In today's digital landscape, companies that manage sensitive information must prioritize data security and regulatory compliance. Understanding the nuances of SOC (System and Organization Controls) compliance—particularly the differences between SOC 1, SOC 2, and SOC 3 requirements—can be challenging for both businesses and the clients they provide services to.
Many organizations struggle to comprehend which type of SOC requirements are best for their needs, or how each affects their operations and customer trust. Without a thorough grasp of each SOC type, businesses risk mismanaging compliance priorities, resulting in data security vulnerabilities, reduced client trust, and potential regulatory fines. This guide unpacks the essentials of SOC 1, SOC 2, and SOC 3 compliance.
What is SOC compliance?
SOC compliance is a framework developed by the AICPA to ensure organizations manage and protect customer data effectively. The intended goal behind SOC compliance is to evaluate service organizations' internal controls, policies, and processes.
The SOC compliance framework is further divided into three sub-frameworks: SOC 1 (financial controls), SOC 2 (data security, privacy, and availability), and SOC 3 (a publicly available summary of an organization's SOC 2 report). There are two different kinds of reports in SOC 1, which are SOC 1 Type 1 and SOC 1 Type 2. Also, there are two different kinds of reports in SOC 2, which are SOC 2 Type 1 and SOC 2 Type 2. The SOC 3 public report is the only kind of SOC 3 report.
Complying with SOC is necessary for meeting regulatory requirements, showing credibility, and lowering the risk of data breaches. An affirmation of SOC compliance is widely used by service providers—particularly SaaS firms—since a SOC compliance report and certification shows clients that the company has the right procedures and activities in place to protect their data,. Additionally, this compliance aids firms in following industry best practices for the operational effectiveness and security of the data they own.
Some of SOC compliance requirements include:
- Developing policies for data security, availability, or confidentiality.
- Training staff on security practices.
- Monitoring systems to ensure they meet compliance requirements.
What is a SOC audit?
An extensive evaluation carried out by a reputable third-party auditor is known as a SOC audit. The aim of this audit is to find out whether a service organization complies with the stringent controls and procedures required for service delivery and data protection.
SOC audits help in:
- Building client confidence in the organization's systems and controls.
- Meeting regulatory requirements and industry standards.
- Identifying and addressing weaknesses in internal controls.
- Enhancing the competitive edge by showcasing a commitment to operational excellence and security.
Example activities of a SOC audit include:
- Reviewing control documentation and evidence.
- Testing the operating effectiveness of controls.
- Preparing and issuing the audit report.
An audit confirms whether the organization is compliant and provides an official report that can be shared with stakeholders. Without compliance, an organization will fail the audit or receive an unfavorable report.
What is SOC 1 compliance?
The term SOC 1 compliance refers to fulfilling the requirements specified in the Service Organization Control 1 (SOC 1) report, which evaluates and verifies a service organization's internal controls that could have an impact on the financial reporting of its clients. It acts as proof that a company has effective and sufficient controls over financial reporting in place for consumers, assurance providers, and authorities.
It is particularly relevant for organizations that provide services—like payroll processing, IT services, or data hosting—where their systems directly impact their customers' financial reporting processes.
Benefits of SOC 1 compliance
- Demonstrate strong financial reporting controls, attaining the trust and credibility of stakeholders and clients.
- Streamline client audit processes by providing third-party assurance over financial-related controls.
- Identify and eliminate risks that could result in inaccurate or erroneous financial reporting.
- Ensure compliance with industry regulations and contractual requirements related to financial controls.
- Increase competitiveness by demonstrating operational excellence and drawing in clients who need assurance.
Types of reports: SOC 1 Type 1 vs SOC 1 Type 2
The two report types that comprise SOC 1 compliance are SOC 1 Type I and SOC 1 Type 2. They differ according to the timeframe of evaluation of the financial controls. Below is a table that highlights the main differences between the reports:
| Report type | SOC 1 Type 1 | SOC 1 Type 2 |
| What is it? | A Type 1 report assesses the controls' design at a specific point in time. Although it does not verify the controls' long-term effectiveness, it ensures that they are appropriately established to achieve the stated goals. | A Type 2 report assesses the controls' operational effectiveness and design over a given time frame, such as six to twelve months. This proves that the controls were correctly developed and consistently operated as intended. |
| Example | A payroll processing company may get a SOC 1 Type 1 report to show that its systems are designed to ensure accurate financial transactions. | The same payroll processing company may obtain a SOC 1 Type 2 report to show its controls operated effectively throughout a six-month period. |
Table 1: SOC 1 type 1 versus type 2 reports.
