While cloud computing offers enhanced scalability, innovation, and operational efficiency, it also introduces a new set of security risks, threats, and challenges. From safeguarding sensitive data to managing access controls, ensuring compliance, and defending against sophisticated cyberattacks, organizations must confront a constantly evolving cloud security landscape. Building a strong foundation in cloud security is essential for protecting both data and business continuity.
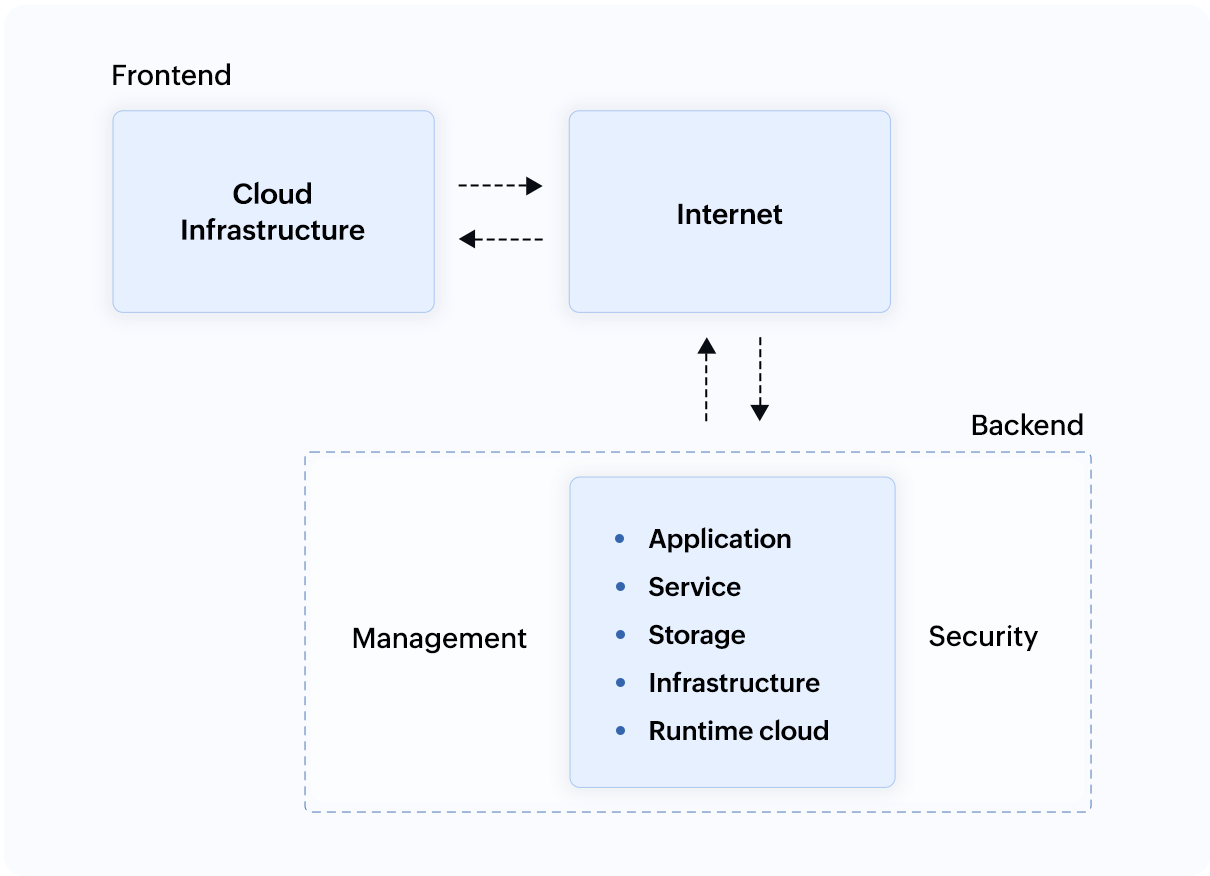
Figure 1: Cloud computing architecture
Cloud security risks vs. cloud security threats vs. cloud security challenges
Before proceeding further, it is important to know the difference between risks, threats, and challenges in a cloud environment in order to tackle them easily. Following are the key differences between the three:
| |
What is it? |
Example scenario |
| Cloud security risks |
A cloud security risk refers to the potential for negative outcomes or consequences arising from vulnerabilities in a cloud system. These risks represent the possibility that an organization's data, operations, or reputation could be compromised due to the exploitation of vulnerabilities, either intentionally by threat actors or unintentionally through errors. Importantly, these vulnerabilities or risks only become actual threats when they are exploited by attackers or insiders. |
A misconfigured cloud storage bucket exposes sensitive customer data, risking a data breach and compliance penalties. |
| Cloud security threats |
Cloud security threats are potential dangers or malicious activities that take advantage of vulnerabilities in cloud systems to cause unauthorized access, data breaches, service disruptions, or other harmful outcomes. These threats may arise from natural disasters, internal actors, or even external attackers. |
A hacker uses stolen credentials to gain unauthorized access to cloud-hosted databases, attempting to exfiltrate sensitive information. |
| Cloud security challenge |
Cloud security challenges refer to the difficulties an organization faces in implementing, managing, and maintaining effective security measures within cloud environments. These challenges often occur due to the complexity of cloud technologies, the shared responsibility model, and evolving cyberthreats. They can hinder an organization's ability to protect data, applications, and services in the cloud. |
An organization struggles to secure a multi-cloud environment due to a lack of skilled personnel and inconsistent security tools. |
