If your organization uses Linux-based devices, you have reason to be wary of Mirai malware. It exploits vulnerabilities in Linux-based devices to fabricate the Mirai botnet and sets the stage for a DDoS attack. Mirai — which is known for self-propagating through remote code execution — has been exploiting 13 known vulnerabilities in Linux-based devices. Since March 2023, Mirai has further enhanced its capabilities and exploits 22 new vulnerabilities in networking devices.
It's important to understand the capabilities of Mirai and prevent your network from becoming a victim of a DDoS attack. Staying ahead of Mirai and other similar attacks requires continuous monitoring of your network. A SIEM solution can simplify your tasks and protect your network. This blog will help you understand:
Mirai attacks kicked off in 2016 with a massive DDoS attack on famous cybersecurity journalist Brian Kerb's website. The website was flooded with 620Gbps of illegitimate requests. This was followed by another Mirai attack on the DNS service provider, Dyn. Around 100,000 infected devices formed a botnet in this DDoS attack. Both attacks involved a Linux-based IoT botnet that included routers, digital video recorders (DVRs), network video recorders (NVRs) and Wi-Fi communication dongles. The Mirai source code was leaked online later that year, liberating a shedload of future DDoS attacks involving IoT botnets.
This is how Mirai malware can sneak into a network and capture devices:
Take a look at our whitepaper, to learn more about DDoS attacks. Figure 1 gives you a pictorial representation of how the Mirai botnet works.
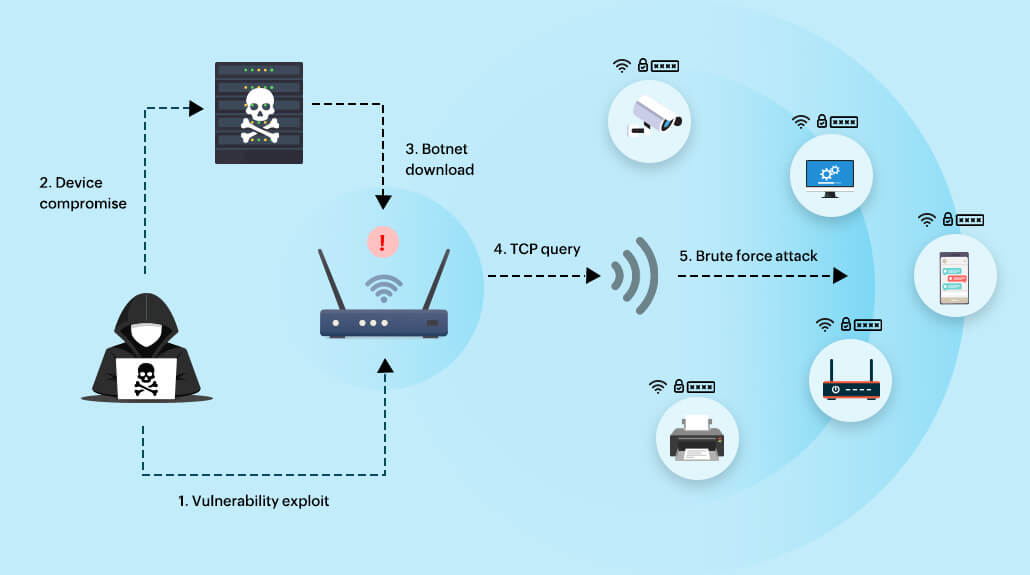 Figure 1. Working of the Mirai botnet
Figure 1. Working of the Mirai botnet
A SIEM solution with advanced threat detection capabilities can help you prevent Mirai from laying its botnet foundation on your network. SIEM can help you protect your devices with a range of predefined detection rules. Let's get into the details of how SIEM can help you prevent a Mirai attack.
The first line of defense against Mirai is to ensure all network devices, especially your routers, are constantly upgraded. Vulnerabilities in devices act as entry point to the Mirai malware. Vulnerability scanners help you detect and close such gaps. Vulnerability reports help you identify unpatched devices in your network that are vulnerable to exploitation. Figure 2 represents an example of a vulnerability report, a patch report that can be generated by a SIEM solution.
