SSH Keys Discovery and Creation
SSH keys serve as a secure means of authentication and establishing encrypted connections between a client and server. They offer a highly secure alternative to password-based authentication for remote logins and file transfers. Widely employed in system administration and secure network communication, SSH keys deliver enhanced security, convenience, and automation features while decreasing reliance on passwords. By adhering to best practices in key generation, management, and usage, one can maximize the advantages and overall security provided by SSH keys. PAM360 allows you to manage the entire life-cycle of SSH keys of your SSH resources.
At the end of this document, you will have learned about discovering the SSH keys in an organization and creating new SSH keys for deployment. Refer to this help document to learn more about managing the discovered or created keys directly from the PAM360 interface.
1. Discovering SSH Keys
The SSH keys management starts with the SSH resource discovery process. To discover the SSH keys from the organization resources via PAM360, it is required to add the respective SSH resources in the PAM360 repository. You can add the SSH resources manually or via the Linux resource discovery process.
Additional Details
The term SSH keys mentioned here only represent the private keys of the SSH resources.
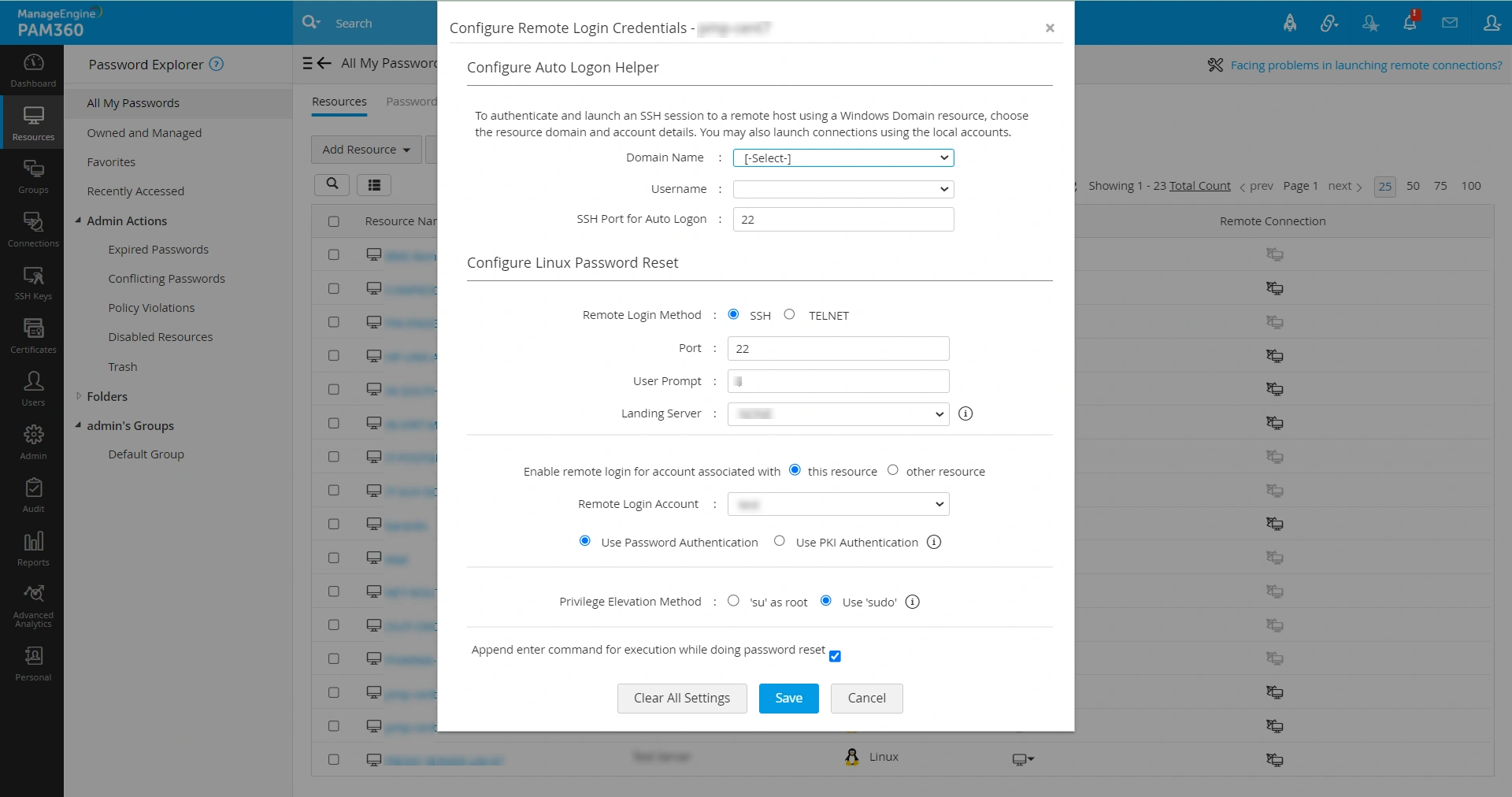
1.1. Elevating Privilege for SSH Keys Management
To discover, associate, deploy, and rotate SSH keys, PAM360 requires a remote login method, a login account for authentication, and privilege elevation configured with root privileges. To configure those above requirements,
- Navigate to Resources >> All My Passwords >> Resources.
- Click the Resource Actions icon beside the respective SSH resource and click Configure Remote Password Reset.
- Select the desired Remote Login Method, Landing Server (if configured), and enter the Port details (if modified).
- Select the remote login account that has to be used for authentication with the respective authentication method.
- Provide the privilege elevation method as 'su' as root or Use 'sudo'. If you choose the option 'su' as root, select the root account with the sudo privilege. If you choose the option Use 'sudo', the account used for remote login will get the root privileges for further operations.