The top 5 cloud security risks
The following are the five most common risks or vulnerabilities related to cloud security:
| Risk |
What is it? |
Causes |
| Data loss |
Unintentional destruction, deletion, corruption, or unavailability of data that renders it unusable or unrecoverable is referred to as data loss. In the context of cloud computing security challenges, data loss is a significant security risk due to the shared responsibility model and the dependency on external cloud providers. |
- Insufficient backup and data recovery plans
- Inadequate access control and permissions
- Human errors and accidental deletion
- Malicious insider threats
- Data encryption failures
|
| Misconfigured services |
Misconfigured cloud services pose a significant security risk in cloud environments. These misconfigurations occur when cloud resources, applications, or services are improperly set up, often leaving them vulnerable to exploitation. This is a common problem due to the complexity of cloud environments and the shared responsibility model. |
- Human errors and manual configuration mistakes
- Overly permissive IAM policies
- Publicly accessible resources and weak access controls
- Unsecured network configurations and open ports
- Lack of automation and configuration management tools
|
| Lack of visibility |
The inability to completely monitor, track, or comprehend data, configurations, and actions within the cloud architecture is referred to as a lack of visibility. This limited visibility creates blind spots, making it difficult to detect security threats in cloud computing, ensure compliance, and maintain operational efficiency. |
- Complexity of cloud architectures
- Insufficient monitoring tools and logging
- Misunderstanding of the shared responsibility model
- Shadow IT and resource mismanagement
- Lack of staff expertise and training
|
| Misunderstanding of the shared responsibility model |
One important paradigm for cloud security is the shared responsibility model, which outlines how the customer and the cloud service provider share security responsibilities. Misunderstanding this model can create significant security risks, leaving critical areas unprotected. |
- Assuming cloud providers handle all security aspects
- Misinterpretation of data protection responsibilities
- Uncertain role definitions between providers and customers
- Neglecting security for the application layer and data
- Lack of awareness about security responsibilities in multi-cloud environments
|
| Regulatory compliance risks |