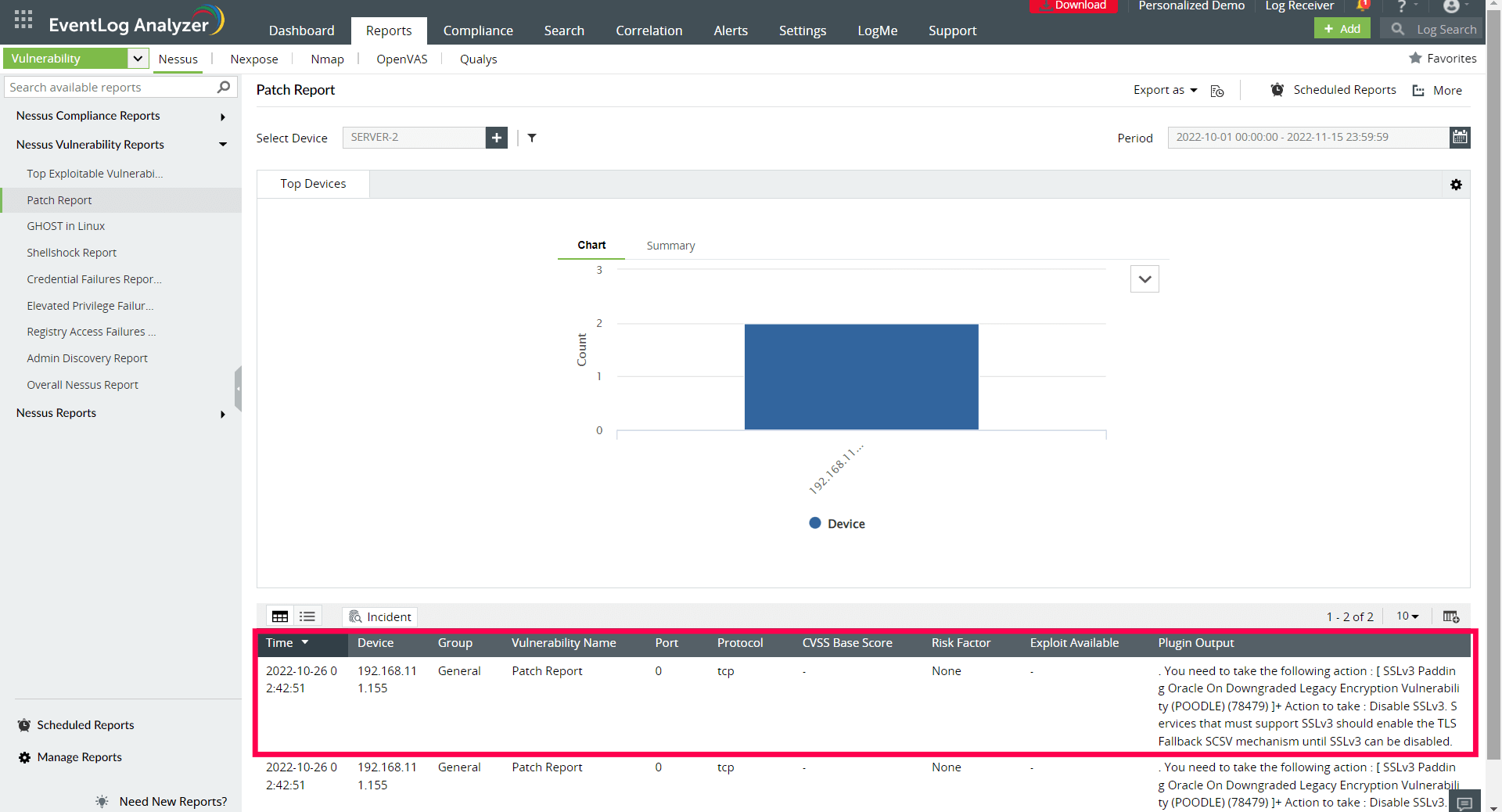 Figure 2. Vulnerability report - Patch report
Figure 2. Vulnerability report - Patch report
Mirai uses TCP SYN queries to scan for other vulnerable devices in the network. The vulnerable devices would receive such queries from legitimate devices as well as bot- infected devices on the network. Therefore, it's crucial to monitor the TCP traffic trends in the network. Traffic trend reports give a clear picture of all TCP requests directed towards your Linux devices and helps you detect any unusual traffic. Figure 3 depicts an example of a traffic trend report for TCP SYN queries generated by a SIEM solution.