- Now, click Save.
1.2 Discovering SSH Keys from SSH Resources
To discover the private keys associated with the accounts of the added/discovered SSH resources,
- Navigate to Resources >> All My Passwords >> Resources and click on the respective Linux resource.
- Select the user accounts from which the SSH keys are to be discovered, or select the accounts in bulk.
- Now, click Discover Keys from the top pane.
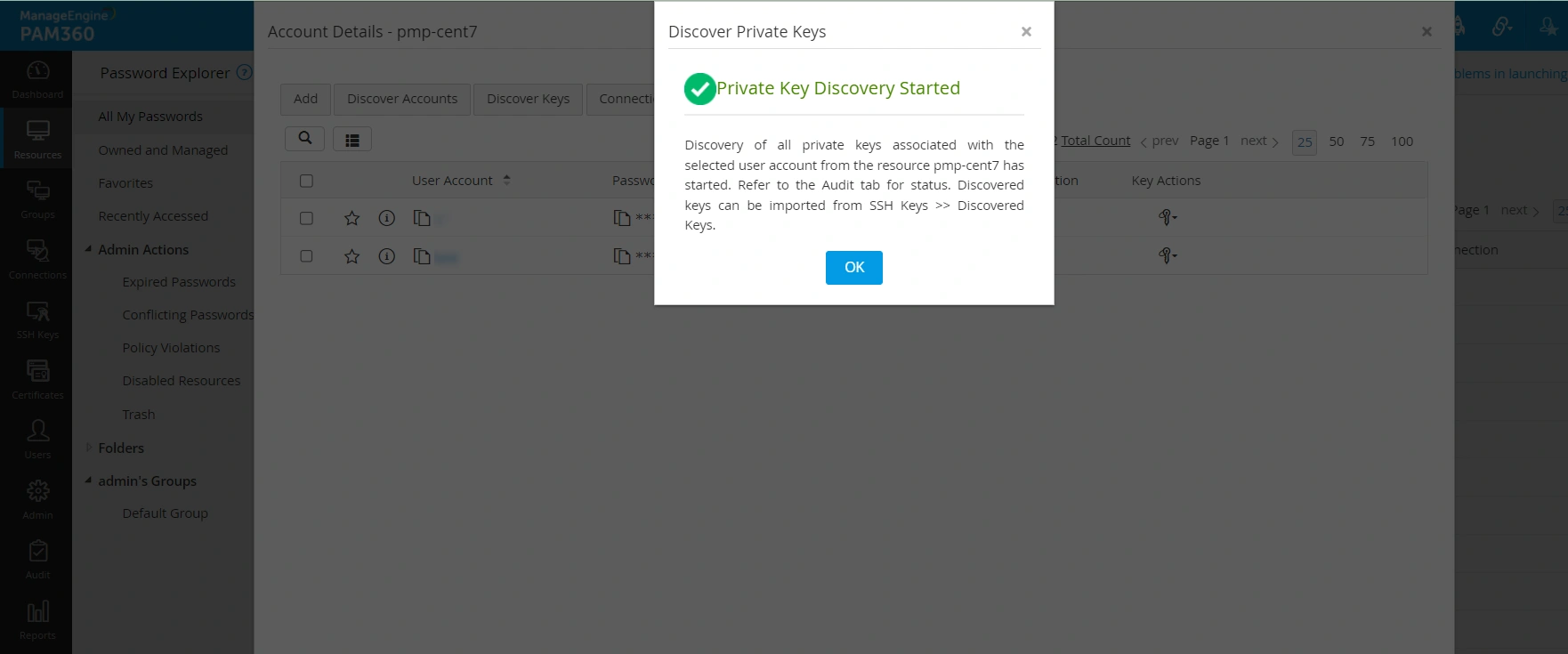
- The SSH keys present in the selected user accounts will be discovered in PAM360 with the relevant audit detail. You can see the discovered SSH keys from the SSH Keys >> Discovered Keys tab.
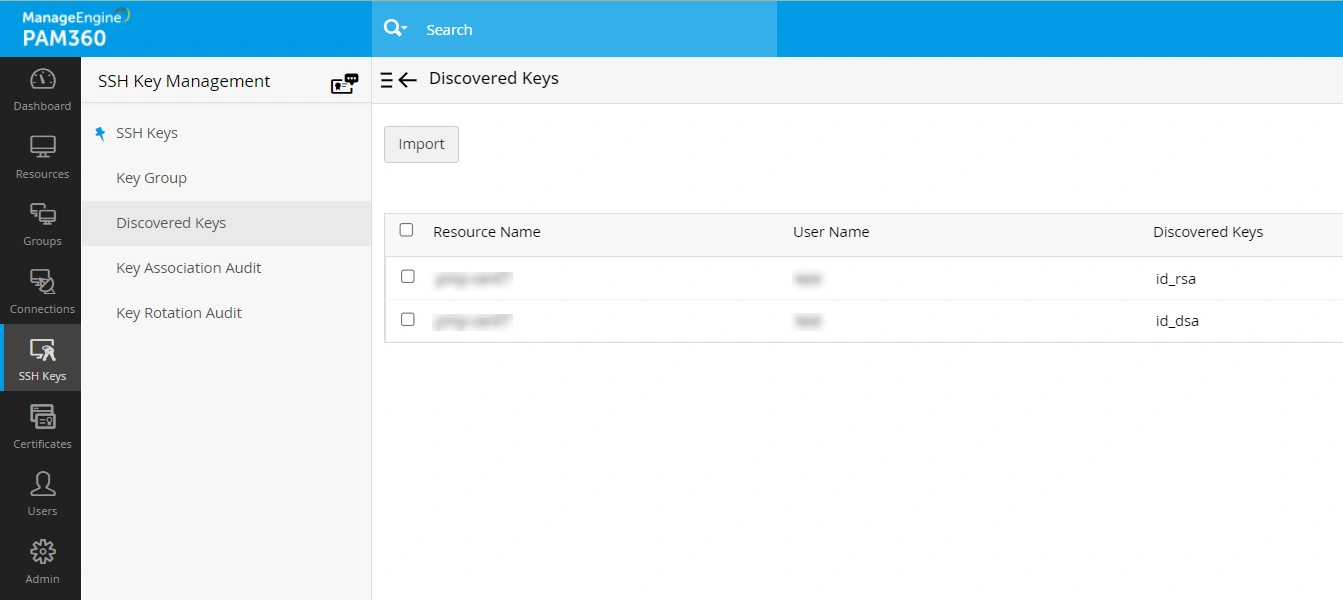
1.3 Importing Discovered Keys to PAM360
PAM360 requires SSH key passphrase for SSH key management. If the credentials are in place, you can import the SSH keys already discovered. To import the key files from the discovered SSH resource:
- Navigate to the SSH Keys >> Discovered Keys tab. On that page that opens, the discovered SSH keys will be listed with their details.