What is SOC 2 compliance?
SOC 2 is a security framework that specifies how organizations should protect customer data from unauthorized access, security incidents, and other vulnerabilities. SOC 2 compliance refers to a service organization's adherence to the criteria and standards outlined in the SOC 2 framework. The AICPA developed SOC 2 around five Trust Services Criteria (TSC): Security, Availability, Processing integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy.
Benefits of SOC 2 compliance
- Demonstrate a commitment to safeguarding consumer information, establishing trust and credibility with clients and partners.
- Lower the chance of system outages, data breaches, and regulatory norm noncompliance.
- Ensure wider compliance by aligning with industry and regulatory frameworks like CCPA, GDPR, and HIPAA.
- Promote the adoption of strong internal procedures, enhancing security and operational effectiveness.
- Differentiate the organization from competitors, providing a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Types of reports: Soc 2 Type 1 vs Soc 2 Type 2
The two report types that comprise SOC 2 compliance are SOC 2 Type 1 and SOC 2 Type 2. They differ according to the evaluation of time of the system and data security controls. Below is a table that highlights the main differences between the reports:
| Report type | SOC 2 Type 1 | SOC 2 Type 2 |
| What is it? | An audit report that assesses a service organization's control design in relation to the TSC at a specific point in time is known as a SOC 2 Type 1 report. | An audit report that assesses a service organization's control design in relation to the TSC over a specified period of time (typically 6-12 months) is known as a SOC 2 Type 1 report. |
| Example | To show that its infrastructure and security processes are built to safeguard customer data, a cloud storage provider may request a Type 1 report. | To demonstrate that its incident response and access control systems have been successfully maintained over the past 12 months, a SaaS provider might request a Type 2 report. |
Table 2: SOC 2 Type 1 versus Soc Type 2 reports.
What is SOC 3 compliance?
A service organization that provides a condensed, publicly accessible version of a SOC 2 report and complies with the TSC—Security, Availability, Processing integrity, Confidentiality, and Privacy—is said to adhere to SOC 3 compliance.
Organizations who wish to show a wide audience their commitment to data security and operational excellence without disclosing sensitive or detailed information included in SOC 2 reports find SOC 3 reporting helpful.
Benefits of SOC 3 compliance
- Prove the organization's adherence to operational reliability and data security standards and demonstrate public transparency.
- Increase trust and credibility with stakeholders, partners, and customers by making a compliance summary publicly accessible.
- Serve as a powerful marketing tool to attract new clients and differentiate the organization from competitors.
- Simplify communication of compliance with the TSC for non-technical audiences.
- Reassure a large audience without disclosing private or confidential information.
Publicly available summary report
An organization's SOC 3 report is comprised of a summary of the , which is usually publicly posted.
| Report type | SOC 3 |
| What is it? | A high-level, publicly accessible summary of a service organization's TSC compliance is called a SOC 3 public report. It is intended to offer broad assurance without revealing private or technical information and is based on the results of a SOC 2 Type 2 audit. |
| Example | Cloud Service Name has successfully completed a SOC 3 audit, demonstrating its commitment to securing client data through robust security and availability controls. This report assures our customers that Cloud Service Name meets the highest standards for data protection and system reliability . |
Table 3: SOC 3 report.
