Related content
What is SIEM?
Security information and event management (SIEM) is a cybersecurity technology that elevates security posture and boosts cyber resilience of enterprises. SIEM solutions empower security operation centers (SOC) to detect, investigate, and respond to threats in real time, while simplifying compliance and providing unified visibility across hybrid environments.
At its core, SIEM tools aggregate, correlate, analyze, and archive data from across an IT infrastructure—endpoints, servers, cloud platforms, firewalls, business applications, and more—to equip your SOC with the intelligence they need to uncover hidden risks and respond swiftly.
This comprehensive article explores the evolution, functionalities, and strategic value of SIEM and its role in addressing contemporary SOC challenges. Learn how SIEM can be your essential tool for advanced threat detection and response, harnessing AI-driven analytics to boost SOC efficiency in today's cyber landscape.
ManageEngine has been recognized in the Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ for SIEM
For seven consecutive years, ManageEngine has been recognized in the Gartner MQ for SIEM. Read the latest MQ to see why. Read the latest report
SIEM: Evolution and modern relevance
The term SIEM was first introduced by Gartner® in 2005, marking the convergence of security information management (SIM) and security event management (SEM). While early SIEM tools primarily focused on log management to meet compliance requirements, the explosion of sophisticated cyberthreats and tightening regulations has fueled rapid innovation in SIEM technology.
Today's SIEM platforms are much more than log collections; they are unified security platforms powered by AI-driven analytics and automated investigation tools. Modern SIEM solutions deliver real-time threat detection, behavioral analytics, integrated threat intelligence, and built-in security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) capabilities. This enables enterprises to proactively hunt threats, automate compliance reporting, and streamline incident response for evolving attack vectors like ransomware, insider attacks, and advanced persistent threats (APTs).
The global SIEM market size was worth USD 4.2 billion in 2024 and is estimated to reach an expected value of USD 10.74 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 11% during the forecast period (2025-2033).
- Security Information and Event Management Market Research Report by Straits Research
Designed for flexibility, next-gen SIEM operates seamlessly across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments, offering a centralized and comprehensive view of security events. By addressing common SOC challenges, including skill shortages, alert fatigue, and the demand for faster and more accurate threat detection, SIEM has become indispensable for organizations with distributed workforces and cloud-first strategies.
ManageEngine SIEM
ManageEngine Log360, a unified SIEM platform for detecting, investigating, and remediating threats and to improve resilience of your enterprise.
SIEM Benefits in 2025: Why it's still essential for modern cybersecurity
In 2025, SIEM still remains a cornerstone of enterprise cybersecurity strategies, evolving to address modern challenges while retaining its core value as a centralized hub for threat detection, investigation, and response (TDIR), and compliance. With hybrid workforces, sprawling cloud environments, and AI-driven attacks, visibility is non-negotiable when it comes to ensuring security. SIEM tackles this by:
-
Providing complete visibility
With traces and evidence spread across systems and applications, data silos are a serious problem for security operations, making sophisticated threats and attacks detection difficult. SIEM solutions provide this visibility by stitching together fragmented logs to map user activity, device behavior, and data flows in real time, eliminating blind spots that attackers exploit.
-
Holistic threat detection and remediation
While security solutions like EDR, XDR and SOAR excel in specific functionalities, SIEM offers a comprehensive security package integrating threat detection, investigation through forensic analysis and compliance reporting. Advanced SIEM solutions now embed the MITRE ATT&CK® tactic and technique mapping along with AI-driven behavioral analytics to prioritize high-risk alerts and reduce false positives.
-
Automating compliance
With customized log retention, effective threat hunting, and post-incident analysis capabilities, SIEM eases compliance audits for standards like GDPR, PCI DSS, and HIPAA with prebuilt reports to analyze the attack surface of enterprises, minimize risks, and stay on top of threats.
-
Customizing data narratives
Modern SIEMs let teams build tailored dashboards, alerts, and reports to align with unique organizational requirements. SIEM solutions have now evolved into a unified security platform, by providing the SOCs the frameworks they need and let them customize its modules depending on the industry or enterprise needs.
-
Integrations as the core
Prebuilt connectors and API-driven data integrations turn SIEM into a central security hub, unifying data from other security stacks like EDRs, NDR, XDR, DLP, SOAR, and threat intel platforms ensuring seamless data flow and correlation for effective threat detection across siloed tools.
