Metrics are at the heart of IT service management, delivering insights on operations and helping identify areas of continual improvement. The usual service desk metrics help showcase the internal operational efficiency. For example, SLA, that measures the number of tickets resolved under the specified time is a key factor that showcases service desk efficiency. On the other hand, failure metrics help teams identify weak chinks in the IT infrastructure and help evaluate responses to failure events. This helps IT teams minimize the cascading effect that failures can cause on critical systems.
What are the key failure metrics to be tracked? In this article we will see the following three KPIs:
- Mean time between failure
- Mean time to failure
- Mean time to repair
Mean time between failure (MTBF)

When there are frequent failures on IT infrastructure assets, be it networks, servers, workstations, etc., they have a cascading impact on the availability of IT and business services. These disruptions lead to loss of revenue and reputation. If a particular IT asset sees frequent downtimes, repair or replacement is often required. Before that, it helps to investigate and understand why the asset goes down often and in what circumstances. This helps plan asset maintenance and improve systems availability. MTBF is the metric that helps identify downtime causes and helps mitigate them or plan for quick recovery and better availability of IT systems.
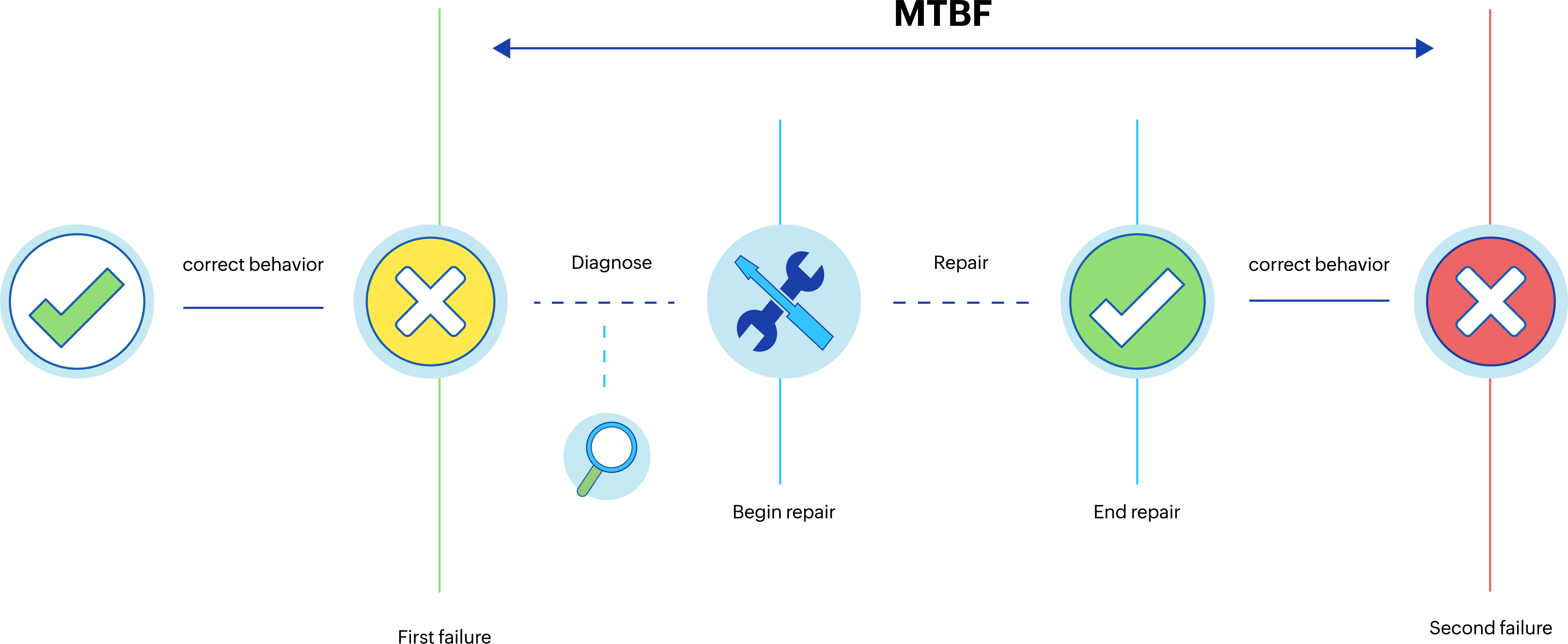
Figure 1. Mean time between failure
If the MTBF of a particular IT asset is low, it means the asset sees frequent downtimes leading to IT and business disruptions.
