What is Shadow IT?
Shadow IT encompasses the use of hardware, software, and digital systems within an organization without the approval or knowledge of the central IT department. This phenomenon includes a range of activities, from employing unauthorized software and hardware to using approved tools in unapproved ways, such as sharing files through unsanctioned platforms or accessing company-managed tools through personal accounts.
Until recent times, IT departments had more or less complete control over technology decisions, but the emergence of cloud applications, mobile devices, and the ease of purchasing subscription services have led to a significant increase in shadow IT. The practice of shadow IT is often a response to the inability of centralized IT departments to meet the diverse needs of various departments, especially in large organizations. Shadow IT potentially creates a parallel IT ecosystem, separate from officially sanctioned IT activities, that causes serious implications for security, regulatory compliance, and overall IT efficiency.
Evolution of Shadow IT
Early Years (Pre 2000s)
- Increased accessibility to technology: With the advent of personal computers in the 1980s and 1990s, technology became more accessible to the average employee.
- Growth of basic software tools: Basic software tools, such as Microsoft Excel and Word, became staples in the workplace.
- Limited IT resources and response times: During the 1980s and 1990s, many IT departments were under-resourced and overwhelmed with requests.
Acceleration and Expansion (2000s-2010)
- Rise of the Internet and cloud services: The rapid boom of the Internet made it easier for employees to access a wide range of applications and resources without going through IT departments.
- Consumerization of IT: The blending of personal and professional technology use, characterized by employees bringing their own devices (like smartphones and tablets) to work, significantly contributed to the growth of Shadow IT.
- Remote work beginnings: As remote work started becoming familiar, employees relied more on their own devices and software, leading to further decentralization of IT control.
Modern Era (2010-Present)
- Advanced cloud computing and SaaS proliferation: The explosion of SaaS applications made it easier than ever for employees to find and use software without IT’s involvement.
- Remote work and COVID-19 pandemic: The pandemic has been a major catalyst for the growth of Shadow IT significantly increasing reliance on personal devices and external IT solutions.
- Increased IT complexity and specialized needs: As organizations grow and evolve, the IT needs become more complex and varied.
Examples of Shadow IT
Identification of shadow IT within an enterprise requires a consideration of common employee activities and the hurdles they face in daily tasks. Key questions about file creation tools, communication apps, document collaboration, and security measures can reveal instances of shadow IT. Shadow IT, comprising unauthorized third-party software, applications, and services, manifests in various forms within the workplace. Notable instances include:
- Productivity tools like Trello and Asana
- Cloud storage and file-sharing platforms such as Dropbox, Google Docs, Google Drive, and Microsoft OneDrive
- Communication and networking apps like Skype, Slack, WhatsApp, Zoom, Signal, Telegram
These tools are quickly embraced by teams due to their user-friendly nature, cost-effectiveness, or free availability. The phenomenon extends to personal devices like smartphones, laptops, USB drives, and external hard drives, facilitated by Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) programs. Traditional asset management systems face challenges in detecting and overseeing these devices.
Individuals may connect work email to personal devices to bypass security protocols, while others might opt for unauthorized tools over company-sanctioned ones for project management or PDF editing, respectively.
The Why Behind the Prevalence of Shadow IT
One of the main reasons for Shadow IT to evolve is a simple desire for quick technology access to encompassing cloud services tailored to specific business needs, often endorsed by third-party or in-house teams, bypassing corporate IT. This includes commonly used applications like Google Docs, Slack, and devices under bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies. Employees, sometimes unaware of the risks, may adopt shadow IT for its perceived benefits in efficiency or competitive advantage. Instances of shadow IT range from benign to potentially harmful, such as data theft.
