Related content
The cybersecurity landscape in 2025 is defined by a paradox: while GenAI empowers defenders with predictive analytics and automated responses, it also equips threat actors with tools to launch hyper-targeted attacks at unprecedented scale.
This escalation coincides with a 47% surge to previous years in cyberattacks per organization, averaging 1,925 weekly attacks globally, according to the CheckPoint Software’s Global Cyber Attack Report (Q1 2025). Enterprises now face a critical imperative: adopt unified security platforms that centralize visibility, automate threat detection, and unify compliance and risk management.
Modern security information and event management (SIEM) solutions have evolved beyond siloed log management into AI-powered command centers and central nervous system of SOCs. By integrating AI-driven analytics, Zero Trust principles, and cloud-native architectures, SIEMs now enable organizations to proactively manage risk, reduce attack surfaces, and stay ahead of adversaries.
SIEM solutions as the central hub: From compliance to customization
Historically, SIEMs are synonymous with log aggregation, retention, and reporting for compliance audits. Contemporary SIEM platforms have transcended their original role as log management tools, now prioritizing threat detection, investigation, and response (TDIR) and real-time behavioral analytics. The shift towards predictive security modeling with the adoption of user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) enables enterprises to identify advanced persistent threats, supply chain attacks, and even AI-powered campaigns.
SIEM solutions now act as the glue that binds disparate tools like endpoint detection and response (EDR), extended detection and response (XDR), and cloud security platforms. Key advancements include:
- Integration-centric design: Seamless interoperability with existing tools (for example, SOAR, firewalls) to automate workflows.
- Customizable analytics: Tailored analytics decode threats through behavioral baselines and risk-scoring models to cut through clutter, spotlight critical incidents faster, and provide compliance-ready reporting.
- Unified visibility: Correlating data across endpoints, networks, and cloud environments to identify known threats like lateral movement, privilege escalations, which are otherwise difficult to detect.
ManageEngine Log360 customer stories
Unlike XDR, which focuses narrowly on threat detection and remediation, SIEMs address the broader risk landscape, including compliance mandates (for example, the GDPR, CCPA) and long-term forensic analysis. This makes SIEM indispensable for enterprises aiming to balance proactive defense with regulatory adherence.
It is important to distinguish SIEM from other security solutions. For example, XDR focuses primarily aggregating data from various tools and stitch them together for threat detection and remediation, functioning similar to a SIEM. While XDR is crucial for rapid response, SIEM takes a broader view, encompassing data retention and compliance requirements as well.
SIEM solutions provide a larger picture of risk management, enabling organizations to proactively address potential threats before they get exploited to gain a deeper understanding of the enterprise's attack surface.
Security-as-data: How AI and Zero Trust adoption extend SIEM’s reach
With "security as data" a core principle, modern SIEM delivers the visibility and control necessary to navigate today's complex threat landscape. A SIEM's workflow that incorporates AI and Zero Trust principles further extends this security fabric across the entire enterprise's ecosystem, rather than limiting it to individual tools.
Expert talks:
By ingesting petabytes of structured and unstructured data, SIEM solutions now have started leveraging AI to:
- Detect anomalies in real time (for example, unusual login attempts, data exfiltration).
- Predict attack vectors using behavioral analytics.
- Automate investigation workflows, reducing mean time to respond.
Zero Trust architecture further enhances SIEM efficacy by enforcing continuous verification of user and device identities. For example, integrating SIEM with identity providers (for example, Okta, Azure AD) ensures policy violations trigger immediate alerts, shrinking the attack surface.
Evolving core capabilities of SIEM in 2025
In 2025, modern SIEMs are defined by three core capabilities—cloud-native or cloud-based architecture, AI for TDIR, and a unified security console that bridges threat detection, compliance, and risk management. These advancements enable organizations to combat today's dynamic threat landscape while future-proofing their defenses. Here are three core capabilities that SIEM solutions are adopting in 2025.
Cloud-native or cloud-delivered: Agility meeting scalability
One of the major complexities of legacy SIEMs is their burdened on-premises infrastructure and rigid architectures, struggle to keep pace with the explosive growth of data in hybrid environments.
