- Free Edition
- Quick links
- Active Directory management
- Active Directory reporting
- Active Directory delegation
- Active Directory permissions management and reporting
- Active Directory automation
- Governance, risk, and compliance
- Microsoft 365 management and reporting
- Microsoft 365 management and reporting
- Microsoft 365 management
- Microsoft 365 reports
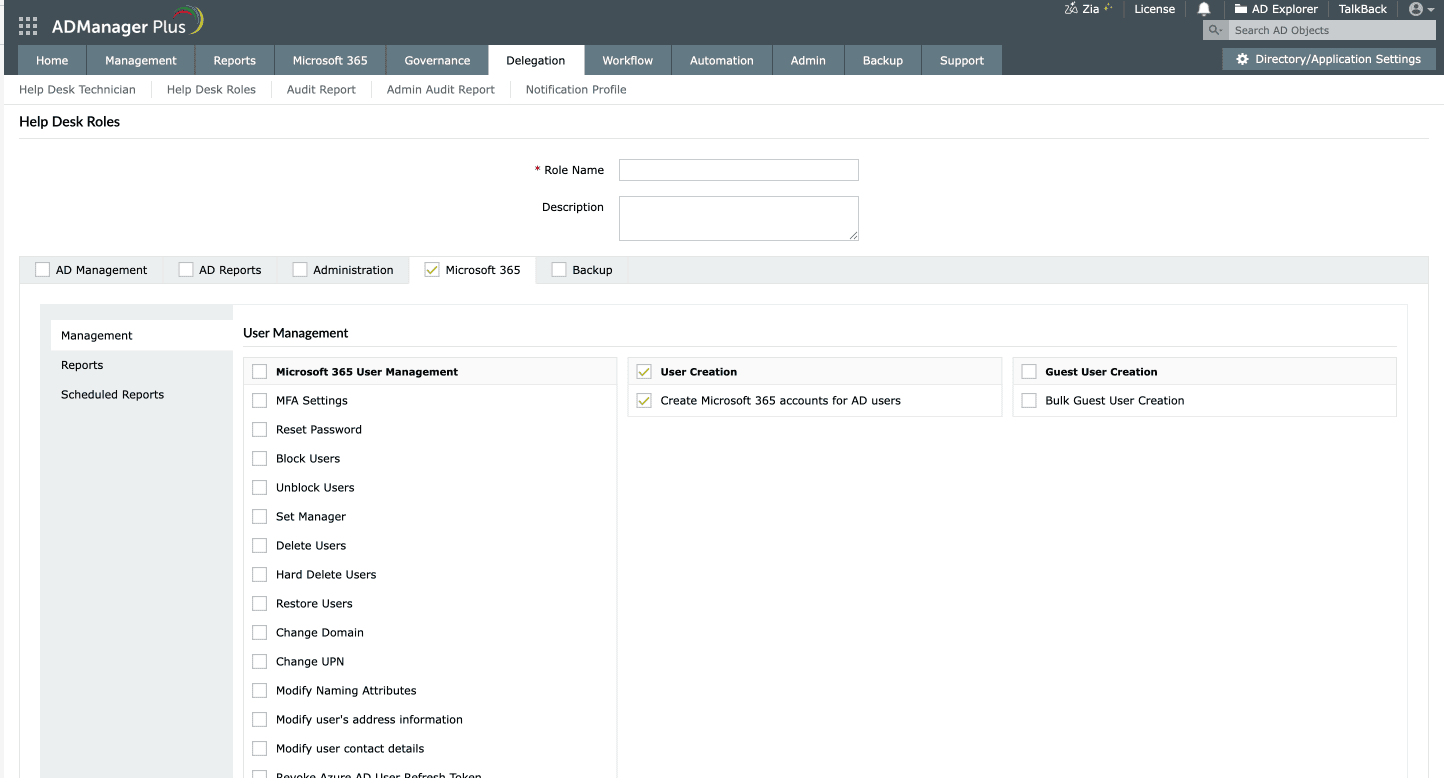
- Microsoft 365 user management
- Microsoft 365 user provisioning
- Microsoft 365 license managementn
- Microsoft 365 license reports
- Microsoft 365 group reports
- Dynamic distribution group creation
- Dynamic distribution group reports
- Exchange management and reporting
- Active Directory integrations
- Popular products
What is Active Directory delegation?
