Related content
Discovering your email addresses have been found on the dark web is alarming and signals potential risks, such as identity theft and unauthorized account access. The dark web serves as a marketplace for cybercriminals trading stolen data, meaning information might have been compromised through a breach.
A dark web alert for a compromised email address highlights the urgency of taking immediate action to protect sensitive data. If left unaddressed, this exposure can lead to phishing attacks targeting contacts and further exploitation of accounts. Taking swift and calculated actions helps reduce the likelihood of further threats and safeguards both personal and organizational data.
Immediate actions to take
1. Confirm if the email is on the dark web
When a dark web alert indicates a compromised email address, the first step is to verify the breach. Tools like Have I Been Pwned or Firefox Monitor can help check whether an email address has been exposed in known data breaches.
For advanced users or security teams, monitoring solutions like Constella Intelligence offer deeper insights into breaches. It’s equally important to assess the extent of the breach and whether it involves only the email or additional data, such as passwords or financial details.
2. Change passwords and enable multi-factor authentication
If an email is found on the dark web, changing the associated passwords is critical. Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts and consider password managers like LastPass, Bitwarden, or Dashlane for secure password creation and storage.
Additionally, enable MFA for accounts tied to the compromised email. App-based or hardware token MFA options, such as Google Authenticator or YubiKey, provide stronger protection than SMS-based verification.
3. Monitor accounts for unusual activity
After securing accounts, check for unauthorized logins or suspicious actions. Email services like Gmail and Outlook offer tools to review recent activity. If any unauthorized access is detected, disconnect the session immediately and recheck security settings for vulnerabilities.
Advanced email security enhancements
1. Strengthen email security protocols
To reduce future risks, implement robust security protocols like DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM), Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC), and Sender Policy Framework (SPF). These measures validate email legitimacy and prevent phishing or spoofing attempts.
For enhanced protection, consider email security solutions like Proofpoint or Mimecast, which scan for threats like malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks.
2. Regularly monitor the dark web for email exposure
Ongoing monitoring is essential to ensure the email or related data doesn’t resurface on the dark web. Continuous dark web monitoring services can provide timely alerts and help mitigate future risks.
Assessing the extent of the breach
1. Analyze the leaked data
When an email is exposed on the dark web, understanding the scope of leaked data is crucial. Breaches may include sensitive details such as passwords, personal identifiers, or financial information. Download the data in a controlled, secure environment (for example, a virtual machine) and use forensic tools for analysis.
This analysis helps identify other accounts or systems requiring enhanced security, such as financial services or social media linked to the compromised email.
2. Conduct a security audit
For business-related email accounts, performing a comprehensive security audit of the organization’s email systems is recommended. Identify infrastructure weaknesses and consider implementing stronger encryption for emails containing sensitive information.
Encryption technologies such as transport layer security (TLS) or pretty good privacy (PGP) can provide additional protection, ensuring that emails in transit remain secure.
Mitigating the risk of future email breaches
Implement a zero trust security model: A zero trust security model can help prevent future incidents by continuously verifying users and devices before granting access to network or email systems. This model assumes that no user or device should be trusted by default and emphasizes frequent authentication checks.
Advanced authentication methods, such as biometrics or adaptive access controls, can ensure legitimacy when accessing email or related systems. Permissions and access to sensitive data should be restricted, granting only the necessary level of access required for tasks.
Educate users on security best practices: One of the most effective defenses against email breaches is educating users on best security practices. Regularly remind users to avoid phishing attempts, update passwords frequently, and report suspicious emails or activities.
Conduct security training sessions that cover how to identify phishing scams, the importance of enabling MFA, and secure email handling practices. This training can reduce the likelihood of human error, which often leads to breaches.
Advanced Incident Response tactics
Use SIEM and SOAR for incident management: Security information and event management (SIEM) and security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) tools can accelerate incident management during a major email breach. SIEM solutions collect and analyze security events across the network, while SOAR platforms automate response workflows for quicker resolution. These tools identify suspicious patterns, enabling the IT security team to act immediately and minimize damage.
Perform digital forensics: Forensic investigation is essential in severe breaches to determine the origin and scope of the attack. Tools like EnCase and FTK facilitate digital forensics by analyzing access logs, identifying malware, and preserving evidence for improving future security measures. Frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK provide insights into attacker techniques, tactics, and procedures, helping address vulnerabilities that led to the breach.
Legal and compliance considerations
Different regions have specific laws regarding data breach notifications. For example, under the GDPR regulations, businesses are required to notify authorities and affected individuals within 72 hours of discovering a breach involving personal data. Similarly, in the United States, the California Consumer Privacy Act, also known as the CCPA, and the California Privacy Rights Act, also known as the CPRA, impose regulations on reporting breaches involving the data of residents of the state. It's critical to understand and comply with the region's data protection regulations to avoid penalties or legal ramifications.
For complex breaches or incidents involving significant data exposure, consulting with cybersecurity experts or legal advisors might be necessary. These professionals can assist in investigating the breach, managing communications with affected individuals, and ensuring compliance with legal requirements.