How SIEM works: Aggregation, analysis, and action
Any SIEM solution works through three core principles: data aggregation, analysis, and remediation. These provide visibility, actionable security insights, and neutralize threats to stay ahead of the curve.
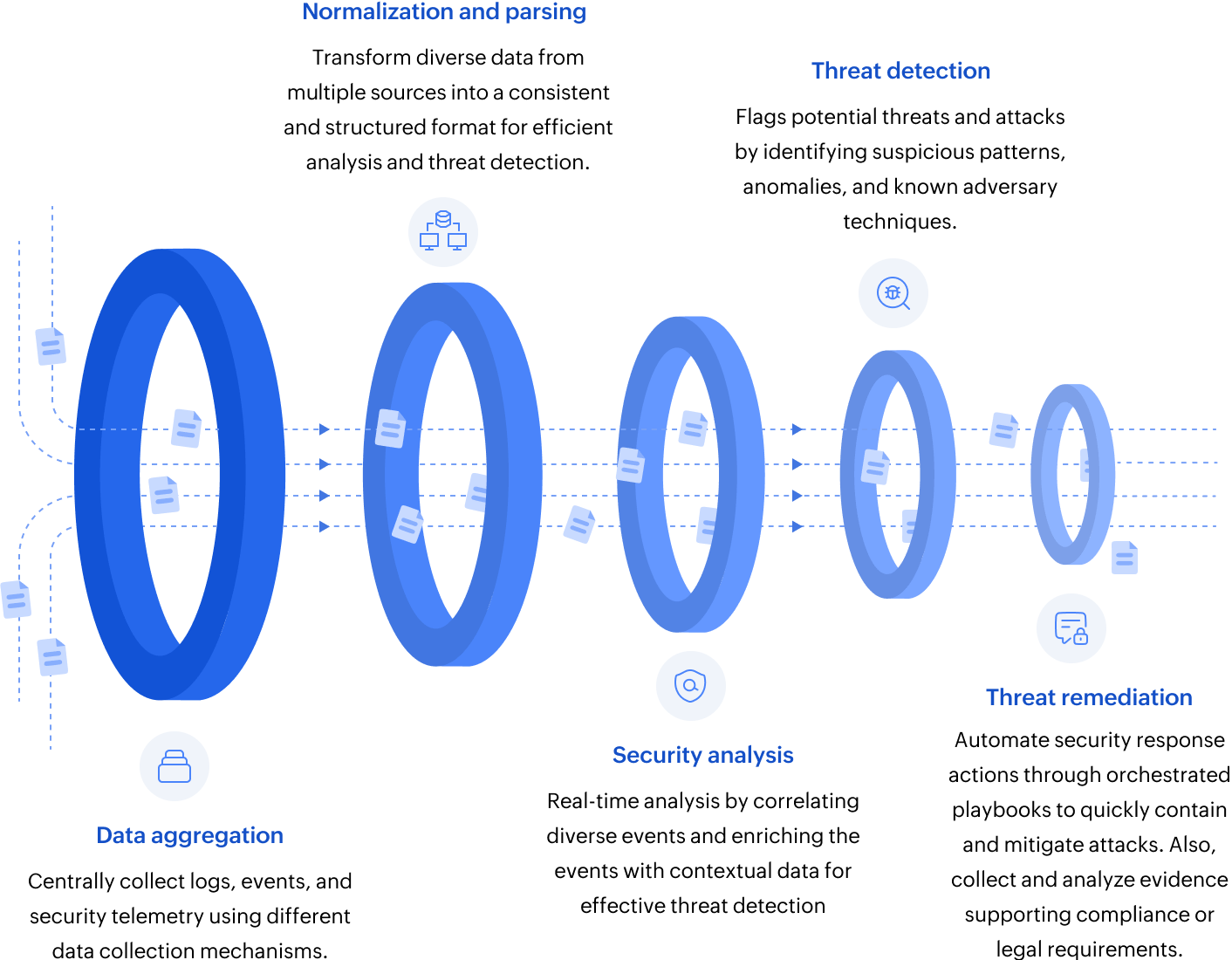
Data aggregation: Gathering the clues
Imagine a detective collecting all the pieces of evidence from a crime scene. SIEM does something similar, but in the digital realm. Modern SIEM solutions use agent-based (for a closed system), agentless, and API-driven (for cloud/SaaS) data collection methods to ensure no blind spots. It collects and archives logs from a vast array of sources, including:
- Network devices: Routers, firewalls, and switches
- Servers: Operating system logs, application logs
- Security devices: Intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), antivirus software, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools
- Cloud services: Activity logs from platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud
- Databases: Audit logs of databases like SQL, Oracle, and more
- Applications: Web server logs, custom application logs
- Security stack: Data loss prevention (DLP), extended threat detection and response (XDR), and other security applications for data enrichment and faster MTTR.