SOC 1 vs SOC 2 vs SOC 3
Here are the differences between each SOC compliance:
| SOC 1 | SOC 2 | SOC 3 | |
| What is the goal? | Focuses on reporting financial information. It evaluates controls relevant to a service organization's impact on a user entity's financial statements. | Emphasizes on the TSC. It involves data management to safeguard the company's and its customers' interests. | A condensed and publicly accessible version of SOC 2. Although it doesn't provide sensitive or in-depth information, it concentrates on the same TSC as SOC 2. |
| Who is the target audience? | Intended for user organizations and their auditors. Typically used by entities needing assurance for financial audits. | For stakeholders like business partners, regulators, or customers who require detailed assurance about non-financial aspects (e.g. security). | For a general audience, such as prospective customers, to demonstrate compliance without exposing sensitive details. |
| What does it include? | Includes controls relevant to financial reporting, along with management's assertion and the auditor's opinion. Follows the SSAE 18 standard. | Contains a detailed description of the system, the controls, and an auditor's opinion based on the TSC. It may also include tests of controls and results. | Provides a high-level summary of SOC 2 results, omitting detailed descriptions, test procedures, and results. |
| Whom is it applicable for? | Beneficial for service organizations whose payroll or billing systems affect financial reporting. | Pertinent to providers of services (such as SaaS and cloud computing) that handle sensitive data or need strong security procedures. | Ideal for marketing purposes, as it communicates compliance without sharing in-depth details. |
| Who can access them? | Limited to particular stakeholders who have an appropriate need to access the report. | Limited to particular stakeholders who have an appropriate need to access the report. | Publicly available, designed for broad distribution. |
| Example | To make sure that its outsourced payroll provider has the right controls in place to protect employee compensation data, a financial services company uses SOC 1 compliance. This compliance helps the company assure its clients that their financial records are handled securely and accurately. Additionally, the SOC 1 audit helps the business comply with financial reporting regulations. | To prove to its clients that it has put strict controls in place to safeguard sensitive data and ensure service availability, a SaaS provider can earn SOC 2 compliance. The compliance confirms that the supplier satisfies the TSC. This assurance helps the provider build trust with customers in highly regulated industries like healthcare and finance. | To demonstrate to the public that it complies with the TSC for availability and security, a cloud hosting provider can earn SOC 3 compliance. All stakeholders can access the SOC 3 report, which offers a high-level, non-technical overview of the organization's dedication to data protection. This helps the business draw in new customers by showcasing its reliability and transparency. |
Table 4: SOC 1 versus SOC 2 versus SOC 3.
How does a SIEM solution help in achieving SOC compliance?
By facilitating the adoption and monitoring of crucial controls mandated by SOC 1, SOC 2, and SOC 3 frameworks, a security information and event management (SIEM) solution can greatly assist an organization in attaining compliance with these standards. For each kind, a SIEM solution helps with compliance in the following ways:
1. SOC 1 compliance (Focus on financial reporting control)
| Feature | How does a SIEM solution help? |
|---|---|
| Log collection and monitoring | A SIEM solution will help in monitoring financial systems and applications (e.g. ERP or accounting software) for unusual activities or errors. Also, it helps to track changes to financial data and systems to ensure accuracy and completeness. |
| Access control monitoring | A SIEM solution will help in monitoring the logs accessed by users in the systems handling financial data to prevent unauthorized changes. Also, it helps to identify and alert on privilege misuse or unauthorized access. |
| Audit trial | A SIEM solution will help in providing detailed logs of all activities impacting financial systems, supporting auditors in verifying control effectiveness. |
Table 5: Features of a SIEM solution that helps in achieving SOC 1 compliance.
2. SOC 2 compliance (Focus on Security, Availability, Confidentiality, Processing Integrity, Privacy)
| Feature | How does a SIEM solution help? |
|---|---|
| Security | A SIEM solution provides real-time monitoring of security events and alerts on potential breaches and also detects anomalies that could compromise data security. |
| Availability | A SIEM solution will help track system uptime and will identify potential disruptions or failures. Also, it helps in maintaining service continuity through proactive monitoring. |
| Processing integrity | A SIEM solution helps in monitoring data processing systems to ensure that they operate accurately and without unauthorized modifications. Also, it helps to log and validate transaction integrity. |
| Confidentiality and privacy | A SIEM solution will identify and alert on unauthorized data access and exfiltration attempts. Also, it helps ensure encryption and data protection policies are enforced through monitored systems. |
| Audit readiness | A SIEM solution helps automate the generation of compliance reports that are specific for SOC 2. Also, it provides evidence of compliance with controls over data handling and security. |
Table 6: Features of a SIEM solution that helps in achieving SOC 2 compliance.
