MariaDB is an open-source, relational database management system (RDBMS). It supports advanced clustering, high availability, and powerful storage engines for enterprise applications. MariaDB is widely used for web applications, cloud services, and large-scale data processing.
The MariaDB extension for Log360Cloud enables integration of MariaDB logs into the Log360 Cloud ecosystem. This extension provides features such as log collection, parsing, reporting, alerting, correlation, and advanced log search capabilities.
MariaDB auditing can be configured using two methods:
plugin_load_add = server_audit server_audit=FORCE_PLUS_PERMANENT server_audit_logging = ON server_audit_file_path = C:/Program Files/MariaDb 11.5/data/server_audit.log server_audit_events = CONNECT,QUERY,QUERY_DDL,QUERY_DML,QUERY_DCL
Open MySQL Client or execute:
mysql -u [username] -p [password]
INSTALL SONAME 'server_audit';
SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'server_audit%';
SET GLOBAL server_audit_events = 'CONNECT,QUERY,QUERY_DDL,QUERY_DML,QUERY_DCL';
Here are the types of audited events captured from MariaDB in Log360 Cloud:
| Category | Events |
|---|---|
| DDL auditing | Database created, Database dropped, Tables created, Tables dropped, Tables altered, Procedures created, Procedures dropped, Procedures altered, Index created, Index dropped, Triggers created, Triggers dropped, Views created, Views dropped, Views altered, Function created, Function dropped, Function altered |
| DML auditing | Select queries, Insert queries, Update queries, Delete queries, Truncate queries |
| Execution analysis | Failed queries |
| Auditing account management | Role created, Role dropped, Role updated, Grant operations, Revoke operations, Password changed, User created, User dropped, User updated, Failed account management queries |
| Logon events | User logon, Failed user logon, User logoff, Logon/logoff trends |
| Server events | Startup, Shutdown |
| Administrative statements | SET and SHOW statements, Transaction and Locking statements, Utility statements, Replication statements, Table maintenance statements, Plugin statements |
After installing the MariaDB extension in Log360 Cloud, configure the scheduled import for the server_audit.log file from the MariaDB Server file path. Ensure that the correct file path is used during configuration.
Navigate to Settings → Configuration Settings → Log Source Configuration → Import Logs → From Device
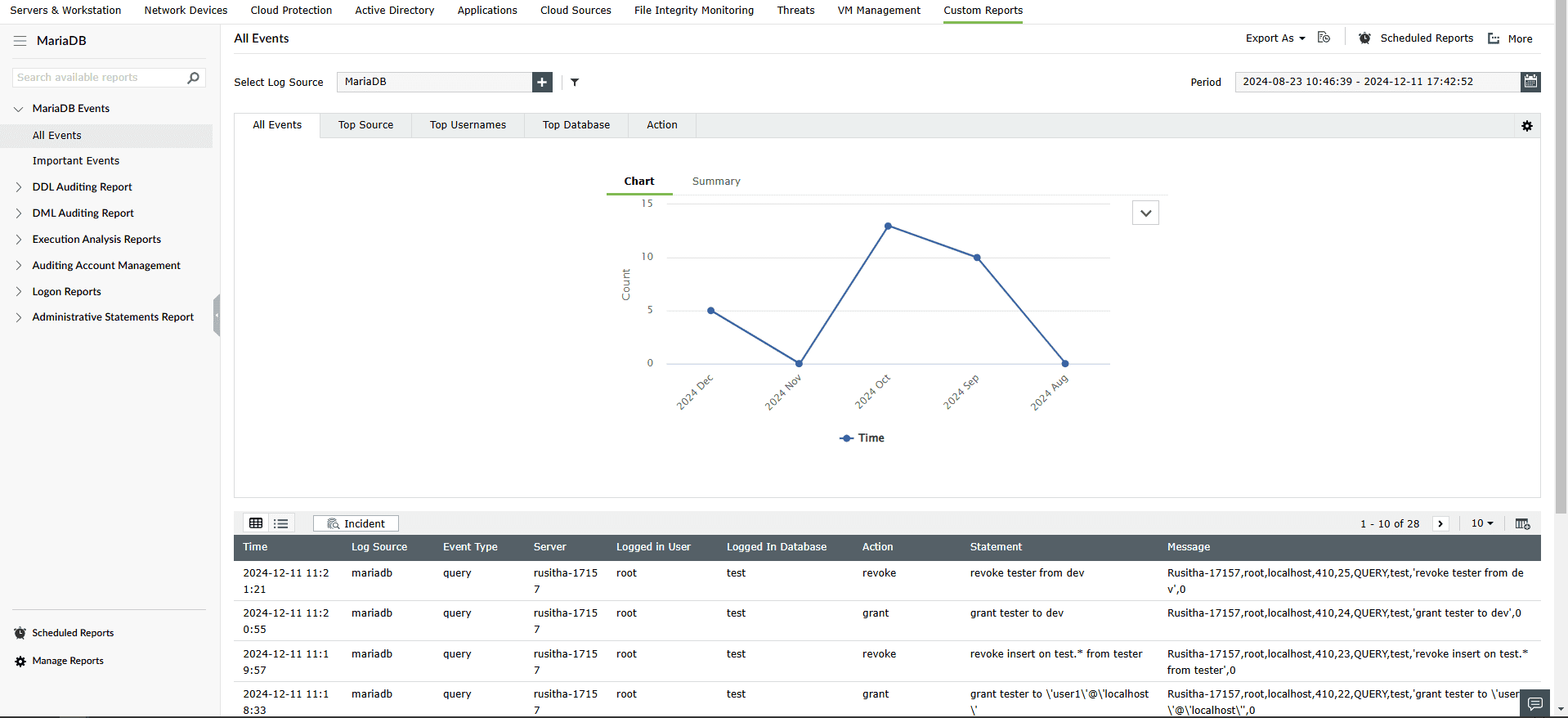
To view MariaDB reports, navigate to the Reports tab and select MariaDB from the Custom Reports sub-tab.
To view the correlation rules, navigate to the Correlation tab -> Manage Rules.
In the Manage Rules page, select MariaDB as the Rule Category to filter out the related correlation rules. You can enable them manually by selecting the rule and clicking on Activate in the Rule Status column.

To view the Alerts, navigate to the Alerts tab -> Manage Alert Profiles.