Is there anything AI can't do? It can write, draw, edit, and code, all at an unhuman speed. Turns out, AI can also be used to protect organizations from cybersecurity threats and automate many of the tasks traditionally handled by a security analyst. Unfortunately, adversaries can leverage the same technology to write malicious code and carry out cyberattacks.
The emergence of advanced AI tools and frameworks has introduced attackers to new ways of simulating and executing their attacks. Any SOC analyst should be aware of the deadly capabilities of adversarial AI, which can find routes for defense evasion, lateral movement, enhanced persistence, and so much more.
SOCs across the world receive an overwhelming amount of alerts on a daily basis, and AI and ML can be leveraged to manage and attend to these alerts. AI utilizes training data to improve decision-making capabilities of the model used for security analytics solutions or any other operational purpose. However, attackers can manipulate a target model by injecting and modifying training data and corrupting the algorithm's logic. This process, known as data poisoning, can impair decision-making and bring catastrophic consequences to the organization.
Narrow AI is created to focus on a single problem and its applications include chatbots, medical diagnoses, facial recognition, and so on. Artificial general intelligence (AGI) is a hypothetical technology that can perform cognitive capabilities similar to humans, allowing it to adapt to various environments and requirements. Attackers currently only have access to narrow AI where they leverage basic ML and NLP capabilities. This means that AGI attacks are, for now, out of their reach. When attackers do get this capability, it could result in more intelligent malicious codes, faster vulnerability detection, and advanced social engineering capabilities.
Let's deep dive into a few ways attackers can leverage AI to surpass the enterprise security posture and execute noxious strikes.
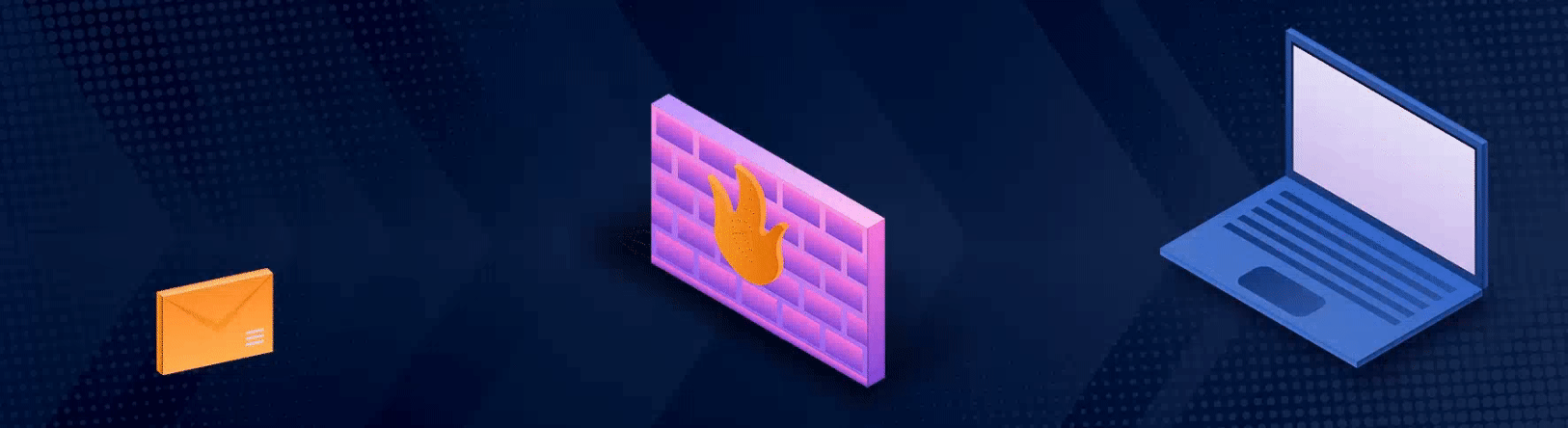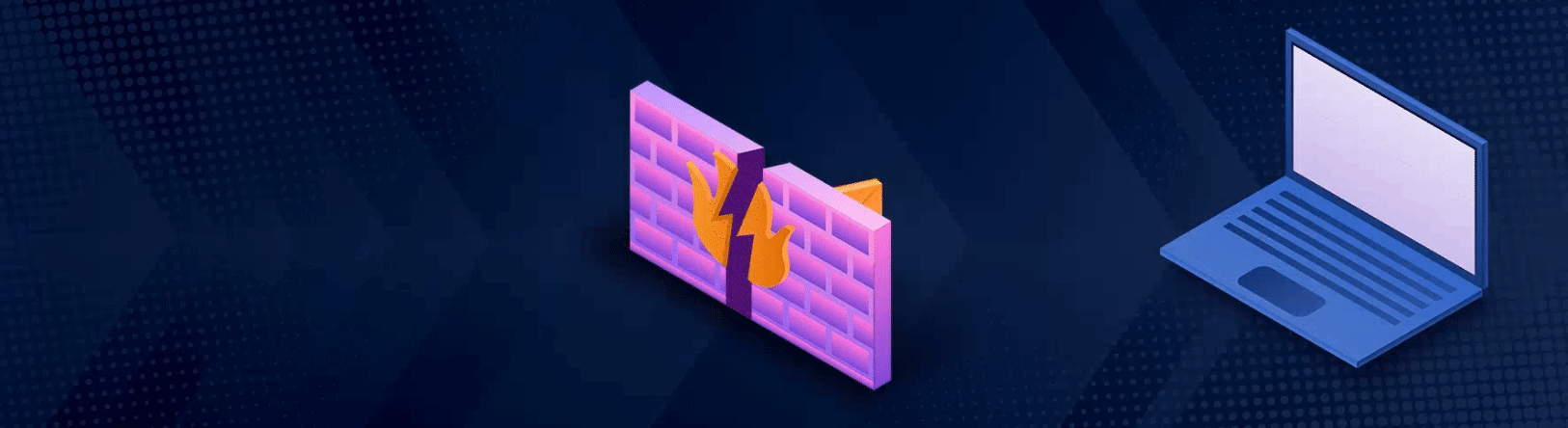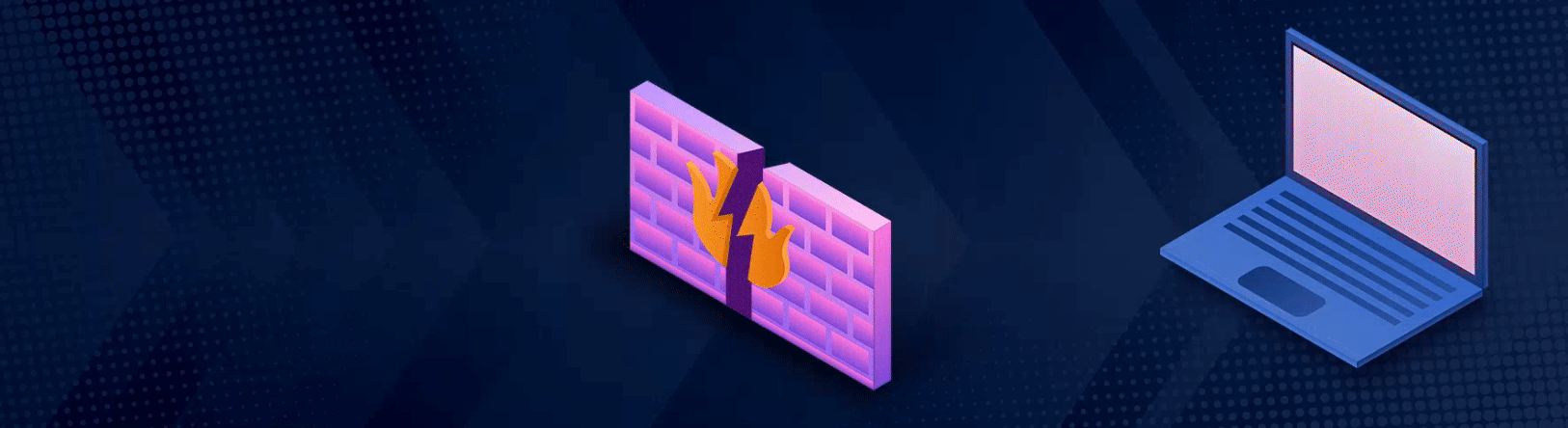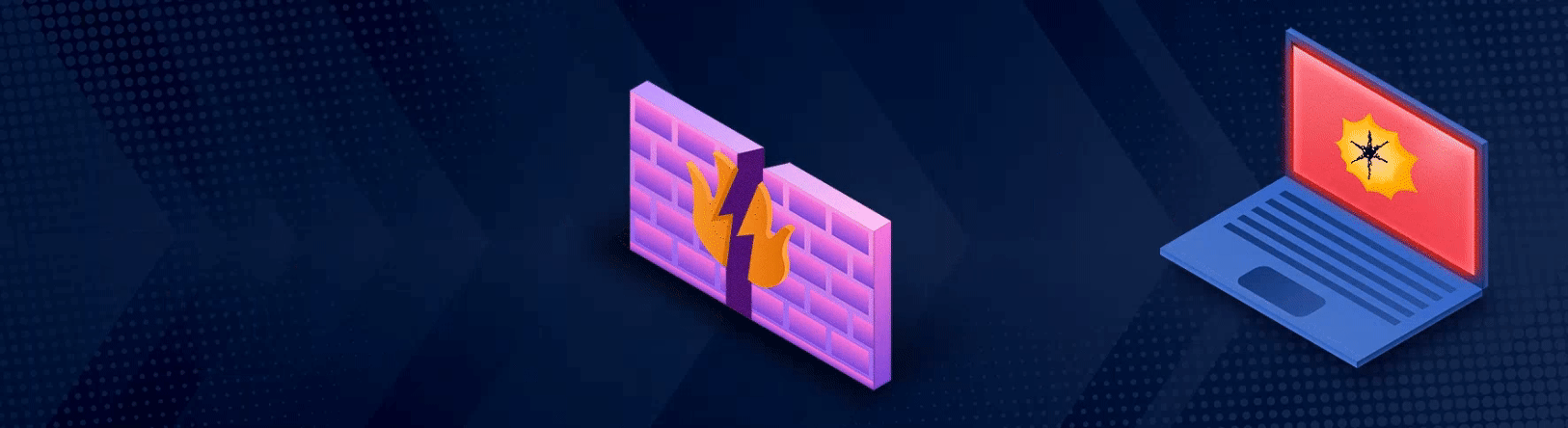 A disguised data packet entering the network, undetected by the firewall, and transforming into malware.
A disguised data packet entering the network, undetected by the firewall, and transforming into malware.
There are many more AI-enabled threats that exist, including target vulnerability discovery, backdoor deployment, and advanced reconnaissance.
The rise of AI has given attackers an advanced platform to execute lethal strikes to the enterprise network. Security professionals must gain awareness of these new threat trends. Challenges are meant to be overcome, so here's how to fight back:
AI is a formidable tool, capable of both boosting and crippling an organization. Being aware of how adversaries can utilize the powerful capabilities of AI as a weapon is sobering and necessary, especially for organizations that use AI to deliver critical products and services to the wider public, such as vehicle manufacturers, government entities, and medical institutions.
Creating a multi-layered security approach, practicing real-time monitoring, and adopting Zero Trust are a few other ways organizations can fortify themselves against AI threats.
To learn more about how to leverage AI to defend against cyberattacks, sign up for a demo of ManageEngine Log360, a unified SIEM solution with integrated UEBA and SOAR capabilities.
You will receive regular updates on the latest news on cybersecurity.
© 2021 Zoho Corporation Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.