3. SOC 3 compliance (Focus on providing a publicly-available summary based on SOC 2 report)
| Feature | How does a SIEM solution help? |
|---|---|
| Demonstration of strong controls | A SIEM solution will help showcase that robust security monitoring and response systems are in place. Also, it provides metrics and summaries for high-level reports that demonstrate the organization’s commitment to security and availability. |
| Ongoing compliance assurance | A SIEM solution will provide continuous monitoring to ensure that the organization maintains compliance with SOC 2 requirements, which is the foundation for SOC 3. |
Table 7: Features of a SIEM solution that helps in achieving SOC 3 compliance.
SIEM features for SOC compliance
Here are a few capabilities of ManageEngine Log360 that can help enhance your SOC compliance.
- Centralized log management: A SIEM solution aggregates logs from multiple systems, providing a single source of truth for auditors.
Log360 automatically discovers the Windows and syslog devices on your network and ingests log data (refer to Figure 1). Additionally, it automatically imports log data from databases and applications like vulnerability scanners at predetermined intervals.
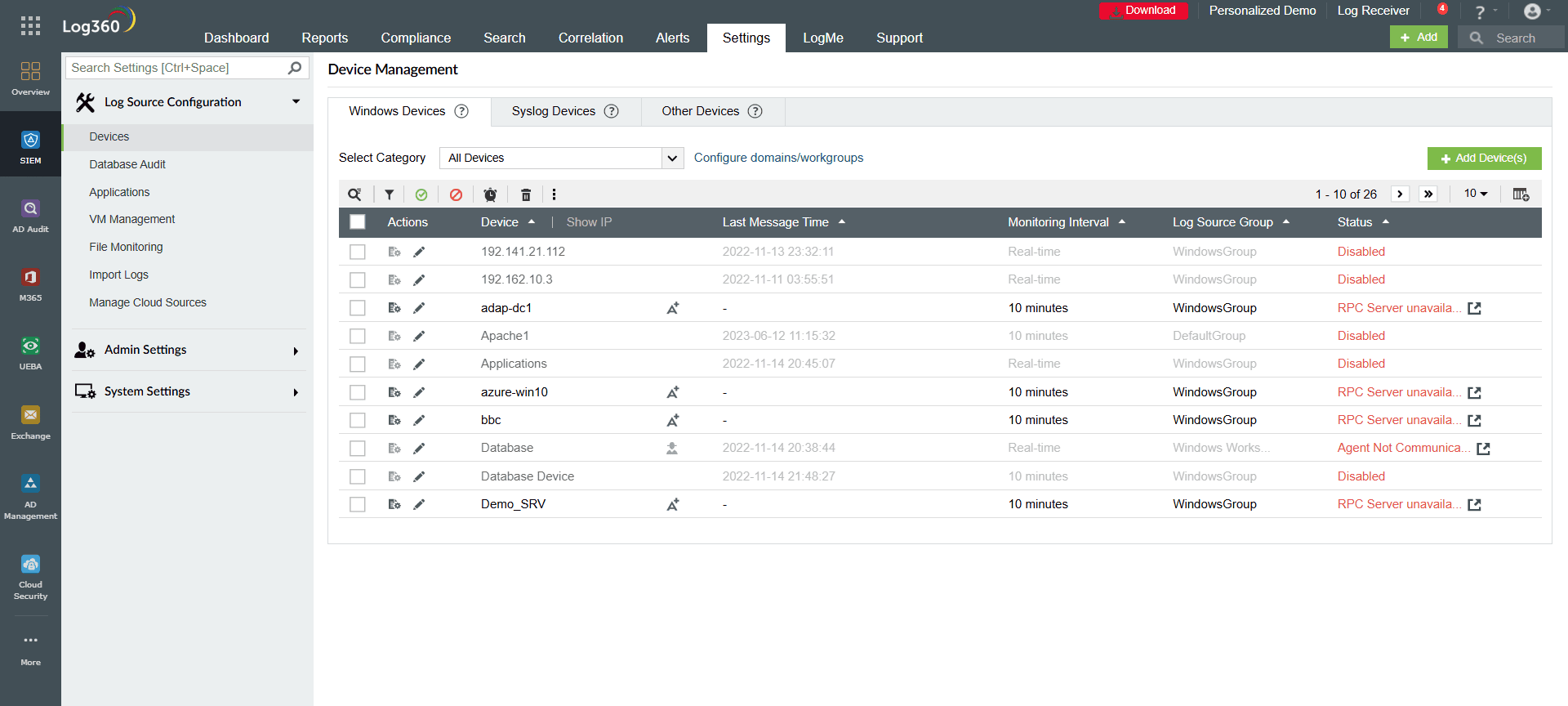
Figure 1: Log source configuration tab in Log360.