The rise in shadow IT is also fueled by various other factors, including time-consuming IT approval processes, restrictive security policies, along with the ease of using cloud-based consumer applications. Misunderstandings about the time it takes to procure IT solutions lead to standard procedures being overlooked. A significant portion of employees use unapproved communication tools, and shadow IT now constitutes a major part of enterprise spending. Moreover, employees and teams often turn to shadow IT to boost efficiency and productivity, driven by familiarity with certain tools and the belief that these may outperform approved options. Many at times, teams, not just individuals, often bypass IT processes to quickly adopt new technologies they deem essential, like cloud services or specific software. Gartner reports that at 74% of technology purchases are at least partially funded outside IT departments, highlighting the shift towards business-led technology acquisition.
Challenges and Implications of Shadow IT
Shadow IT, often driven by the desire for convenience, introduces a range of potential risks and challenges for organizations, leading to various costs and consequences. Some of the main challenges of shadow IT are:
1. Financial implications
Shadow IT can result in extra costs for organizations due to the use of unauthorized technology and equivalent enterprise software. This can lead to overspending on duplicate products and potentially paying premium rates instead of negotiated discounts.
2. Cybersecurity and compliance risks
Lack of proper reviews or security assessments in shadow IT adoption can introduce vulnerabilities to cyberattacks and non-compliance with regulatory requirements. This exposure puts sensitive data and intellectual property at risk.
3. Performance and user experience issues
Shadow IT often bypasses the rigorous IT review process, which could lead to performance problems and user experience issues within the existing environment.
4. Vendor and licensing problems
