- Knowledge base
- Active Directory management
- Active Directory reports
- Active Directoy integrations
- Active Directory automation
- Active Directory delegation
- Governance, risk, and compliance
- Microsoft 365 management and reporting
- AD migration
- Access certification
- Identity risk assessment
- Risk exposure management
- FAQs
- Pricing
- Online demo
- Request support
- Get quote
What is an email alias?
An email alias is a secondary email address associated with a user's primary mailbox. Emails sent to the alias are delivered to the same inbox as the primary email address without requiring a separate mailbox or additional license.
For example:
- Primary email: john.doe@company.com
- Email alias: j.doe@company.com or sales@company.com
Both addresses deliver emails to the same mailbox.
Why email aliases matter in Active Directory environments
Email communication in modern organizations often requires flexibilityemployees may need multiple email addresses for different roles, departments, or brand identities. This is where email aliases become essential.
Organizations use email aliases for several practical reasons:
- Support name changes without disrupting email delivery
- Provide role-based addresses like hr@company.com or support@company.com
- Maintain consistent branding across departments
- Simplify external communication while keeping a single mailbox
- Reduce the need for additional mailboxes or licenses
This concept is commonly seen in consumer platforms as well. For example, Gmail alias email addresses allow users to receive mail sent to variations of their main address. In enterprise environments, email aliases are typically managed through Active Directory and Exchange attributes.
When managed correctly, email aliases improve communication while keeping identity management clean and centralized.
How email aliases work in Active Directory
In Active Directory-integrated email systems like Microsoft Exchange or Microsoft 365, email aliases are stored in the proxyAddresses attribute of a user object.
- The primary email address is prefixed with SMTP: (uppercase)
Example: SMTP:john.doe@company.com
- Alias email addresses are prefixed with smtp: (lowercase)
Example: smtp:j.doe@company.com or smtp:sales@company.com
Understanding this attribute is key for when you add or manage email aliases in Active Directory.
Considerations for adding a secondary email address
Before adding a secondary email address in Active Directory, review the following to avoid mail flow issues and management overhead:
- Ensure alias uniqueness: Each email alias must be unique across all users, groups, and mail-enabled objects to prevent conflicts.
- Follow naming standards: Use consistent alias formats to simplify management and maintain directory hygiene.
- Verify the SMTP prefix: Always use lowercase smtp: for secondary aliases. The uppercase SMTP: prefix specifies the primary email address.
- Confirm the correct object type: Ensure the alias is assigned to the intended mailbox-enabled or mail-enabled object.
- Review life cycle impact: Revisit aliases during role changes or offboarding to avoid mail being delivered to inactive accounts.
- Validate alias after changes: Confirm the alias appears correctly in the proxyAddresses attribute and that mail delivery works as expected.
How to add an email alias using ADUC
Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC) allows admins to add an email alias by editing the user object's email-related attributes. This method is commonly used for single-user updates and basic alias configuration.
- Open Active Directory Users and Computers.
- Click View > Advanced Features.
- Locate and right-click the user account, then select Properties.