Regulatory compliance risk in cloud security arises when organizations fail to adhere to legal, industry, or contractual requirements for securing data and systems. This risk can lead to severe consequences, including financial penalties, legal action, and reputational damage. |
- Failure to meet data privacy regulations (e.g., the GDPR or HIPAA)
- Non-adherence to industry-specific standards (e.g., the PCI DSS or FedRAMP)
- Data residency and sovereignty violations
- Inadequate compliance monitoring and reporting
- Improper third-party vendor management
|
Top 5 cloud security threats
The following are five common threats related to cloud security:
| Threat |
What is it? |
Causes |
| Data breach |
A data breach in a cloud environment refers to unauthorized access to or theft of sensitive data stored, processed, or transmitted in the cloud. It can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, legal penalties, and loss of customer trust. |
- Weak IAM
- Misconfigured cloud services
- Insider threats
- Vulnerable applications and APIs
- APTs and malware
|
| Insecure APIs and interfaces |
Interfaces and APIs are essential parts of cloud environments because they allow users, apps, and systems to communicate and interact. However, when these APIs are insecure, they become a significant attack vector for malicious actors, leading to unauthorized access, data breaches, and service disruptions. |
- Lack of authentication and authorization
- Poor input validation and error handling
- Exposed endpoints with weak security controls
- Unpatched vulnerabilities in API code
- Overly permissive access and data exposure
|
| Account hijacking |
In cloud systems, where hackers obtain unauthorized access to user accounts in order to steal confidential information, modify services, or interfere with operations, account hijacking poses a severe risk. This threat can compromise an organization’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability in the cloud. |
- Weak or compromised credentials
- Phishing attacks
- Lack of MFA
- Exploitation of API keys or tokens
- Insufficient monitoring for suspicious activities
|
| Distributed denial-of-service |
Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks are a significant threat in cloud environments, where attackers flood cloud servers, networks, or applications with traffic to overwhelm and disable services. The scalability of cloud resources can make it both a target and an enabler for DDoS attacks, and these attacks can cause severe disruptions, downtime, and financial loss. |