- Log monitoring: A SIEM solution provides real-time alerts on suspicious activities such as unauthorized access or privilege misuse. This will help in resolving the incidents as soon as possible.
Log360 provides real-time event alerts for important updates, including changes made to the devices or applications by the users. You can set up alerts by configuring the alert criteria according to your needs (refer to Figure 2). Alert criteria can also be created based on custom thresholds and user actions.
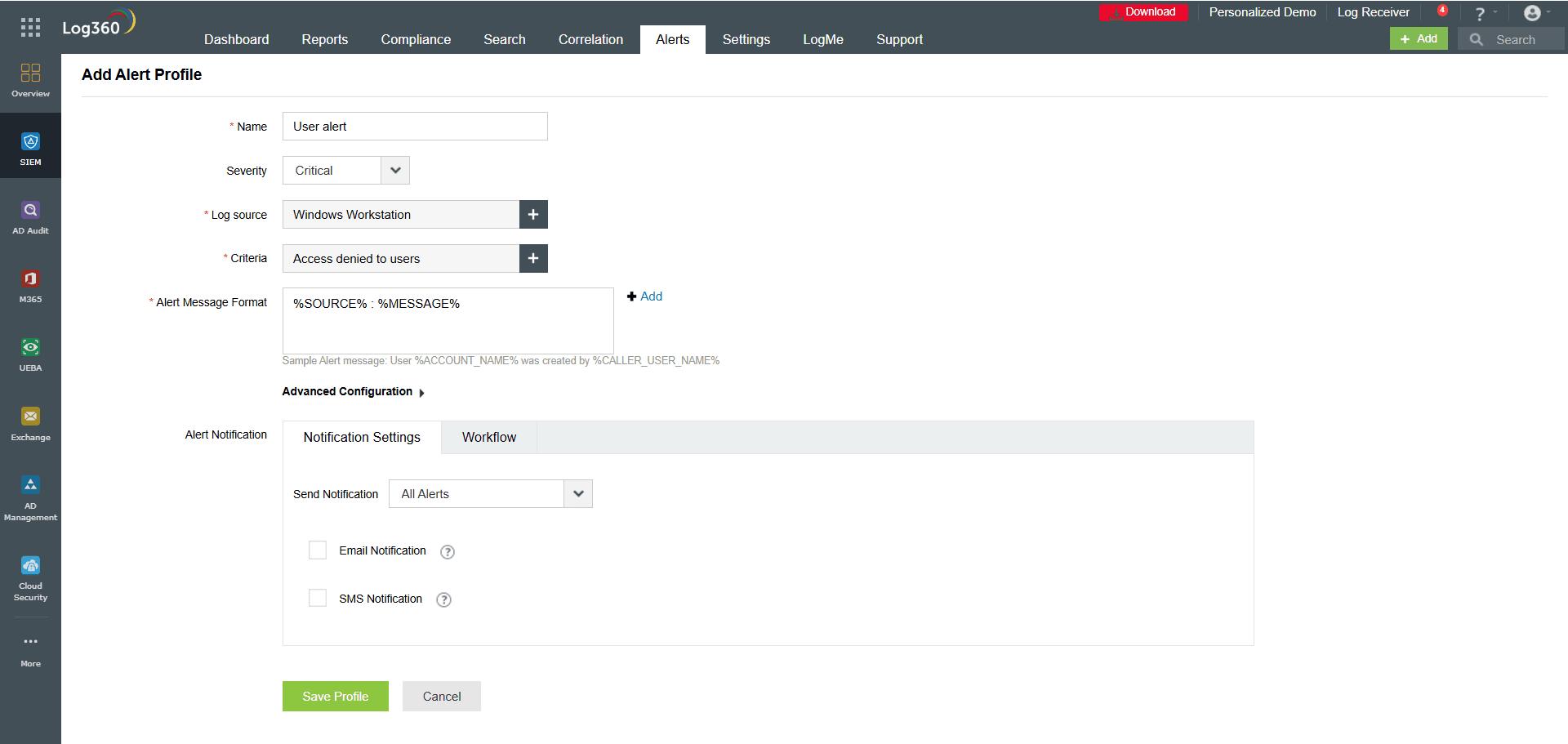
Figure 2: Creating an alert on the Alerts tab of Log360.