Modern SIEM solutions prioritize cloud-native deployments, leveraging the elasticity of platforms like AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and Zoho Cloud to ingest, process, and analyze petabytes of data in real time. This shift eliminates the cost and complexity of maintaining physical servers while enabling:
- Scalability: Automatically adjust resources during traffic spikes (for example, DDoS attacks or merger-driven data surges).
- Seamless multi-cloud integration: Native connectors for AWS CloudTrail, Azure Sentinel, and Kubernetes clusters provide visibility into misconfigurations, shadow IT, and lateral movement across distributed environments.
- Cost efficiency: Pay-as-you-go models reduce upfront investments, with pricing based on usage rather than fixed hardware.
For example, a multinational retailer using a cloud-native SIEM can monitor its e-commerce platform, supply chain APIs, and IoT devices from a single pane of glass, correlating threats across regions without latency.
Platforms like ManageEngine Log360 Cloud exemplify this shift, providing a cloud-native architecture, prebuilt templates for cloud log parsing, threat detection and automated compliance audits tailored to frameworks like PCI DSS and ISO 27001.
Interested in exploring ManageEngine Log360 Cloud adopted by thousands of enterprises across industries?
AI-driven investigations: From alerts to actions in minutes
Detecting real threats from false positives and quickly investigating them to ascertain the impact are crucial to carry out timely response. Modern SIEM solutions combat alert fatigue by embedding AI threat detection and ML-driven behavior analytics capabilities that accelerate the initial phase of an security incident life cycle. While enterprises are yet to realize the complete implementation of AI, vendors are looking to implement AI in predictive threat detection, investigation to bring contextual data for reduction in mean time to investigate, and recommend response to mitigate threats.
- Contextual threat detection: Machine learning models analyze historical data to establish behavioral baselines, flagging deviations such as unusual login times or data access patterns. For instance, an AI model trained on healthcare data can distinguish between routine after-hours access by a surgeon and a ransomware attacker exfiltrating patient records.
- Automated investigations: NLP translates alerts into plain-English summaries, while GenAI suggests root causes (for example, “89% match to MITRE TTP T1059.003: Command-Line Scripting”).
- Predictive analytics: Proactively identify vulnerabilities by correlating threat intelligence feeds (for example, CVE databases) with internal asset criticality scores. AI-driven SIEM can detect zero-day exploits with its behavioral analytics and profiling before a legacy SIEM solution can.
According to IBM's Cost of Data Breach 2024 Report, AI and automation use grew to 31% in 2024 compared to 28% in 2023. Although it's just a 3% difference, it represents a 10.7% increase in use. Further, more organizations used AI and automation to lower their average costs, which is a significant finding. Organizations not using AI and automation had average cost of USD 5.72 million, while those extensively use AI and automation had average costs of USD 3.84 million, a savings of USD 1.88 million.
Unified security platform: Bridging silos for holistic security
Modern SIEMs transcend traditional systems by acting as a central hub of SOC that unifies disjointed tools, policies, and datasets into a cohesive defense strategy. In an enterprise security stack, the average number of security products can range from 45 to 130. Without a consolidated view, it is difficult to gain deeper and holistic visibility on what is happening in the network. Further, without this visibility, detecting threats, and jumping to different tools for investigating them, as well as responding to them in a different tool, makes security operations complex.
SIEM's evolution into a platform and acting as a central hub of SOC emerged to solve this complexity. This unified platform provides:
- Integration-centric design: Prebuilt APIs and connectors fuse data from other security tools such as EDR, cloud detection and response, firewalls, threat intels, identity providers and more, enabling cross-platform threat detection, contextual analysis and hunting.
- Risk-centric analytics hubs: Modern SIEM solutions have transcended traditional log aggregation to become enterprise-wide risk intelligence engines. By unifying threat intelligence feeds, vulnerability assessments, and business-critical context with immutable log retention, SIEMs now serve as the nexus for quantifiable risk management. This evolution empowers organizations to map their attack surface with surgical precision, prioritize vulnerabilities based on operational impact, and orchestrate proactive defenses—turning raw data into a strategic asset for preemptive risk mitigation.
