Delegating permissions in Active Directory (AD) is a critical administrative function that enables organizations to assign specific rights to users or groups without granting full administrative access. Delegation streamlines user management, enforces least privilege, and allows help desk or junior IT staff to perform necessary tasks. This page covers how to delegate AD permissions using PowerShell, Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC), and ADManager Plus.
PowerShell lets you delegate permissions to users and groups at the OU, container, or object level using the dsacls.exe utility.
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
Here's a basic PowerShell script to delegate a permission (e.g., reset password) to an AD user using dsacls.exe. This script assigns the permission on a specified OU to a specified user or group.
$OUPath = "OU=Target,DC=domain,DC=com"
$DelegateUser = "domain\GroupName"
dsacls $OUPath /I:T /G "$DelegateUser`:RPWP;Reset Password;user"
This script delegates the right to reset user passwords and force a password change at next logon for all user objects within a specific OU to a specified AD user.
$OU_Path = "OU=Users,DC=contoso,DC=local"
$Delegate_User = "HelpDesk"
Write-Host "Delegating Password Reset permissions for $OU_Path to user $Delegate_User..."
dsacls "$OU_Path" /G "$Delegate_User`:RPWP;Reset Password;user" /I:S /P:Y
dsacls "$OU_Path" /G "$Delegate_User`:RP;pwdLastSet;user" /I:S /P:Y
dsacls "$OU_Path" /G "$Delegate_User`:WP;pwdLastSet;user" /I:S /P:Y
Write-Host "Delegation complete. Replication may take some time."
This script delegates the right to read and write the lockoutTime attribute for all user objects within a specific OU to a specified security group.
$OU_Path = "OU=Office Employees,DC=contoso,DC=local"
$Delegate_Group = "HelpdeskGroup"
Write-Host "Delegating Unlock Account permissions for $OU_Path to group $Delegate_Group..."
dsacls "$OU_Path" /G "$Delegate_Group`:WP;lockoutTime;user" /I:S /P:Y
dsacls "$OU_Path" /G "$Delegate_Group`:RP;lockoutTime;user" /I:S /P:Y
Write-Host "Delegation complete. Replication may take some time."
This script grants the Helpdesk Admins group full control over the Sales Users OU, effectively delegating full administrative privileges.
$OU_Path = "OU=Sales Users,DC=yourdomain,DC=com"
$Delegate_Group = "Helpdesk Admins"
Write-Host "Granting Full Control on OU $OU_Path to group $Delegate_Group..."
dsacls "$OU_Path" /G "$Delegate_Group`:GA" /I:T
Write-Host "Full Control delegation complete. The group $Delegate_Group now has full administrative rights over all objects in $OU_Path."
This script allows grants a security group the permissions to create and delete user accounts within the target OU.
$OU_Path = "OU=Office Employees,OU=Users,DC=contoso,DC=local"
$Delegate_Group = "SG-User-Provisioning"
Write-Host "Delegating Create/Delete User Accounts permissions for $OU_Path to group $Delegate_Group..."
Write-Host "------------------------------------------------------------------------------------"
dsacls "$OU_Path" /G "$Delegate_Group`:CC;user" /I:S
dsacls "$OU_Path" /G "$Delegate_Group`:DC;user" /I:S
Write-Host "Delegation complete. The group $Delegate_Group can now create and delete user accounts within $OU_Path."
