How to get mailbox permission changes in Office 365
Last updated on:In this page
- How to get mailbox permission changes using the Microsoft Purview compliance portal
- Get mailbox permission changes using the Search-UnifiedAuditLog cmdlet in Exchange Online PowerShell
- How to get the mailbox permission changes report using M365 Manager Plus
- Monitor your Exchange Online mailboxes and more
- Important tips
- Frequently asked questions
Monitoring Microsoft 365 (previously Office 365) mailbox permissions in Exchange Online is vital for security and compliance. Unapproved modifications can expose data or interrupt operations, yet manually scouring audit logs for who did what, and when changes occurred is an arduous, complex, and time-consuming process for administrators.
With a streamlined auditing system that clearly displays all changes made, administrators can easily enforce the principle of least privilege and gain the control needed to neutralize potential security threats swiftly. In this page, we will see how to track Microsoft 365 mailbox permission changes with the native tools, and how to do it easily, swiftly, and efficiently with ManageEngine M365 Manager Plus, a dedicated Microsoft 365 administration tool.
- Microsoft Purview
- Graph PowerShell
- M365 Manager Plus
Method 1: How to get mailbox permission changes using the Microsoft Purview compliance portal
Prerequisites
You must be assigned at least the Audit Reader role to access and run audit log searches in the Microsoft Purview compliance portal.
Steps
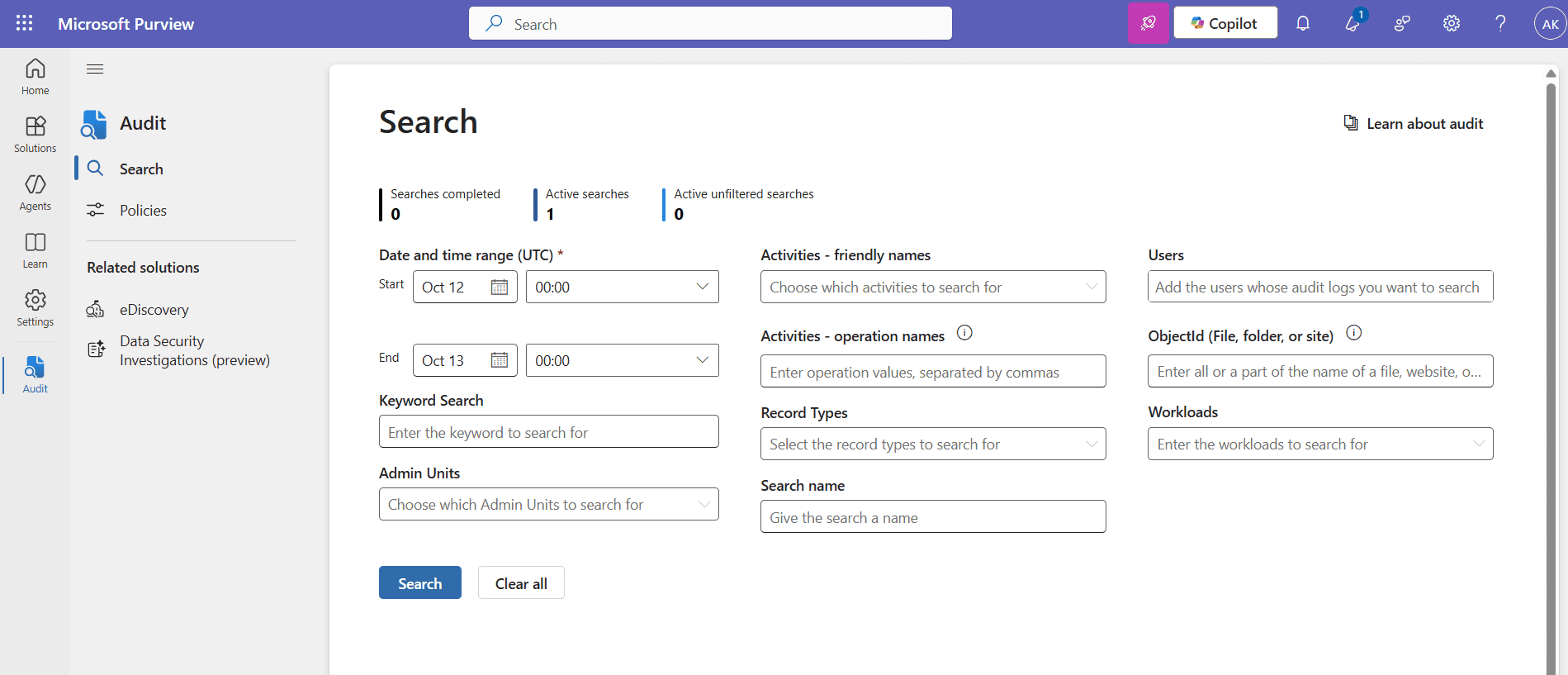
- Log in to the Microsoft Purview compliance portal and select Audit from the sidebar or the main menu.
