the default admin user or delete the account after adding another administrator user.
Onboarding users is a crucial step in setting up your PAM360 account. PAM360 allows you to onboard users manually or import them from various sources such as a file, Active Directory, Microsoft Entra ID, or LDAP. Detailed instructions for each method can be found through the provided links. Using the administrator account, you can add or import users and assign them roles based on their required permissions. PAM360 offers six predefined user roles but also provides the flexibility to create custom user roles. These custom roles enable you to modify access and permissions according to your organizational needs.
Additionally, PAM360 allows you to organize users into groups based on factors like designation, department, or location, facilitating efficient user management and simplifying permission assignments.
Furthermore, PAM360 supports the creation of API user accounts necessary for application-to-application password management. Users with administrator privileges can add API users. For detailed steps on adding an API user, click here.
6.1 Enabling Two-Factor Authentication
Two-Factor Authentication (TFA) is a security mechanism that requires users to provide a secondary authentication factor to access their PAM360 account. Enabling TFA enhances account security by adding an extra layer of protection. Once TFA is enabled, users must authenticate using the selected TFA mechanism after logging in with their username and password. Administrator accounts have the ability to set up and disable TFA.
PAM360 supports various TFA mechanisms, including OTP via email, Google Authenticator, and Duo Security. Administrators can choose any of the supported mechanisms and configure them accordingly. Refer to this document for detailed steps on setting up two-factor authentication.
7. Adding Resources into PAM360
The first step in password management with PAM360 is adding your resources to the PAM360 database. Resources refer to the servers, applications, or devices whose user accounts and passwords will be managed by PAM360.
Resources can be added manually or imported from a file along with their user account and password information. Depending on your needs, you can set up the password reset method to be either remote or agent-based. For ease of management, resources can be grouped together to perform bulk operations. Additionally, you can create nested resource groups, maintaining a hierarchical structure for navigational convenience.
By default, only the user who added the passwords can view and edit them. However, you can share resource passwords with other PAM360 users or user groups as needed. This allows users to access and modify passwords that are owned by them or shared with them.
7.1 Access Control Approval Workflow
After adding resources, administrators can implement an access control workflow for enhanced security. Upon successful authentication into PAM360, users gain access to passwords owned by them or shared with them. In some cases, administrators might want to grant temporary access to passwords for specific users for a limited time.
Set up the access control workflow according to your organization’s requirements.
However, if you are a user responsible for viewing assigned passwords, no additional configuration is needed. You can directly view and edit the passwords of the resources or accounts if you have the necessary permissions.
8. Setting up Disaster Recovery
To set up disaster recovery, follow these steps:
- Configure Database Backup: Schedule regular backups of the entire PAM360 database.
- Export Resource Information: Export resource information in a readable format of your choice to maintain copies.