- Incident detection and response: A SIEM solution helps track security incidents and ensures timely response, which is essential for demonstrating operational controls.
Log360 enables you to create and execute incident workflows and automate common incident response steps (refer to Figure 3). When alerts are triggered, these workflows get executed automatically to remediate the incidents.
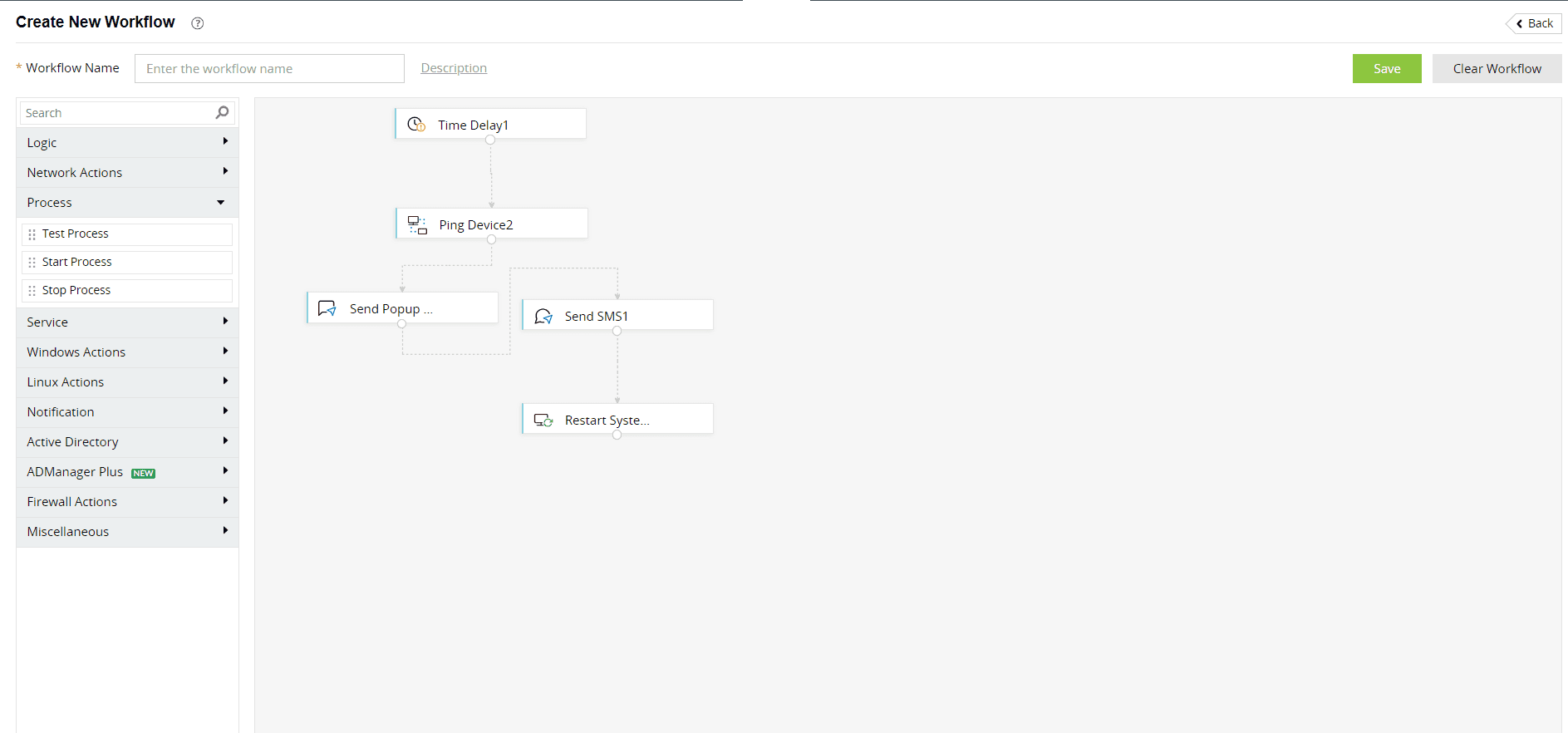
Figure 3: Creating incident workflows using Log360.
