Cloud infrastructures are primarily dominated by Linux-based machines, owing to advantages such as open source, lower costs, reliability, and flexibility. However, they are not immune to attacks by hackers, impacting the security of your cloud. One of the most prevalent methods of attacking Linux machines is through SSH channels. Let's find out what happens in an AWS SSH brute force attack and the ways to detect and defend the attack.
What is SSH?
Secure Shell (SSH) is an encryption-based network protocol that operates on port number 22 by default. This protocol establishes a remote access connection between two machines after authenticating with a password or a public-private key pair and sends encrypted data across the channel to ensure security on-premises and in the cloud.
The role of SSH in AWS cloud security
The shared security model proposed by Amazon Web Services (AWS) allows you to secure remote access to the hosted Linux instances through SSH. When an EC2 instance is launched, you'll be given the option to assign a key pair. AWS uses the user name along with a PEM file associated with the key pair to authenticate with the server and opens an SSH session.
SSH brute force attack on AWS
Leaving SSH services exposed is a common misconfiguration that increases the vulnerability of Linux systems. Brute-forcing SSH channels is a popular way of gaining access to the cloud. Attackers deploy bots known as bruteforcers to carry out these attacks. An experiment revealed that an AWS EC2 instance with exposed SSH services is likely to be attacked by the first bruteforcer bot in less than 10 hours of being deployed.
Once they have compromised the SSH service, they can infect AWS Linux hosts with cryptominers, replace legitimate executables with malicious ones, execute data breaches, and more.
To cover up their tracks, they can disable audit functions of the OS. They may also establish persistence by creating backdoors. One way is to insert an attacker-owned SSH public key to the authorized keys file on the server to ensure remote connection to the server without being noticed. Attackers can also initiate lateral movements with worm-like botnets to maneuver through the cloud and even eventually move to on-premises IT environments as well.
How to detect and defend SSH brute force attacks in AWS
- Deploying a security information and event management (SIEM) solution that supports analysis of events happening on cloud platforms can help you detect and mitigate SSH attacks on Linux AWS. Logs help in thoroughly tracking and analyzing incidents in the network. ManageEngine Log360, an easy-to-use SIEM solution, can help you simplify log management and enhance cloud security with out-of-the-box reports on AWS activities.
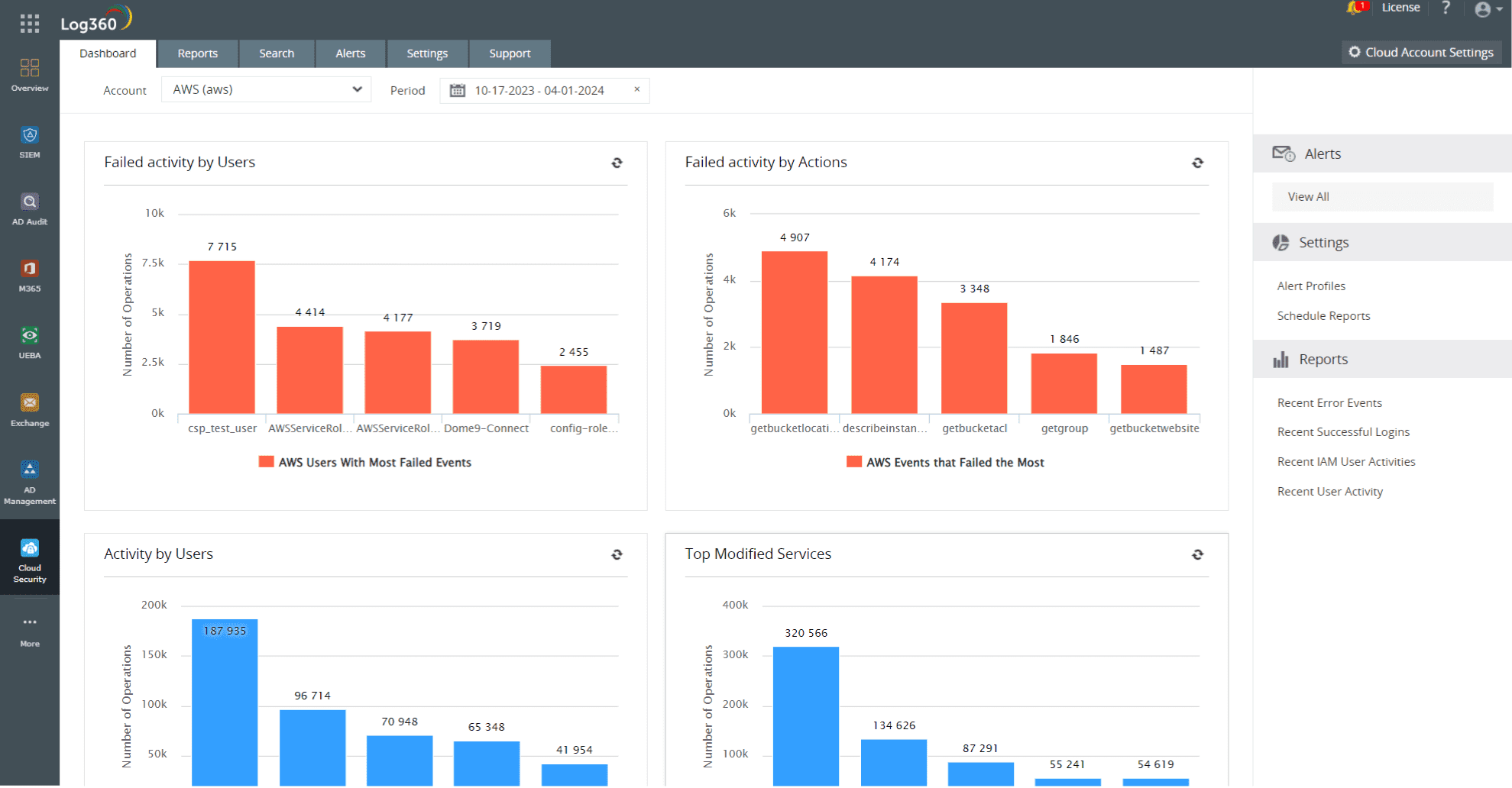
Figure 1: Comprehensive cloud security dashboard in Log360
- Monitoring AWS Linux instances for multiple failed logons in an unusually short period can help you detect a potential brute-force attack. Once a brute force attack is identified, you can note the IP address of the attacker and block it. Log360 provides detailed reports on recent logon failure activities in AWS that can indicate potential attempts of a brute force attack.
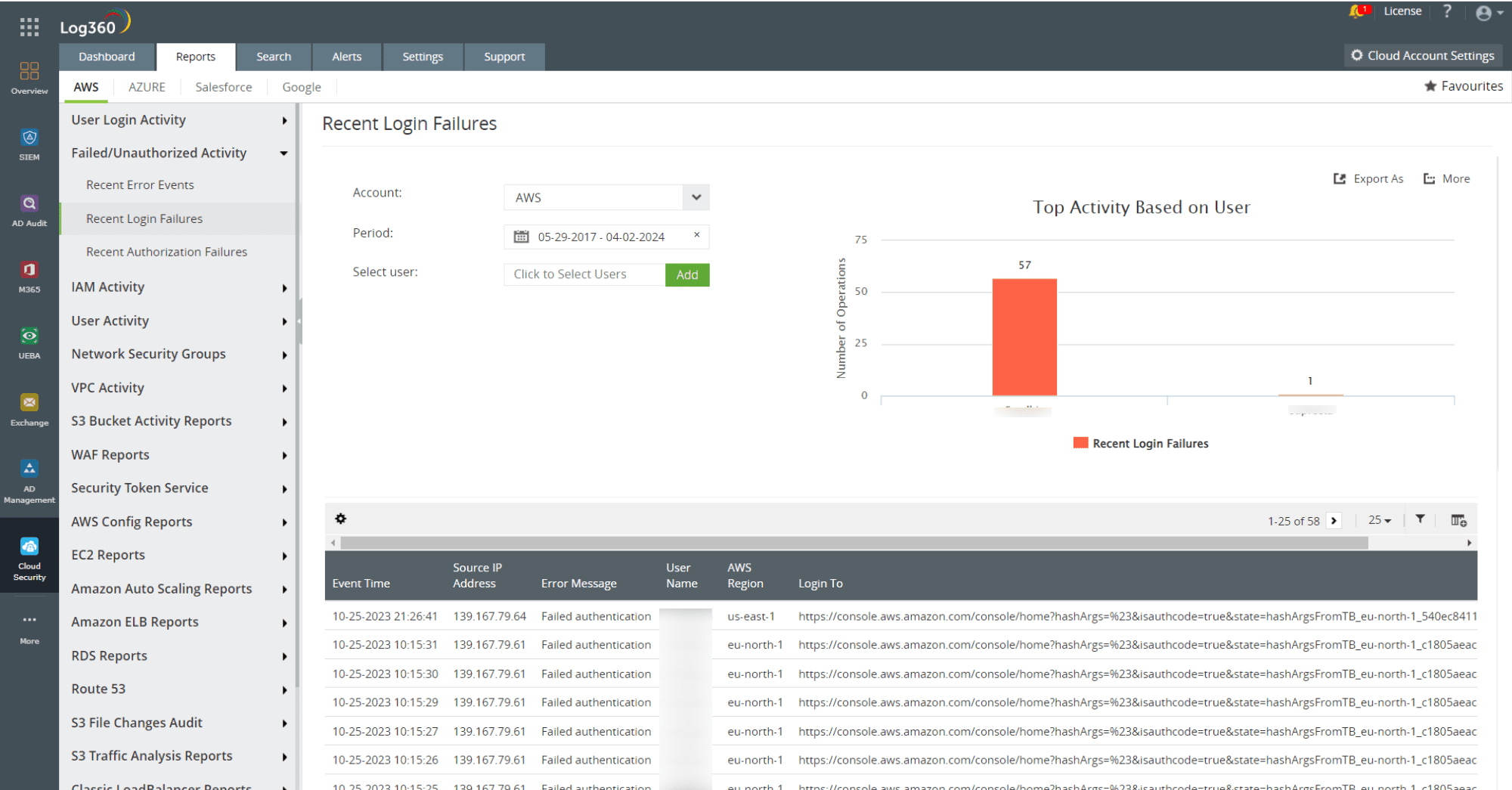
Figure 2: AWS login failure report in Log360
- Apart from brute forcing, attackers can gather SSH keys and credentials from source control, public repositories, or open buckets. They can also steal them from machines compromised in parallel or unrelated campaigns, or even purchase them on remote access markets where they are sold as a service. Analyzing recent key pair activities in AWS can help you identify suspicious attempts to modify SSH keys. Activities related to Linux EC2 instances can be monitored using EC2 reports in Log360 that provide detailed reports on EC2 key pair activity.
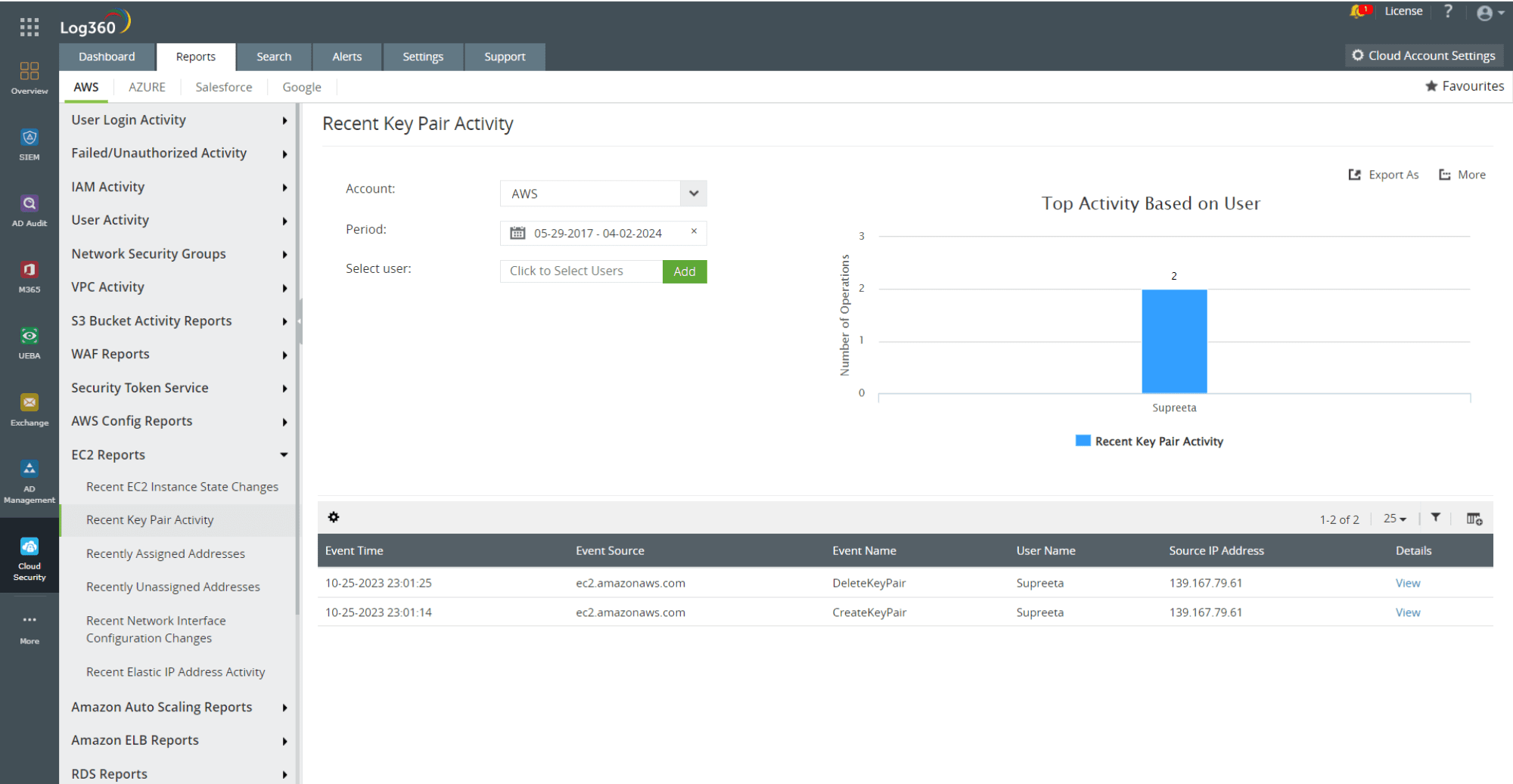
Figure 3: AWS EC2 key pair activity report in Log360
- To reduce the risk of SSH attacks, ensure none of your SSH services on your Linux hosts are exposed. Adding an extra layer of security, such as two factor authentication, also makes your Linux hosts less susceptible to brute-force attacks and ensures the security of the AWS cloud platform.
Enhancing cloud security with Log360
ManageEngine Log360 is a comprehensive SIEM solution that supports cloud platforms such as Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud Platform, Salesforce, and Microsoft Azure along with on-premises security monitoring. The solution enables you to secure your cloud infrastructure and helps you reinforce your cloud security posture with advanced threat detection, real-time correlation, alert generation, UEBA-powered anomaly detection and proactive incident response mechanism. You may wish to sign up for a personalized demo of Log360 to learn more.



