Related content
The websites that we frequently come across are just the tip of the iceberg of the vast amount of content that's available on the internet. The internet has many distinct layers, each differing in its characteristics and how they are accessed.
Despite the fact that the terms deep web and dark web are often perceived interchangeably, there are a few key distinctions that set the two apart. The deep web hosts content like private corporate sites, medical records, databases, and paywalled websites that are not accessible to regular users. While the dark web typically boasts content that is deliberately hidden and needs special software, such as the Tor browser, to access. The dark web is associated with anonymity and is widely known for hosting illegal activities. However, it also serves legitimate purposes for privacy protection.
This article dives deeper into the differences between the deep and dark web, elaborates on the risks associated with the dark web, and how ManageEngine's SIEM solution, Log360, can help with dark web monitoring.
How deep web is different from dark web?
The web content that you see on popular search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo, social media platforms, and YouTube make up the surface web.
Just below the surface web is the deep web, which includes private databases, web pages not indexed by search engines, password protected accounts, and more. Lastly, there's the dark web, a concealed part of the deep web known for its high anonymity.
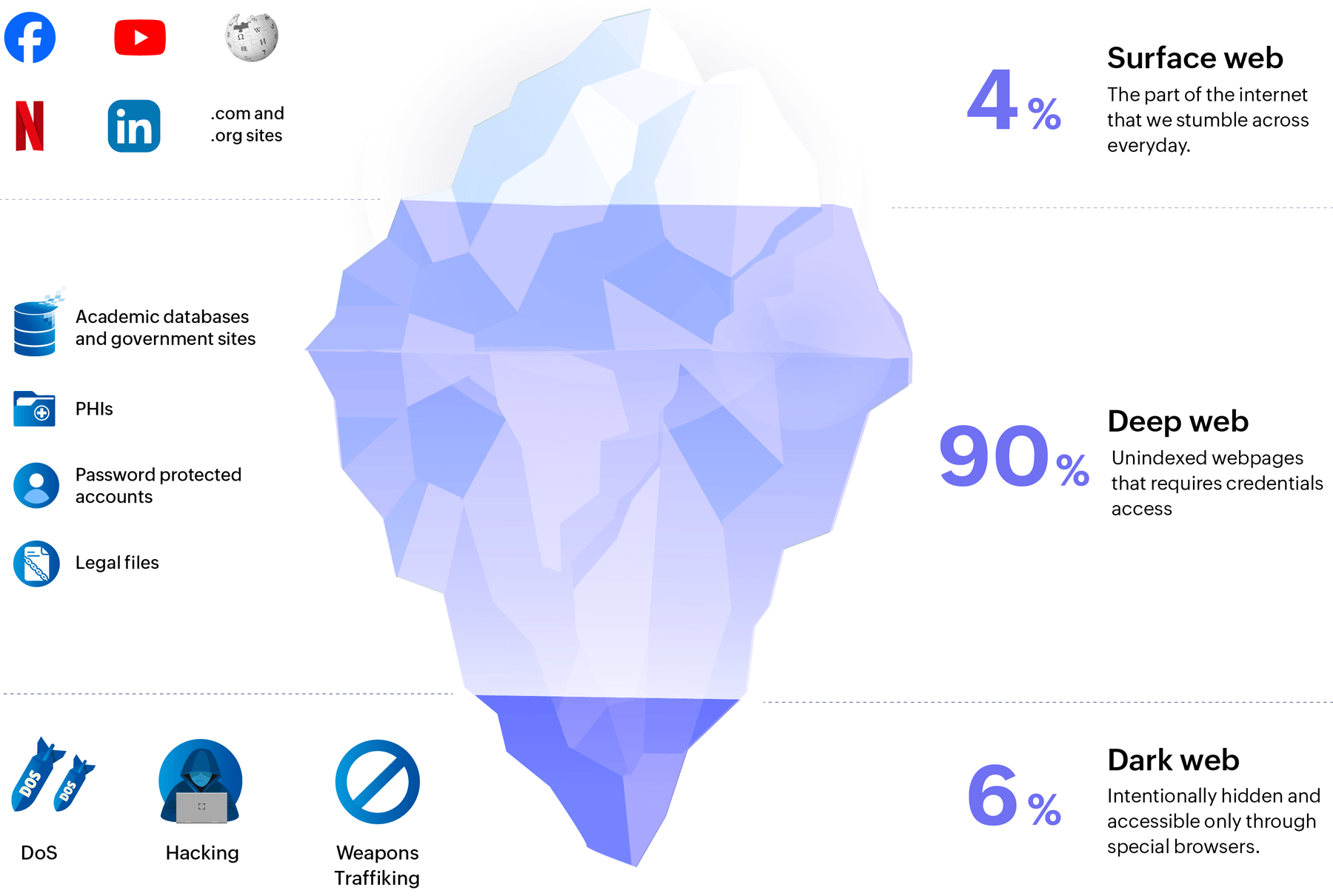
Here are some of the key differences between the deep web and the dark web:
| Deep web | Dark web |
|---|---|
| Includes content that isn't indexed by standard search engines. This comprises 90% of the internet. | This subsection of the deep web, used for illegal activities, makes up just 0.01% of the entire web. |
| Accessible through web browsers with valid credentials. | Users must know specific URLs or utilize special browsers, like Tor, to access. |
| Used for legitimate activities like privacy protection and running specific campaigns. | Journalists and whistle-blowers utilize the dark web to leak sensitive information while protecting their identities among other use cases. |
| Potential risks include data breaches and phishing attacks targeting personal credentials. | The threats of dark web browsing include PII exposure and being subjected to ransomware and social engineering attacks. |
Now, let's explore their differences in more detail, how to access them, and dispel some misconceptions along the way.
What is the deep web?
The deep web resources, such as databases and private sites, are intentionally designed to be inaccessible to crawlers, either through password protection or by being explicitly disallowed in their robots.txt files.
The deep web constitutes parts of the internet that are not indexed by standard search engines. The web pages on the deep web are protected by credentials, paywalls, and are intentionally made private. However, these websites can still be accessed using common web browsers like Chrome or Firefox by knowing the URL of the page and the necessary credentials.