- Select the keys that you want to import and click the Import button. Now, the imported keys can be viewed from the SSH Keys >> SSH Keys tab.
Caution
If the keys are protected with a passphrase, even though the import operation will execute successfully while associating with user accounts, you need to enter the passphrase to use the key.
1.4 Importing Keys from Systems
In addition to the discovery of key files from the SSH resources, you can also specify the location, and import the keys present in any system. To import the key files from the system:
- Navigate to the SSH Keys >> SSH Keys >> More and click Import Keys.
- Click the Browse button and select the key files within the system.
Caution
You can either import SSH keys from systems individually or in bulk. If you opt for the individual import process, enter the passphrase of the respective SSH key. For the bulk import process, the selected SSH keys should either share the same passphrase or should be passphrase-free.
- Enter the name and passphrase of the key.
- Enter a Key Comment for your reference.
- Click the Add button to include the keys in the SSH keys repository.
To edit a Key Comment in the already imported keys, follow the below steps:
- Navigate to the SSH Keys >> SSH Keys tab.
- Select the required key from the repository.
- Click the More drop-down from the top menu, choose Edit, and enter the required comment.
- Select the checkbox 'Update the comment in the authorized keys file of the associated user(s) account' to apply the updated key comment in the associated end servers as well. This option eliminates the need to update the key comments manually in the authorized_keys file in the end servers.
Additional Details
Key Comment can be edited for only one key at a time.
2. Create and Deploy New SSH Keys
PAM360 also allows you to create new key pairs and deploy them on target systems. The create and deploy feature of PAM360 can be used for one-click generation and deployment of keys. Unique key pairs are generated for each user account, and the corresponding keys are deployed automatically in the user accounts of the target servers.
The SSH key pair can be generated using RSA / DSA algorithms as per the details below:
- RSA — 1024, 2048, or 4096-bit keys
- DSA — 1024-bit keys.
- ECDSA — 256, 384, or 521-bit keys
- ED25519
2.1 Creating SSH Keys
- Navigate to the SSH Keys tab and click the Create button.
- In the Create SSH Key window, enter the details of the key, and select the key type and length.
- Click the Create Key button to generate the key pair.