- Exploitation of cloud elasticity and resources
- Weak network layer protections
- Inadequate application layer security
- Lack of rate limiting and traffic filtering
- Misconfigured firewalls or security groups
|
| Insider threat |
In a cloud environment, insider threats are security concerns offered by people who work for a company, such as contractors, employees, or external or third-party suppliers, and who intentionally or unintentionally use their access to cloud systems for malicious purposes. These threats may result in service interruptions, monetary losses, or data breaches. |
- Malicious intent by employees or contractors
- Negligence or human error
- Lack of proper access controls
- Unclear role definitions and privileges
- Inadequate monitoring and auditing
|
Top 10 cloud security challenges
The following are the most common cloud security challenges:
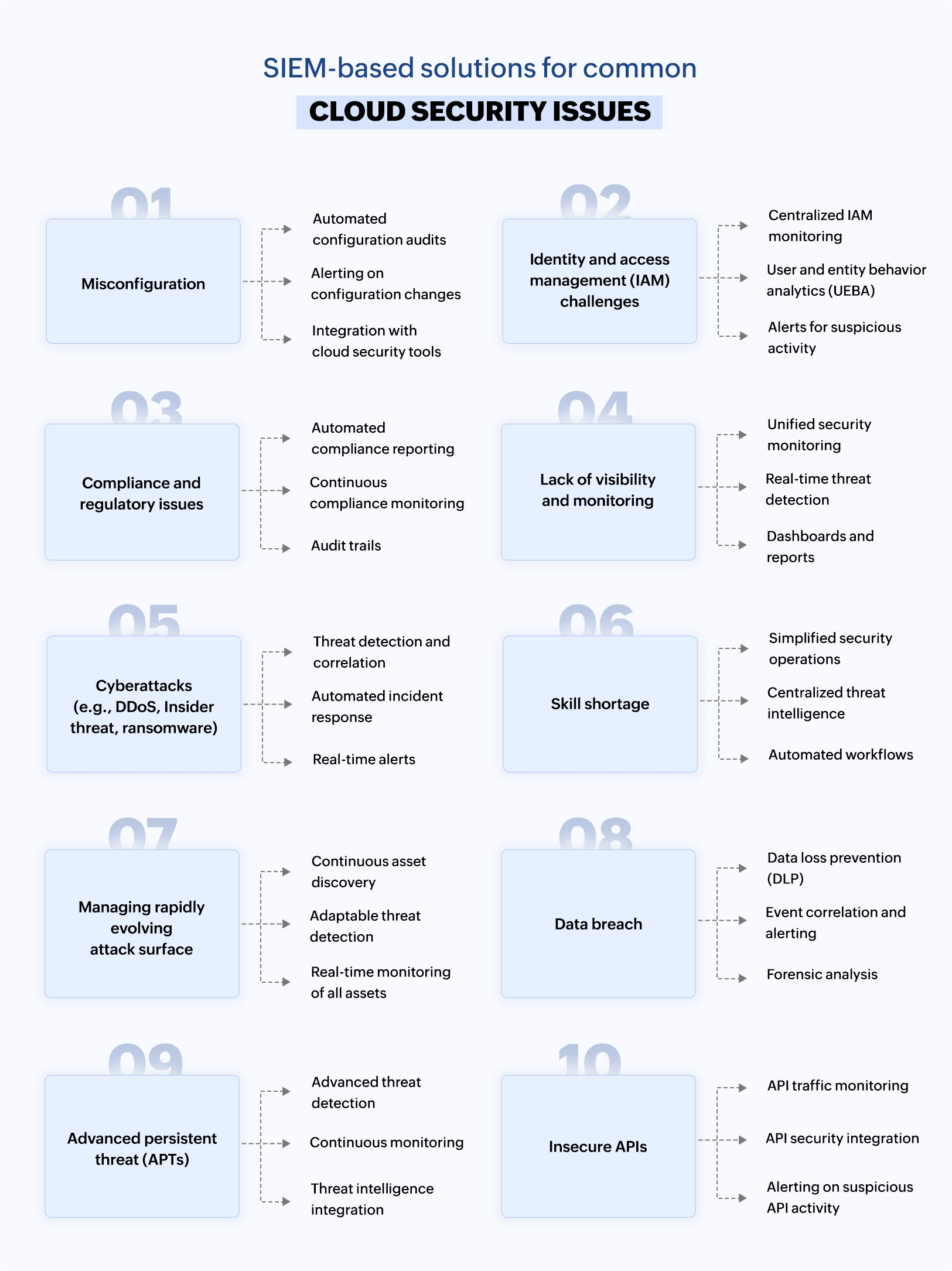
Figure 2: Cloud security challenges.
1. Misconfiguration
| What is it? |
One of the most prevalent and important cloud security issues is misconfiguration. It occurs when cloud resources, services, or applications are improperly configured, leaving them vulnerable to exploitation. |
| Causes |
- Complexity of cloud environments
- Human error
- Lack of visibility and asset management
- Rapid scaling and automation issues
- Weak or inconsistent security practices
|
| Solution with SIEM |
- Automated configuration audits: SIEM solutions can automatically check configurations against security best practices and policies, flagging policy violations in real time.
- Alerting on configuration changes: SIEM solutions can monitor configuration changes and alert security teams about suspicious modifications that may expose vulnerabilities.
- Integration with cloud security tools: SIEM solutions can integrate with cloud-native tools (e.g., AWS Config or Azure Security Center) to continuously validate configurations and track deviations.
|
2. Identity and access management challenges
| What is it? |
Managing permissions and access for a lot of users and cloud services might result in unauthorized access and over-privileged accounts. |
| Causes |
- Overly permissive access controls
- Misconfigured roles and policies
- Identity sprawl and poor management
- Weak authentication practices
- Complexity in multi-cloud and hybrid environments
|
| Solution with SIEM |
- Centralized identity and access management (IAM) monitoring: SIEM solutions collect and analyze IAM logs to track user activities, privilege escalations, and unauthorized access attempts.