Deploying technology without IT involvement can result in issues with vendors, especially if unauthorized applications lack the necessary licenses. This can potentially incur substantial fees.
5. Missed opportunities
Choosing shadow IT over official IT channels may lead to missed opportunities for the IT team to develop unique, competitive technologies in-house or make more strategic purchases.
6. People issues
Managing suspected shadow IT users, retaining legal expertise for IT-related litigation, and addressing potential legal costs in cases of employee termination for security breaches.
7. Technology and facilities operations
Expenses related to purchasing specialized technology to track shadow IT, dismantling unauthorized activities, reconfiguring network resources, and addressing data center infrastructure issues.
Shadow IT can also exacerbate vulnerabilities, increasing the likelihood of ransomware and other information security incidents, adding to the overall risk and cost burden for organizations. While shadow IT may offer temporary convenience to some employees, its broader implications for security, compliance, operational efficiency, and financial stability are significantly adverse and require careful management.
Essential Capabilities of Shadow IT Management Solutions
Comprehensive Cloud Traffic Monitoring
Gain full visibility and control over cloud application usage with the ability to monitor web traffic to all websites and web servers. The capability encompasses techniques such as deep packet inspection to verify the integrity of network traffic and employs robust encryption methods to maintain secure communications across the cloud environment.
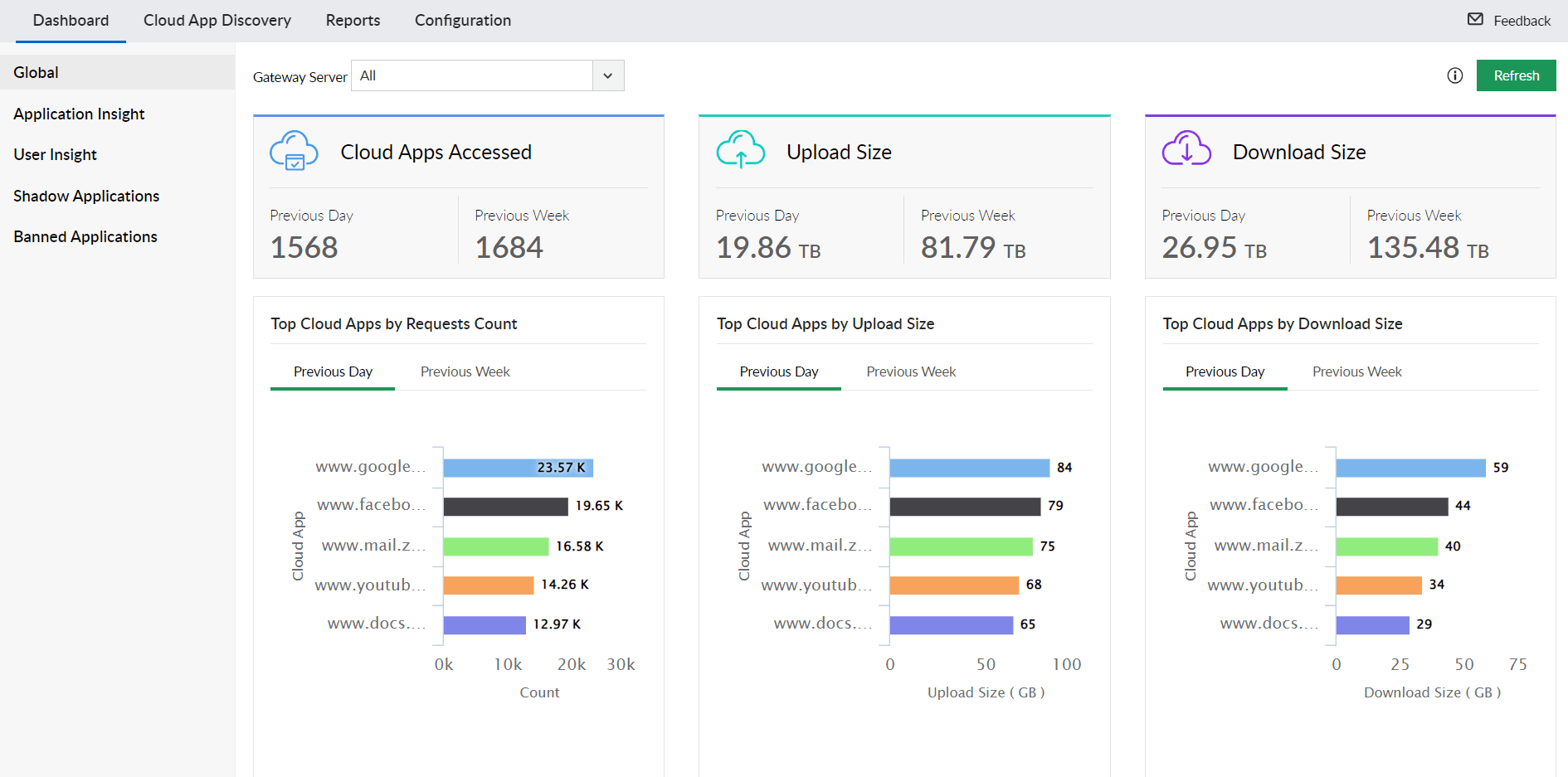
Unauthorized Application Usage and Detection
Detect and manage shadow applications, those that are not officially sanctioned or banned by your organization. Get detailed granular insights into application usage, identify top cloud applications and users based on their activity, and mitigate potential security risks.