The collected raw logs are then normalized and parsed. These processes standardize data into a unified format to eliminate inconsistencies like time zone mismatches or vendor-specific jargons.
Analysis: Connecting the dots
The real power of a SIEM tool lies in its ability to analyze the massive volume of information it collects in real-time. SIEM solutions use sophisticated analysis techniques such as event correlation, advanced analytics, and often ML algorithms to:
- Correlate events from different sources: A single failed login attempt might be benign. However, when combined with unusual network traffic and attempts to access restricted resources, SIEM can recognize a potential attack in progress. Many SIEM solutions come with the out-of-the-box security content, which includes thousands of correlation rules to detect known threats.
- Identify suspicious patterns and anomalies: A sudden surge in login attempts from an unusual location, a user accessing sensitive files outside of their normal working hours–these are the kinds of red flags SIEM can detect using its ML based behavioral analytics.
Action: Remediation and forensics:
The insights gained from the analytics engine of SIEM aren't just for observation; they drive crucial action. This principle encompasses two key aspects:
- Remediation: When a threat is detected, SIEM solutions can automatically or manually trigger remediation actions to contain and neutralize the threat. This might involve isolating an infected host, blocking malicious IP addresses, or terminating suspicious processes. Next-gen SIEM solutions either have this as their native capability or achieve this via integration with SOAR platforms.
- Forensics: With all the logs serving as evidence, in the aftermath of a security incident, SIEM provides the detailed forensic data needed to understand the attack vector, the extent of the compromise, and the actions taken by the attackers. The historical logs and correlated events within the SIEM platform are invaluable for incident analysis, helping organizations learn from attacks and improve their security posture for the future. This again, stands out as a differentiator between SIEM and other security solutions like XDR and SOAR which focuses only on specific capability.
Explore ManageEngine SIEM's capabilities with a personalized walkthrough
Critical capabilities of SIEM
Centralized data aggregation and cloud data lake storage
A core capability of modern SIEM solutions is robust data aggregation, enabling the collection and centralized storage of log and event data from a wide range of sources, including servers, databases, applications, endpoints, firewalls, routers, and cloud systems. Most SIEM solutions collect data through agentless, agent-based, and API-based methods, ensuring flexible and comprehensive coverage across the enterprise network.
Seamless data lake integration for scalable storage
With the exponential growth of security data, enterprises require scalable and cost-effective log and data storage mechanisms. Next-gen SIEM platforms leverage data lake technology—either on-premises or in the cloud, to provide nearly unlimited, low-cost storage for massive volumes of structured and unstructured data. Data lakes allow organizations to retain historical data, not just filtered or summarized logs, enabling deeper analysis, long-term forensic investigations, and compliance reporting. Cloud-native SIEMs further simplify this adoption by allowing enterprises to add storage nodes on demand, ensuring linear scalability and predictable costs as data volume grow.
Data sovereignty and compliance through preferred data lakes
sensitive information such as log data and user details in their preferred locations, be it on-premises or within cloud, enterprises maintain control over where their data resides, while leveraging the advanced analytics, threat detection, and automated response capabilities of cloud-SIEM solutions. With this, enterprises can adopt SIEM technology easier, and without compromising data privacy and governance policies.
Advanced event correlation and analytics
Correlating data from multiple sources to identify complex attack patterns that would be difficult to detect using manual analysis is one of the core capabilities of SIEM solutions. Modern SIEM tools come with sophisticated rule sets, ML, and contextual analysis, to prioritize high-risk events, flagging those that require immediate attention while automating the response to lower-risk incidents.