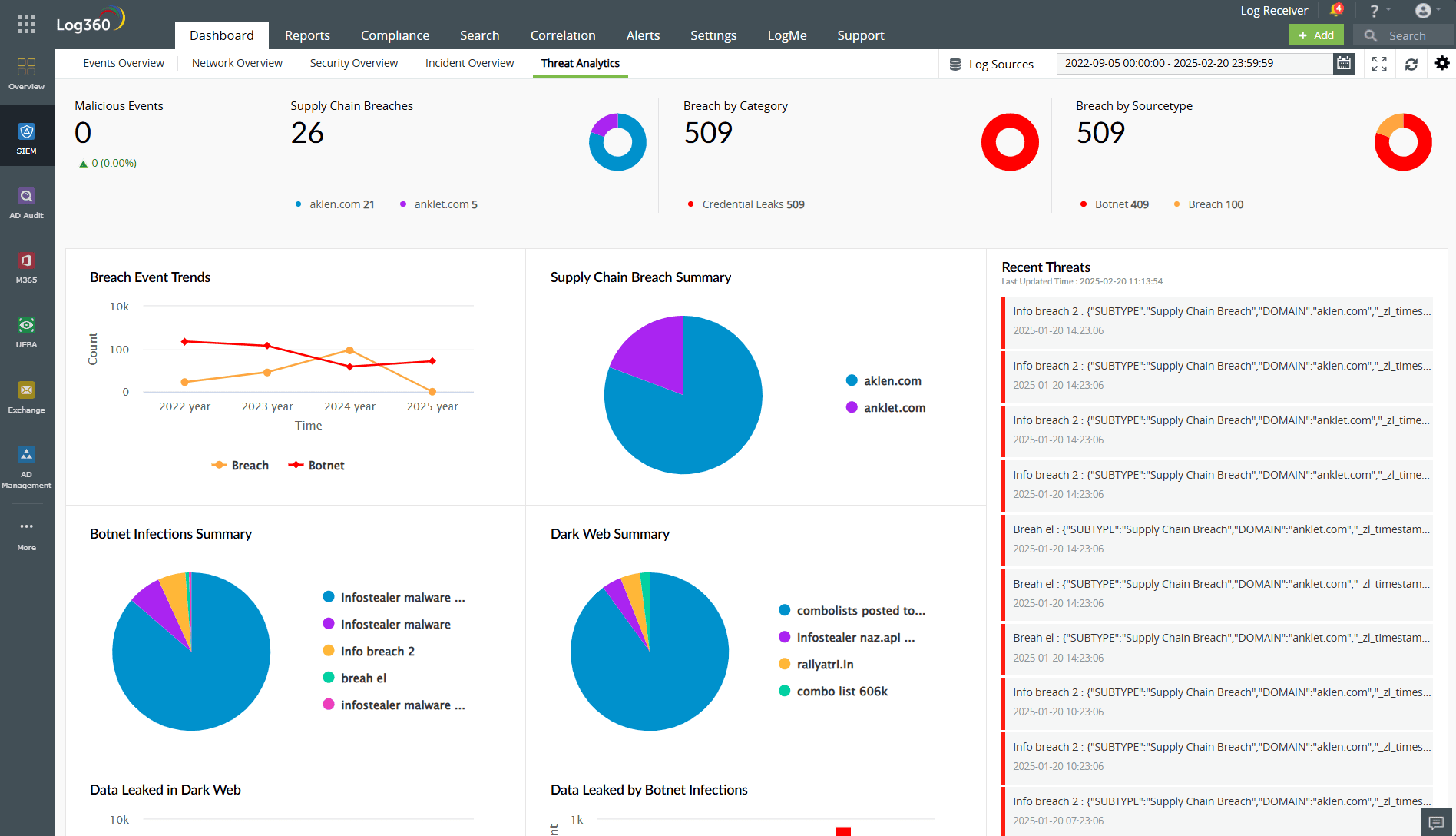
Proactive response to compromised emails on the dark web with Log360
ManageEngine Log360, a comprehensive SIEM solution, provides robust protection for your organization against potential threats. With its integration with Constella Intelligence, Log360 leverages real-time threat intelligence to detect compromised credentials, including email addresses, through 24/7 dark web monitoring.
Log360 takes a proactive approach to safeguarding against leaked credentials by automating key response workflows, such as enforcing password resets and tightening access controls for compromised accounts. Additionally, the Incident Workbench provides comprehensive insights, including breach history and leaked information, enabling effective threat containment and investigation.
Beyond monitoring, Log360 ensures faster resolution of potential breaches by delivering instant alerts for compromised credentials and sensitive data, such as credit card details or PII. This early detection enables organizations to prevent threats from escalating. By aligning with regulatory mandates like the GDPR and PCI DSS, Log360 strengthens compliance while safeguarding against evolving security risks, ensuring a robust defense against dark web threats.
FAQs
- What should I do if my email was found on the dark web but I haven’t noticed any suspicious activity?
-
Even if no unusual activity is detected, it's best to update passwords, enable MFA, and monitor account access logs. Cybercriminals may hold stolen credentials for future attacks, so staying proactive minimizes risks.
- Can changing my email address prevent future dark web exposures?
-
Changing an email address may reduce immediate exposure but isn’t a foolproof solution. Strengthening security practices, using unique passwords, and enabling MFA are more effective long-term strategies.
- Are corporate and personal email breaches handled differently?
-
Yes, corporate breaches require incident response protocols, legal compliance checks, and possible notification to stakeholders. Personal email breaches mainly involve securing accounts and preventing fraud.
- Can using a password manager help if my email is exposed?
-
Yes, a password manager helps create and store strong, unique passwords, reducing the risk of credential reuse in case of exposure.
What's next?
Ready to safeguard your organization from dark web threats? Try Log360 Cloud with a free, 30-day trial, or schedule a call with our experts to explore its features through a personalized demo.
- Immediate actions to take
- Advanced email security enhancements
- Assessing the extent of the breach
- Mitigating the risk of future email breaches
- Advanced Incident Response tactics
- Legal and compliance considerations
- Proactive response to compromised emails on the dark web with Log360