- Configure the Start and End fields with the required dates.
- In the Activities - operation names drop-down, enter the following:
- Add-MailboxPermission, Remove-MailboxPermission
- In the Users field, type the mailboxes you want to investigate. You can leave this blank to search all mailboxes.
- Click Search to generate the Microsoft 365 mailbox permission change report. This displays the mailboxes where permission changes occurred.
Method 2: Get mailbox permission changes using the Search-UnifiedAuditLog cmdlet in Exchange Online PowerShell
Prerequisites
Before using Exchange Online PowerShell, please verify that:
- The Exchange Administrator role is applied to the account you use to sign in to Exchange Online PowerShell.
- You are connected to the Exchange Online module
- To check if the ExchangeOnlineManagement PowerShell module is installed, use this script:
Install-Module ExchangeOnlineManagement -Scope CurrentUser Update-Module ExchangeOnlineManagement - Connect to Exchange Online PowerShell with this script:
Connect-ExchangeOnline
- To check if the ExchangeOnlineManagement PowerShell module is installed, use this script:
The Search-MailboxAuditLog cmdlet was used previously to parse through audit logs and find mailbox permission changes made by administrators and delegates. However, the Search-MailboxAuditLog cmdlet is deprecated.
You will have to use its replacement, the Search-UnifiedAuditLog cmdlet, to get mailbox permission changes for a specific mailbox:
Search-UnifiedAuditLog -StartDate (Get-Date).AddDays(-90) -EndDate (Get-Date) -RecordType ExchangeAdmin -Operations "Add-MailboxPermission", "Remove-MailboxPermission" -FreeText "shared.mailbox@yourdomain.com"
Supported parameters
The following table contains some key parameters that can be used with the Search-UnifiedAuditLog cmdlet to audit your Microsoft 365 mailbox permissions.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| -StartDate, -EndDate | Defines the date range for the audit log search. |
| -RecordType | Filters the search by the type of activity. For mailbox permission changes made by an administrator, use ExchangeAdmin. |
| -Operations | Specifies the exact actions to search for, such as Add-MailboxPermission or Remove-MailboxPermission. |
| -UserIds | Narrows the search to actions performed by specific users. |
| -FreeText | Searches for a specific string in the audit log entry, which can be useful for targeting a particular mailbox. |
Use case for the Search-UnifiedAuditLog cmdlet
Scenario: A compliance officer needs a report of all permission changes made to any mailbox in the organization over the last 30 days.
This is the cmdlet you will have to run to generate the mailbox permission changes report across the organization:
$StartDate = (Get-Date).AddDays(-30)
$EndDate = Get-Date
$permissionChanges = Search-UnifiedAuditLog -StartDate $StartDate -EndDate $EndDate -RecordType ExchangeAdmin -Operations "Add-MailboxPermission", "Remove-MailboxPermission" -ResultSize 5000
$results = foreach ($entry in $permissionChanges) {
$auditData = $entry.AuditData | ConvertFrom-Json
if ($auditData.ObjectModified -like "*RecipientTypeDetails SharedMailbox*") {
[PSCustomObject]@{
Date = $auditData.CreationTime
User = $auditData.UserId
Action = $auditData.Operation
Mailbox = $auditData.ObjectId
TargetUser = ($auditData.Parameters | Where-Object { $_.Name -eq 'User' }).Value