You will get confirmation that the new key has been created. All the keys that are created are automatically added to the centralized repository of PAM360. You can view these keys from the SSH Keys >> SSH Keys tab in the user interface. PAM360 allows you to search SSH Keys using Key Name, Key Type, Key Length, Finger Print, Created By, Age, and additional fields (if available).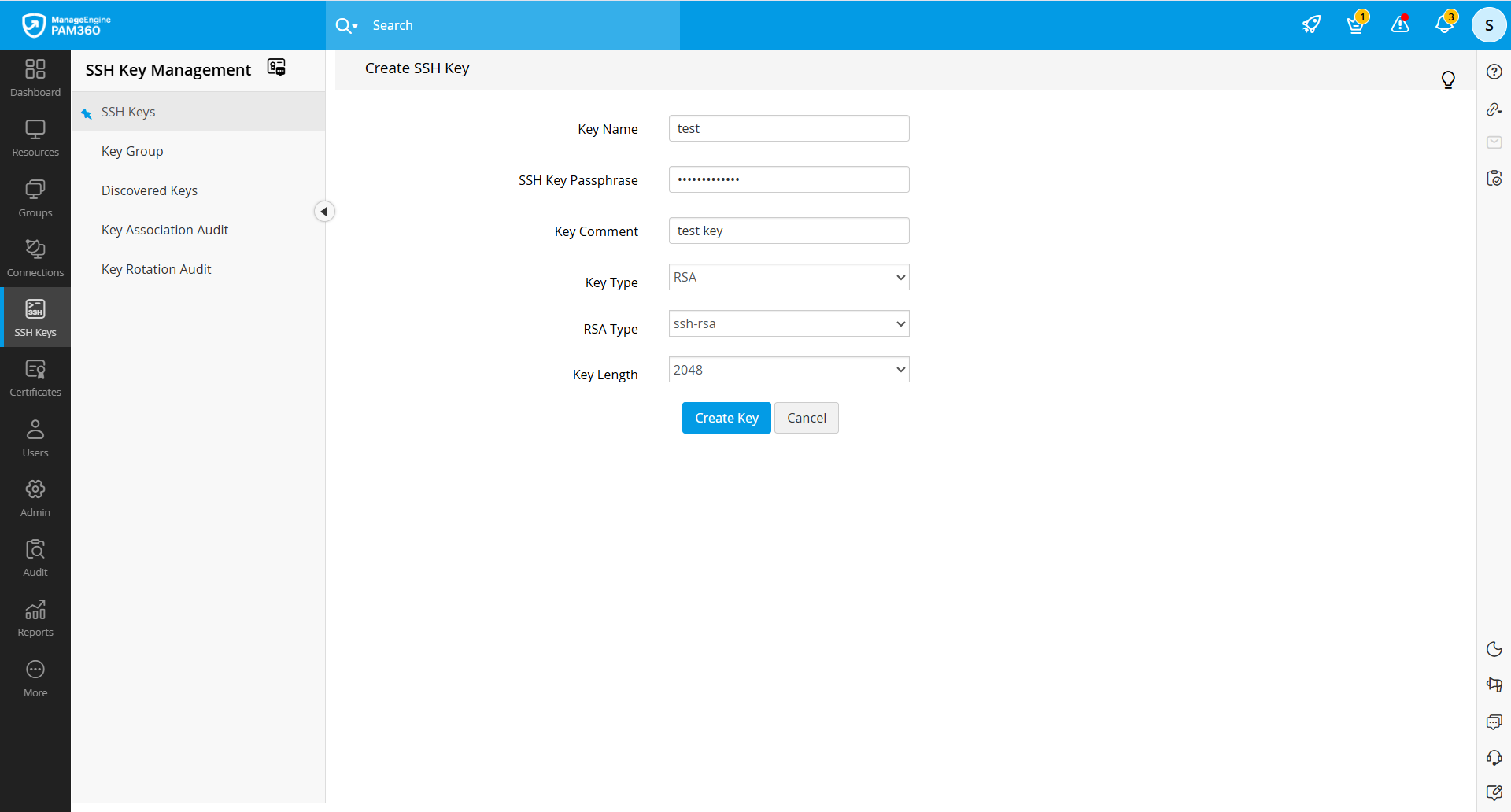
Administrators can view the passphrases of keys by clicking on the show passphrase icon provided at the right end of the keys.