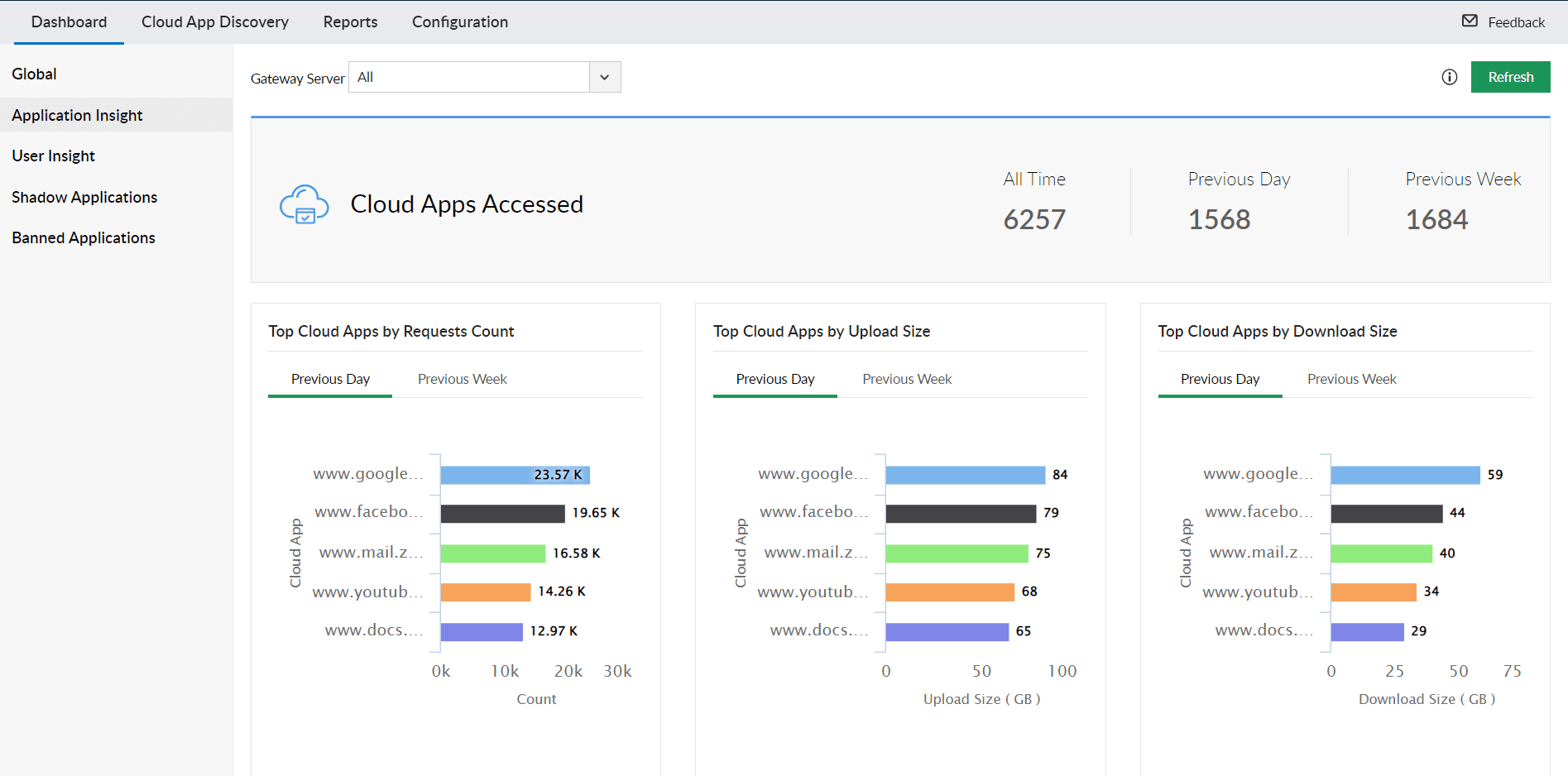
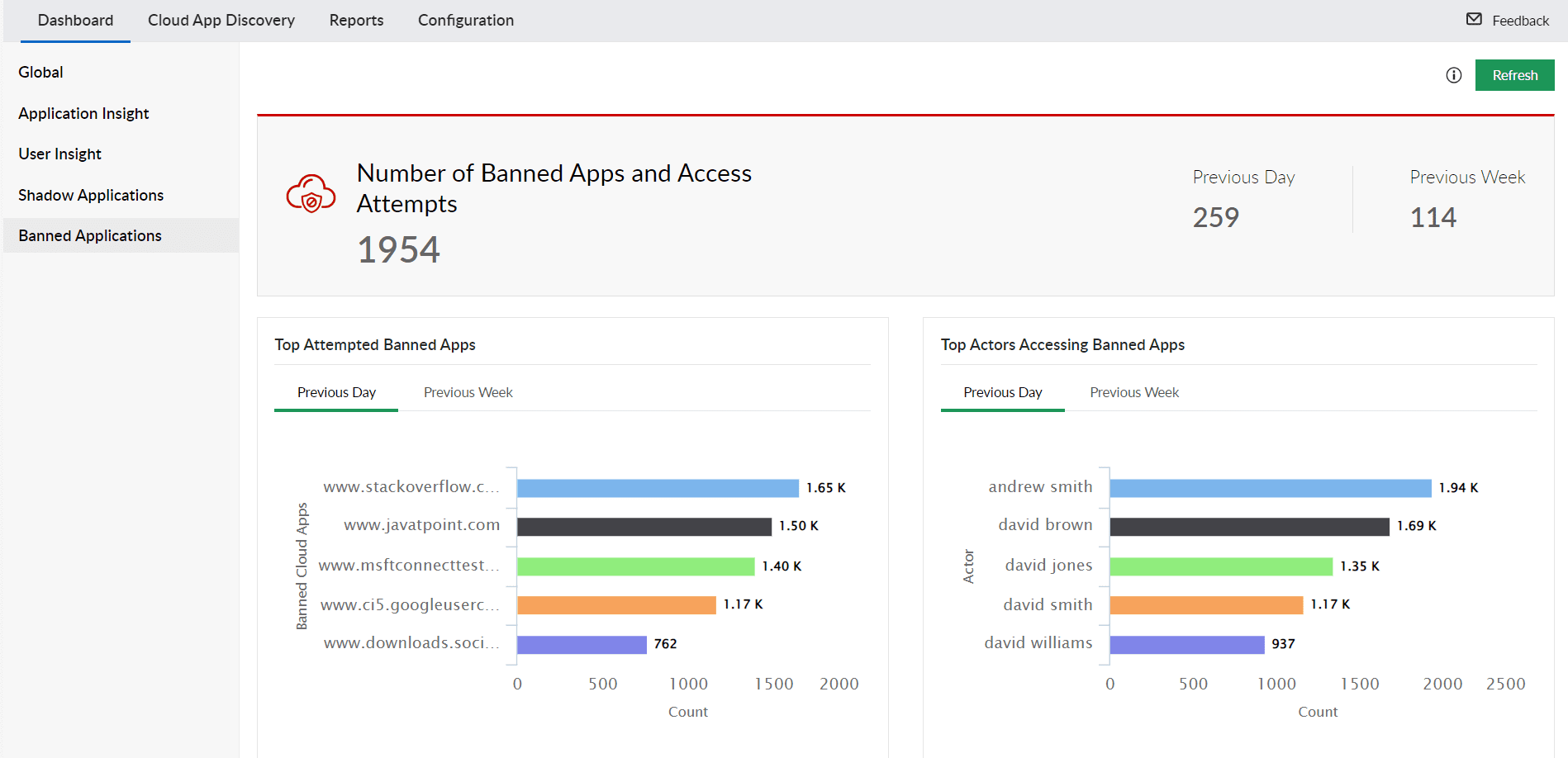
Sanctioned and Banned Application Management
Efficiently categorize cloud applications as either sanctioned or banned according to your security policies with an easy-to-use interface for adding or removing applications. Monitor sanctioned applications for abnormal traffic to prevent attacks, and block untrusted or banned applications to safeguard your network.
