How to find inactive Exchange mailboxes using PowerShell
Last updated on:In this page
Inactive mailboxes consume your oraganization's storage resources and create security risks when employees leave or test accounts are deserted. These abandoned mailboxes can complicate compliance audits and increase operational costs. This article covers three methods to identify inactive mailboxes using the Exchange admin center, PowerShell scripts, and specialized Exchange reporting tools like ManageEngine Exchange Reporter Plus.
- Exchange admin center
- PowerShell
- Exchange Reporter Plus
Method 1: Find inactive Exchange mailboxes using the Exchange admin center
Prerequisite
Before using the Exchange admin center, ensure the account you use to log in is a member of one of these role groups: Organization Management, Recipient Management, or View-Only Organization Management.
Using the Exchange admin center to find inactive mailboxes
You can find inactive mailboxes indirectly through the Exchange admin center using the web interface.
- Open your web browser and navigate to https://servername/ecp (here, replace servername with your Exchange Server name).
- Sign in using your Exchange admin account.
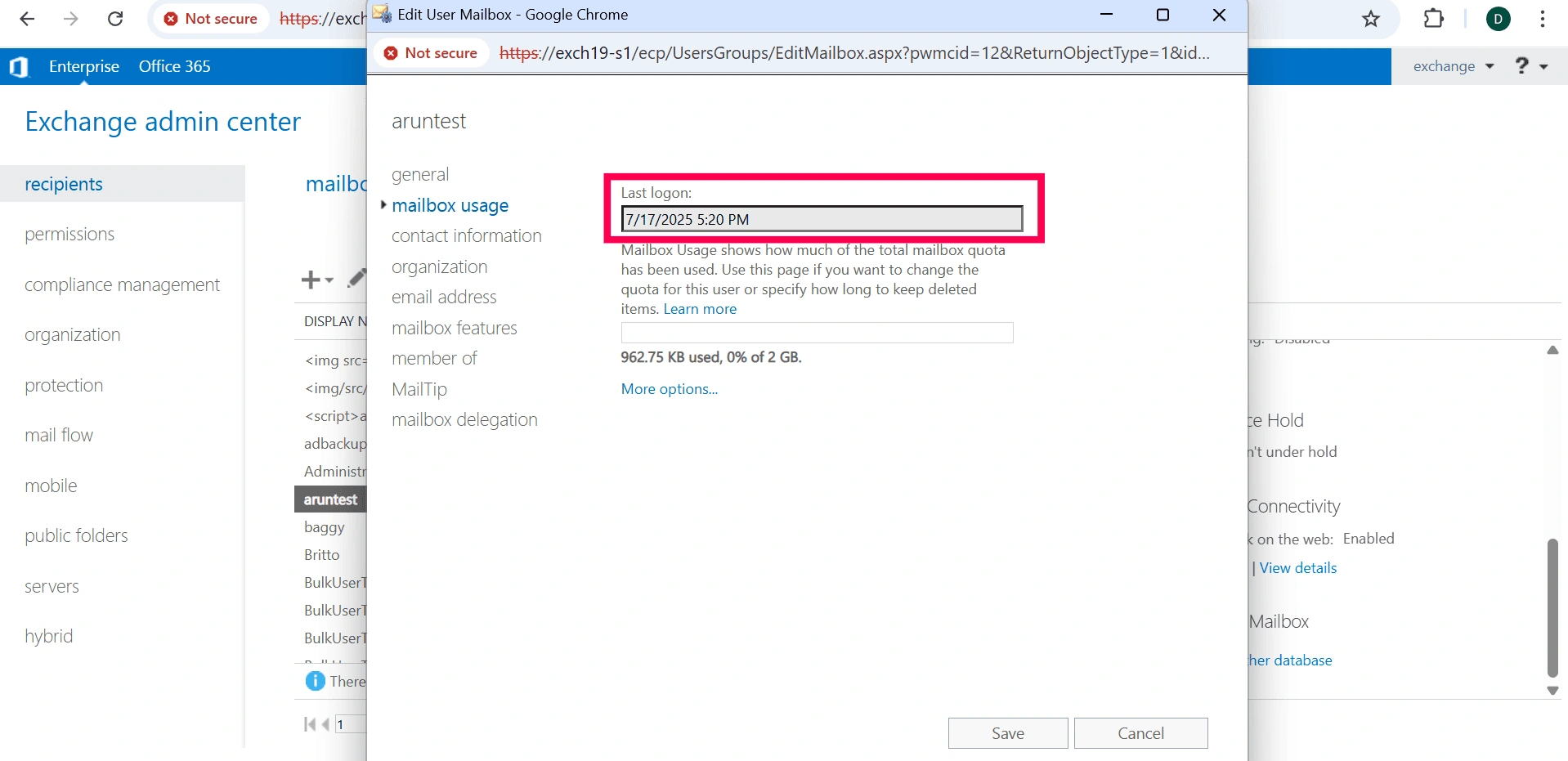
- Navigate to Recipients > Mailboxes.