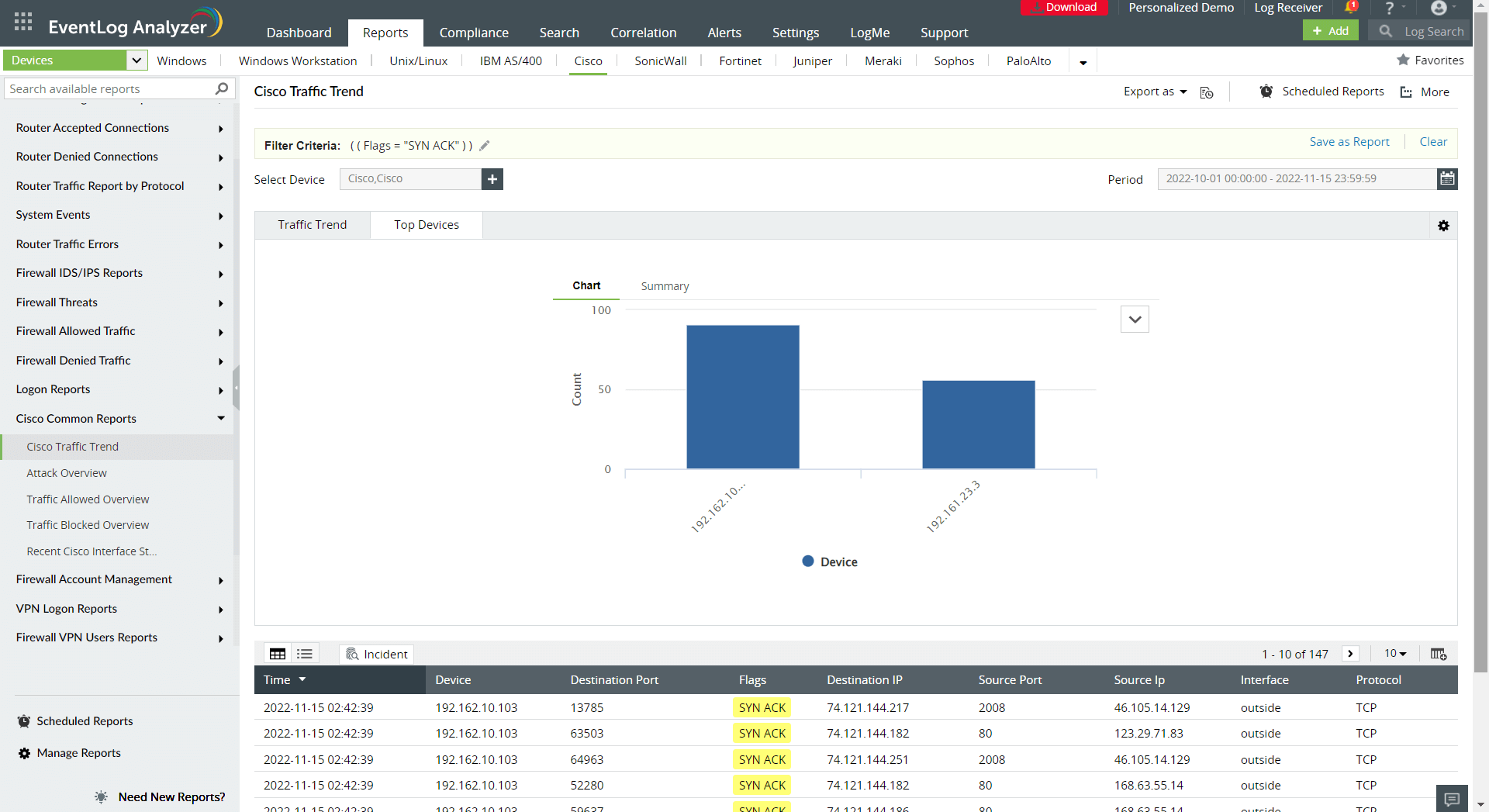 Figure 3. Traffic trend report
Figure 3. Traffic trend report
The Mirai malware infects vulnerable devices by establishing a telnet or SSH connection and then brute forces these devices using default usernames and passwords. It's imperative to change the default usernames and passwords of the devices after installation and keep track of all the SSH logon events that take place on your routers. Multiple failed logons can be potential indications of impending brute force attacks. Figures 4 and 5 depict how a SIEM solution can track successful and failed SSH logons, respectively.
