High Availability with PostgreSQL Database
(This feature is available in Premium and Enterprise editions only)
Note: The procedure detailed in this document is applicable for Password Manager Pro builds 13140 and above only. For High Availability configuration using PostgreSQL database in builds preceding 13140, please refer to this help document.
In mission-critical environments, one of the crucial requirements is to provide uninterrupted access to passwords. The PostgreSQL High Availability setup in Password Manager Pro ensures continuous access, fault tolerance, and performance by using primary and secondary servers with a shared database, along with a read-only server that maintains a real-time replica. This architecture enables seamless operations even during primary and secondary server failures. This document outlines the steps to set up and maintain the PostgreSQL High Availability configuration in your environment.
The following topics are covered in this help document:
- Prerequisites
- High Availability Architecture
- Configuring the Application Servers for High Availability
- High Availability Monitoring
- High Availability Audit Trails
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Troubleshooting Tips
1. Prerequisites
- If you are using the existing High Availability with PostgreSQL Database in your environment, you should remove the existing configuration before setting up the new high availability configuration. Explore this link for the detailed steps to remove the existing high availability configuration in your environment.
- Ensure the web server port (7272) is open in all the servers and the database server port (2345) is open in the primary and read-only servers. If you have configured a custom port for web and database servers in your environment, ensure those ports are open.
2. High Availability Architecture
The PostgreSQL-based High Availability (HA) architecture in Password Manager Pro is designed to deliver robust performance, fault tolerance, and service continuity. This architecture comprises a Primary and a Secondary server, both fully functional and capable of handling read and write operations, connected to a shared PostgreSQL database running as an independent service. In addition, it includes a dedicated Read-Only server that maintains a real-time replica of the primary database through PostgreSQL’s native streaming replication, supporting read operations only.
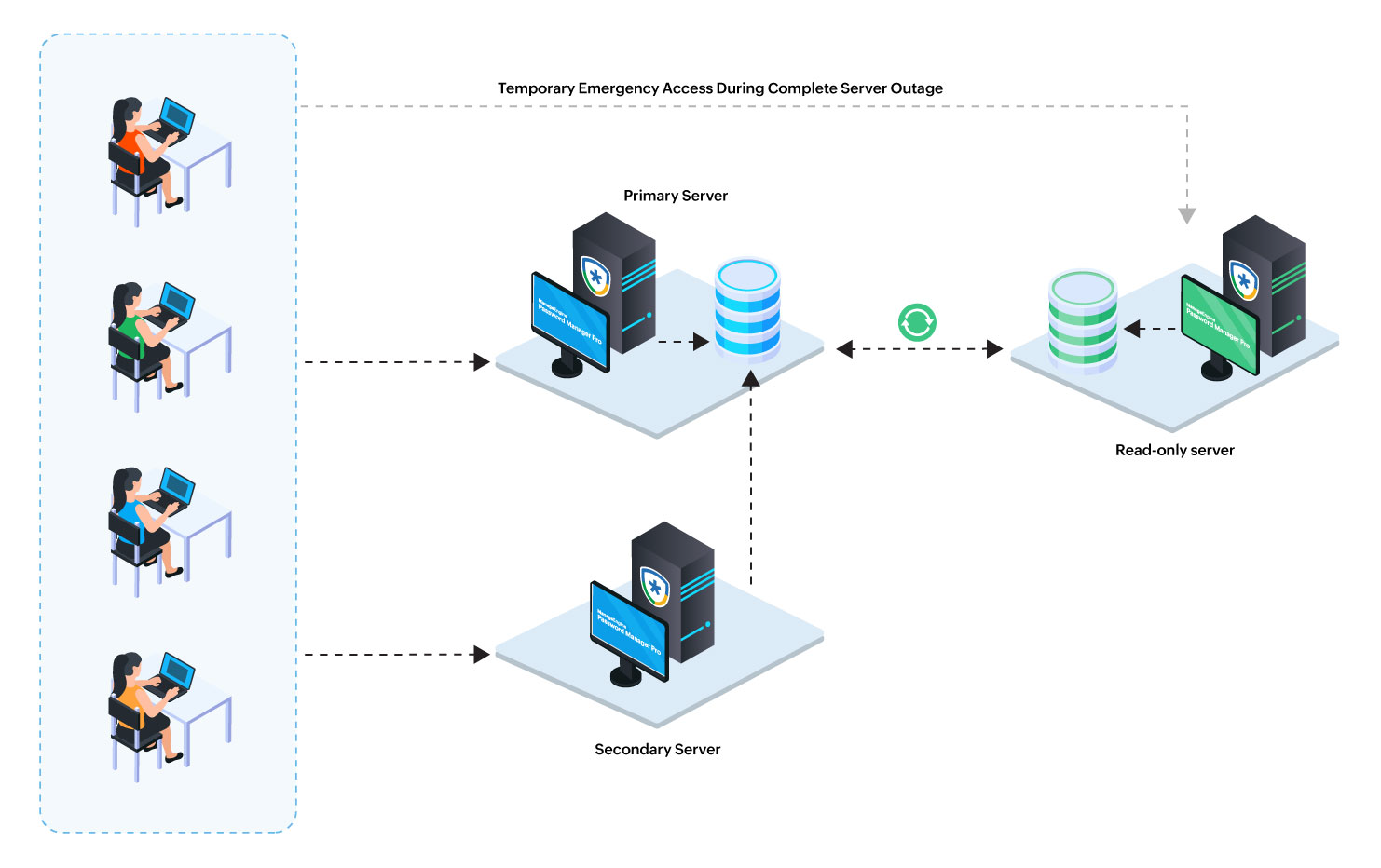
Important Notes:
- The read-only server in this architecture is provided as a fallback server and not for permanent access.
- The schedules will run only on the primary server.
- The read-only server cannot be accessed while the primary or secondary server is active. The following redirection logic is applicable when users access the Password Manager Pro application using the read-only server URL:
- If the primary server is active, users will be automatically redirected to it.
- If the primary server is inactive but the secondary server is active, users will be redirected to the secondary server.
- If both the primary and secondary servers are inactive, the users will maintain uninterrupted access to privileged passwords via the read-only server.