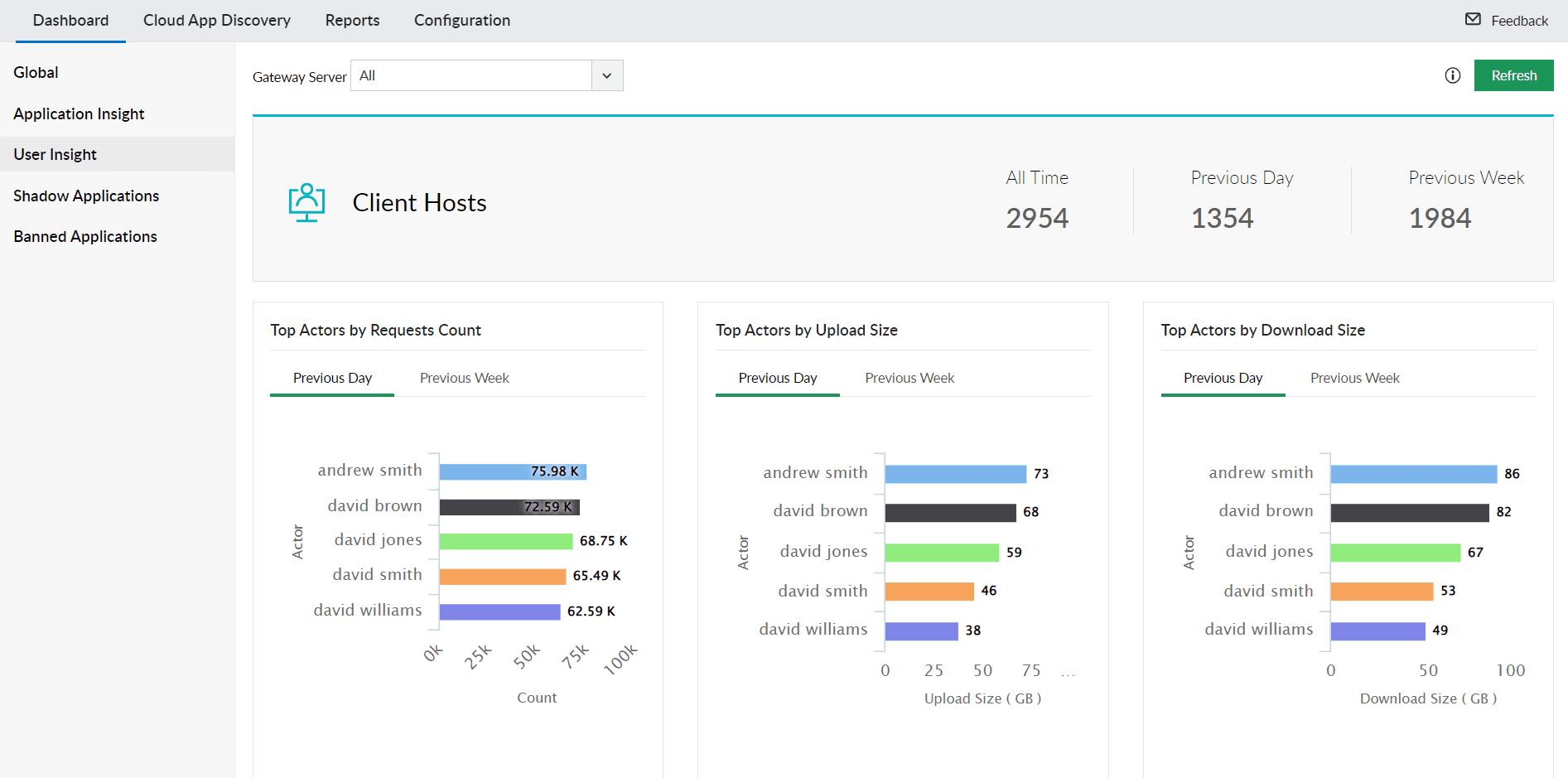
User Access and Activity Insights
Analyze user behavior and access patterns to cloud applications with actionable insights. This helps in identifying potential internal threats and ensures compliance with security policies. Track metrics like top users by request count, access to banned applications, and top shadow activity by users.