- Select the mailbox you want to check from the list.
- Click the Edit icon (pencil symbol) to open the mailbox properties.
- In the mailbox properties window, click mailbox usage in the left navigation pane to view the last login time. This will help you determine whether the mailbox is active or not.
Limitations to consider
This method only allows you to check one mailbox at a time and requires navigating through individual mailbox properties for each mailbox you want to check.
Method 2: Find inactive Exchange mailboxes using PowerShell (Get-MailboxStatistics)
Prerequisites
Before using the Get-MailboxStatistics cmdlet, please verify that the below mentioned prerequisites are satisfied:
- Exchange Management Shell is installed and accessible on your Exchange Server or management workstation.
- You have appropriate Exchange Server permissions (the Recipient Management, View-Only Organization Management, or Organization Management role).
- PowerShell is being run with administrative privileges.
Using the Get-MailboxStatistics command to find inactive Exchange mailboxes
The Get-MailboxStatistics cmdlet is used to return information about a mailbox, such as the size of the mailbox, the number of messages it contains, and the last time it was logged on to. The syntax for it is given below:
The syntax for it is given below:
Get-MailboxStatistics
[[-StoreMailboxIdentity] <StoreMailboxIdParameter>]
-Database <DatabaseIdParameter>
[-CopyOnServer <ServerIdParameter>]
[-DomainController <Fqdn>]
[-Filter <String>]
[-IncludeMoveHistory]
[-IncludeMoveReport]
[-IncludeQuarantineDetails]
[-NoADLookup]
[<CommonParameters>]
Supported parameters
The table given below lists out some of the Get-MailboxStatistics parameters for identifying inactive Exchange mailboxes.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| -Identity | Specifies the mailbox that you want to return statistics for. You can use any value that uniquely identifies the mailbox, such as name, alias, distinguished name (DN), email address, GUID, or SAM account name. |
| -Database | Returns statistics for all mailboxes on the specified database. You can use any value that uniquely identifies the database, such as name, DN, or GUID. |
| -Server | Specifies the server from which you want to obtain mailbox statistics. When you specify a value for the Server parameter, the command returns statistics for all the mailboxes on all the databases for the specified server. |
| -DomainController | Specifies the domain controller that's used by this cmdlet to read data from or write data to AD. |
| -NoADLookup | Specifies that information is retrieved from the mailbox database and not from AD. This switch helps improve cmdlet performance when querying a mailbox database that contains many mailboxes. |
Example use cases using the Get-MailboxStatistics cmdlet
Getting all mailboxes with their last logon time
Get-Mailbox -ResultSize Unlimited | Get-MailboxStatistics | Select-Object DisplayName, LastLogonTime
Getting all mailboxes inactive for more than 90 days
Get-Mailbox -ResultSize Unlimited | Get-MailboxStatistics | Where-Object { $_.LastLogonTime -lt (Get-Date).AddDays(-90) } | Select DisplayName, LastLogonTime
For this cmdlet, the number inside the AddDays parameter sets the inactivity threshold. For example, -90 checks for mailboxes that haven’t been logged into for the past 90 days. You can change this value to any number you prefer, such as -180 for 180 days.
Method 3: Find inactive Exchange mailboxes using Exchange Reporter Plus
You can use Exchange Reporter Plus to identify inactive Exchange mailboxes with ease. The product supports multiple versions of Exchange Server, including Exchange Server 2003, 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and Exchange Server Subscription Edition (SE). The steps to identify inactive mailboxes are provided below.