SIEM's comprehensive detection engineering should also be integrated with threat intelligence to identify the key external known threats and to reduce alert fatigue. Choose SIEM solutions that have:
- An integrated detection engineering that spots threats based on different methodologies—rule-based correlation, ML powered behavior-based detection models, and signature-based methods.
- Predefined set of correlation and anomaly rules mapped with threat modeling framework such as MITRE ATT&CK® to detect known techniques and tactics
- Tightly integrated threat intelligence that enriches the rules for enhanced detection
Significant challenge of SIEM's detection engineering
False positives are one of the most significant challenges in SIEM solution's detection engineering, often overwhelming security teams with irrelevant alerts and contributing to alert fatigue, which can cause real threats to be overlooked. This persistent issue stems from rigid or generic detection rules, misconfigurations of rules, and sheer volume of data ingested by the SIEM platform.
When you're implementing SIEM, look for a SIEM solution that provides different technological ways to reduce false positives. Some of the known technologies include: - Adopting adaptive thresholds that dynamically adjust to an organization's unique baseline activity.
- Contextual analysis, ML, and AI-driven detection to further refine their detections
Comprehensive incident response and automation
Case management and collaboration capabilities help security teams synchronize their efforts, share knowledge, and respond to threats efficiently. Today, effective SIEM tools either have native SOAR or integrate themselves with a SOAR tool to automate playbooks and workflows that accelerate remediation, reduce manual workload, and ensure consistent, policy-driven responses to security incidents.
When assessing SIEM solutions for comprehensive incident response and automation, it's essential to look beyond just data ingestion and consider how well the SIEM integrates with your existing security stack and infrastructure. Deep, bi-directional API-based integration is crucial as it enables automated, coordinated responses that can dramatically accelerate threat remediation and reduce manual effort.
Choose SIEM tools that have:
- A native SOAR with out-of-the-box playbooks for common incident scenarios or a tight integration with the leading SOAR providers to enable rapid and consistent response without starting from scratch.
- AI-driven capabilities to recommend mitigation steps and remedial actions, helping analysts make faster, more informed decisions and further reducing response times.
Striking the right balance: Automation and human oversight in modern SIEM
Enterprises today are seeking a balanced approach to automation within SIEM, aiming to maximize efficiency without sacrificing control or accuracy. The current expectation is for SIEM solutions to automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks such as alert triage, enrichment, correlation rule building, and execution of standard playbooks. Automated workflows are especially valued for their ability to accelerate incident containment and reduce the risk and cost of data breaches, which are critical given the persistent cybersecurity skill gap.
However, while automation can handle much of the routine work, enterprises still prioritize having a "human in the loop" (HITL) for critical decisions, complex investigations, and final approval of high-impact remedial actions. HITL is essential for interpreting context, making nuanced judgements, and adapting to novel or sophisticated threats that automation alone may not fully understand.
Compliance and forensic readiness
Compliance and forensic readiness ensures enterprises can meet both regulatory obligations and effectively respond to security incidents. This capability is especially critical for organizations operating in regulated industries—such as finance, healthcare, education, and critical infrastructure—where failing to demonstrate proper evidence handling or compliance can result in severe financial penalties, reputational damage, or even legal consequences. Additionally, the constant monitoring and evidence gathering inherent in forensic readiness serve as a deterrent to malicious insiders, making it more difficult for attackers to evade their actions.
Choose a SIEM solution that has:
- Automated, secure log collection and long-term retention capabilities to support audit and investigation requirement.
- Comprehensive audit-ready report templates tailored to specific regulatory frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOX, and more, enabling rapid and accurate compliance audits.
- Mechanisms for evidence collection, digital forensic and incident response (DFIR) frameworks to streamline the investigation process and enable swift containment and recovery.
Integrating risk-policy based management into modern SIEM:
A notable trend is the use of automation to continuously map entity-level and security events compliance requirements, providing real-time risk dashboards and remediation recommendations. Some SIEMs also integrate with GRC tools to centralize risk visibility and automate policy enforcement, ensuring that risk and compliance management is not a one-time activity but an ongoing and adaptive process.
Unmatched customization and seamless integration
Customization and integration are now essential pillars of an effective SIEM, directly impacting an organization's ability to detect, respond to, and manage security threats across complex, modern environments. As you grow and diversify your technology stacks spanning on-premises, cloud, and hybrid infrastructure, the need for a SIEM can adapt to unique workflows and ingest data from a wide array of sources has never been greater.
Without strong integrations with existing stacks, security teams risk blind spots and delayed responses, while limited customization can lead to irrelevant alerts and inefficient operations. Additionally, the 2024 Gartner Critical Capabilities for SIEM report evaluates vendors specifically on their ability to deliver customizable SIEM solutions, with customization recognized as a key differentiator in supporting diverse enterprise requirements and use cases.
When evaluating SIEM platforms, look for solutions that support:
- Flexible rule creation, customizable dashboards, and the ability to tailor workflows to specific business needs.
- Seamless integration with endpoints, network devices, cloud services, identity providers, and business-critical applications for achieving full visibility and rapid response.
- Robust API-based data ingestion, enabling easy connection to both legacy and next-gen security tools as well as automation platforms like SOAR, to streamline incident response and reduce manual effort.
Big data, AI, and seamless integration:
Current trends in the SIEM market include leveraging big data architectures for scalability, using AI and ML to enrich and correlate event data, and providing out-of-the-box use case packages that accelerate deployment and security operations. The ability to rapidly integrate new sources and customize detection logic allows organizations to stay agile in the face of evolving threats and regulatory requirements. The unmatched customization and seamless integration empower enterprises to maximize their security investments, reduce operational complexity and maintain a unified, adaptive defense posture.
ManageEngine Log360 customer stories
Modern SIEM use cases
A cutting-edge SIEM leverages advanced analytics, ML, and integrated threat intelligence to illuminate the unseen, connect the seemingly disconnected, and empower your security team to stay not just one, but several steps ahead of the adversary. Here's how a modern SIEM can actively defend your organization:
Real-time threat detection and advanced persistent threats (APT) hunting:
The challenge
Sophisticated attackers often use low-and-slow tactics, blending into legitimate network traffic to evade traditional defenses. APTs can dwell for months, exfiltrating sensitive data undetected.
The SIEM solution
Modern SIEM ingests vast amounts of data from endpoints, networks, cloud environments, and applications. It employs AI-driven behavioral analytics to establish baselines of normal activity. When a user account logs in from an unusual location, attempts to access sensitive files outside of typical hours, or exhibits patterns indicative of data exfiltration (even small, consistent transfers), the SIEM correlates these seemingly disparate events to flag a potential APT or insider threat immediately. It detects subtle indicators of compromise (IOCs) that siloed tools would miss, building a comprehensive attack narrative.
Insider threat detection:
The challenge
Employees, contractors, or even compromised credentials pose significant risks. Detecting malicious intent or accidental data exposure from within requires deep insight into user activity.
The SIEM solution
By leveraging UEBA, SIEM establishes individual user baselines. If "Finance Joe" suddenly attempts to access HR records or downloads an unusual volume of data to a personal drive, the SIEM immediately flags this deviation. It can identify patterns like privilege escalation attempts, access to unauthorized systems, or attempts to bypass security controls, providing early warnings before major breaches occur.
Cloud security monitoring and compliance adherence
The challenge
The sprawling nature of cloud environments makes centralized visibility and compliance adherence a major headache. Misconfigurations and unauthorized access can leave critical assets exposed.
The SIEM solution
Modern SIEMs integrate seamlessly with leading cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud), ingesting logs from cloud identity services, network flows, and VMs. They provide unified visibility across hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructures. Prebuilt compliance packs for GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and ISO 27001 automate reporting, identify policy violations (e.g., unencrypted S3 buckets, public-facing RDP ports), and ensure continuous adherence to regulatory mandates.
Automated incident response & orchestration
The challenge
Security alerts flood in, overwhelming analysts and leading to alert fatigue. Manual incident response is slow and inefficient, increasing dwell time for attackers.
The SIEM solution
Beyond detection, modern SIEMs integrate with SOAR platforms. Upon detecting a high-fidelity threat, the SIEM can automatically trigger predefined playbooks: Isolating compromised endpoints, blocking malicious IPs at the firewall, revoking user access, or initiating forensic data collection. This drastically reduces response times and empowers security teams to focus on strategic threat hunting.