- If the application servers are deployed across different networks in your environment, redirection from the read-only server to the primary or secondary server may fail due to network limitations. In such scenarios, it is recommended that users access Password Manager Pro directly using the primary server URL, rather than the read-only server URL.
This full HA model is our recommended deployment for organizations seeking maximum availability and disaster recovery readiness. It ensures uninterrupted operations even during server or database failures. In the event of a Primary server failure, the Secondary seamlessly takes over. If both Primary and Secondary servers are unavailable, access to privileged passwords continues via the Read-Only server. Administrators can also temporarily promote the Read-Only server to restore full read-write functionality, ensuring minimal disruption and data consistency across all nodes.
However, if your infrastructure or operational requirements do not call for the complete HA setup or if provisioning multiple servers is a constraint, you can opt for one of the supported alternative deployment type:
- Primary Server with a Read-Only Server
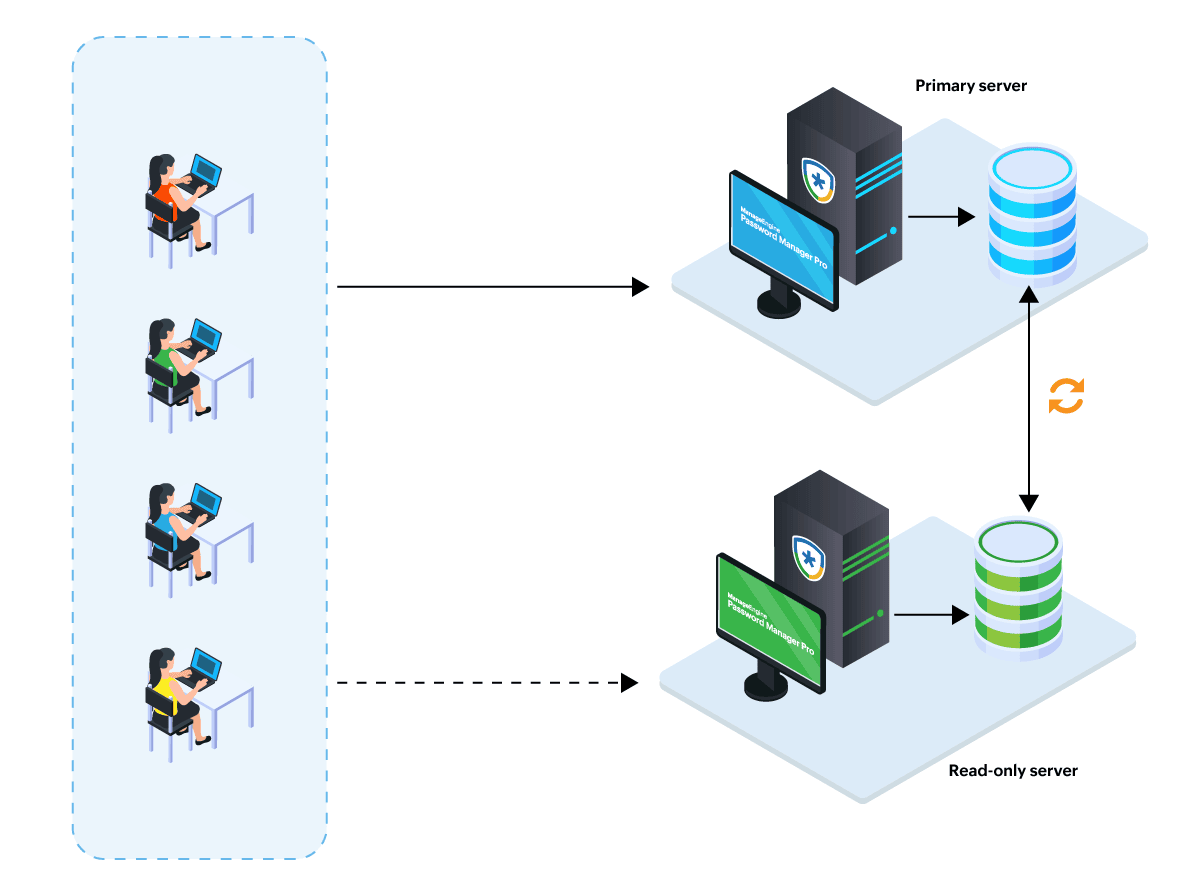
- Primary and Secondary Server with a Shared Database
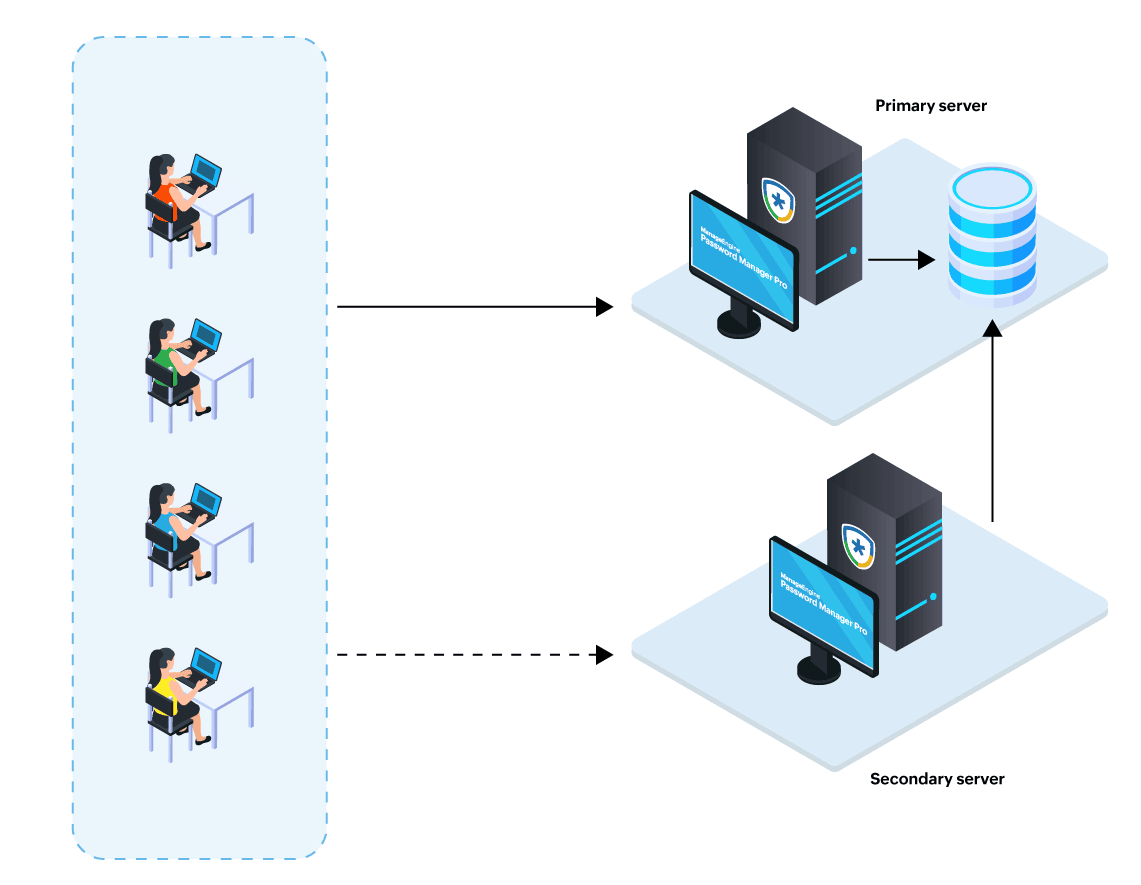
Each of these models offers varying degrees of availability and scalability to suit different organizational needs. Refer to the upcoming section to follow the appropriate deployment steps for the model you choose.