MTBF example
In an organization, new updates to the storage drive kept failing whenever new Windows firmware updates were applied. This occurred a few times and the MTBF became worse. After analysing the issue, the team determined that the third-party driver caused the API required to carry out the update to either not be implemented, or to be faulty. When a new update is scheduled, if third-party drivers do not implement the necessary APIs, there are two possible solutions to explore. Swapping the APIs with the Windows alternatives for SATA and NVMe storage protocols, or obtaining a new and better supported version of the driver from the OEM can help implement updates, fix bugs, and close security loopholes. Monitoring and tracking driver upgrades and downtime helps improve the availability of the storage drives.
How to improve MTBF
- Implement a process to observe asset health to track and monitor failures. This helps identify the cause of disruptions.
- Analyze the root cause of the problem to create awareness, address long-term causes, and improve asset performance.
- Create a quick response strategy to effectively tackle and reduce downtimes that impact operations. The objective is to achieve fewer and more time between disruptions.
Mean time to
failure (MTTF)

Assets failing regularly can interrupt your organization's IT operations, and result in the deterioration and underperformance of IT infrastructure. The MTTF metric helps determine the typical lifespan of an asset, device, or component. For IT assets and components with a low MTTF, it is often more time-efficient, and minimizes operational impacts and costs, to replace the IT component instead of fixing the component.
This applies especially to IT components linked to crucial operational elements of the infrastructure like a mainframe server stack or a network access point.
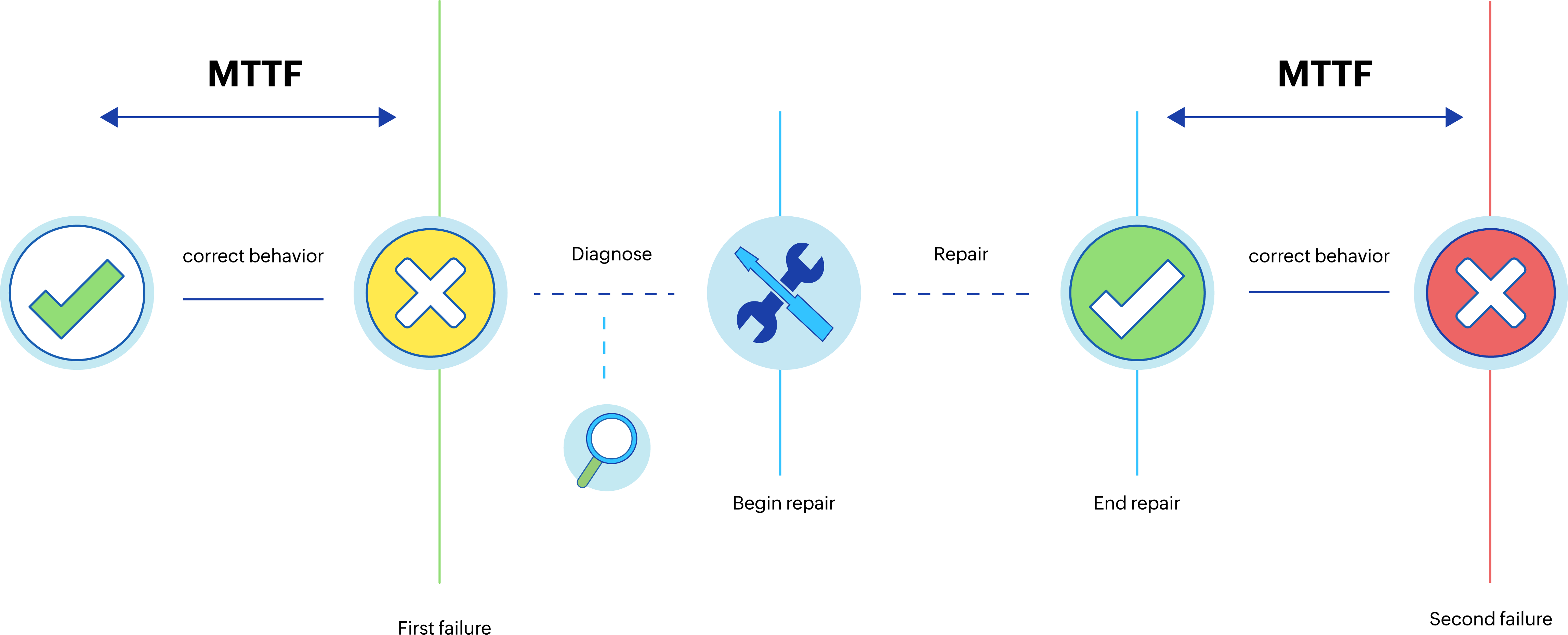
Figure 2. Mean time to failure
If the MTTF of an asset is unfavorable and fails regularly, it indicates that the IT asset is unreliable and needs frequent replacement to avoid impacting IT operations.