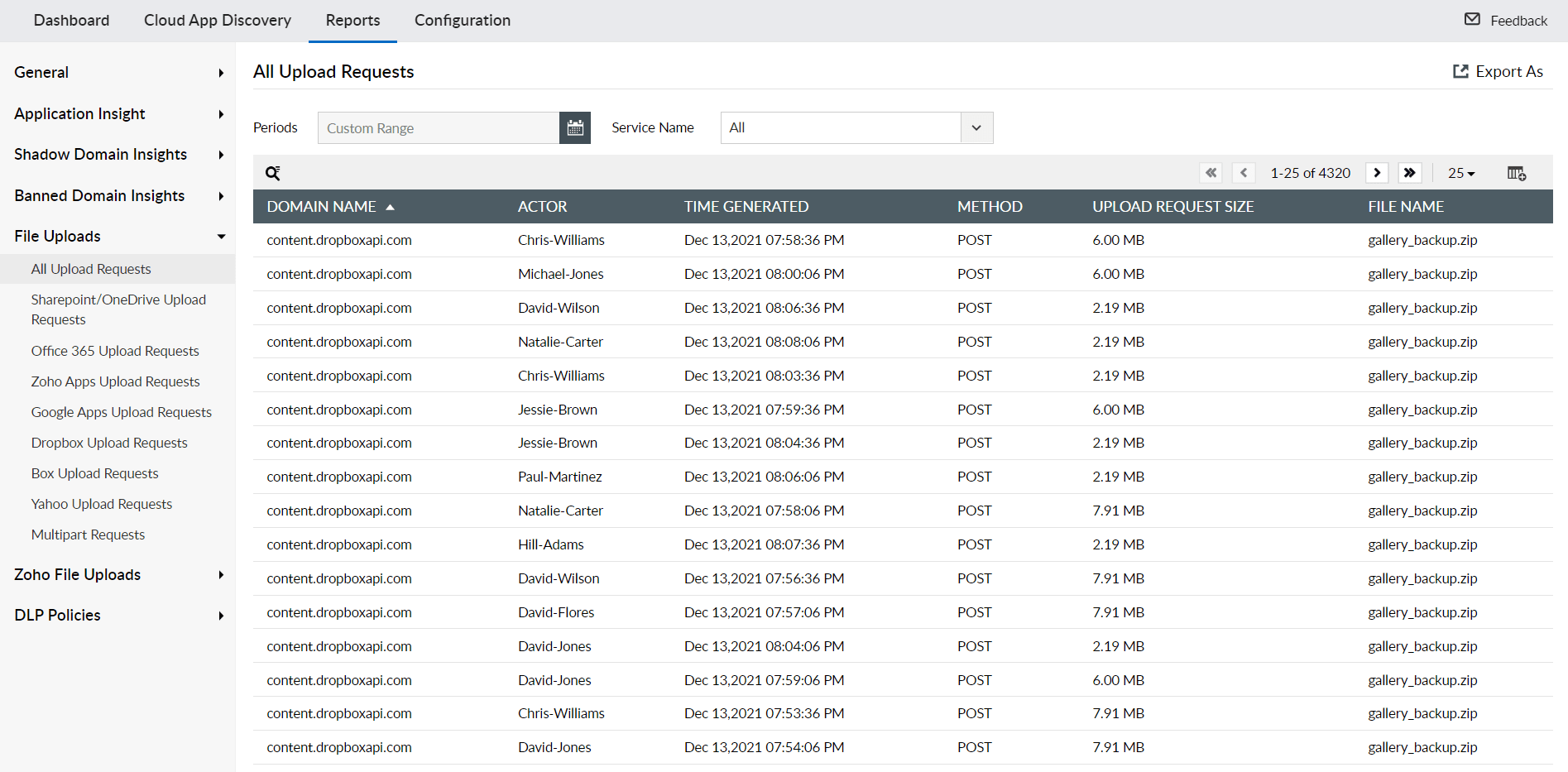
File Upload Monitoring and Security Analysis
Keep track of all file upload activities to detect malicious web activity and data theft. Monitor successful and failed file upload requests, with specialized reports for major cloud storage services like SharePoint, OneDrive, and Dropbox. This capability is crucial for preventing data breaches and ensuring secure file sharing practices.