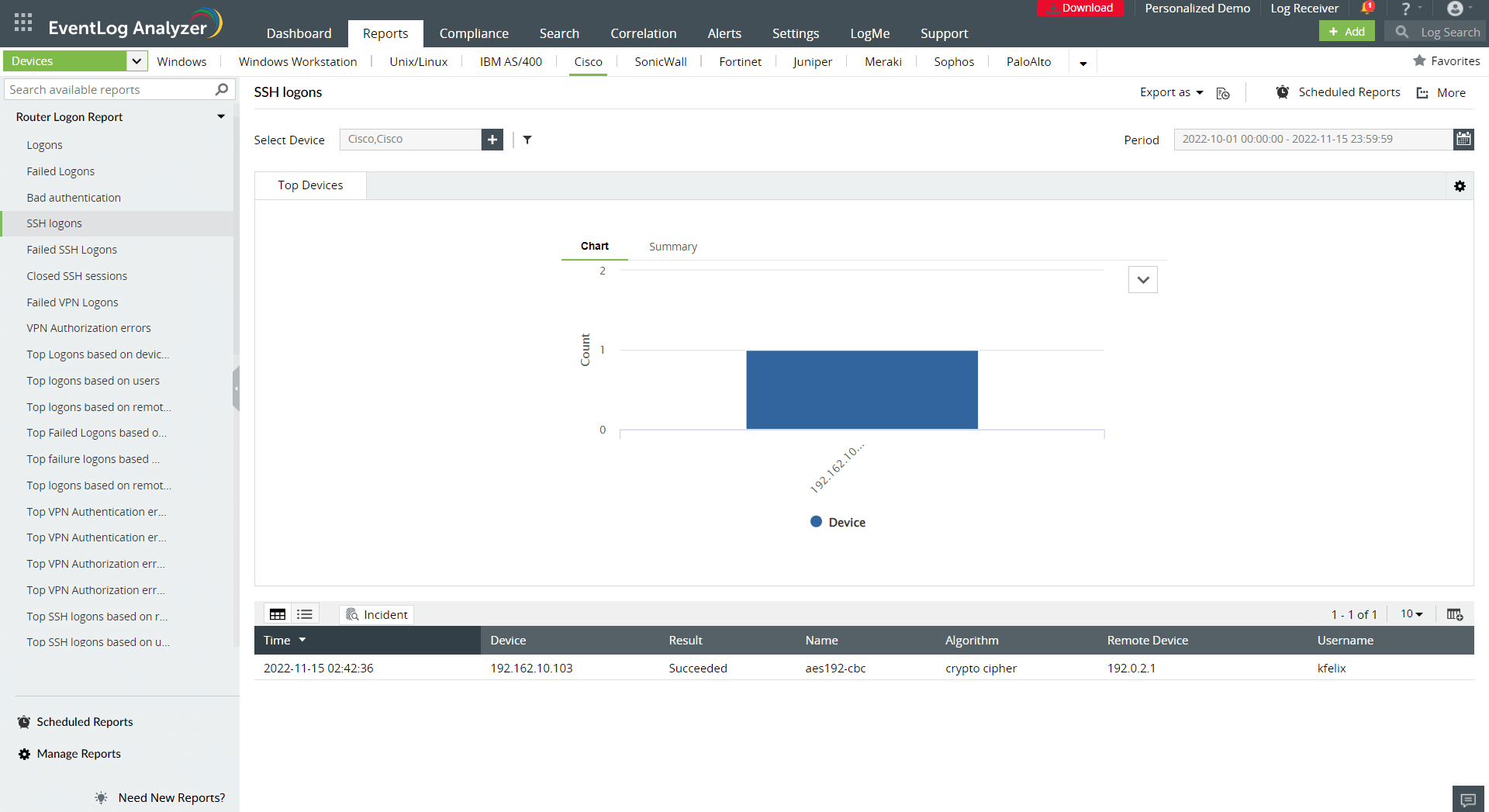 Figure 4. SSH logon report
Figure 4. SSH logon report
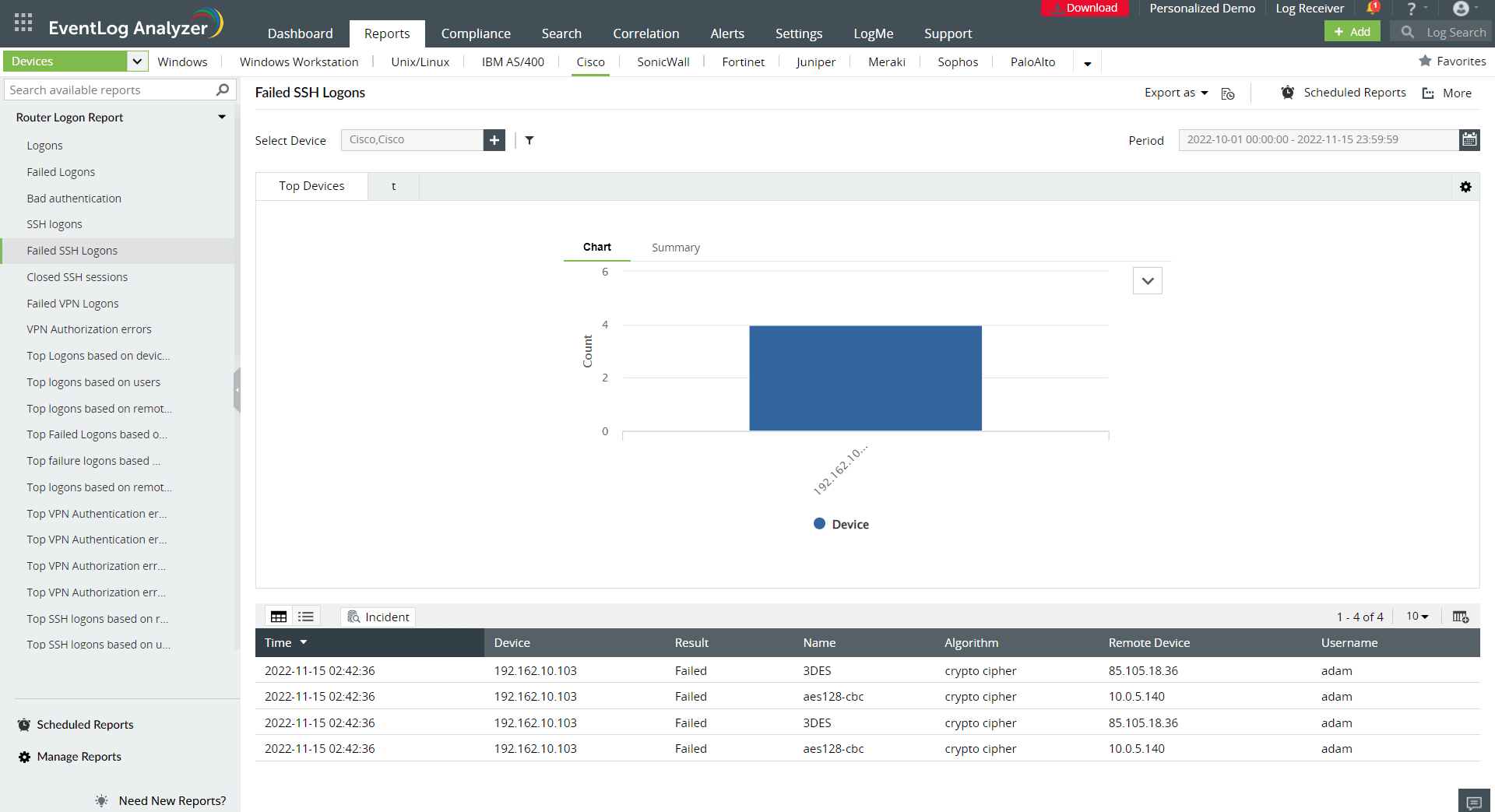 Figure 5. Failed SSH logon report
Figure 5. Failed SSH logon report
All the events that take place during a Mirai attack, which include vulnerability exploitation, anomalous TCP SYN traffic and malicious SSH logons can be correlated and detected with a custom detection rule for Mirai attacks. SIEM provides an inbuilt correlation engine that comes with predefined detection rules and also allows you to create custom rules to detect Mirai-like attacks. Figure 6 shows an example of a predefined correlation rule for failed SSH logon on a router in a SIEM solution.
