LDAP: error code 49
This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and troubleshooting LDAP: error code 49, a common issue IT administrators face when managing Active Directory (AD).
What does error code 49 mean?
When applications or services fail to authenticate users or service accounts against an LDAP directory server, the system logs show an authentication failure with the message LDAP: error code 49, along with diagnostic codes.
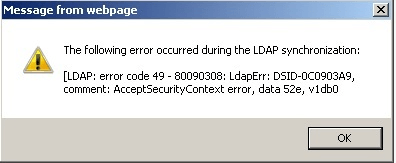
The key components of this error are:
- LDAP: error code 49: This is the generic LDAP error for invalid credentials.
- 80090308: This is a Windows-specific hexadecimal error code that often accompanies LDAP: error 49 in AD environments.
- data 52e: This sub-code helps us identify the specific reason for the authentication failure.
Common LDAP: error code 49 data sub-codes
While we know that the root cause for this error is authentication failure, we need to understand what the data code in the error message is for a more specific diagnosis. Here are the most commonly encountered data codes along with LDAP: error code 49.
| Data code |
Hexadecimal value |
Meaning |
Common causes |
| 52e |
0x52e |
Invalid Credentials |
Incorrect username or password. |
| 530 |
0x530 |
Not permitted to logon at this time |
User's logon hours are restricted in AD. |
| 531 |
0x531 |
Not permitted to logon at this workstation |
User is not allowed to log on from the computer they are using. |
| 532 |
0x532 |
Password expired |
The user's password has expired and needs to be changed. |
| 533 |
0x533 |
Account disabled |
The user's account is disabled in AD. |
| 701 |
0x701 |
Account expired |
The user's account has expired. |
| 773 |
0x773 |
User must reset password |
The User must change password at next logon flag is set. |
| 775 |
0x775 |
Account locked out |
The user's account is locked out due to too many failed login attempts.df |
Prerequisites
Ensure that you have the following permissions before trying to troubleshoot this error:
- Administrative access to your AD domain.
- Access to AD configuration files and logs.
- Network connectivity between the application server and the LDAP server on the required ports (typically 389 for LDAP or 636 for LDAPS).
Resolution
To resolve LDAP: error code 49 - 80090308, follow these troubleshooting steps, paying close attention to the data code in your error message.
Step 1: Diagnose using the data code
Identify the specific data code from your application's error log. This will guide your troubleshooting.
Step 2: Address the specific cause
- Verify user credentials for data 52e
- Ensure the username and password are correct.
- If the credentials are for a service account, try resetting the password in the directory and updating it in the application's configuration.
- LDAP servers can be sensitive to the username format. Try the following formats:
- User Principal Name: username@domain.com
- sAMAccountName: DOMAIN\username
- Distinguished Name: CN=Username,OU=Users,DC=domain,DC=com
- Review account status issues for data 532, 533, 701, 773, and 775
- Open Active Directory Users and Computers.
- Locate the user or service account.
- Right-click the account and select Properties.
- Navigate to the Account tab.
- Based on the status of the user account, perform the suitable action:
- Account disabled: If the account is disabled, enable it.
- Password expired: Reset the password for the user.
- Account locked out: Unlock the account.
- Account expired: Extend the account's expiration date.
- User must change password at next logon: Uncheck this option or have the user change their password.
- Verify logon restrictions for data 530 and 531
- Check logon hours: Ensure the user is allowed to log on at the current time.
- Check workstation restrictions: Ensure the user is allowed to log on from the workstation they are using.
- Verify bind account: If you are using a service account to bind to the LDAP server, verify the following for that service account:
- The password has not expired.
- The account is not locked out or disabled.
- The account has the necessary permissions to search the directory.
Validation and testing
Once you have applied a potential fix, validate the resolution by performing the following:
- Ask the user to try logging in again, or restart the service that was failing to authenticate.
- Use ldp.exe to perform a direct bind test to the LDAP server using the exact same credentials. This helps confirm the credentials are valid and isolates the issue to the application if the test succeeds.
- Monitor the application and security event logs for successful authentication messages.
By systematically diagnosing the data code and finding the root cause, you can quickly troubleshoot the error and restore service for your users.
Simplify AD management and prevent errors with ADManager Plus
Manually troubleshooting AD authentication issues like LDAP: error code 49 can be time-consuming and confusing. A proactive approach to AD management can prevent these problems from occurring in the first place.
ADManager Plus is a comprehensive AD management and reporting solution that simplifies these tasks instead of navigating the complexities of native tools.
- Proactively manage account status: Generate reports based on users' account status to find locked out, disabled, and soon-to-expire user accounts and passwords before they cause login failures.
- Streamline user management: Perform bulk user management actions like unlocking accounts or resetting passwords from a simple, intuitive console.
- Delegate with precision: Securely delegate routine AD tasks like password resets and account unlocks to help desk technicians with granular, role-based access controls, reducing the burden on senior admins.
By centralizing and automating AD management, ADManager Plus helps you maintain a healthier directory, reduce troubleshooting time, and minimize service disruptions for your users.
You might also face these errors after fixing LDAP: error code 49:
Select a language to translate the contents of this web page: