The advent of cloud computing, IoT, and the increasing trend of remote working have necessitated a shift from traditional perimeter-based security models to more flexible and adaptive frameworks. Due to this shift, numerous entry points have emerged that malicious actors might exploit, and the typical security approach is unable to safeguard all of these areas. Cybersecurity mesh can be useful in this situation.
According to Gartner "Cybersecurity mesh, or cybersecurity mesh architecture (CSMA), is a collaborative ecosystem of tools and controls to secure a modern, distributed enterprise." The idea behind the concept is to build a "mesh" of interoperable security products that can cooperate to offer all encompassing defense against cyber threats. It is achieved by following a distributed strategy for network and infrastructure security that enables the security perimeter to be set up around the identities of users and computers on the network. Cybersecurity mesh also helps to break down silos between different solutions, thereby letting them work together more efficiently.
Below is a comparison table that illustrates the differences between the traditional security approach and CSMA, which emphasizes how CSMA offers a more adaptable and modernized approach to network security in response to the evolving threat landscape and distributed network environments.
| Aspect | Traditional security approach | Cybersecurity mesh architecture (CSMA) |
|---|---|---|
| Perimeter defense | Relies heavily on a static perimeter defense, such as firewalls and VPNs, to protect the network. | Moves away from a fixed perimeter and emphasizes decentralized security. |
| Trust model | Typically follows a perimeter-based trust model where entities inside the network are trusted by default. | Adopts a Zero Trust model, assuming that no entity is trusted, and verification is required for all access. |
| Network boundaries | Often based on physical or logical network boundaries, making it challenging to protect distributed resources. | Offers flexible protection for resources, regardless of their location or type, within a unified strategy. |
| Access Control | Typically relies on network segmentation and VLANs, which can be complex to manage and lack granularity. | Implements microsegmentation for fine-grained access control and reduced lateral movement for attackers. |
| API Integration | May lack native integration with applications and services, making it challenging to secure modern software. | Utilizes API-driven security to integrate controls directly into applications, enhancing security natively. |
| Continuous monitoring | Monitoring may be periodic, lacking real-time insights, and making it harder to detect and respond to threats promptly. | Incorporates continuous real-time monitoring and analytics to detect and respond to threats proactively. |
| Automation | Limited automation capabilities may result in slower response times and human errors in security policy enforcement. | Employs automation for security policy enforcement, threat detection, and response, enhancing agility and accuracy. |
| Global deployment | May struggle to provide consistent security across globally distributed locations. | Supports global deployment, ensuring consistent security policies and controls across geographically diverse sites. |
CSMA provides visibility, control, and protection against cyber threats, enabling organizations to better manage security risks and respond to threats effectively. It is made up of four foundational layers, each of which supports for a specific task and responsibility.
This layer focuses on collecting and analyzing all the real-time security data from various security tools. Once analyzing all the data, it will concoct an effective threat response. Solutions like SIEM, SOAR, and UEBA -powered tools help to examine potential threats and trigger threat response.
It helps to manage identity and access control in a decentralized and distributed manner. Due to its decentralized network of nodes, there is no single point of vulnerability, thereby making it a reliable approach. It includes decentralized identity management, adaptive access, entitlement management, directory services, and identity proofing capabilities.
It helps to manage cybersecurity policies and implement security posture across an entire organization's network and infrastructure. With the help of CPPM, organization can enforce security policies across all devices and applications. This certifies that all assets are protected against vulnerabilities and that compliance with regulatory requirements are maintained.
This layer involves the aggregation of security data from multiple sources and it is then presented in a single dashboard. This helps the security analysts to monitor and analyze security events or incidents across the organization in real time. The modular dashboards help the security teams to identify and respond to threats easily by providing information like security alerts, compliance reports, system performance metrics, etc.