The following essential parameters can be used for delegation tasks in PowerShell:
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| /G <account>:<permissions> | Grants specified permissions (e.g., RPWP for reset/write password, CC for create child) to the specified user or group. |
| /I:<flag> | Controls scope: S for this object only, C for children only, T for both this object and children. |
| <ObjectDN> | Distinguished Name of the target object or OU to which permissions apply (e.g., OU=Sales,DC=domain,DC=com). |
| :RPWP;user | Indicates reset password and write permissions on user objects. |
| :WP;lockoutTime;user | Write-right permission for the lockoutTime attribute (used for unlocking accounts). |
| :RP;lockoutTime;user | Read-right permission for the lockoutTime attribute (often paired with write for unlock delegation). |
| :GA | Generic All (Full Control) permission grant. |
| /P:Y | Propagates permissions to sub-objects (useful for inheritance). |
| -Identity | Specifies the user, group, or computer for delegation (used in some PowerShell cmdlets like Add-ADPermission). |
| -Add, -Remove, -Clear | Used to add, remove, or clear delegation settings programmatically. |
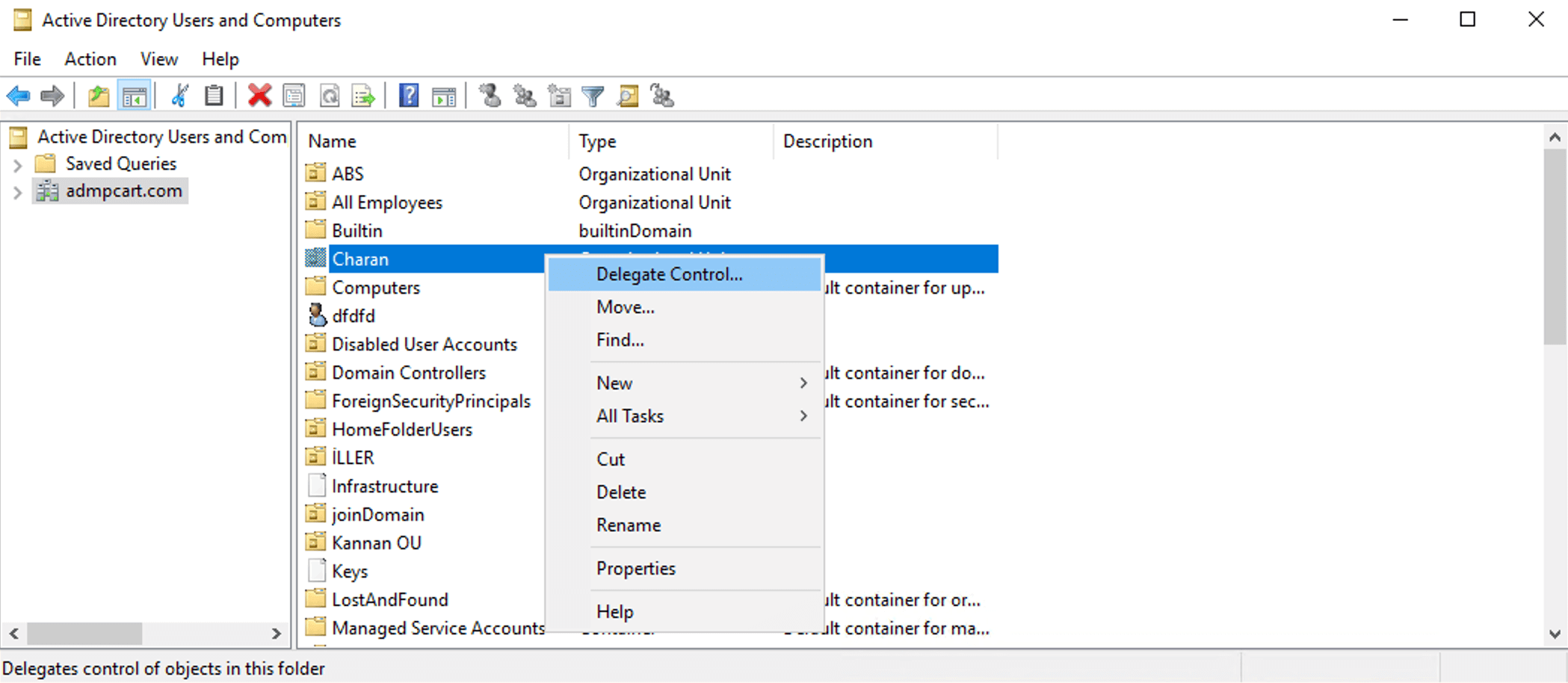
ADUC offers a GUI-based method to delegate permissions:
ADManager Plus simplifies delegation by providing a web-based interface with role-based access control:
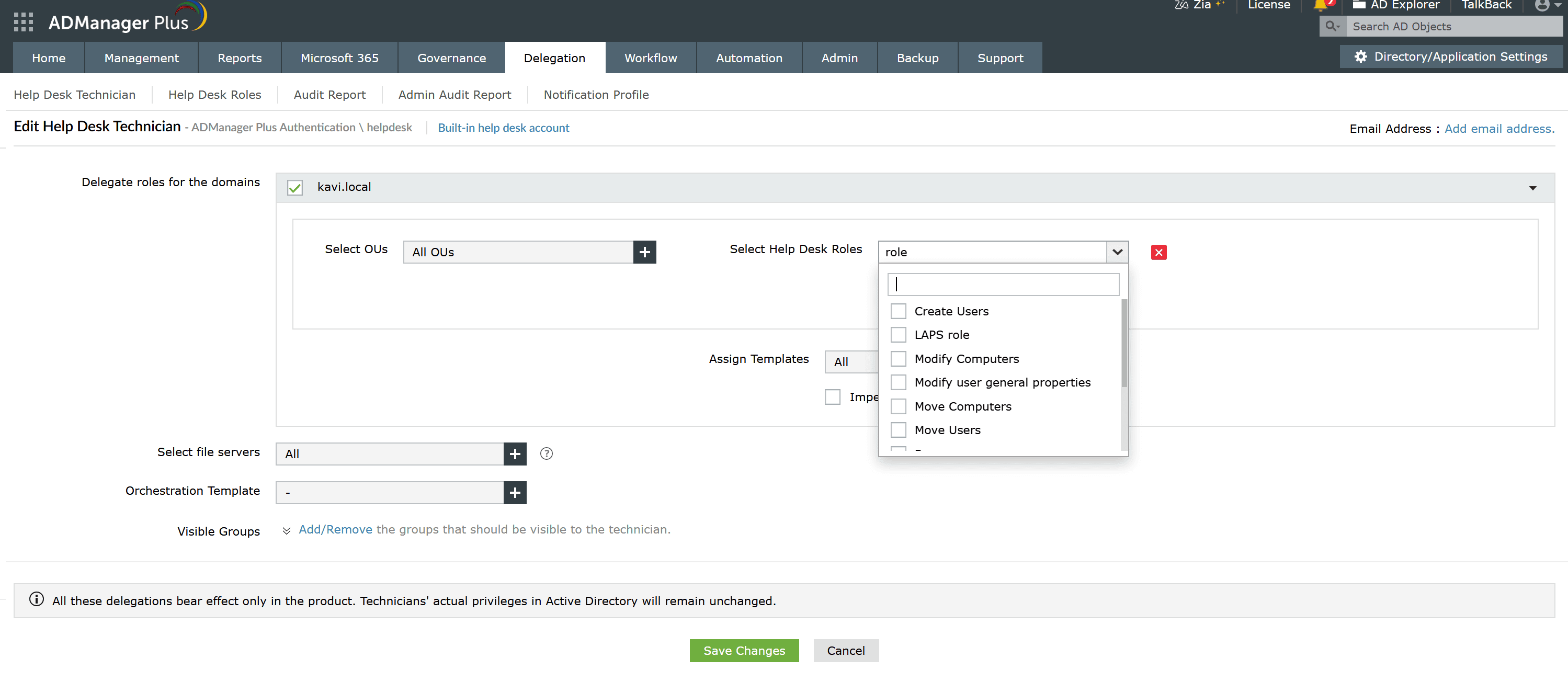
Select the delegated scope of the technician
Select from a list of pre-built and custom roles
Note: To create a custom role, navigate to Delegation > Help Desk Delegation > Help Desk Roles and click + Create New Role.
While they're powerful, relying solely on PowerShell and ADUC for delegation can present challenges:
ADManager Plus is an all-in-one AD, Exchange, and Microsoft 365 management solution that lets you delegate control over managing and reporting on different AD objects.