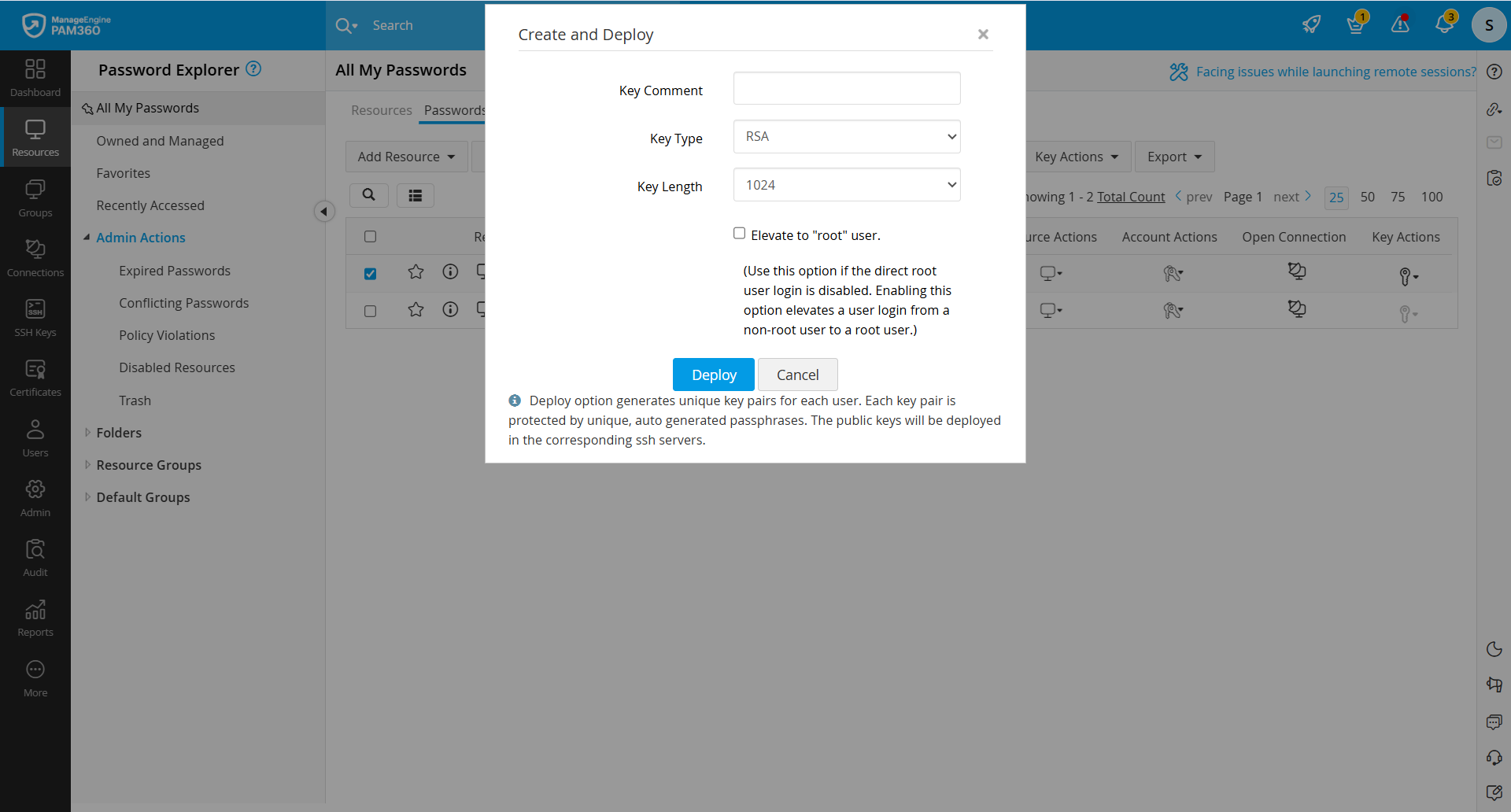
2.2 Create and Deploy SSH Keys
To create and associate keys with all the user accounts in a discovered resource:
- Navigate to Resources >> All My Passwords >> Passwords.
- Select the required account and select Create and Deploy under the Key Actions in the top pane to deploy the keys in all its enumerated user accounts.
- Select the Key Comment, Key Type, and Key Length.
- Select the checkbox to Elevate to "root" user.
Caution
For security reasons, root user login might be disabled for servers/machines. Enabling this option elevates a user login from a non-root user to a root user and allows you to associate keys with all other users on the server. Users have to provide root user and any non-root user credentials to PAM360 to elevate to a root user.
- Click the Deploy button to create key pairs and deploy them simultaneously in all the user accounts of the resource for which the credential is available.