Active Directory (AD) delegation is the practice of selectively assigning permissions to users or groups, allowing them to perform common, high-volume AD management tasks like password resets, account unlocks, or group management. In large organizations, managing AD without delegation is impractical.
However, delegating using Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) is often risky and lacks transparency as permissions assigned in ADUC are difficult to track and revoke. A secure AD delegation tool ensures that administrative responsibilities are distributed efficiently while maintaining visibility and control. This is where ADManager Plus comes in, offering a centralized, auditable, and role-based delegation framework.
Why is AD delegation important?
A strategic delegation model is a cornerstone of modern IT security and efficiency.
- Enhanced security: It allows you to enforce the principle of least privilege, ensuring users and technicians have only the permissions necessary to perform their jobs, drastically reducing the attack surface.
- Increased IT efficiency: It frees senior IT administrators from routine, low-level tasks. This allows them to focus on high-value projects like infrastructure, security policy, and strategy.
- Improved productivity: It empowers help desk staff, HR personnel, and even team managers to resolve common issues instantly without contacting IT teams, reducing user downtime and long ticket queues.
- Clear auditing and compliance: When done correctly, delegation provides a clear trail of who performed what action and when. This is essential for meeting regulatory requirements like the GDPR, SOX, and HIPAA.
Understanding key delegation terms
To understand delegation, you need to know its building blocks:
- Security principal: Any object in AD that can be assigned permissions, such as a user account, group, or computer.
- Access control list (ACL): A table attached to every AD object that lists who has what permissions on that object.
- Access control entry (ACE): A single line item within an ACL is called an ACE. Each ACE specifies a permission for a specific security principal on a specific action.