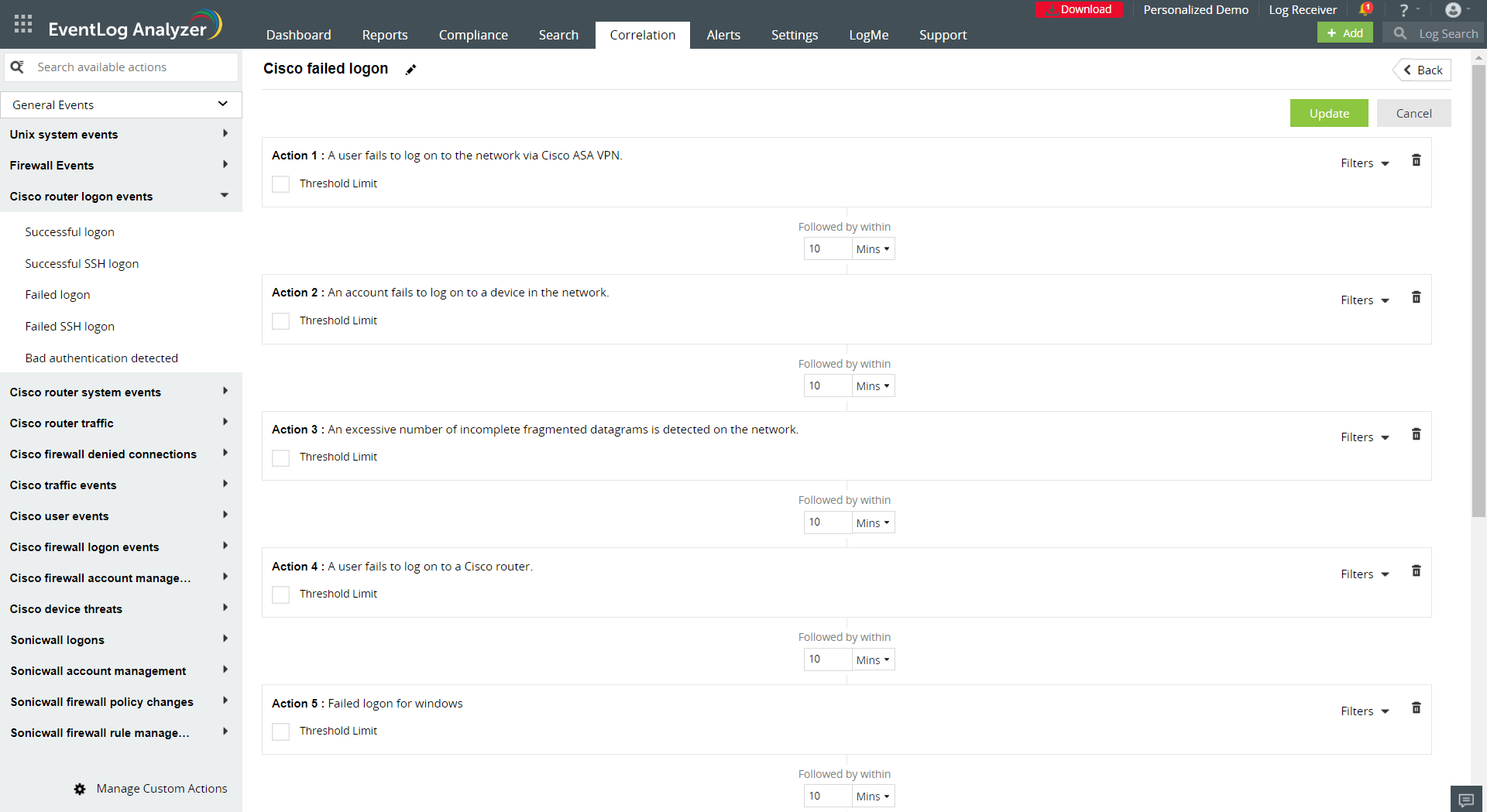 Figure 6. Failed SSH logon correlation rule
Figure 6. Failed SSH logon correlation rule
Hopefully this blog helped you discern the significance of a SIEM solution to detect and combat Mirai-like malware. ManageEngine Log360 is one such SIEM solution that can help you put these implications of SIEM into action. It is a unified solution with advanced capabilities of attack detection and anomaly detection.
If you're interested in finding out more, sign up for a personalized demo.
You will receive regular updates on the latest news on cybersecurity.
© 2021 Zoho Corporation Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.