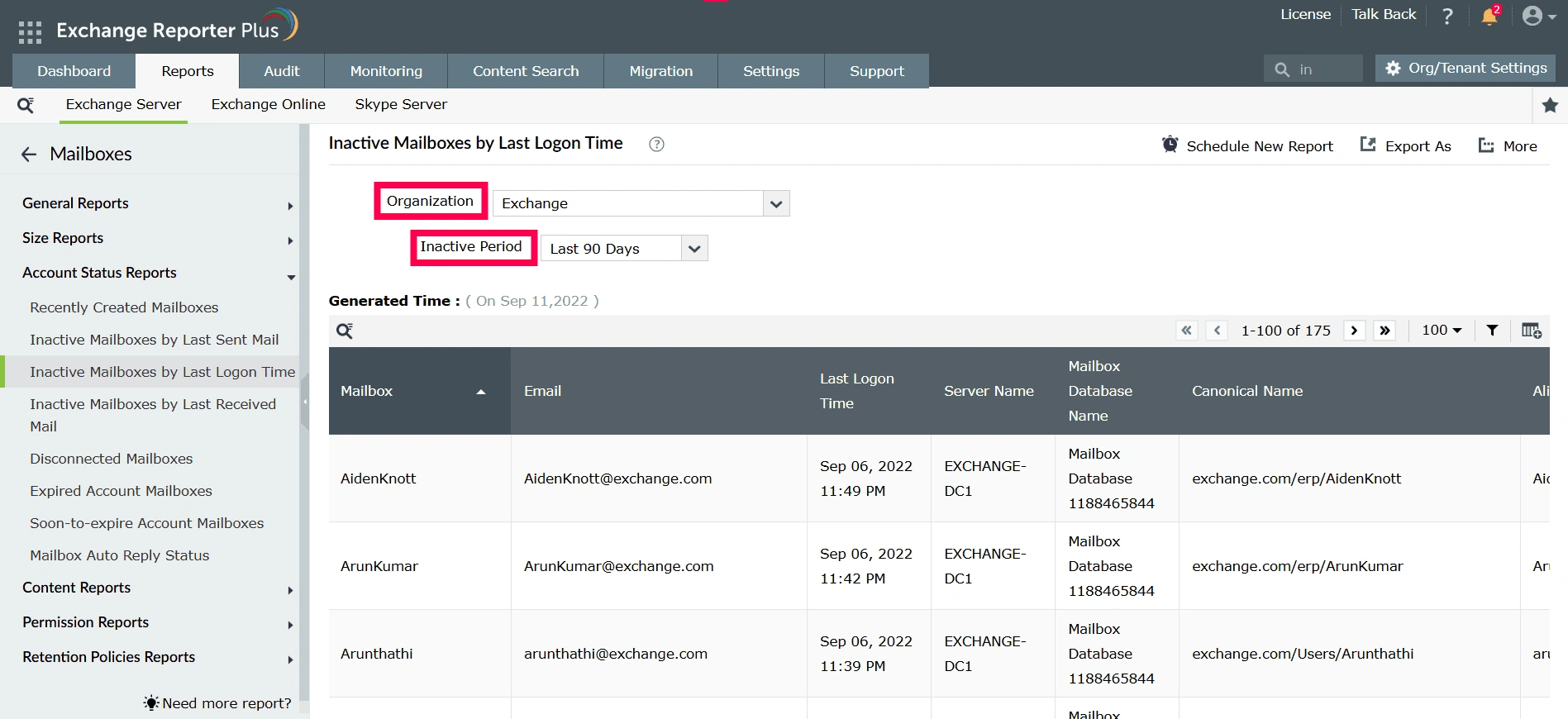
- Log in to Exchange Reporter Plus and go to Reports > Exchange Server > Mailboxes and click Inactive Mailboxes by Last Logon Time under Account Status Reports.
- Select both the required Exchange Organization and the Inactive Period to filter the data.
Stay informed about inactive Exchange mailboxes
Exchange Reporter Plus empowers administrators with comprehensive visibility into mailbox activity patterns across their Exchange environments. This Exchange reporting solution helps Exchange admins identify inactive Exchange mailboxes with detailed, exportable reports.
Comprehensive mailbox activity analytics
View and analyze mailbox activity patterns based on additional criteria, such as the last time a mailbox sent or received an email.
Automated inactive mailbox reports
Schedule mailbox activity reports to be generated and distributed automatically.
Disconnected and orphaned mailbox reporting
Generate reports on disconnected and orphaned mailboxes to make informed decisions about storage reclamation.
Customizable inactivity thresholds
Configure custom time periods to define mailbox inactivity based on your organization's specific requirements and policies.
Export reports in multiple formats
Export the generated inactive mailbox reports in multiple formats suitable for compliance and audit documentation purposes.
Important tips
Before taking action on inactive mailboxes, verify with department managers and check organizational retention policies to avoid accidental data loss or compliance issues.
Review disconnected and orphaned mailboxes separately from standard inactive accounts, as these may require immediate attention to prevent security vulnerabilities.
Use automated scheduling to generate inactive mailbox reports weekly or monthly, ensuring consistent reporting without manual intervention.