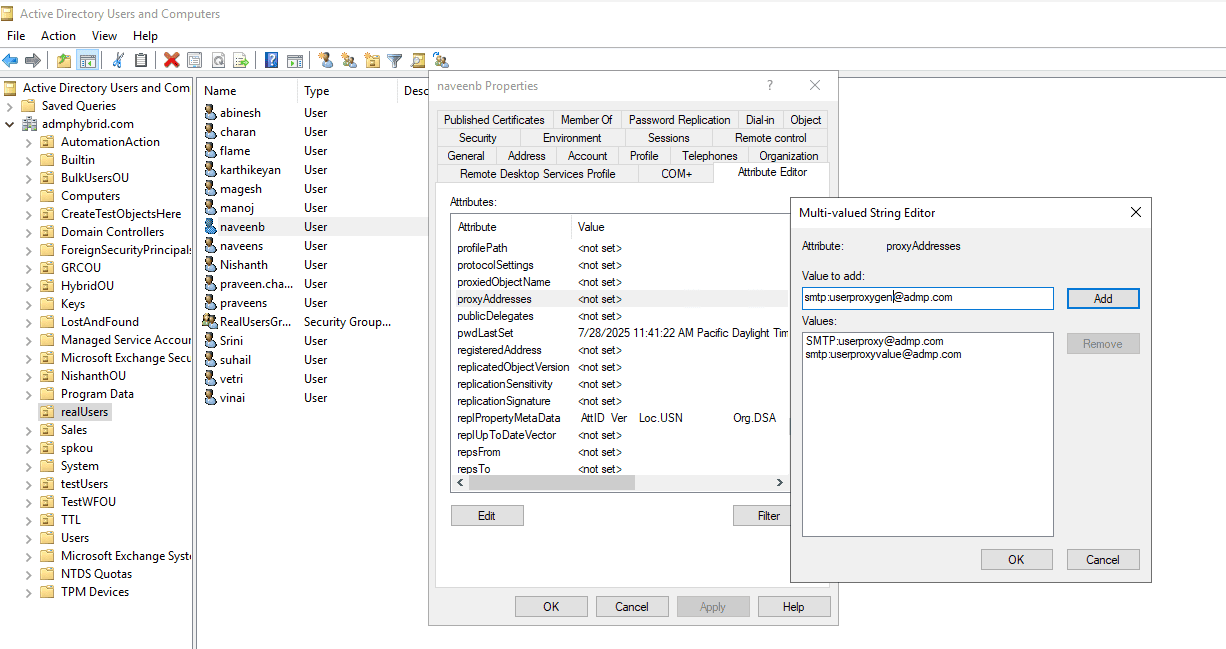
- Go to the Attribute Editor tab.
- Select the proxyAddresses attribute and click Edit.
- Add a new entry in the format smtp:alias@domain.com, then click OK.
- Click OK again to save the changes. Emails sent to the alias will now be delivered to the user's mailbox.
- Open the proxyAddresses attribute.
- Select the alias email address you want to modify.
- Edit the value to the new alias: smtp:newalias@domain.com
- Click OK.
Note: Only one entry should use the uppercase SMTP: prefix.
How to add an email alias using PowerShell
PowerShell is a popular choice for admins who need greater control and scalability. By using cmdlets such as Set-ADUser, admins can directly modify the proxyAddresses attribute to add or update alias email addresses.
Prerequisites
- Open PowerShell as an administrator.
- Ensure the Active Directory module is loaded. If not, import it by running the script below:
Import-Module ActiveDirectory
- Identify the target user accurately using their sAMAccountName, UserPrincipalName, or DistinguishedName.
Using Set-ADUser to add an email alias
Use the Set-ADUser cmdlet with the -Add parameter to append a new alias to the existing proxyAddresses attribute without overwriting current values:
proxyAddresses="smtp:j.doe@company.com"
}
This command adds the alias while preserving the user's primary email address and any existing aliases.
This script retrieves all email addresses associated with a user account. It helps confirm that an alias email address has been added correctly to Active Directory:
Select-Object -ExpandProperty proxyAddresses
Limitations of using native tools
While powerful, native tools offer limited flexibility in environments that require consistency, bulk updates, or stronger admin controls.
Key limitations of native tools include:
- No bulk alias creation in ADUC
- Manual, repeated edits that increase the risk of formatting errors
- No built-in validation for duplicate or conflicting aliases
- Limited auditing and visibility into changes
How ADManager Plus simplifies email alias management
ManageEngine ADManager Plus provides a centralized, UI-driven approach to managing email aliases in Active Directory without manual attribute edits or complex scripts.