- Permission inheritance: By default, permissions applied to a parent object flow down or inherit to all child objects. This is powerful but can be complex to troubleshoot.
- Effective permissions: The actual set of permissions a user has on an object. This is calculated by combining all permissions from their user account, all group memberships, and inheritance.
- Principle of least privilege: A foundational security concept stating that users should only be granted the absolute minimum permissions necessary to perform their jobs.
- Role-based access control: A model for managing permissions where you assign permissions to roles and then assign users to those roles. This is far more manageable than assigning permissions directly to individual users and helps implement the principle of least privilege.
How to delegate control in AD
You can delegate control using built-in tools like ADUC or PowerShell, but both have significant drawbacks.
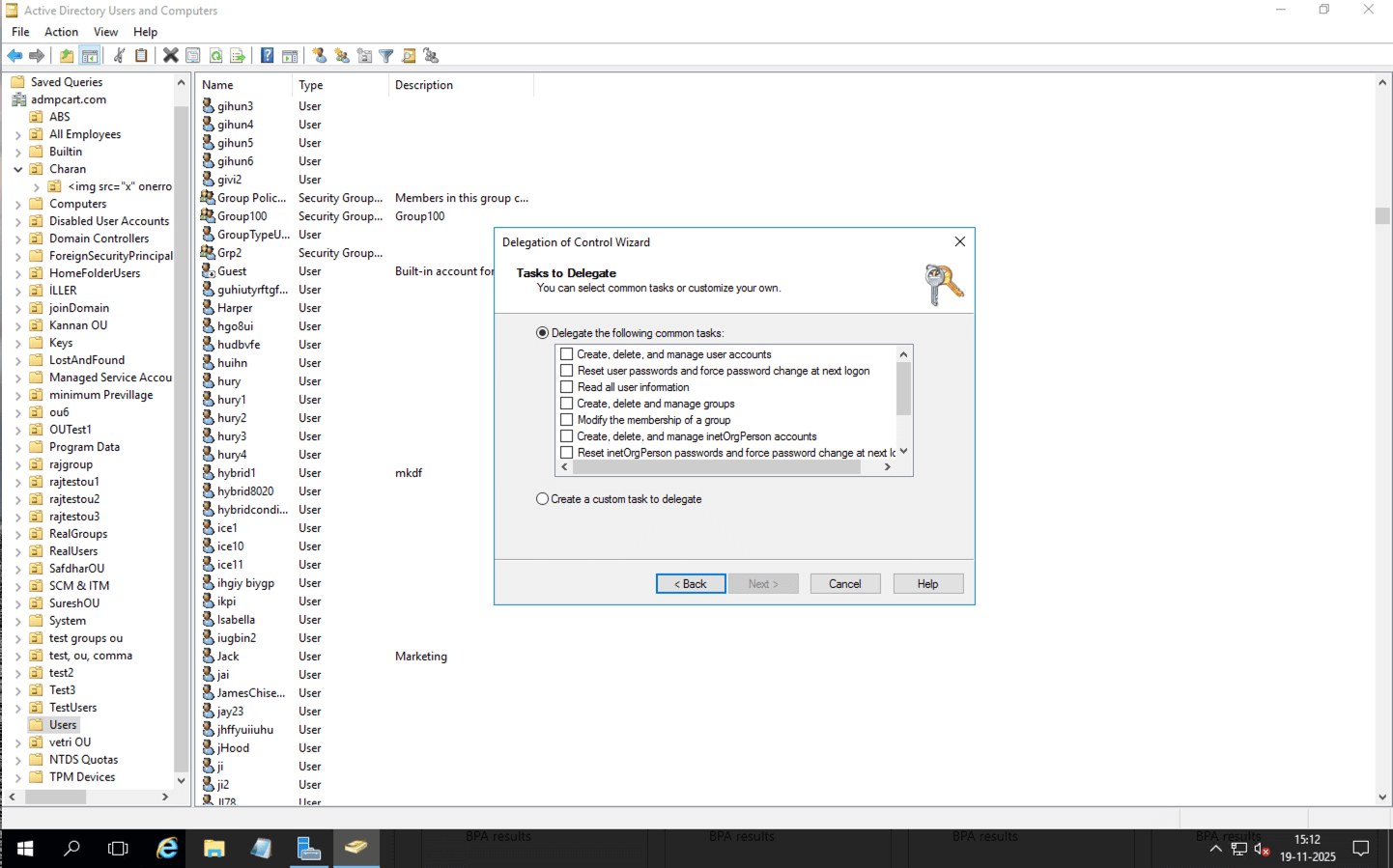
Using the ADUC Delegation of Control Wizard
- Launch ADUC and locate the target OU.
- Right-click the OU you wish to delegate control over and click Delegate Control.
- In the Delegation of Control Wizard, select the users or groups you want to delegate permissions to.
- Click Next.
- On the Tasks to Delegate screen, select from a list of common tasks or create a custom task for more granular control.
- Specify the permissions that the users or groups will have.
- Review the summary of changes and click Finish to apply the new ACEs to the OU's ACL.
Using PowerShell
- Import the Active Directory PowerShell module.
- Set variables for your target OU, the user or group getting the rights, and the specific rights you're granting.
$OU_DN = "OU=Sales,DC=example,DC=com"
$Principal = "EXAMPLE\HelpDesk"
- Get the ACL of the target OU using the Get-Acl cmdlet.
- Define the user or group that will receive the permissions.
- Add this new rule to the ACL object and apply the newly modified ACL back to the OU using the Set-Acl cmdlet.
$acl.AddAccessRule($ace)
Set-Acl -Path "AD:$OU_DN" -AclObject $acl
For a detailed walk-through of how to delegate control using ADUC and PowerShell, refer to this article.