- Automated reporting and dashboards: A SIEM solution generates audit-ready reports tailored to SOC compliance requirements.
Log360 allows you to view dashboards and reports on all the file creations, deletions, changes, owner alterations, and permission modifications (refer to Figure 4). All failed attempts to access the data are also recorded. For your security team, these capabilities offer several advantages, including early detection of possible dangers like ransomware, malware, and IT sabotage. This helps your organization reduce its mean time to detect (MTTD) incidents.
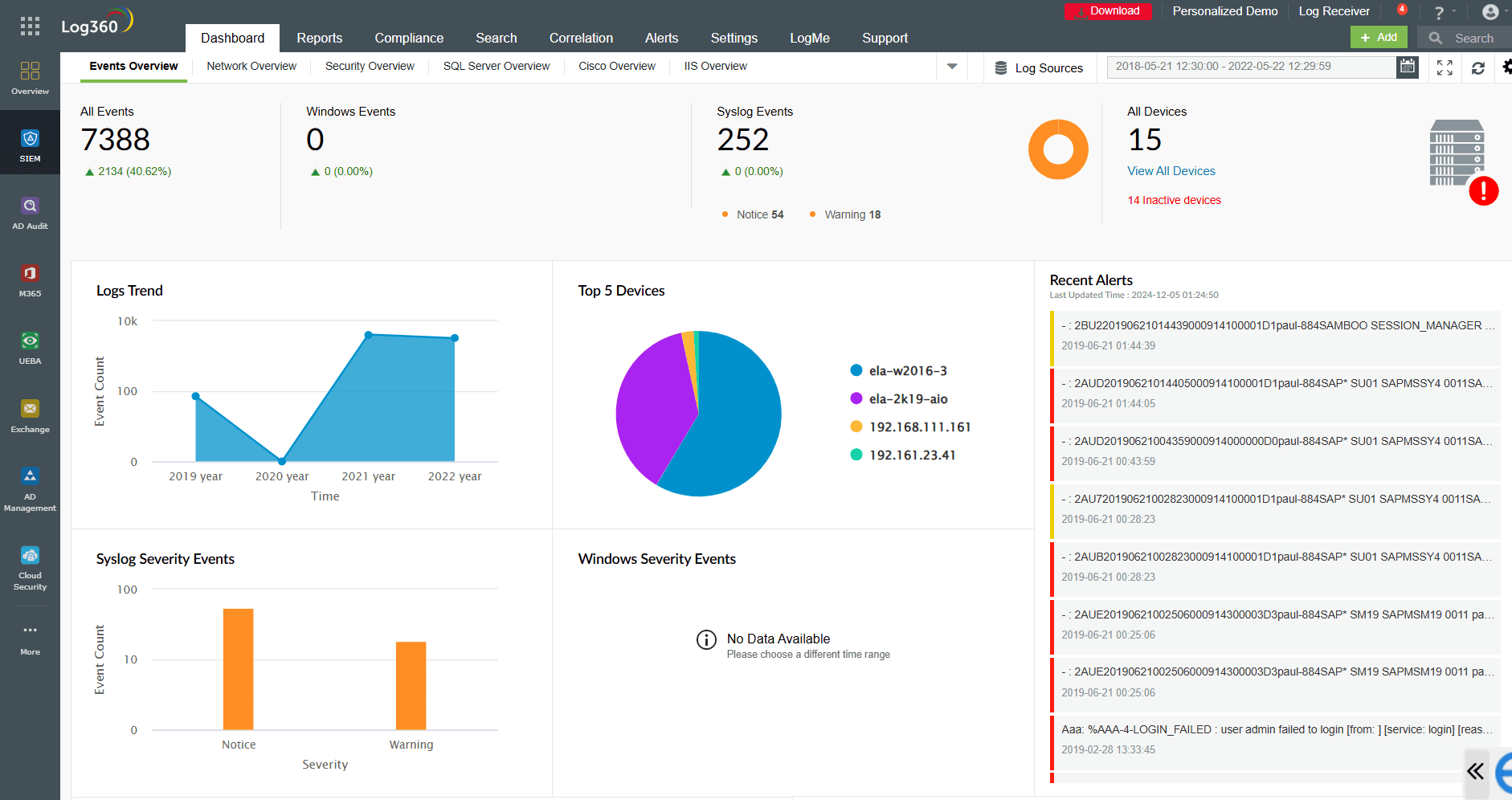
Figure 4: Dashboard view of all the activities that occurred in a device or application.