You can also use the website's search feature to locate content that web crawlers have not indexed. This is particularly useful for information-heavy sites such as government resources or academic databases.
Some of the larger part of the deep web comprise:
- Unindexed pages: These are web pages that search engines cannot access due to a multitude of reasons like paywalls, being behind a login, or restrictions set by website hosts.
- Subscription services: Content on platforms like Netflix, Amazon, and other streaming services is usually locked behind paywalls. Users must subscribe or pay to access this material, which is not visible to those who do not have an account.
- Sensitive data repositories: Databases that store an organization's sensitive information such as their client's medical records, PII, financial records, and more. These databases are typically stored within the private network operated by the organization, making them inaccessible via the internet.
The deep web resources are mostly gated, meaning they require authentication to access the content with specific credentials to ensure data privacy. Even if these resources are indexed by the search engines, one must possess credentials to be able to access the pages or sites that are guarded through authentication.
It is believed that the deep web is 400 to 500 times the surface web, making up about 90% to 95% of the total internet.
What is the dark web?
The dark web, being considered a concealed part of the deep web, paves the way for a secure communication channel that can be accessed only by special browsers. The Tor browser is the most popular among its counterparts due to its larger user base. It ensures anonymity through a technique called onion routing, which involves multi-layered encryption and routing through various nodes.
The dark web gained traction for its association with individuals engaging in illicit activities like the trading of illegal goods and services, coordinating attacks, drug trafficking, and more.
While the dark web is often associated with illegal activities, it also serves several legitimate purposes that are pivotal for privacy, security, and free expression. Some of the dark web's legitimate use cases:
- Privacy protection: Individuals concerned about government surveillance or corporate tracking may turn to the dark web for anonymity. It allows them to exchange sensitive information without being monitored by third parties.
- Intel gathering: Researchers and cybersecurity professionals often explore the dark web to gather intelligence on emerging threats, cybercriminal activities, and trends in illicit markets. This knowledge can inform better security practices and policies.
- Political activism: The dark web is used by activists, particularly those in authoritarian countries, for sharing information anonymously. This is vital for protecting their identities and ensuring their safety while advocating for human rights and social change.
The dark web constitutes only about 0.01% of the deep web, with its total number of sites estimated in the thousands.
What are the risks of accessing the dark web?