- Operational flexibility: SIEM platforms now embrace low or no-code agility and customizable data narratives, enabling SOC teams to design adaptive playbooks tailored to their unique threat landscape. This shift from developer-reliant workflows to intuitive, no-code automation doesn’t just accelerate response times—it fosters a culture of innovation, where security teams can rapidly prototype defenses against emerging TTPs without sacrificing scalability or compliance. The result? A future-ready security posture that aligns with business velocity, not bottlenecks.
This unified approach not only streamlines SOC operations but also empowers CISOs to align security investments with business objectives, such as minimizing downtime or protecting intellectual property.
Unified security platform
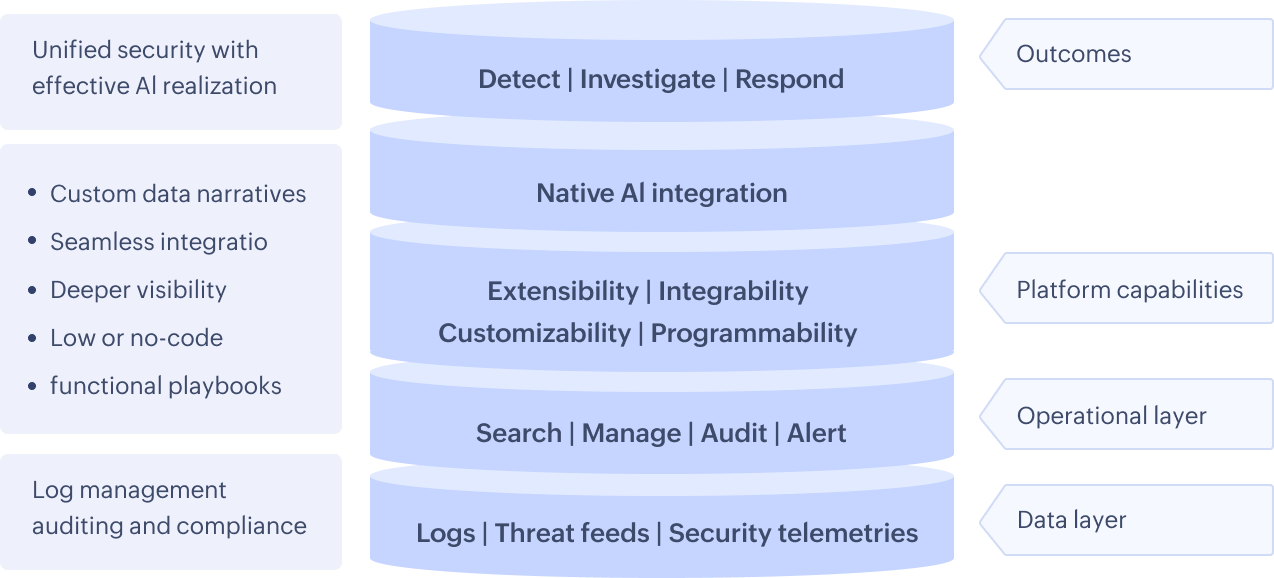
Beyond SIEM: Total SOC Control
Unified security platform for deeper visibility, quicker detection and remediation to threats
Buyer's guide: SIEM adoption in 2025
For organizations looking to adopt or upgrade SIEM solutions in 2025, here is a checklist of key considerations:
- Cloud-native architecture: Prioritize cloud-native or cloud-based solutions for scalability, flexibility, and reduced overhead.
- AI and machine learning: Evaluate and implement solutions that leverage AI and machine learning for advanced threat and anomaly detection and automated analysis. Make sure to test their AI adoption architecture and capabilities extensively.
- Integration capabilities: Ensure seamless integration with your existing security stack including identity providers, identity security tools, EDR, XDR, firewalls, DLPs, and other tools.
Threat detection and response: The core capability of a SIEM solution is to detect a wide range of threats and to facilitate rapid and effective response. Check its threat detection coverage, adaption of threat modeling framework like MITRE ATT&CK® for their threat mapping and remediation.
- User experience: Choose a solution with an intuitive interface, customizable dashboards, out-of-the-box detection rules, and efficient workflows for streamlined operations. The less the deployment and training time, the more effective.
- