Direct Inward Dialing: +1 408 916 9892
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was introduced in 1996 to regulate electronic billing and data protection of patients in the healthcare sector. Numerous healthcare organizations fail to have proper security measures in place and can become the victim of cyber attacks. This can have adverse consequences for both their business operations, and the safety of their patients.
HIPAA requires healthcare organizations to recognize the patients' right to their information.
The Privacy Rule applies to cloud service providers, data centers, third-party contractors and vendors. The Privacy Rule mandates that these providers must have safeguards in place to protect electronic protected health information (ePHI). This comprises of any personal health information that is maintained electronically, such as electronic health records and electronic medical records.
Patients have the right to authorize sharing of their health records with third-party vendors. They can also request a copy of health records or request corrections to their records whenever required. HIPAA mandates that records should be retained for a period of six years.
The Security Rule specifies what kind of safeguards must be in place to protect ePHI. The rule requires healthcare organizations to have all required technical, administrative and physical safeguards in place to protect health information.
According to the HIPAA Security Rule, technical safeguards are “the technology and the policy and procedures for its use that protect electronic protected health information and control access to it.”
HIPAA defines administrative safeguards as, “administrative actions, and policies and procedures, to manage the selection, development, implementation, and maintenance of security measures to protect electronic protected health information and to manage the conduct of the covered entity’s workforce in relation to the protection of that information.”
HIPAA defines “physical measures, policies, and procedures to protect a covered entity’s electronic information systems and related buildings and equipment, from natural and environmental hazards, and unauthorized intrusion.”
HIPAA violation penalties are within a bracket of $100 to $50,000 per violation based on the level of negligence by those involved.
Violations are treated as two kinds: i) Reasonable cause ii) Willful neglect Reasonable cause violation penalties vary between $100 to $50000 per violation, whereas willful neglect of HIPAA protocol could incur fines between $10000 and $50000, and could lead to pressing of criminal charges.
ADAudit Plus offers you a series of pre-configured reports to help manage different security aspects of your network. The intuitive dashboard also has a special section displaying reports related to various compliance laws.
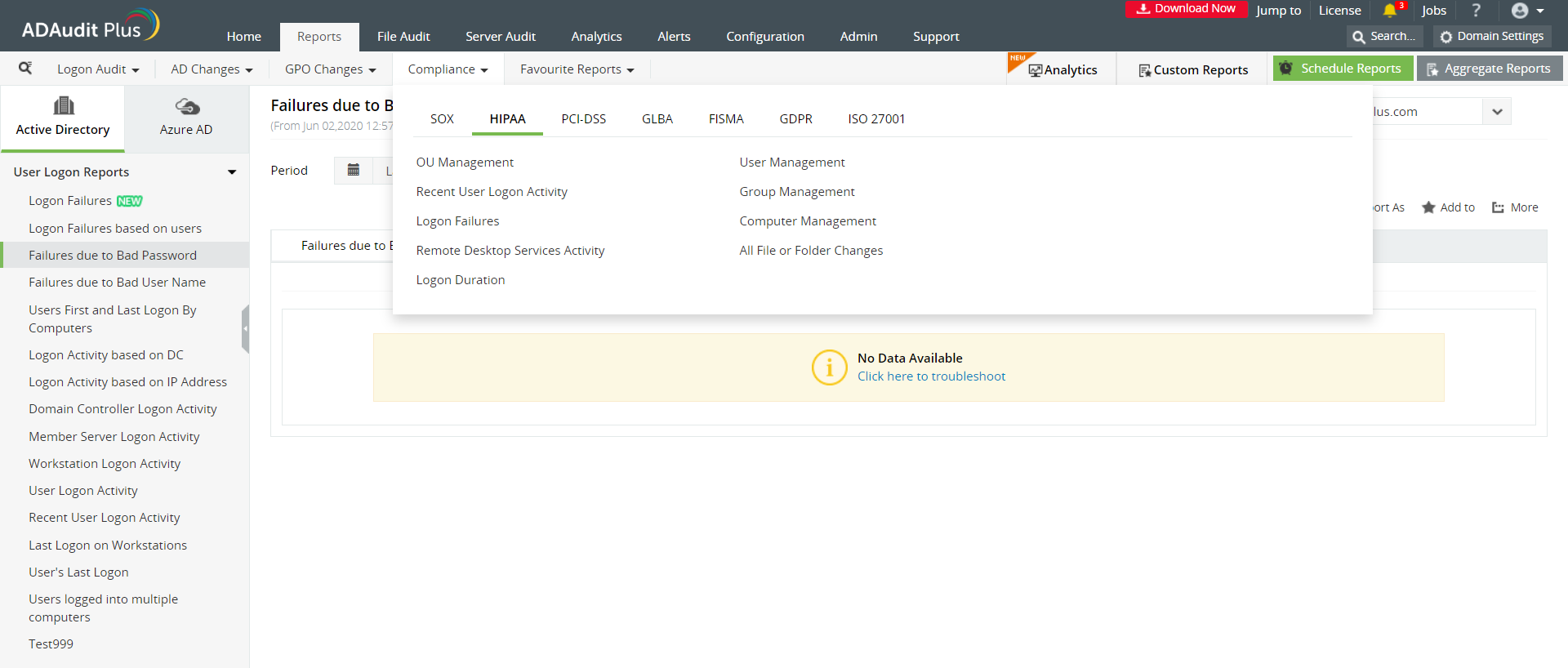 Image: The 'Compliance' tab shows reports that help you stay HIPAA compliant.
Image: The 'Compliance' tab shows reports that help you stay HIPAA compliant.
This report shows you changes made to security and distribution groups; for example a user being added to or deleted from a group.
This report shows you all the changes made to organizational units. For example, a new OU was created, or an existing OU was deleted.
The report displays recently logged on users, from which workstations they have logged on from, if the logon was a success and why a logon failed.
The report displays a list of logon failures with comments on what type of error caused the logon failure; for example, a bad password entry.
This category of reports shows you a list of user accounts that were created, deleted or disabled.
This section shows you a list of computer accounts that may have been created or deleted or modified.
This report describes a user's logon-related details like logon and logoff time, logon type, which workstation the user logged in from, and for how long they were logged in.
This report lists all the changes made to a file or folder. For example a folder's owner was changed, or a file was created or deleted or modified. You can also see if a content of a file were copied and pasted elsewhere.
This report describes any attempts to logon to your network remotely.
ADAudit Plus is a real-time, web-based Windows Active Directory (AD) change reporting software that audits, reports and alerts on Active Directory, Windows servers and workstations, and NAS storage devices to meet the demands of security and compliance requirements. You can track AD management changes, processes, folder modifications, permissions changes, and more with 200+ reports and real-time alerts. You can also get out-of-the-box reports for compliance mandates such as the HIPAA. To learn more, visit https://www.manageengine.com/active-directory-audit/
Try ADAudit Plus login monitoring tool to audit, track, and respond to malicious login and logoff actions instantaneously.
Try ADAudit Plus for free