MTTF example
In an IT software development company, when a cable was connected or disconnected from the switch in the data and network server stack, the network cables would get loose, and disconnect or get damaged. This led to files becoming corrupted due to interrupted data transfer. Further analysis by the network team revealed that the snagless plastic cover kept breaking on the CAT6 RJ45 patch cable. This was due to the cable being procured from a manufacturer who used cheap material. The IT team then replaced the old cables with cables of better quality to make sure there would be no issues, like the loss or corruption of data, in future when cables are moved. This is a classic example, but tracking the MTTF of the cable on a regular basis helps IT teams understand the impact of critical assets, like components, so they can make informed decisions about repair and replacement.
How to increase MTTF
- Increase the asset life span by procuring assets of high quality and decommissioning assets of low quality and cost.
- Prevent large-scale disruptions to business operations by scheduling regular checks on components linked to critical assets.
- Implement a just-in-time inventory process that estimates the time an asset is operational, leading to reduced overhead costs for asset storage.
Mean time to
repair (MTTR)

When a critical IT system fails, IT teams must get the system running as soon as possible. Delays in restoring IT systems can lead to loss of revenue and impact critical business operations. A well-organized recovery and response system can help IT teams respond to unplanned downtime and restore operations effectively. MTTR measures the average time taken to repair or troubleshoot an asset and return it to its operational capability.
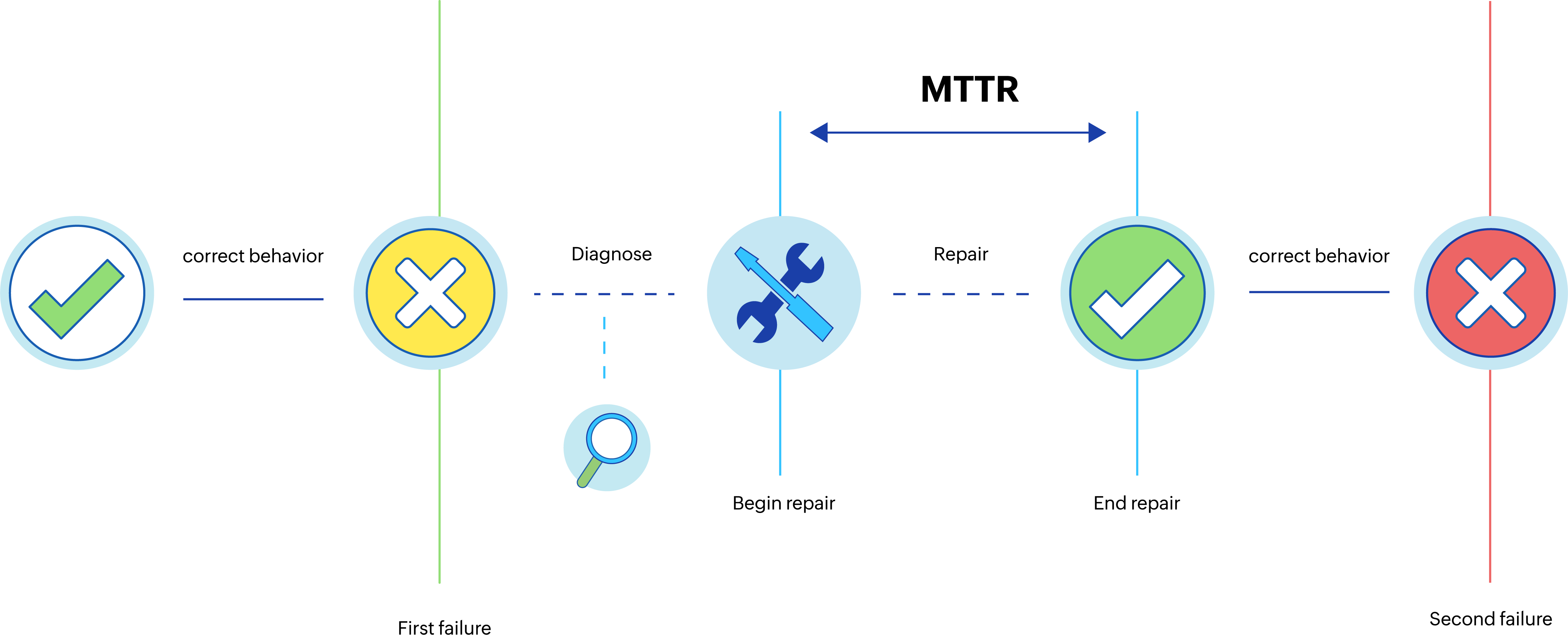
Figure 3. Mean time to repair
The cost of a downtime increases as the MTTR increases. High MTTR suggests that your recovery and response operations are not quick and effective. System failures are unavoidable, but MTTR enables teams to react to asset failures in a timely and strategic way.
MTTR example
A software company faced a zero-day attack on a video game it was developing due to vulnerability in a code. The attack disrupted operations like Wi-Fi and surveillance systems. This led to the attackers accessing the organizations' network domain and confidential business files. The cybersecurity team informed employees about zero-day attacks and where they could report them. Every IT asset in the organization was equipped with next-generation antivirus (NGAV). The attack