Gain Expert SIEM Insights: Tune into Ctrl Alt Secure Podcast
Kris s
Principal Consultant Bluechip Infotech
Australia

Selim Ourtani
CEO and Founder of
Sertalink
Belgium

Saulo Meneghini de Britto
Founder at PINPOINT
Brazil

Manish Naik
Chief Business Officer Softmanage Solutions
India
Comparing SIEM and other security solutions
The cybersecurity landscape is a maze of evolving solutions, and is tough to navigate. To make sense of it all, it's critical to understand the core differences between SIEM and the other tools in your security arsenal.
Before we dive into how SIEM stacks up against other security tools, let's look at how SIEM has evolved, building capabilities that once required separate integrations.
SIEM and UEBA
SIEM vendors realized that relying solely on rule-based alerts wasn't going to cut it for detecting today's sophisticated threats, especially advanced persistent threats. This realization led to a significant shift in SIEM engineering, with a focus on incorporating ML algorithms to detect deviations from normal baselines. This marked the integration of ML-based UEBA into SIEM's core capabilities, which dramatically expanded the threat detection coverage of SIEM solutions. Furthermore, the integration of risk-scoring mechanisms improved the detection of slow-moving attacks and insider threats.
How SIEM leveraged native UEBA capabilities
Here's how SIEM tools have leveraged UEBA capabilities for effective threat detection:
- Behavioral baseline establishment: UEBA within SIEM establishes a baseline of normal behavior for users and entities, enabling the detection of deviations that may indicate malicious activity.
- Anomaly detection: By continuously monitoring and analyzing user and entity behavior, SIEM can identify anomalies that fall outside the established baseline, such as unusual login patterns, unauthorized access to sensitive data, or abnormal network activity.
- Contextual analysis: UEBA provides SIEM with additional context around security events, allowing for a more accurate assessment of potential threats. For example, atypical activity by a high-privileged user is rated with higher severity than the same activity from a low-privileged user.
- Risk scoring: UEBA assigns risk scores to users and events based on the severity of the detected anomalies. This helps security teams prioritize and focus on the most critical threats.
SIEM and SOAR: How SIEM is evolving to include native SOAR capabilities:
SIEM vendors have recognized that detection alone isn't enough and are moving to embed SOAR functionalities directly within their platforms. Here's how SIEM leverages native SOAR capabilities for enhanced security operations:
- Automated playbooks: SIEMs now come equipped with built-in customizable playbooks that automate routine response actions such as isolating endpoints, blocking IPs, or resetting compromised accounts, immediately upon threat detection.
- Orchestrated workflows: Native SOAR allows SIEM to coordinate actions across multiple tools like firewalls, EDR, ticketing systems, and more, ensuring a rapid and cohesive response to incidents.
- Case management: Integrated SOAR provides centralized case management, enabling security teams to track, document, and collaborate on incident investigations without switching platforms.
- Enrichment and contextualization: Automated enrichment pulls in threat intelligence, asset data, and user context, empowering analysts to make faster, and more informed decisions.
- Continuous improvement: SOAR's feedback loop enables SIEM to learn from past incidents, refine response strategies, and adapt playbooks for evolving threats.
By bringing SOAR into the SIEM core, organizations benefit from reduced response times, lower manual workload, and more consistent, repeatable incident handling. This shift is as transformative as the earlier UEBA consolidation, enabling security teams to be efficient, even with limited resources.