3. Configuring the Application Servers for High Availability
The following are the three types of deployment models are to suit varied operational needs. Refer to one of the desired models for the configuration procedure:
- Primary and Secondary Server with a Shared Database and an Additional Read-Only Server (Recommended)
- Primary Server with a Read-Only Server
- Primary and Secondary Server with a Shared Database
4. High Availability Monitoring
Note: The High Availability monitoring described here is for a Primary and Secondary Server with a shared database and an additional Read-Only Server. This may vary depending on your chosen High Availability deployment model.
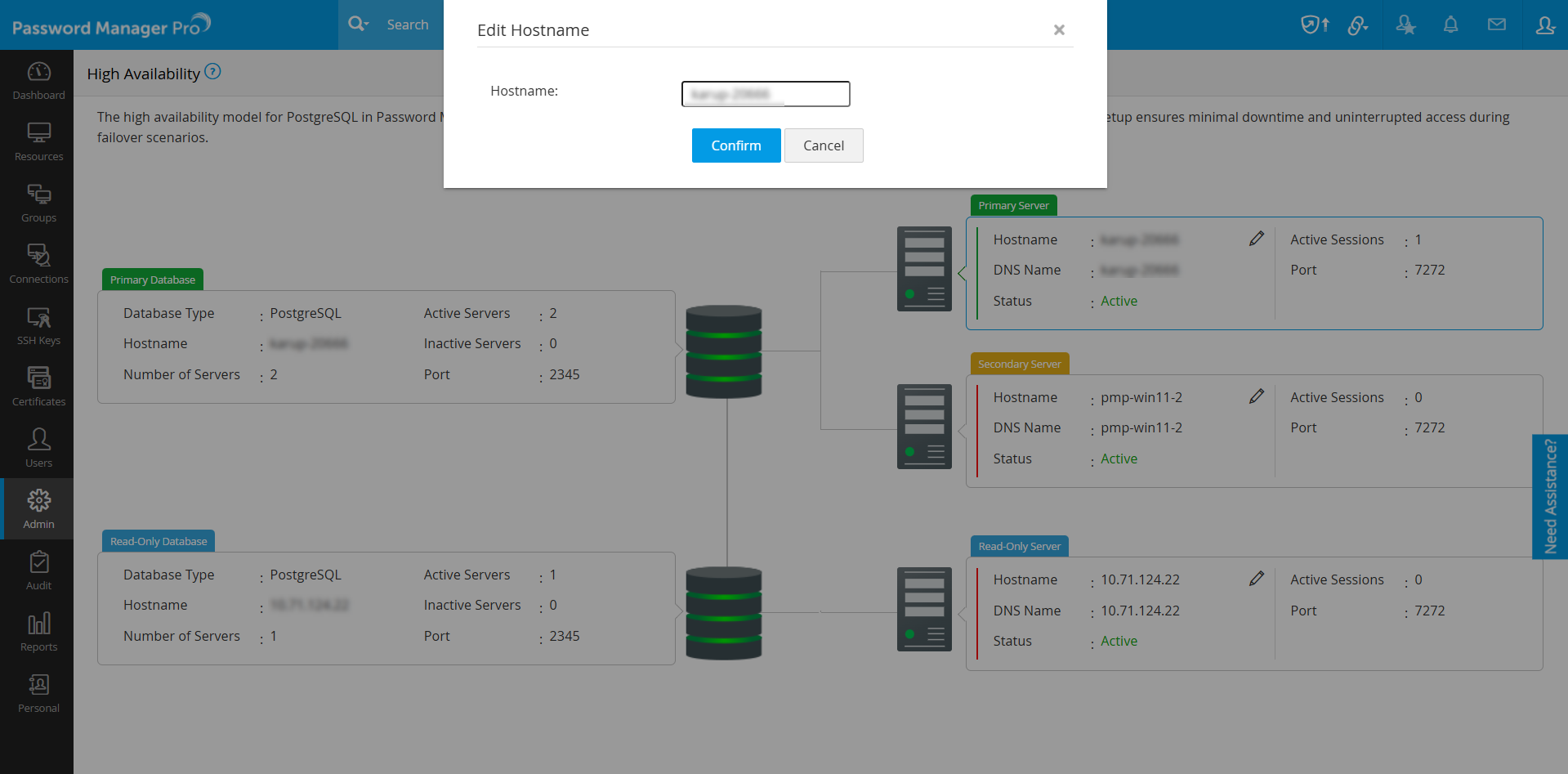
Continuous monitoring of the application servers and associated databases is essential to ensure business continuity and minimize the risk of downtime due to unexpected server failures. Password Manager Pro offers a centralized High Availability Monitoring dashboard that provides real-time visibility into all configured components such as the primary, secondary, and read-only servers, as well as the primary and read-only databases. It provides real-time insights into server availability, connectivity status, database replication health, and server roles. To access the High Availability Monitoring dashboard, navigate to Admin >> Configuration >> High Availability.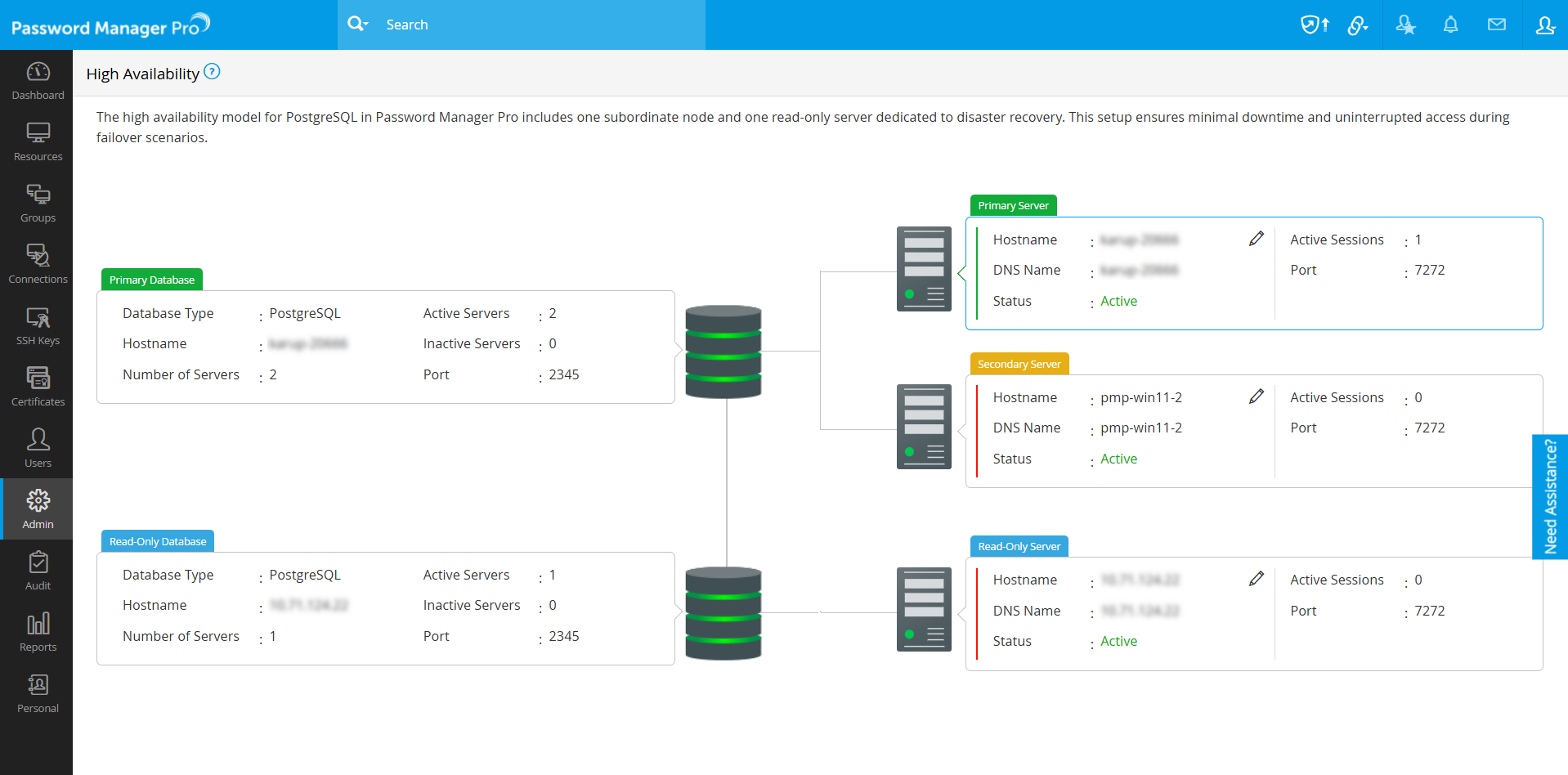
The dashboard displays the High Availability architecture deployed in your environment with the following details:
