Direct Inward Dialing: +1 408 916 9892
Here is how you can track employees' idle time using ADAudit Plus:
Enable 'Audit logon events' policy and 'logon/logoff' auditing.
Launch ADAudit Plus
Find the Reports tab and select 'Local Logon and Logoff' reports and then navigate to 'User work hours'. You can also directly search for it in the search tab on the upper right corner.
This will give you a list of employees' idle time during business hours and after as well.
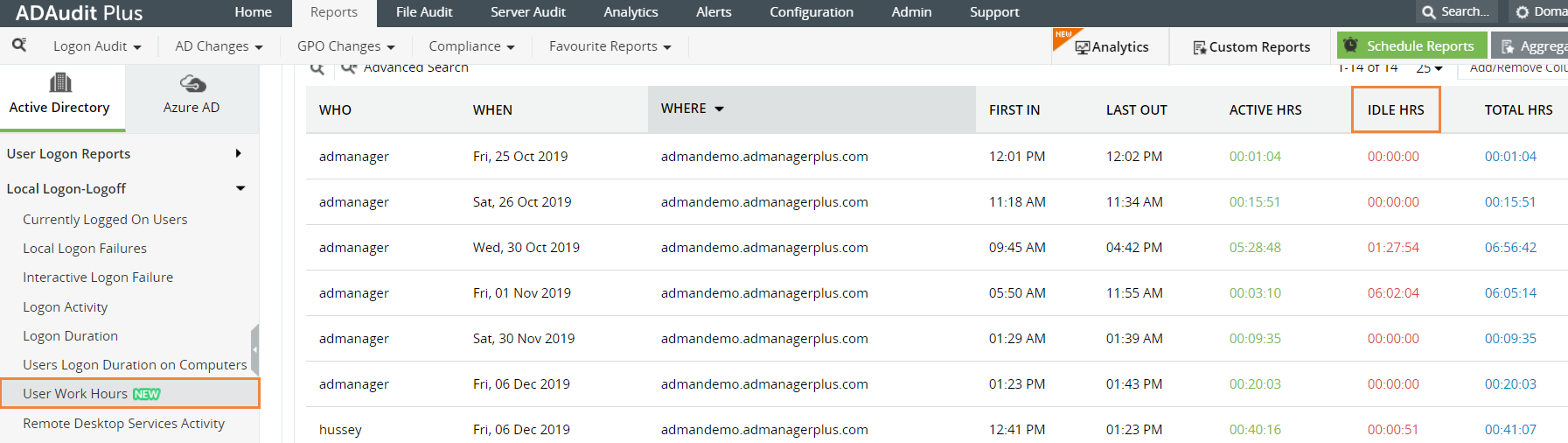
ADAudit Plus generates 'User Idle Time' reports from the AD event viewer, specifically from the logon/logoff related event IDs that are listed above.
You can also configure the working hours based on your business. If you need to find information for a specific employee, use the filter available under the 'Advanced Search Option'.
Here's how you can monitor your employees' idle hours with native AD auditing:
Open Server Manager on your Windows server.
Under Manage, select Group Policy Management to view the Group Policy Management Console.
Navigate to Forest>Domain>Your Domain>Domain Controllers.
Either create a new group policy object or you can edit an existing GPO.
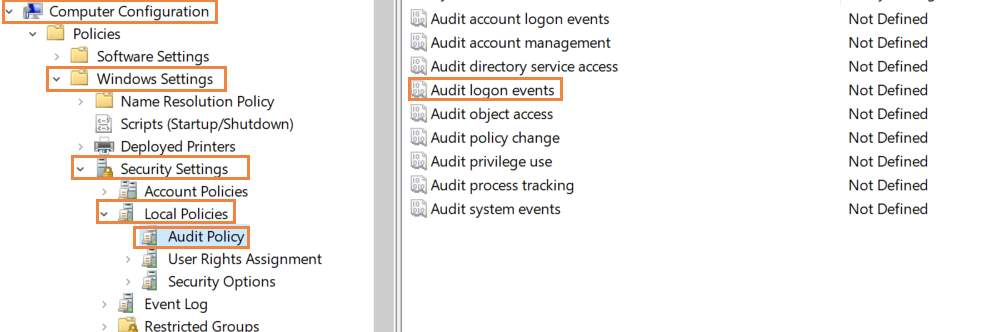
In the Group Policy Editor, navigate to Computer Configuration > Windows settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Audit Policy.
In Audit Policy, select Audit logon events and enable it for Success and Failure.
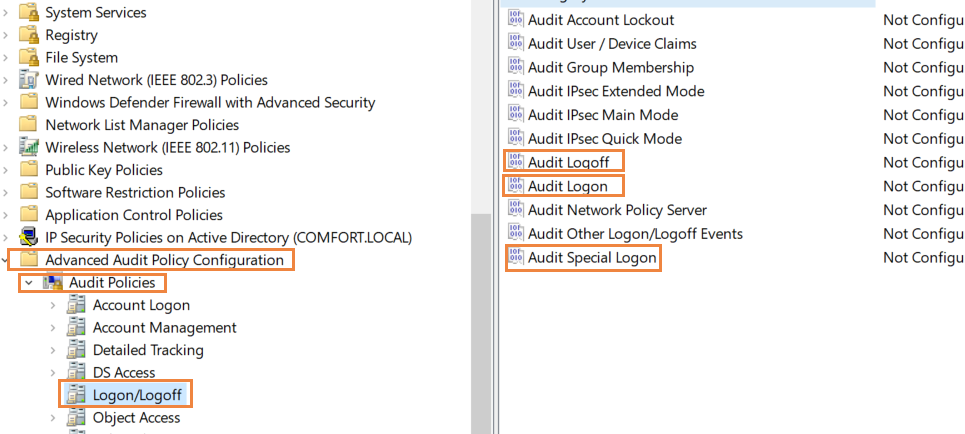
Again, navigate to Computer Configuration> Windows Settings>Security settings>Advanced Audit Policy Configuration>Audit Policies>logon/logoff.