With ADManager Plus, admins can:
- Add or modify aliases during user creation
- Update aliases for existing users using bulk actions
- Automatically format alias email addresses
- Validate conflicts before applying changes
Adding email aliases using ADManager Plus
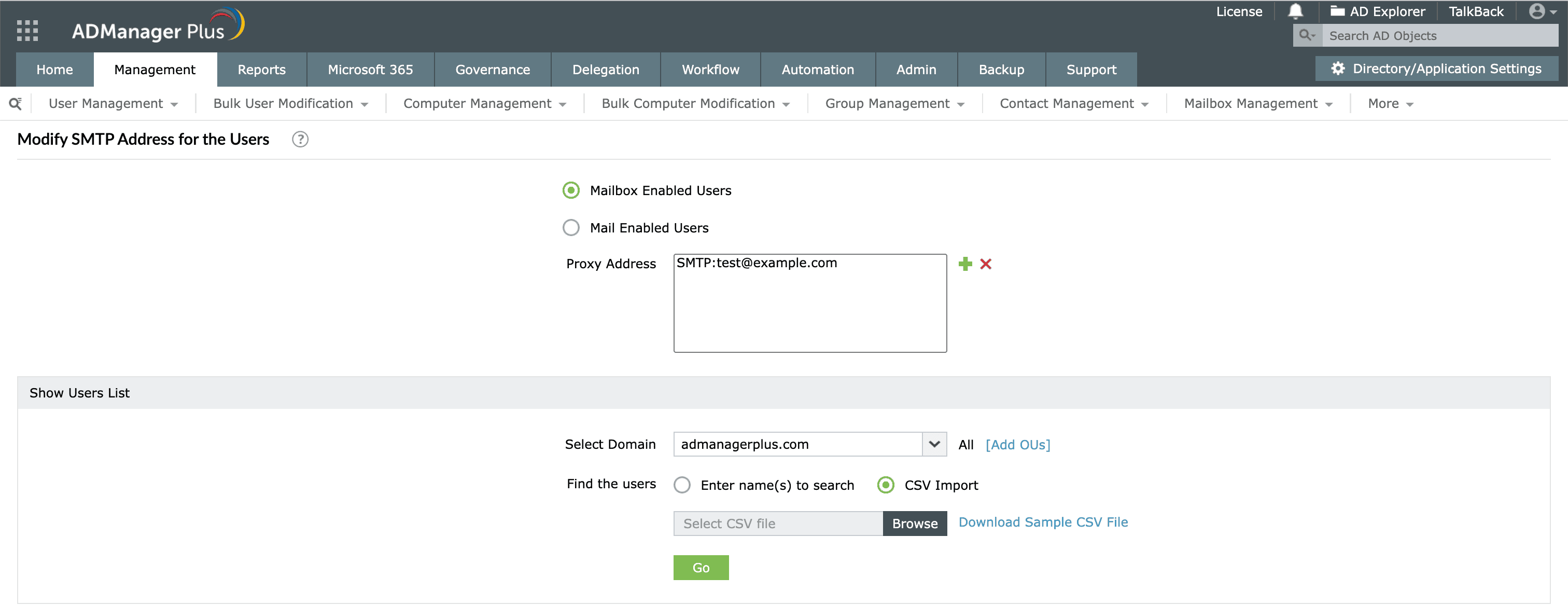
- Navigate to Management > User Management > Bulk User Modification > Exchange Tasks > Modify SMTP Address.
- Select Mailbox Enabled Users or Mail Enabled Users as the user category.
- In the Proxy Address field, click + to add the SMTP address. Use SMTP: before the address for the primary alias, or smtp: for all secondary aliases (e.g., SMTP:user@domain.com or smtp:alias@domain.com).
- Under Show Users List, select the domain and enter the names of the users for whom you would like to add the new email alias. To add aliases in bulk, click CSV Import and upload a file containing the user list.
- On the following screen, review the selected users and click Apply.
Key advantages of ADManager Plus over native tools
Compared to native Active Directory tools and PowerShell, ADManager Plus offers a centralized, user-friendly approach to managing email aliases.
- Bulk management: Add or update email aliases for hundreds of users in a single action, eliminating the need to modify each account individually.
- No scripting required: Manage email aliases through an intuitive, point-and-click interface, removing the dependency on complex scripts.
- Error prevention: Access built-in validation checks that help prevent duplicate or conflicting email aliases before changes are applied to Active Directory.
- Auditing: Maintain a clear audit trail that records who added, modified, or removed email aliases and when the changes were made.
- Delegation: Securely delegate email alias management tasks to help desk technicians using role-based access without granting full admin privileges.