Secure and auditable AD delegation
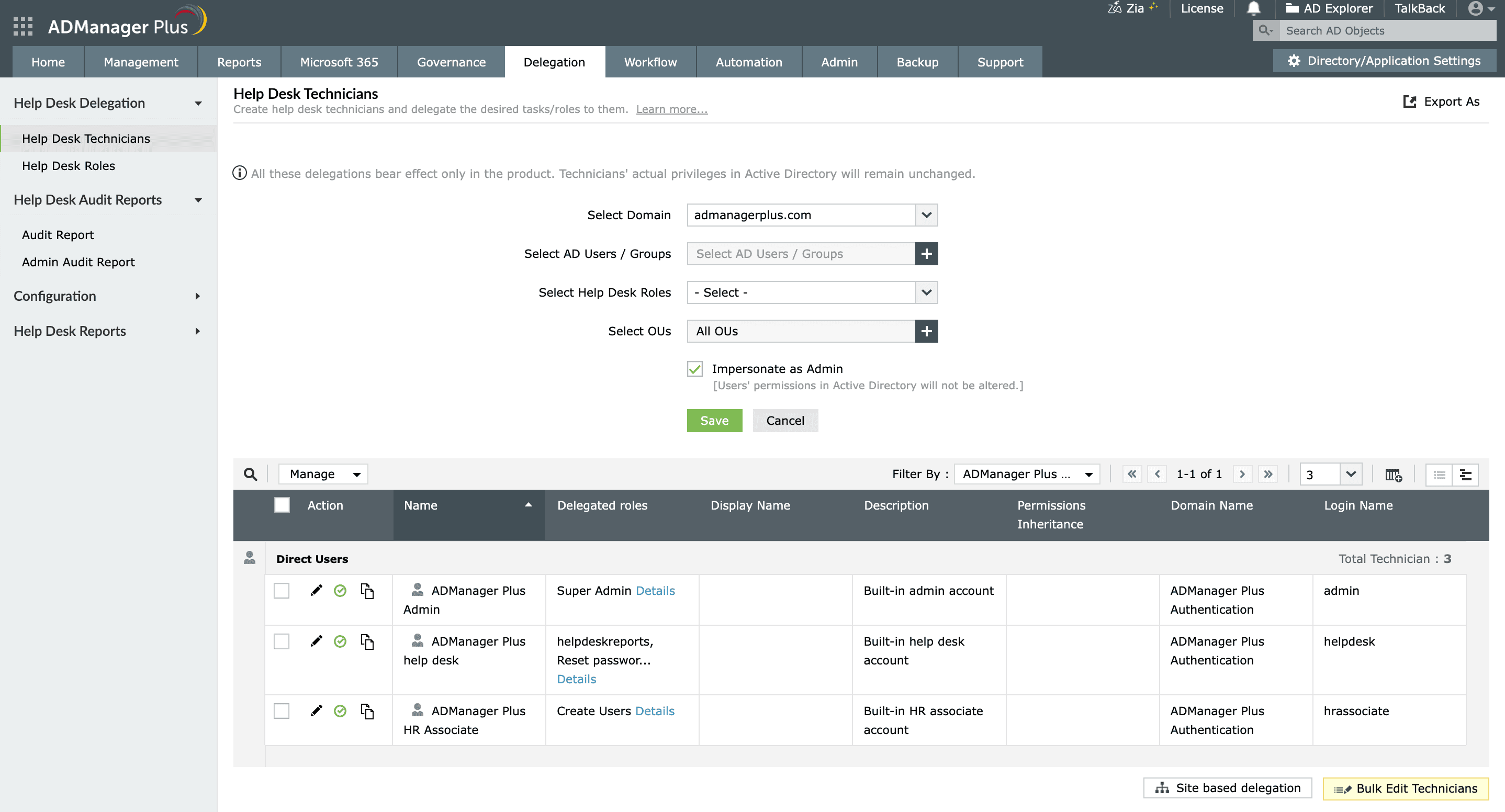
ADManager Plus, an AD delegation tool, empowers administrators to securely delegate AD tasks to help desk technicians without compromising on security. With ADManager Plus, admins can:
- Granularly delegate tasks without elevating AD permissions.
- Create custom help desk roles based on tasks.