Establishing Shadow IT Policies
To navigate the challenges posed by shadow IT and to establish a framework for secure, compliant, and efficient technology usage, organizations can institute a shadow IT policy. This policy serves as a set of guidelines and protocols crafted to address the adoption, approval, and management of new technologies, aiming to mitigate risks, control costs, and ensure operational integrity. Establishing a robust shadow IT policy is integral to an organization, guiding the adoption, approval, and management of new hardware and software.
Crafted by IT departments, these guidelines specify acceptable applications, devices, and technologies for work, reducing noncompliance and proving compliance during IT audits. Collaboration is key in creating an effective shadow IT policy, involving IT, security, HR, legal, and audit departments. Addressing people, process, technology operations, security operations, facilities operations, financial performance, and company performance issues is crucial for a comprehensive policy. Additionally, external expertise may be enlisted to address disruptions caused by significant shadow IT events.
Key Steps for Creating an Effective Shadow IT Policy:
1. Policy framework:
The policy should encompass key sections such as the objective, intended audience, ownership, monitoring and enforcement methodology, accountability, and employee responsibility.
2. Establishing IT procurement processes:
A critical component of a robust shadow IT policy is the creation of an IT procurement process. This involves outlining clear procedures for proposing and accepting shadow IT systems or projects.
3. User education and support:
Educating users is essential for fostering understanding and garnering support for the shadow IT policy. This step enables IT to explain the associated risks, providing practical examples of acceptable practices.
4. Continuous identification and classification:
Continuous identification, listing, and classification of shadow IT assets are imperative. Categories may include sanctioned, authorized (low danger), and prohibited (high danger).
5. Multifaceted collaboration:
Collaboration across the organization is vital for a comprehensive shadow IT policy. This extends from security considerations to HR, IT operational processes, tech operational processes, financial processes, security processes, PR and communications, and ongoing employee education.
6. Financial implications:
Financial implications and potential noncompliance areas should be addressed in collaboration with the accounting department. This ensures a holistic approach to managing the financial aspects of shadow IT.
7. Ongoing employee education and communication:
Ongoing employee education is crucial, covering the risks of shadow IT, policy details, approved technology, and how to identify and respond to security threats.
How to Manage Shadow IT?
To manage shadow IT within an organization effectively, a holistic and proactive approach is essential.
Here are some key strategies that can be adopted:
1. Implement shadow IT detection tools:
Utilize tools like shadow IT discovery software and Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs) to monitor and analyze both approved and unauthorized systems. This includes employing solutions for continuous monitoring and instant alerting to cyber threats.
2. Enhance security and risk management training:
Elevate employee awareness through comprehensive training sessions. Educate them about the risks associated with shadow IT and best practices for secure technology use, including the dangers of using personal email for corporate resources.
3. Promote open communication and collaboration:
Encourage a culture of open dialogue between IT teams and employees. Understand their technology needs and preferences, fostering a collaborative approach to selecting and using IT resources. Regular dialogue with department managers help align security requirements with IT needs.
4. Develop comprehensive IT policies and governance frameworks:
Establish clear, company-wide IT policies and a practical governance framework that considers flexible working arrangements and departmental needs. This should also include updating Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies and establishing protocols for rapid responses to shadow IT detections.
5. Implement access and application controls:
Enforce stringent access controls, like multi-factor authentication, and maintain an inventory of all applications in use. Block dangerous applications and establish an internal app store containing approved software to reduce confusion and risks.
6. Regular audits and risk assessment:
Conduct regular audits to identify unauthorized software or services and assess each instance of shadow IT individually to understand specific risks. Implement proactive measures for continuous detection and mitigation.
7. Encourage cloud adoption and prioritize end-user experience:
Support cloud integration and adoption while maintaining control over the selection of cloud applications. Understand employee preferences and invest in tools that align with their needs for long-term benefits.



