It is highly recommended to audit your database regularly. Auditing is an effective method for enforcing strong internal control, and enabling your organization to meet compliance requirements. Moreover, you can also monitor your business operations and identify the activities that deviate from the company policy. By enabling auditing by default, you can generate the audit record for auditing and for the compliance personnel.
When the Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA) is used to create a new database, Oracle Database automatically configures the database to audit the most commonly used security-relevant SQL statements and privileges. It also sets the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter to DB.
You can customize the initialization parameter. For instance, you can set the AUDIT_TRAIL initialization parameter to OS, if you want to write the audit trail records to the operating system files.
Oracle Database will still continue to audit the privileges that are audited by default. The auditing will not take place if the AUDIT_TRAIL parameter is set to NONE.
Oracle Database audits the following privileges by default:
Oracle Database audits the following SQL statement shortcuts by default:
If you wish to audit only selective events and not enable all the events in the default auditing list, you can do so by using the AUDIT and NOAUDIT statements.
Note: It is essential to verify the version of the Oracle Database that your application is using. If your application uses the default audit settings from DB 10g Release 2 (10.2), then the audit settings must be modified accordingly. For this, run the undoaud.sql script. If your application conforms to the Release 11g audit settings, you can either manually update the database to use the required audit configuration or run the secconf.sql script to apply the Release 11g default audit settings.
The undoaud.sql and secconf.sql scripts are in the $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin directory. While the undoaud.sql script affects the audit settings only, the secconf.sql script affects both audit and password settings. They won't affect other auditing settings.
Default auditing capabilities provide information on activities that happen in the database. However, it is difficult to analyze manually the details of every audited event and it's also difficult to audit other events that goes beyond the default auditing capability. To overcome these, it is recommended to deploy a log management that is capable of auditing different events.
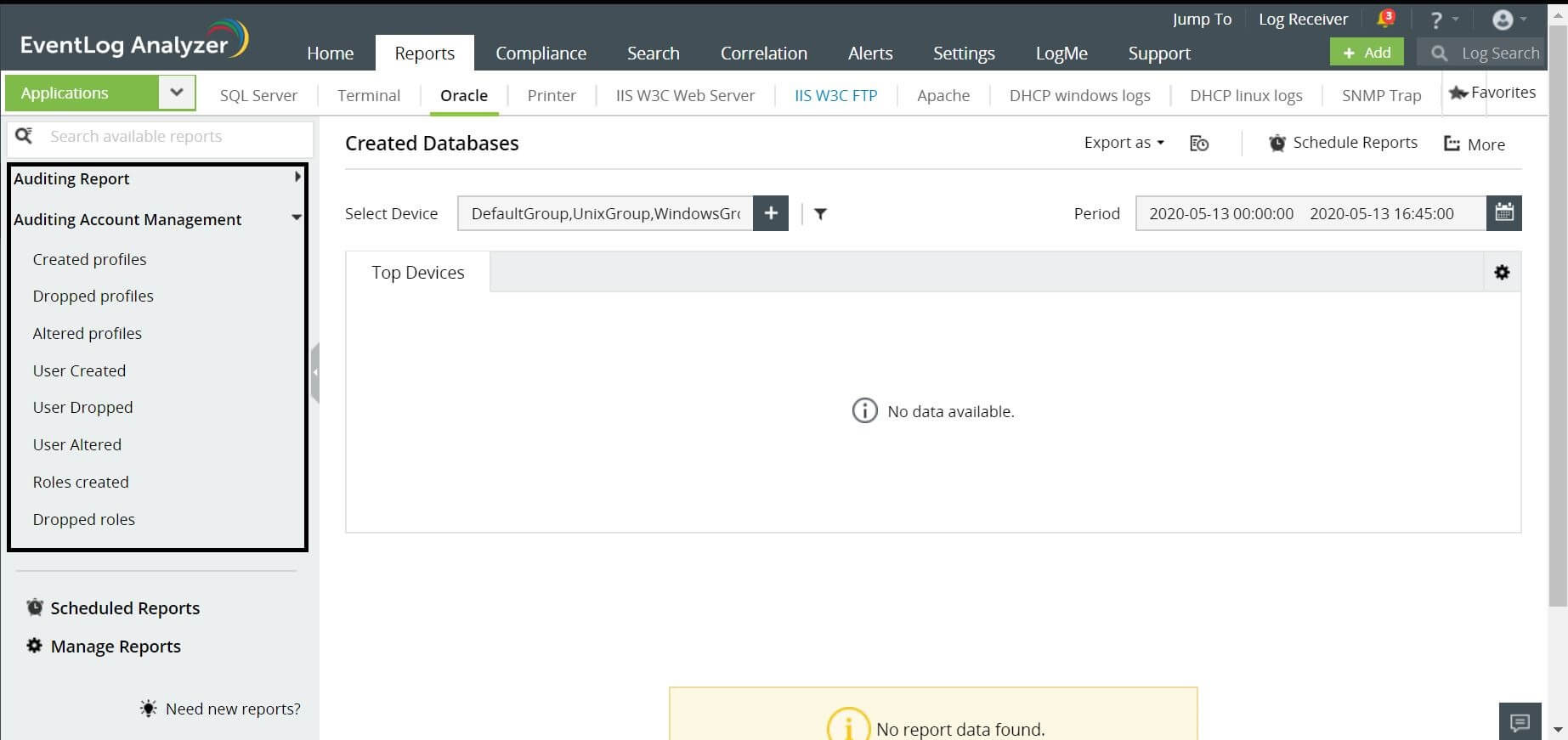
EventLog Analyzer is one such comprehensive log management solution that can help you with out of box reports and real time alerts. It can provide reports for events such as Created Database, Altered Database, Dropped Databases, and more.
Interested in a
log management
solution?
Manage logs, comply with IT regulations, and mitigate security threats.
Our support technicians will get back to you at the earliest.
Zoho Corporation Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.