Run the script below to check delegated rights. It uses the Get-ACL cmdlet to retrieve Access Control Entries (ACEs) and helps identify which users or groups have been delegated permissions.
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
$acl = Get-Acl "AD:$OU"
Write-Host "`nDelegated permissions on: $OU`n" -ForegroundColor Cyan
$acl.Access | Where-Object { -not $_.IsInherited } | Select-Object `
IdentityReference,
ActiveDirectoryRights,
AccessControlType,
ObjectType,
InheritanceType |
Format-Table -AutoSize
For a script-free approach, ADManager Plus helps admins view delegated permissions with detailed reports.
Unconstrained delegation in AD allows a computer or service account to impersonate any user and access any resource on their behalf once the user authenticates to it. When enabled, the user's Kerberos Ticket-Granting Ticket (TGT) is stored on that system, allowing it to request access to other services freely. While this can simplify authentication for multi-tier applications, it poses a major security risk if the delegated system is compromised. Attackers can use stored TGTs to move laterally or gain elevated privileges.
Delegating GPO permissions in AD using PowerShell involves using the Set-GPPermission cmdlet from the GroupPolicy module. The script below will delegate the GpoEditDeleteModifySecurity permission level, providing full control over a particular GPO, including the ability to edit, delete, and modify its security settings.
Import-Module GroupPolicy
$gpoName = "My Test GPO"
$targetGroupName = "GPOAdmins"
$permissionLevel = "GpoEditDeleteModifySecurity"
if (Get-GPO -Name $gpoName -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue) {
Set-GPPermission -Name $gpoName -PermissionLevel $permissionLevel -TargetName $targetGroupName -TargetType Group
Write-Host "Permissions successfully delegated to '$targetGroupName' for GPO '$gpoName'."
} else {
Write-Host "GPO '$gpoName' not found." -ForegroundColor Red
}
For a script-free approach, ADManager Plus enables you to delegate GPO management and reporting tasks through its intuitive, GUI-based console.