- Audit and report on every single action performed by the technicians.
Non-invasive help desk delegation
Traditional ADUC-based delegation modifies ACLs, which can expose the AD environment to misconfigurations and security gaps. ADManager Plus offers non-invasive delegation, which means permissions are controlled within the tool and not directly in AD, ensuring that your AD environment remains secure and unchanged.
Role-based delegation
Easily create help desk roles tailored to your organization's structure. You can build roles from the ground up with only those permissions required to complete an AD task. For example, you can create a password reset role that allows technicians only to reset passwords and not create or delete a user.
Secure and granular delegation
ADManager Plus supports secure and granular delegation, enabling administrators to define exactly which OUs, groups, or users a technician can manage and report on. From resetting passwords in a specific OU to modifying only contact attributes, every action can be fine-tuned.
Audit logs
Every delegated action is logged and can be viewed using audit reports. Track who performed what action, when, and on which object to maintain complete visibility and compliance. These reports also help organizations meet IT audit and regulatory requirements such as the GDPR, SOX, and HIPAA.
Approval workflows
Ensure delegated tasks are executed only after proper review with approval workflows. ADManager Plus allows you to enforce a multi-level approval workflow for any task to ensure accountability and optimize task execution. Build simple, single-step approvals or complex, multi-stage workflows to match your business processes, adding a critical layer of control.
Flexible delegation models to meet your delegation needs
ADManager Plus offers multiple ways to define the scope of your delegation, ensuring it can map perfectly to your organization's hierarchy.
OU-based delegation model
Assign help desk technicians to manage and report on specific OUs and empower them to manage only the users, computers, and groups belonging to the assigned OU and not rest of the company's AD structure.
Group-based delegation
Group-based delegation in ADManager Plus enables bulk delegation and ensures that anybody who is a member of a particular AD group inherits the assigned roles and their permissions. For example, you can create a role that allows managers to view their direct reports' details and assign it to the Managers group.
Site-based delegation
For large organizations with multiple physical locations, you can delegate tasks based on AD sites. This allows a site-specific technician to manage all users and computers associated with their particular location, streamlining administration for geographically dispersed teams.
How to develop a delegation model
You can create a secure, custom help desk role and assign it to a technician in ADManager Plus in just a few simple steps.
- Create a help desk role
Define the specific AD tasks this role can perform from a comprehensive list. Within ADManager Plus, you can build this role by selecting only the specific tasks needed, such as Reset Password and Unlock Account, while explicitly excluding high-risk actions like Delete User. This granular approach is the foundation for enforcing the principle of least privilege.
- Assign role to technicians
Once roles are defined, you assign them to the appropriate technicians. This links a specific user a security group to the permission set you just created. A key security benefit of this model is that the technicians themselves remain standard domain users in Active Directory. Their elevated permissions exist only within ADManager Plus, not in native AD, which prevents security gaps.
- Define scope
Choose the OUs over which the technician can perform the delegated task. Granting a role isn't enough; you must also define on which OU that role can be used. This ensures that the help desk technician assigned to one OU cannot see or modify users in the other OUs.
AD delegation best practices
Follow these best practices to keep your environment secure and manageable:
- Embrace the principle of least privilege: Always grant the minimum level of permission required for a user to do their job.
- Delegate to groups, not individual users: Always assign permissions to a security group as this is infinitely easier to manage than tracking permissions on individual user accounts.
- Organize OUs for delegation: Structure your OUs based on your delegation needs, not just your company's organization chart.
- Avoid Deny permissions: Using Deny ACEs can create unpredictable results and make troubleshooting a nightmare. A well-designed model built on Allow permissions is always superior.
- Regularly audit permissions: Periodically review who has what permissions using certification campaigns.