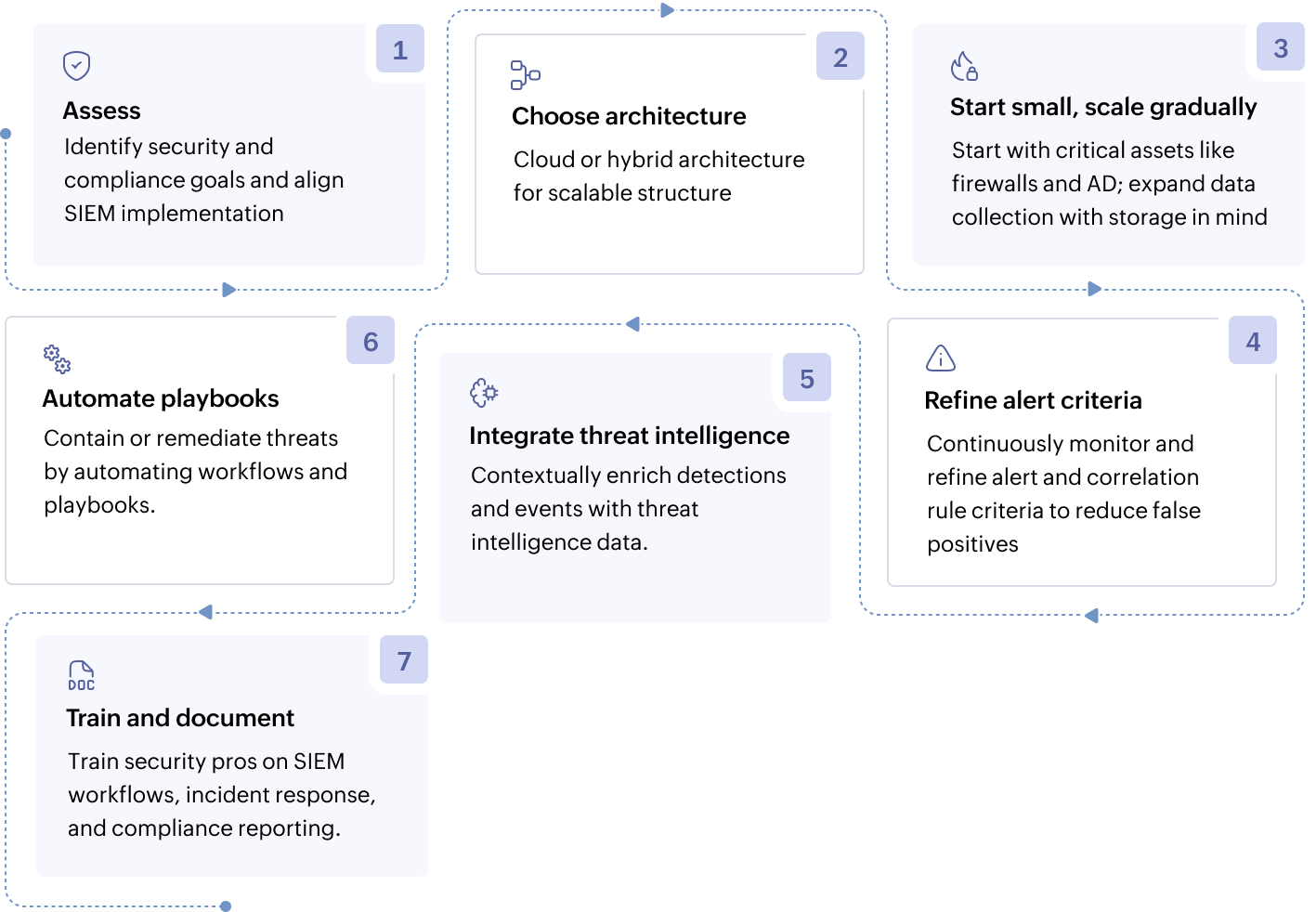
SIEM implementation best practices checklist
- Assess needs and define goals: Identify compliance requirements, critical assets, and use cases that you want to implement with SIEM implementation. Align SIEM with organizational priorities.
- Plan for scalability: Choose architectures, preferably cloud or hybrid, that handle future data growth and new log sources.
- Start small, scale gradually: Begin with high-value data sources, such as firewalls and AD, and expand to avoid alert overload. Prioritize relevant data collection to optimize storage and reduce noise.
- Fine-tune alerts and reduce false positives: Refine correlation rules and thresholds to focus on actionable alerts.
- Integrate threat intelligence: Enrich alerts with external threat feeds to improve detection accuracy. Integrate with open-source or reputable threat intelligence feeds, leveraging what your chosen vendor supports.
- Automate response workflows: Integrate with SOAR tools or use native automation for automating routine tasks. Leverage out-of-the-box playbooks and workflows such as blocking IPs and resetting accounts, to automate threat containment and remediation.
- Train teams and document processes: Ensure your SOC teams and security professionals understand SIEM workflows, incident response, and compliance reporting.