The dark web poses risks to enterprises as they host an illicit marketplace where cyberattacks get planned. The extent to which the dark web can have serious legal, financial, and psychological consequences for users is quite alarming. Below are some of the risks associated with using the dark web:
- Illicit marketplaces: The dark web hosts several illegal marketplaces where users can trade drugs, stolen data, and other illegal goods. Engaging with these markets can lead to serious legal ramifications.
- Ransomware: Users are at risk of succumbing to downloading malware, including viruses, trojans, and ransomware. These malicious programs can compromise personal data, steal sensitive information, or lock users out of their devices until a ransom is paid.
- Social engineering attacks: Dark web forums form the basis for social engineering tactics where users may be manipulated into revealing sensitive information or falling victim to extortion attempts.
- Phishing: Cybercriminals on the dark web sell phishing kits that enable others to launch fraudulent email campaigns aimed at stealing personal information or credentials. Users may fall victim to these scams, leading to identity theft or severe financial loss.
Best practices for browsing the deep and dark web safely
The risks associated with browsing on the deep and dark web can be alleviated with effective monitoring, robust security measures, and keeping tabs on the incidents involving appalling usage of the dark side of the internet.
Some common practices to follow to avoid getting exploited:
- Utilize VPNs: Employ VPNs alongside privacy-focused browsers like Tor to enhance anonymity and protect data from surveillance.
- Timely software updates: Keep all software, including browsers and security tools, updated to protect against known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers.
- Adopt stronger credential practices: A robust password would make it difficult for attackers to gain access to your sensitive information.
- Endpoint security: Ensure all devices are equipped with antivirus software and firewalls, regularly scanning for malware, especially after accessing the dark web.
- Staying informed on the latest: Keep tabs on the latest cybersecurity news and best practices to ward off new threats that come your way.
Why dark web monitoring is important for security operations?
Cyberthreats have grown more sophisticated with advancements in technology and the evolving tactics of cybercriminals. This means that the dark web is evolving too, and your business needs a well-rounded cybersecurity solution to monitor the dark web, get cues of data leaks, and prevent a larger attack targeting your organization. Dark web monitoring is often seen as a proactive security measure that can help you:
- Remain complaint with regulatory mandates.
- Identify risks at earlier stages and mitigate them.
- Take proactive measures and respond promptly to threats at their early stages.
A dark web monitoring solution fetches threat intelligence feeds from the dark web, analyzes them, and gives you recommendations to preempt data breaches and attacks.
How ManageEngine Log360 can help you with dark web monitoring with around-the-clock web investigations for security teams
ManageEngine Log360, a comprehensive security information and event management (SIEM) solution, comes with a dark web monitoring capability that lets you detect activities targeting your organization in the dark web. Log360 integrates with Constella Intelligence, the AI-driven identity intelligence provider, to continuously monitor dark web for security threats. By instantly alerting you to any PII exposure on the dark web, Log360's monitoring capability reduces the risk of identity theft and data abuse for any gain, fraud, or extortion attempts.
It also notifies users of any potential threats like phishing, social engineering attacks, and account takeover with its real-time alerts to bolster their defenses preemptively.
With Log360, you can monitor the dark web for exposure of sensitive information like credit card numbers, compromised passwords, usernames, email information, domain names, and other illicit data sales orchestrated by cybercriminals.
