How to get mailbox size using PowerShell
Last updated on:In this page
Exchange admins frequently need to monitor and report on mailbox sizes to manage storage allocation, identify oversized mailboxes, and ensure optimal Exchange Server performance. This can be accomplished through several methods: The native Exchange admin center (EAC), PowerShell scripting, or by utilizing specialized Exchange reporting tools like ManageEngine Exchange Reporter Plus. Let's explore these different approaches below.
- Exchange admin center
- PowerShell
- Exchange Reporter Plus
Method 1: Getting the mailbox size using EAC
Prerequisite
Before using the EAC, ensure the account you use to log in is a member of the Recipient Management role group at the minimum.
Using the Exchange admin center to get mailbox size
You can view mailbox sizes directly using the traditional EAC in the web interface.
- Open your web browser and navigate to https://servername/ecp (here, replace servername with your Exchange Server name).
- Sign in with an account that has Exchange admin privileges.
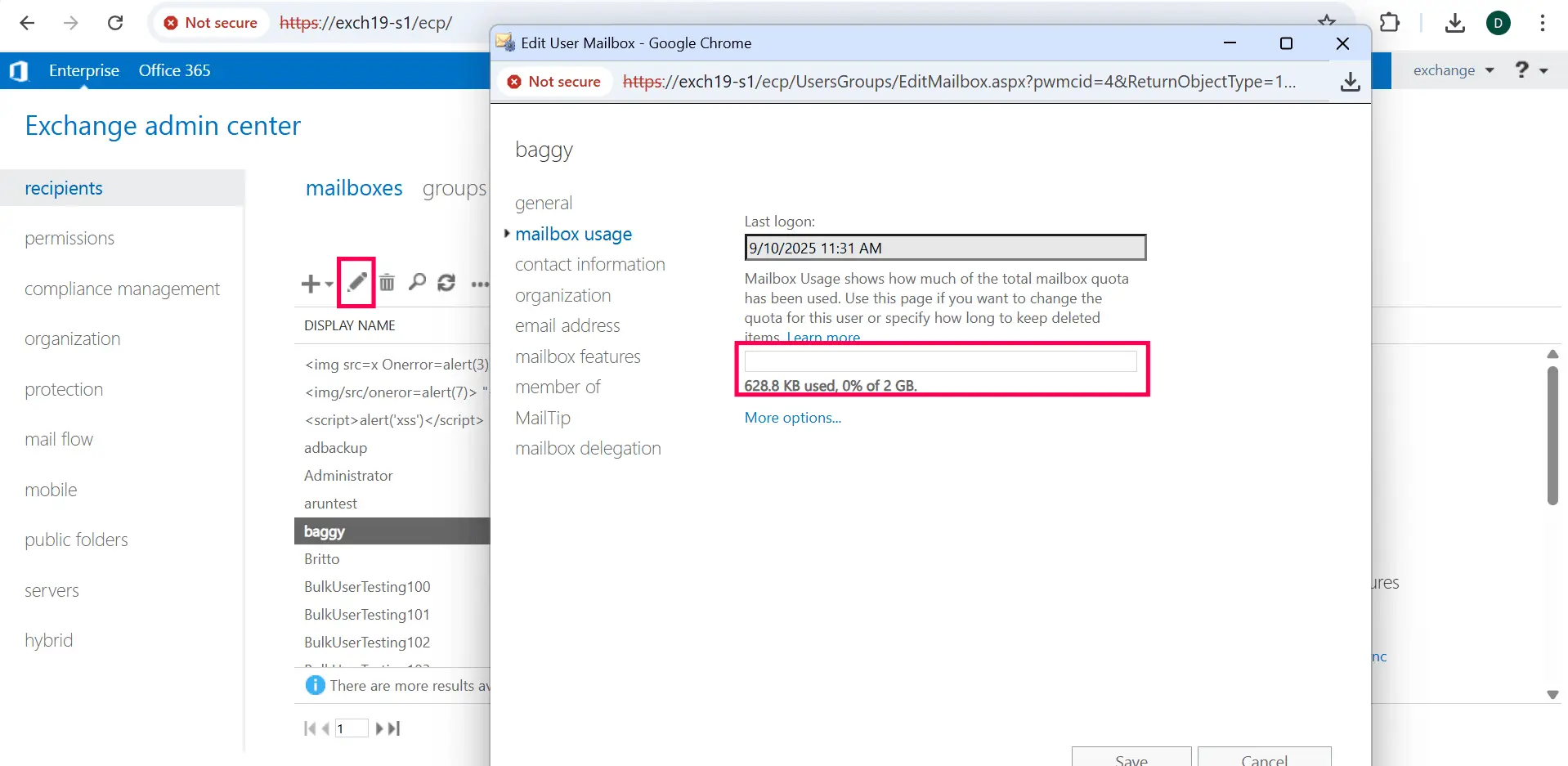
- Navigate to Recipients > Mailboxes.
- Select the mailbox you want to check from the list.
- Click the Edit icon (✏) to open mailbox properties.