How to choose a SIEM solution that best fits your needs
How can you choose a SIEM solution that best fits your organizational needs? That depends a lot on understanding your organization's security goals, compliance requirements, and IT environment. Evaluate SIEM vendors for critical capabilities along with their ease of use, and support to ensure it aligns with your current and future security operations. Use the SIEM selection matrix below to compare different SIEM platforms systematically and make informed decisions.
| Evaluation criteria | Why it matters | What to look for in SIEM vendors |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment flexibility | Supports your on-premises, cloud, or hybrid adoption policies | Cloud-native or cloud-based deployment options |
| Integration capabilities | Ensures seamless data collection and better threat detection coverage | Different methods to ingest data: agent-based, agentless, and API-based data connectors |
| Advanced analytics | Contextual and advanced analytics enables accurate correlation and detection | AI and ML-based anomaly detection, threat intelligence integration, UEBA, and security telemetry ingestion for contextual analysis |
| Compliance and reporting | Simplifies the auditing process and regulatory adherence |
Audit ready reports for regulatory mandates like PCI DSS, HIPAA, SOX, GDPR, and more. Option for customized storage retention. Customization for audit reports to meet internal security standards. |
| Automation and response | Accelerates threat containment and mitigation |
SOAR integration or native support. Out-of-the-box playbooks |
| Ease of use | Reduces the learning curve and operational effort | Intuitive UI, customizable dashboards, minimal training effort |
| Cost and transparency | Prevents hidden expenses | Clear licensing models, predictable pricing, and easy upgrading options |
| Support | Ensures smooth onboarding and troubleshooting | Training resources, onboarding and implementation assistance, and professional support services |
Need to explore ManageEngine SIEM? Schedule a SIEM tour with our experts
starts at $2,130
To assist your evaluation Log360 offers:
- 30-day, fully functional free trial
- No user limits
- Free 24/5 tech support
Thanks for your interest in ManageEngine Log360
We have received your request for a personalized demo and will contact you shortly.
Fill this form to schedule a personalized web demo
Frequently asked questions
What is SIEM?
Security information and event management (SIEM), a cybersecurity technology for security operations centers (SOCs), that elevates security posture and boosts cyber resilience. SIEM tools centrally collect, analyze, and archive security and event data to effectively detect, investigate, and respond to threats in real time, while also simplifying compliance and providing unified visibility across hybrid environments.
What is the role of SIEM in cybersecurity?
In cybersecurity, SIEM tools act as a crucial defense layer, correlating security events and logs to detect attacks, policy violations, and fraudulent activities across an organization's IT infrastructure. With its extensive customization and integration capabilities, SIEM solutions are now evolving into a unified security platform to provide an operations layer for investigating threats across the enterprise security stack, centralize policy management, and enhance the security posture.
What are some of the top SIEM tools available in the market?
Some popular SIEM tools in the market include ManageEngine Log360, Splunk Enterprise Security, Microsoft Sentinel, IBM QRadar, Exabeam Fusion, and Elastic Security. Read our guide to know more about critical capabilities of SIEM tools and tips to choose a SIEM solution.
What are some of the essential SIEM use cases?
Initially, SIEMs were primarily adopted for log management and to fulfill basic IT and compliance requirements. However, their role has expanded significantly.
Today, advanced organizations leverage SIEM tools to actively detect sophisticated threats like insider threats, data exfiltration, lateral movements, privilege escalations, and ransomware. They also gauge their SIEM's effectiveness in threat coverage by aligning it with established threat modeling frameworks such as MITRE ATT&CK®.
What is ManageEngine's SIEM solution?
ManageEngine's SIEM solution, Log360, offers extensive log management, real-time correlation, UEBA, threat intelligence integration, and automated incident response for comprehensive security monitoring and compliance. With dark web monitoring, cloud protection and data security capabilities, Log360 offers guided investigations and contextual enrichment to expedite threat investigations and rapid threat containment. It also offers automated incident response, compliance reporting for various regulations, and unified security monitoring across on-premises and cloud environments.
- What is SIEM?
- SIEM: Evolution and modern relevance
- SIEM Benefits in 2025: Why it's still essential for modern cybersecurity
- How SIEM works: Aggregation, analysis, and action
- Critical capabilities of SIEM
- Modern SIEM use cases
- Comparing SIEM and other security solutions
- SIEM and SOAR: How SIEM is evolving to include native SOAR capabilities
- SIEM implementation best practices checklist
- How to choose a SIEM solution that best fits your needs
- Frequently asked questions