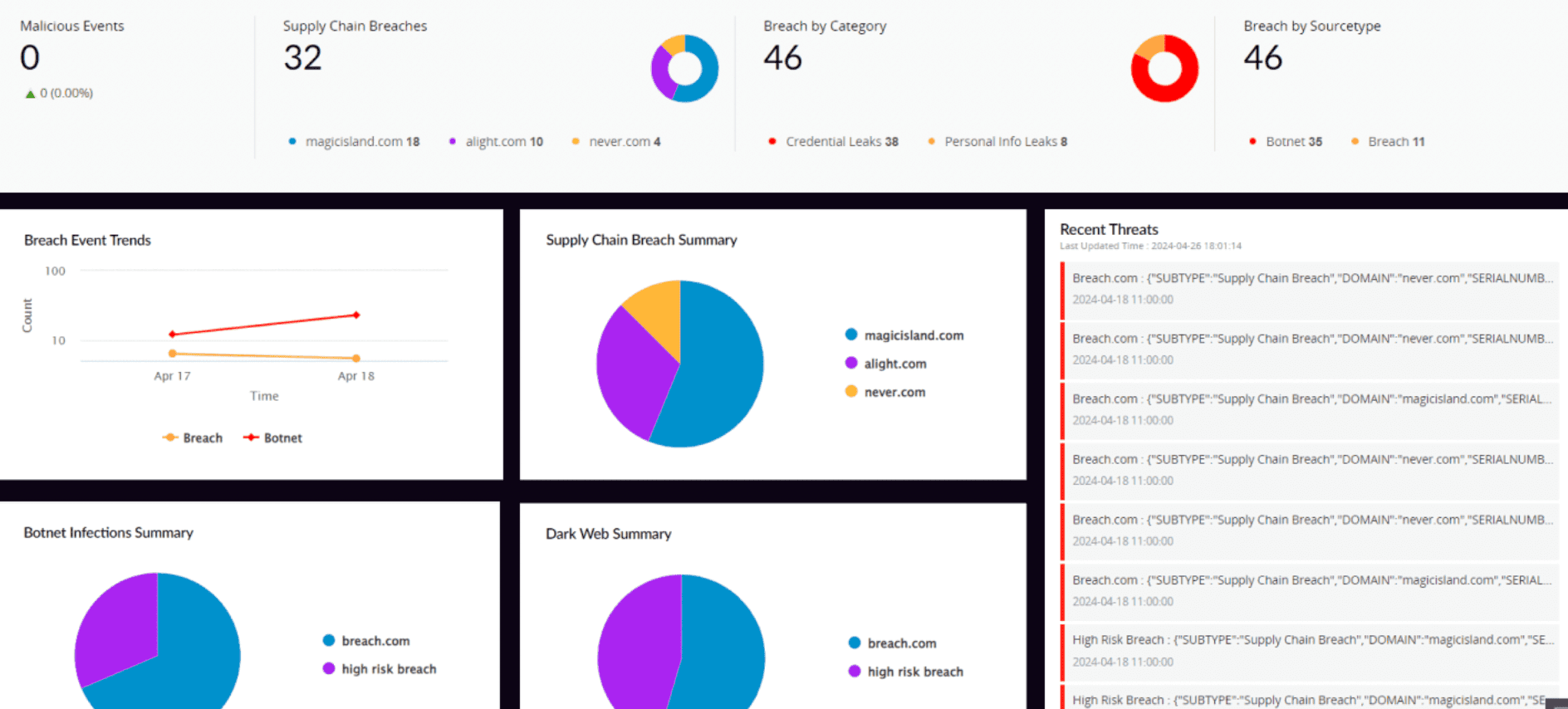
The impact of threats like compromised employee credentials is colossal. Log360 uses its threat intelligence and incident response to leverage the extensive coverage of dark web sources to identify such threats sooner and empowers you to take actions promptly.
FAQs
- Is it illegal to browse the dark web?
-
Using the dark web in itself is not illegal by any means. However, there are numerous malicious activities that take place in the dark web like illicit transactions, selling and buying prohibited items, supporting RaaS, and scams which requires you to remain vigilant.
- Can I access the dark web through a conventional browser?
-
No, you cannot access the dark web through a regular browser, like Google Chrome, Firefox, etc. There are specialized browsers that are meant for dark web browsing like Tor browser and Whonix.
- Is the deep web dangerous?
-
The deep web is not inherently perilous. However, it's wise to be cautious while accessing the content from suspicious sources to avoid illegitimate content.
- What was the dark web made for?
-
The dark web was developed to enable a secure and anonymous platform for communication and information sharing, particularly for individuals facing censorship or persecution.
- How big is the deep web compared to the dark web?
-
Reports suggest that the deep web comprises about 90% to 95% of the entire internet while the dark web accounts for 0.01% to 5% of it.
What's next?
Interested to know more about the advanced features of Log360? Explore the free, 30-day trial with technical assistance.
- How the deep web is different from the dark web
- What is the deep web?
- What is the dark web?
- What are the risks of accessing the dark web?
- Best practices for browsing the deep and dark web safely?
- Why is dark web monitoring important for security operations?
- How ManageEngine Log360 can help you with dark web monitoring with around-the-clock web investigations for security teams