- In the mailbox properties window, click on Mailbox usage in the left navigation pane to view the space consumption by that particular mailbox.
Method 2: Getting the mailbox size using PowerShell (Get-MailboxStatistics)
Prerequisites
Before using the Get-MailboxStatistics cmdlet, please verify that the below mentioned prerequisites are satisfied:
- Exchange Management Shell is installed and accessible on your Exchange Server or management workstation.
- You have appropriate Exchange Server permissions (View-Only Organization Management or Organization Management role).
Using the Get-MailboxStatistics command to get the mailbox size
The Get-MailboxStatistics cmdlet is used to return information about a mailbox, such as the size of the mailbox, the number of messages it contains, and the last time it was accessed.
The syntax for it is given below:
Get-MailboxStatistics
[[-StoreMailboxIdentity] <StoreMailboxIdParameter>]
-Database <DatabaseIdParameter>
[-CopyOnServer <ServerIdParameter>]
[-DomainController <Fqdn>]
[-Filter <String>]
[-IncludeMoveHistory]
[-IncludeMoveReport]
[-IncludeQuarantineDetails]
[-NoADLookup]
[<CommonParameters>]
The Get-MailboxStatistics cmdlet requires at least one of the following parameters to execute successfully: server, database, or identity.
Supported parameters
The following table contains some parameters that can be used along with the Get-MailboxStatistics command to retrieve the mailbox size efficiently.
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| -Identity | Specifies the mailbox that you want to return statistics for. You can use any value that uniquely identifies the mailbox such as name, alias, distinguished name (DN), email address, GUID, or the SAM account name. |
| -Database | Returns statistics for all mailboxes on the specified database. You can use any value that uniquely identifies the database such as name, DN, or GUID. |
| -Server | Specifies the server from which you want to obtain mailbox statistics. When you specify a value for the Server parameter, the command returns statistics for all the mailboxes on all the databases for the specified server. |
| -Archive | Specifies whether to return mailbox statistics for the archive mailbox that's associated with the mailbox. |
| -Filter | Uses OPATH syntax to filter the results by the specified properties and values. |
| -DomainController | Specifies the domain controller that's used by this cmdlet to read data from or write data to AD. |
| -NoADLookup | Specifies that information is retrieved from the mailbox database, and not from AD. This switch helps improve cmdlet performance when querying a mailbox database that contains many mailboxes. |
Example use cases using the Get-MailboxStatistics cmdlet
Getting mailbox size for a single user
Get-MailboxStatistics -Identity "user_email_address" | Select-Object DisplayName, TotalItemSize, ItemCount
For this cmdlet, replace "user_email_address" with the actual email address of the user.
Getting mailbox sizes for all users on a specific server
Get-MailboxStatistics -Server "exchange_server_name" | Select-Object DisplayName, TotalItemSize, ItemCount | Sort-Object TotalItemSize -Descending
For this cmdlet, replace "exchange_server_name" with your actual Exchange Server name.
Getting disconnected mailboxes from all databases
Get-MailboxDatabase | Get-MailboxStatistics -Filter 'DisconnectDate -ne $null' | Select-Object DisplayName, TotalItemSize, DisconnectDate
This cmdlet does not require any parameter replacement as it queries all databases for disconnected mailboxes.
Method 3: Getting mailbox size reports using Exchange Reporter Plus
- Log in to Exchange Reporter Plus and go to Reports > Exchange Server > Mailboxes and click Mailbox Size under Size Reports.
- Select the required Exchange Organization, choose the desired date to filter the data, and then click Apply.

Stay informed about growing mailbox sizes
Exchange Reporter Plus empowers administrators with deep visibility into mailbox sizes and storage trends across their Exchange environments. The tool is designed to help Exchange admins monitor usage and identify potential storage bottlenecks with comprehensive, exportable reports.
Automated scheduling and export
Schedule and export the generated mailbox size reports in multiple formats suitable for compliance and audit documentation purposes.
Detailed mailbox size reporting
View and analyze current mailbox sizes and growth rates with easy-to-understand visualizations and trend graphs.
Inactive and archived mailbox insights
Discover inactive, hidden, or disconnected mailboxes to reclaim valuable storage space and streamline compliance checks.
Mailbox growth and quota alerts
Receive alerts when mailboxes approach configured limits, allowing proactive action before users encounter issues.
Database and server storage analytics
Aggregate mailbox size data at the database and server level for smarter storage capacity planning.
In summary, Exchange Reporter Plus offers comprehensive mailbox size reporting and analytics that enable administrators to monitor storage trends and identify potential risks. With its extensive range of detailed, exportable reports, you can gain clear insights into your Exchange environment’s mailbox storage usage from a single, intuitive console.
Important tips
Monitor archive mailbox usage and encourage end users to enable archiving to optimize storage and ensure critical emails remain accessible over time.
Use inactive mailbox reports to locate and manage mailboxes that haven’t been accessed recently, reclaiming valuable storage and improving server performance by eliminating storage bottlenecks.
Regularly review the mailbox size reports to identify users nearing their storage quota and prompt them to archive or clean up unnecessary emails.