- User and entity behavior analytics: SIEM solutions can detect anomalous behavior that deviates from a user's normal patterns, such as accessing sensitive resources they don't typically use.
- Alerts for suspicious activity: SIEM solutions provide real-time alerts for risky behavior, like failed login attempts, privilege escalation, or unusual access times.
|
3. Compliance and regulatory issues
| What is it? |
It can be challenging to comply with cloud regulations like the GDPR, HIPAA, or the PCI DSS, especially with shared responsibility models and data sovereignty concerns. |
| Causes |
- Lack of understanding of regulatory requirements
- Data residency and sovereignty challenges
- Inadequate security controls and auditing
- Failure to maintain consistent compliance across multi-cloud environments
- Insufficient documentation and reporting mechanisms
|
| Solution with SIEM |
- Automated compliance reporting: SIEM tools automate the collection and analysis of logs from cloud environments, making compliance reporting easier and more consistent.
- Continuous compliance monitoring: SIEM solutions can monitor cloud services for compliance violations, such as unauthorized access or data movement, and generate real-time alerts.
- Audit trails: SIEM tools provide secure log retention for audits, helping organizations demonstrate compliance during regulatory inspections.
|
4. Lack of visibility and monitoring
| What is it? |
Limited visibility into cloud environments makes it difficult to detect threats and manage security incidents. |
| Causes |
- Insufficient cloud asset inventory
- Limited access to real-time logging and metrics
- Inconsistent monitoring across multi-cloud and hybrid environments
- Overwhelming volume of alerts and false positives
- Lack of integration between monitoring tools and systems
|
| Solution with SIEM |
- Unified security monitoring: SIEM solutions aggregate logs from all cloud services, providing a centralized view of all cloud activities, events, and potential security incidents.
- Real-time threat detection: SIEM tools apply real-time analysis to detect anomalies, suspicious activity, or emerging threats that could go unnoticed in a complex cloud environment.
- Dashboards and reports: SIEM solutions provide customizable dashboards for visualizing cloud security data and generating insightful reports on security posture.
|
5. Cyberattacks (e.g., DDoS, insider threat, or ransomware)
| What is it? |
Cloud environments are susceptible to a range of cyberattacks, including DDoS, insider threats, ransomware, and advanced threats like APTs. |
| Causes |
- Exploitation of vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure
- Ineffective access control and privilege management
- Sophisticated social engineering and phishing tactics
- Inadequate patch management and outdated software
- Insider threats and compromised credentials
|
| Solution with SIEM |
- Threat detection and correlation: SIEM uses behavioral analytics and machine learning to correlate events from multiple sources and detect cyberattacks early, such as abnormal login patterns or unusual traffic spikes.
- Automated incident response: SIEM solutions can automatically trigger responses to mitigate attacks, such as blocking suspicious IPs or isolating compromised accounts.
- Real-time alerts: SIEM solutions provide immediate alerts for suspicious behavior, such as DDoS attacks or insider threats, enabling swift intervention.
|
6. Skill shortage
| What is it? |
It is challenging to effectively manage and safeguard cloud infrastructures due to a global shortage of cybersecurity talent. |
| Causes |
- Rapid evolution of cloud technologies
- High demand for skilled cloud security professionals
- Limited training and development opportunities
- Inadequate focus on cloud security in traditional IT education
- Difficulty retaining experienced security talent
|
| Solution with SIEM |
- Simplified security operations: SIEM reduces operational complexity by automating threat detection, incident response, and log management, requiring fewer resources for effective monitoring.
- Centralized threat intelligence: SIEM platforms often include threat intelligence integration, which can guide security teams and help them detect emerging threats without needing specialized expertise.