- Servers - Hostname, DNS name, status, server type, port in use, and the number of active user sessions
- Databases - Hostname, database type, port in use, total number of configured servers, and the number of active servers
Additionally, you can modify the name of the servers available in your environment for easier identification. Follow these steps to rename a server:
- On the High Availability dashboard, click the edit icon beside the hostname of the desired server.
- On the Edit Hostname window that appears, enter the name that you wish to use for the selected server in the Hostname field.
- Click Confirm to save the configured changes.
This monitoring feature enables administrators to track the health and connectivity of all servers and databases in real-time, helping them proactively respond to disruptions and maintain uninterrupted privileged access across the environment.
5. High Availability Audit Trails
By default, Password Manager Pro offers comprehensive audit trails covering Resource, User, Key, Certificate, and Task activities. When High Availability is enabled, auditing capabilities are further enhanced with server-specific tracking for Resource, User, and Task audits. Each of these audit categories will feature dedicated tabs for the Primary, Secondary, and Read-Only servers, enabling administrators to trace actions based on their originating servers. This enhancement offers a comprehensive view of all activities across the clustered environment. Click here to learn more about audit trails in Password Manager Pro.
6. Frequently Asked Questions
- Can I enable High Availability using PostgreSQL without disrupting the current setup?
No, if you have an existing high availability configuration using PostgreSQL, you must remove this configuration before setting up the new one. Follow the steps provided in this link to safely remove the existing setup. - What happens if both the primary and secondary servers go down?
In such cases, users can maintain continuous access to privileged passwords via the read-only server. If required, users with the administrator privileges can temporarily reconfigure the read-only server to act as the primary server to maintain full functional capabilities. Refer to this link for the detailed steps to configure the read-only server into the primary server. - How can I verify the status of all nodes?
You can view the status of all the servers under Admin >> Configuration >> High Availability, where the status of all the servers will be displayed.
7. Troubleshooting Tips
1. What should I do when one of the servers appears inactive on the High Availability dashboard?
If one of the servers' status appears as inactive under Admin >> Configuration >> High Availability, it could be due to the Password Manager Pro service not running, a potential issue with the PostgreSQL replication setup, or an issue with the network communication between the primary, secondary, and read-only servers. Follow these steps to resolve this issue:
- If the primary or secondary server is displayed as inactive, ensure that the respective servers are alive and the password manager pro service is running properly.