AD delegation: Native AD tools vs. ADManager Plus
| Native AD tools | ADManager Plus |
|---|---|
| Native tools delegate permissions by modifying live Active Directory ACLs directly. | ADManager Plus manages permissions non-invasively, with all controls contained within the tool's interface. |
| Permissions granted are written permanently into AD's security structure, elevating the user's rights. | No permissions are ever elevated in AD itself, which keeps the underlying AD structure secure. |
| Delegation is often an all or nothing assignment for many common tasks. | It provides highly granular control, allowing delegation of specific tasks and attributes. |
| Auditing is difficult to implement and requires complex SACL configuration. | Auditing is built-in and comprehensive, automatically logging every single delegated action for easy review. |
| Revoking permissions is a complex and risky process that requires an administrator to manually find and remove individual ACEs. | Revocation is instant and safe as an administrator can simply uncheck a box or remove the user from the role. |
| Native tools are limited to supporting AD only. | It is hybrid-ready, allowing you to delegate tasks across AD, Microsoft 365, and Exchange from one console. |
Commonly delegated tasks in AD
ADManager Plus gives you granular control over the most common and critical IT tasks.
- User management
- Group management
- Group membership management
- Group creation and deletion
- Computer management
- Enabling and disabling computer accounts
- Microsoft 365 management
- Mailbox creation
- Distribution list management
- License management
Use cases
Use case 1: OU-based delegation for regional IT teams
A multinational company has separate OUs in AD for each region—Asia, Europe, and North America. Each region has its own IT team responsible for managing users and groups within its area. However, granting global admin rights to all regional admins poses security and management challenges. Using ADManager Plus, global administrators can create custom roles and assign specific OUs to regional technicians. For instance, the Asia IT team can manage users, groups, and computers only within the Asia OU.
Use case 2: Delegating Microsoft 365 user management tasks to HR teams in a hybrid AD environment
The HR department often needs to create or update user accounts when employees join, leave, or change roles across AD and Microsoft 365. Traditionally, this requires coordination with the IT team, leading to delays in account provisioning and deprovisioning. Using ADManager Plus, administrators can delegate user creation in Microsoft 365 to the HR team without actually granting Microsoft 365 rights.
FAQs
No. Your help desk users only need to be standard AD users to use ADManager Plus. However, to perform AD management and reporting actions using ADManager Plus, they have to be delegated with the relevant roles.
ADManager Plus provides non-invasive, role-based delegation that doesn't alter a technician's AD permissions. Technicians can only perform the delegated role in the delegated OU and only using ADManager Plus, making it safer and easier to manage.
Yes, every single action performed by a delegated technician is tracked, recorded, and available in the form of comprehensive, audit-ready reports.
A help desk role is a specific role or a set of roles delegated by an administrator to a unique non-administrative user to perform actions.
Help desk delegation helps in disseminating the workload from an administrator's desk. It reduces the burden on the administrator, allowing them to concentrate on core admin activities. It increases the productivity of users by eliminating the administrator's intervention in self-manageable activities.
Other features
Bulk User Management
Fire a shotgun-shell of AD User Management Tasks in a Single Shot. Also use csv files to manage users. Effect bulk changes in the Active Directory, including configuring Exchange attributes.
Active Directory Logon Reports
Monitor logon activities of Active Directory users on your AD environment. Filter out Inactive Users. Reporting on hourly level. Generate reports for true last logon time & recently logged on users.
Active Directory Delegation
Unload some of your workload without losing your hold. Secure & non-invasive helpdesk delegation and management from ADManager Plus! Delegate powers for technician on specific tasks in specific OUs.
Microsoft Exchange Management
Create and manage Exchange mailboxes and configure mailbox rights using ADManager Plus's Exchange Management system. Now with support for Microsoft Exchange 2010!!
Active Directory Cleanup
Get rid of the inactive, obsolete and unwanted objects in your Active Directory to make it more secure and efficient...assisted by ADManager Plus's AD Cleanup capabilities.
Active Directory Automation
A complete automation of AD critical tasks such as user provisioning, inactive-user clean up etc. Also lets you sequence and execute follow-up tasks and blends with workflow to offer a brilliant controlled-automation.
Need Features? Tell Us
If you want to see additional features implemented in ADManager Plus, we would love to hear. Click here to continue