- Automated workflows: SIEM automates repetitive tasks like log analysis and incident response, making the job easier for security teams.
|
7. Managing a rapidly evolving attack surface
| What is it? |
The potential attack surface is increased by the dynamic nature of cloud environments, where infrastructure and services are always changing. |
| Causes |
- Dynamic scaling and expansion of cloud environments
- Proliferation of IoT and edge devices
- Increased adoption of multi-cloud and hybrid architectures
- Frequent deployment of new applications and services
- Lack of comprehensive asset and risk visibility
|
| Solution with SIEM |
- Continuous asset discovery: SIEM platforms integrate with cloud asset management tools to identify and track new resources, ensuring they are monitored for security risks.
- Adaptable threat detection: As cloud environments evolve, SIEM systems adapt to changes and update detection rules to account for new cloud resources and attack vectors.
- Real-time monitoring of all assets: SIEM solutions continuously monitor cloud services and resources for signs of compromise, ensuring that newly deployed or updated resources are always protected.
|
8. Data breach
| What is it? |
Data breaches in the cloud can occur due to poor access control, misconfigurations, or targeted attacks, leading to significant security risks. |
| Causes |
- Misconfigured cloud resources (e.g., storage buckets or databases)
- Weak authentication and authorization mechanisms
- Insider threats and unauthorized access
- Exploitation of software vulnerabilities
- Inadequate data encryption practices
|
| Solution with SIEM |
- Data loss prevention (DLP): SIEM tools can integrate with DLP tools to monitor and block unauthorized data transfers, preventing sensitive data from being leaked or stolen.
- Event correlation and alerting: SIEM solutions correlate events from cloud applications, databases, and user activity logs to detect potential data breaches, such as large-scale data downloads or unauthorized access attempts.
- Forensic analysis: In the event of a breach, SIEM allows for retrospective analysis to identify the source and scope of the incident, enabling a faster and more effective response.
|
9. Advanced persistent threat
| What is it? |
Advanced persistent threats (APTs) are complex, prolonged cyberattacks that frequently evade conventional security measures and target cloud environments over time. |
| Causes |
- Sophisticated social engineering tactics
- Exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities
- Weak identity and access management practices
- Insufficient network segmentation and isolation
- Lack of proactive threat intelligence and monitoring
|
| Solution with SIEM |
- Advanced threat detection: SIEM leverages machine learning, behavioral analytics, and threat intelligence to detect indicators of compromise associated with APTs, even if the attack is slow and stealthy.
- Continuous monitoring: SIEM solutions provide persistent monitoring for unusual patterns of behavior that may indicate an APT, such as lateral movement or data exfiltration.
- Threat intelligence integration: SIEM tools integrate with threat intelligence feeds to help identify and respond to known APT tactics, techniques, and procedures.
|
10. Insecure APIs
| What is it? |
Insecure APIs expose cloud services to attacks like data breaches or unauthorized access, as APIs are often the primary interface for communication between cloud services. |
| Causes |
- Lack of proper authentication and authorization
- Excessive data exposure through APIs
- Failure to validate and sanitize user inputs
- Insufficient rate limiting and throttling mechanisms
- Outdated or poorly maintained API endpoints
|
| Solution with SIEM |
- API traffic monitoring: SIEM solutions can monitor API requests and responses, looking for anomalies like unexpected data access or unusual request patterns that may indicate an attack.
- API security integration: SIEM platforms integrate with API security tools to identify vulnerabilities or misconfigurations in the APIs and ensure they are protected against common threats (e.g., injection attacks or data leakage).
- Alerting on suspicious API activity: SIEM tools alert security teams about suspicious API calls, such as repeated failed login attempts, unauthorized access to sensitive data, or high volumes of requests from a single IP.
|
Visit this page to learn more about best practices and the significance of obtaining insight into cloud app usage and user behavior to prevent security breaches.
Also, to read more about cloud security, visit this page.
Ready for the next step?
Are you looking for ways you can protect your organization's sensitive information from being misused? Sign up for a personalized demo of ManageEngine Log360, a comprehensive SIEM solution that can help you detect, prioritize, investigate, and respond to security threats.
You can also explore on your own with a free, fully functional, 30-day trial of Log360.