disabled the LAN and employee self-service portal, crippling the operations of the organization. Within an hour of the attack, the cybersecurity team was informed and helped by NGAV's ability, which leverages threat analytics and behavior patterns of users, and identified the suspicious activity. The cybersecurity team immediately ran a patch management script to rectify the vulnerability in the code, and locked down its on-premises network to avoid further impact operations and data theft.
How to reduce MTTR
- An efficient asset management strategy helps drive better decision-making by identifying bottlenecks, and designating that assets be repaired or replaced. This saves money and storage space.
- Define the responsibilities and roles for technicians to streamline the incident detection and resolution process.
- Provide technicians with detailed standard operating procedures to reduce miscommunication and confusion during a downtime.
- Measure MTTR using an Enterprise Asset Management solution that centralizes asset maintenance and monitoring information. This also helps optimize the utilization of assets, collect asset data, and predict possible downtime.
Conclusion
These failure metrics help teams identify the bottlenecks in operations and their responsiveness to incidents. They empower IT teams to achieve higher operational efficiency by pinpointing the root cause of persistent incidents. IT teams can improve their incident response strategy with a clear picture of areas where IT operations are impacted. These metrics can be implemented in organizations by using them as KPIs rather than just performance objectives. The metrics point out areas for process simplification and operational improvements, and are not merely targets to hit.
A quick summary of each metric:
- MTBF provides better insights into your service desk's effectiveness at preventing future disruptions.
- MTTF helps you understand the lifecycle of an asset and its reliability.
- MTTR indicates the time spent on repairing and how quickly your IT teams are able to diagnose disruptions.
About the author
Saket Pasumarthy, a product expert at ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus, is an ITSM enthusiast and is fascinated in understanding the latest advancements in the IT space. Saket writes articles and blogs that help IT service management teams globally handle service management challenges. Also he presents user education sessions in the ServiceDesk Plus Masterclass series. Saket spends his free time playing football and flying planes on a flight simulator.