- Log retention and integrity: A SIEM solution stores logs for the required duration to meet compliance standards. Also, it ensures logs are immutable and tamper-proof, satisfying audit requirements for data integrity.
Log360 generates thorough reports (file monitoring reports, correlation reports, compliance reports, and more) with accurate integrity information (refer to Figure 5). These reports can be exported in multiple formats, including CSV and PDF. You can automatically receive the reports at regular intervals with the help of flexible report scheduling.
Figure 5: A Log360 report on all the event actions that occurred.
- Regulatory alignment: A SIEM solution offers pre-configured compliance templates for SOC 1, SOC 2, and SOC 3, simplifying the process of demonstrating compliance.
Log360 generates major compliance reports required for the IT department in various industries, such as healthcare, finance, etc. (refer to Figure 6).
Figure 6: Compliance reports in Log360.
Empower your enterprise !
Our cutting-edge security technology can help your security team reach its full potential! Are you ready to improve your threat detection and response capabilities? Sign up for a personalized demo of ManageEngine Log360, a comprehensive SIEM solution that can help you detect, prioritize, investigate, and respond to security threats.
FAQs
- 1. What is the difference between a SOC 1 and SOC 2?
-
Financial reporting controls are the main emphasis of SOC 1, particularly for organizations that affect their clients' financial statements. Controls pertaining to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy are assessed by SOC 2. While SOC 2 is crucial for technology and cloud service providers to safeguard data security and privacy, SOC 1 is mostly used by auditors for financial reporting. Financial impact is covered by SOC 1, while operational and security measures are evaluated by SOC 2.
- 2. What is the difference between SOC 2 and SOC 3?
-
With an emphasis on specific internal controls, SOC 2 assesses an organization's controls about security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. These same criteria are evaluated by SOC 3, which produces a more comprehensive report intended for the general public. SOC 3 is a summary report designed for wider public release, whereas SOC 2 studies are in-depth and targeted at particular stakeholders. SOC 3 is less granular and focuses on providing a high-level assurance of the organization's controls.
- 3. What is the difference between SOC 1 Type 2 and SOC 2 Type 2?
-
Although their scopes are different, SOC 1 Type 2 and SOC 2 Type 2 both assess controls in service organizations. Financial reporting controls are the main emphasis of SOC 1 Type 2, which evaluates how well a service provider handles client-relevant financial data. Non-financial controls are assessed by SOC 2 Type 2, with a focus on data security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. SOC 2 is more comprehensive in addressing security and privacy issues beyond financial operations, but both types are evaluated over time.
- 4. What is the difference SOC vs SOX?
-
SOC focuses on auditing IT systems and operational controls, such as security, availability, and confidentiality. SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act) is a U.S. federal law aimed at ensuring the accuracy of financial reporting and preventing corporate fraud. SOC is relevant to service organizations and their processes, while SOX applies to publicly traded companies and their financial practices. SOC reports assess IT and data controls, whereas SOX enforces internal controls for financial compliance. SOC is an audit framework, while SOX is a legal requirement. Both enhance organizational accountability but serve distinct purposes.