- If the read-only server is displayed as inactive, ensure that the read-only server is alive and the password manager pro service is running properly.
- If the service is running but the status is displayed as inactive, it could be due to an issue with the database replication. Follow these steps to check the replication configuration on the primary server:
- Navigate to the <pmp_installation_directory>/pgsql/data folder.
- Open the pg_hba.conf file and ensure the following entries are present and correctly configured:
2. How do I ensure business continuity with full functional capabilities when both the primary and secondary servers are unrecoverable?
When both the primary and secondary servers are unrecoverable, you can configure the read-only server to act as the primary server temporarily to support both the read and write operations. Follow these steps to configure the read-only server into the primary server:
- Stop the Password Manager Pro service running on the read-only server.
- Remove the standby.signal file from the <pmp-installation-directory>/pgsql/data folder.
- Open the postgres_ext.conf file located in the <pmp-installation-directory>/pgsql/ext_conf folder and delete all entries listed under the section recovery props.
- Delete the entry readonly.mode=true in the <pmp-installation-directory>/conf/configurations.properties file.
- Open the serverstate.conf file from the <pmp-installation-directory>/conf folder, locate the entry ro, and replace it with master.
- Start the Password Manager Pro service on this server. It will now function as the primary server supporting full functionality.
- Now, execute the following commands to clean up database references to the old read-only configuration:
- Windows
- <PMP_Installation_Folder>\bin\DeleteROServerIP.bat <IP_Address_of_RO_that_was_converted_to_Primary>
- <PMP_Installation_Folder>\bin\DeleteSlot.bat <slotName_of_RO_that_was_converted_to_Primary>
- Linux
- <PMP_Installation_Folder>/bin/DeleteROServerIP.sh <IP_Address_of_RO_that_was_converted_to_Primary>
- <PMP_Installation_Folder>/bin/DeleteSlot.sh <slotName_of_RO_that_was_converted_to_Primary>
You have now successfully reconfigured the read-only server as the primary server in your High Availability setup. Once the primary and secondary servers are recovered in your environment, you can revert the acting primary server to its fallback role. After restoring the primary and secondary servers, ensure that you do not start the Password Manager Pro service on these servers without restoring the database backup from the acting primary server (previously read-only server) to the primary database as this might lead to data loss.
Note: Please note that restarting the primary server without restoring the database backup will result in data loss.
Follow these steps to restore the database backup from the read-only database to the primary database:
- On the acting primary server, navigate to Admin >> Configuration >> Database Backup, and click the Backup Now button on the Database Backup window. The backup file will be generated in the destination directory.
- Stop the Password Manager Pro service on the acting primary server.
- Use the generated backup file to restore the data from the acting primary server to the restored primary server. Explore this link for the detailed steps to restore the backup data.
- After restoring the database backup, start the Password Manager Pro service on the restored primary server to initialize the server and the database.
Note: When the database backup is being restored on the primary server, no servers will be available to handle user requests in the environment.
The acting primary server, previously the read-only server, cannot be reconfigured to its previous fallback role. Decommission this server and build a new read-only server from scratch by following the steps detailed below:
- Stop the Password Manager Pro service running on the restored primary server.
- Generate the read-only server setup pack on the restored primary server as detailed in Section 3.1.
- Follow the procedure outlined in Section 3.2 to configure the read-only server using the newly generated setup pack.
As detailed above, when primary and secondary servers are beyond recovery or cannot be brought back online quickly, you can promote the read-only server to act as a fully functional primary server to ensure business continuity. Once the primary and secondary servers are recovered, generate the database backup from the acting primary server and restore it on the recovered primary server to ensure data consistency with the most recent changes made while the primary was down. Decommission the acting primary server (previously read-only server) and reconfigure a new read-only server to act as a fallback server.
If the issue persists and a server still appears as inactive after verifying the above configurations, collect logs from the following locations and send them to passwordmanagerpro-support@manageengine.com for further assistance:
- <PMP_Installation_Directory>/logs
- <PMP_Installation_Directory>/pgsql/data/pg_log