Permissions = ($auditData.Parameters | Where-Object { $_.Name -eq 'AccessRights' }).Value
}
}
}
$results | Export-Csv -Path "C:\Reports\SharedMailbox_PermissionChanges_Last30Days.csv" -NoTypeInformation
Method 3: How to get the mailbox permission changes report using M365 Manager Plus
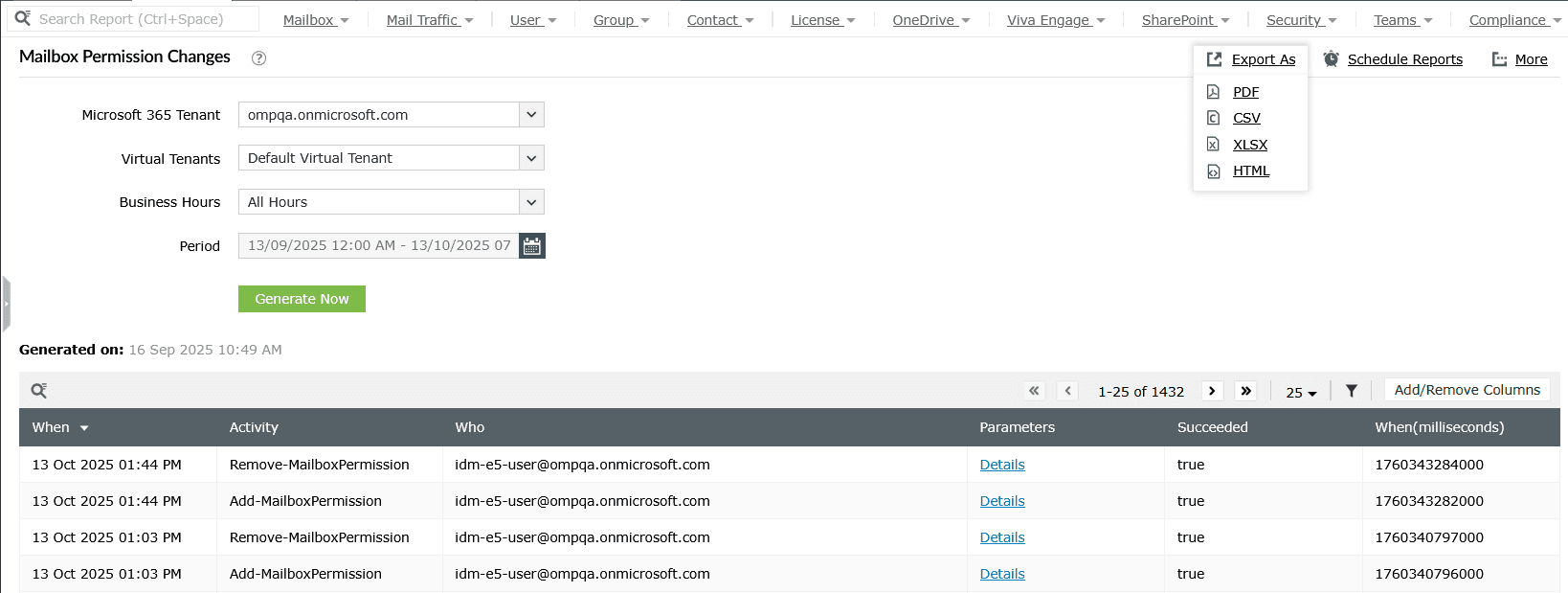
- Log in to M365 Manager Plus and click the Reports tab.
- Navigate to Other Services > Compliance Reports, and select the Mailbox Permission Changes report.
- You can now see which users have changed the mailbox permissions. Click Details in the Parameters column and check the User field to see who has modified their permissions.
- Click Export As and select a file format (CSV, PDF, XLSX, or HTML) to export your Microsoft 365 mailbox permissions report.
Monitor your Exchange Online mailboxes and more
M365 Manager Plus simplifies the complex task of auditing Microsoft 365 mailbox permissions, giving you complete visibility and control over your Exchange Online environment.
Mailbox permission management
Effortlessly add, remove, or modify mailbox permissions in bulk from a simple, GUI-based interface, eliminating the need for complex and error-prone PowerShell scripts.
Reports on Microsoft 365 mailboxes
Generate dozens of preconfigured reports on mailboxes, including permissions, size, activity, and more to maintain tight control over your collaborative workspaces.
Real-time alerts on mailbox permission changes
Configure alerts for any modifications to mailbox permissions. Get instant notifications when access rights are changed, allowing you to revert unauthorized modifications quickly.
Simplify PowerShell
Generate detailed mailbox folder permission reports with a single click, avoiding the complexity of PowerShell cmdlets. This reduces dependency on scripting and minimizes the risk of errors.
Important tips
Regularly audit mailbox permissions: Schedule periodic reviews of mailbox permissions, especially for mailboxes containing sensitive data (e.g., HR or Finance), to ensure access levels remain appropriate.
Differentiate between Full Access and other folder permissions: Use Full Access for managers who need complete control over a mailbox. Use granular folder permissions for team members who only need to interact with specific folders like the Inbox or Calendar.
Clean up stale permissions regularly: Periodically review and remove permissions for mailboxes that are no longer accessed. This declutters your access lists and strengthens security.
Frequently asked questions
You can use the Get-EXOMailboxPermission cmdlet to see who has Full Access permission to a mailbox and to check shared mailbox permissions in Microsoft 365:
Get-EXOMailboxPermission -Identity "user@yourdomain.com"
The Search-UnifiedAuditLog cmdlet is the primary command used for this purpose. It allows you to query the mailbox audit logs in Microsoft 365 for specific operations like Add-MailboxPermission and Remove-MailboxPermission.
Send As allows a delegate to send emails that appear to come directly from the other mailbox. Send on Behalf allows the delegate to send emails on behalf of the other mailbox, and the recipient will see both the delegate's and the mailbox's name (e.g., John Doe on behalf of the Sales Department).
By default, mailbox audit log records are retained for 90 days. For users with certain licenses (like Office 365 E5), the retention period can be extended up to one year.