Under that, turn on auditing for 'Audit logoff', 'Audit logon' and 'Audit special logon' and enable it for both 'Success' and 'Failure'.
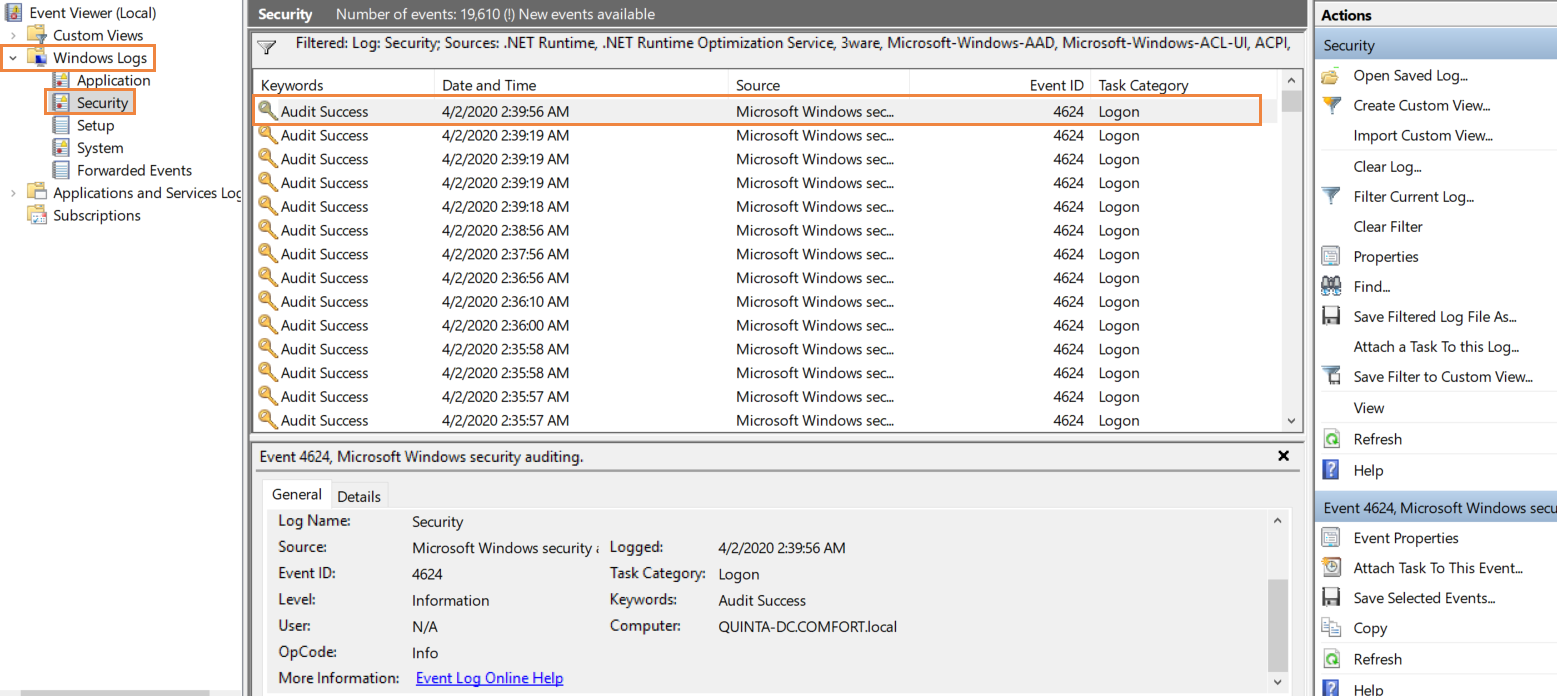
The Event Viewer will now track the logon, logoff and special logons from all the devices in the domain and lists them against their corresponding event IDs. To check these logs, open Event Viewer, click Windows logs>Security. The window that opens will display a list of event logs from which you can find the ones that are relevant to you. Look for event IDs 4624 (Account was logged on), 4634 (Account was logged off), 4647 (user initiated logoff) and 4672 (special logon), 4800 (the workstation was locked), 4801 (workstation was unlocked).
These logs show the amount of time a employee has spent working on their workstation. The rest of the time can be considered as an idle time. You will have to calculate the amount of time between each logoff and logon throughout the business hours to arrive at the idle time. You will have to repeat this process every time you need to find an employee's idle hours.
Native auditing becoming a little too much?
Audit employees' idle time with ADAudit Plus.
Get Your Free Trial Fully functional 30-day trial