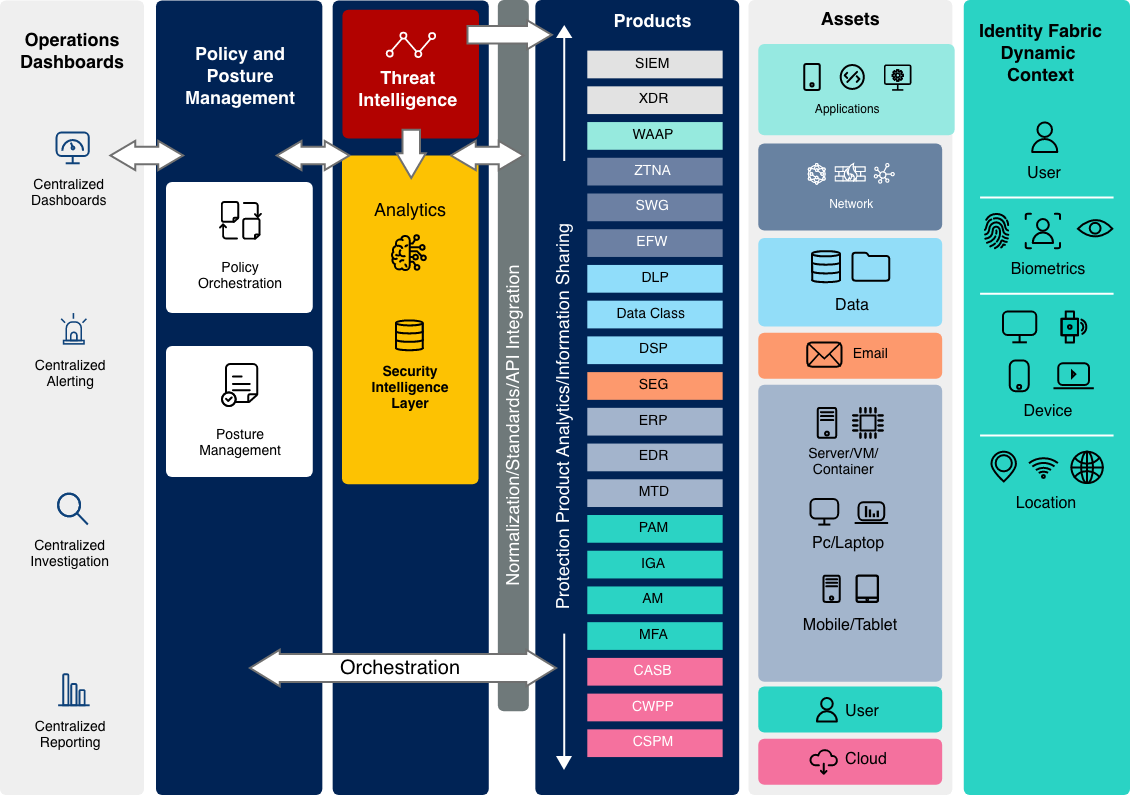
The Zero Trust architecture is a security model which goes by the principle "never trust, always verify." Therefore it will continuously examine user activities and their access privileges. CSMA is an extension of Zero Trust and it protects each device and access point. It is mapped out in such a way that it is more flexible and adaptable to create a unified strategy.
CSMA acts as a go-to solution to defend against the alarming rise of cyber threats as it provides security throughout the enterprise, thereby letting for a more granular and responsive security model. As organizations continue moving towards a distributed or a remote work setting, a decentralized approach is more preferred. Also,Gartner predicts that organizations that do adopt cybersecurity mesh architecture are likely to see a reduction on the financial impact of security incidents by 90%.
The following benefits will explain why adopting CSMA for an organization will improve security posture.
By integrating the cybersecurity mesh with threat intelligence feeds and services, we can identify and correlate not only threat events with known indicators but also enhance security analytics with external threat information. This helps IT admins to detect and mitigate emerging threats and sophisticated attack techniques.
A cybersecurity mesh enables the correlation and analysis of security logs and events from various networked devices and services. With the help of this skill, security analysts can spot trends, find correlations between seemingly unconnected occurrences, and find covert indicators of compromise (IOCs). It aids in the detection of insider threats, complicated assault scenarios, and advanced persistent threats (APTs).
The 4 layers of CSMA are built around the core capabilities, therefore it allows an organization to plan a secure architecture and utilize best solutions. Because of the architecture's flexibility in terms of security, it keeps the evolving infrastructure protected consistently.
CSMA helps security teams to collaborate with each other or with various other security solutions. This helps to improve the speed and efficiency of threat detection, response time to threats, security analysis, mitigation techniques, prevention solutions, etc.
The CSMA mesh is designed to be scalable and adaptable because when organizations add more devices and resources to their networks the mesh can expand to accommodate them. This benefit is vital in the era of IoT and remote work, as these result in users and devices growing rapidly.
Due to the intricacy of cybersecurity, organizations find it difficult to maintain their security in-house. MSSPs provide specialized expertise and technologies to businesses as they offer better security, mitigate cyber risks, and implement long-lasting IAM solutions.
A decentralized architecture with distributed security enforcement points and controls should be used to construct the mesh. This decreases the likelihood that the system will be compromised by a single point of failure and eliminates dependence on a single point of control.
In recent years there has been a rise in phishing attacks and cyber threats, and the existing approaches are not sufficient to protect an organization. With the help of CSMA, one can protect their organization's security infrastructure and also create an environment that is secure and scalable.
Organizations that deploy CSMA would need solutions that work well together to make sure that all nodes are visible and facilitate centralized management. To ensure that all of these linked solutions recognize and react to the same threats and warnings, they should also leverage a common threat intelligence database. Insider threat management, DLP, CASB, IAM, SIEM, and SOAR are among the several solutions needed to adopt a CSMA approach.
To integrate CSMA with an existing security solution, security analysts should follow certain criteria for an effective implementation like:
Security analysts should integrate the available technologies in each layer and create a cohesive cybersecurity mesh. They should also configure and test if the new solutions are working seamlessly together with the existing ones.
Comprehensive visibility into network activity, device behavior, and security events should be made possible via the mesh. To gather and analyze security-related data from diverse sources, it should include reliable monitoring capabilities. Logs, telemetry, network flows, and threat intelligence feeds fall under this category.
Create incident response workflows and processes that use the integrated security infrastructure. Define the handling and response to security alerts and incidents discovered by the cybersecurity mesh and the current security solution.
Businesses are evolving rapidly and are moving towards cloud-based infrastructure for storage but can't notice any security threats that come with these changes. Cybersecurity mesh helps to protect your network from threats and helps to elongate the perimeter-based security policy, to make better decisions and also encourages integration and collaboration in your organization.
Zoho Corporation Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.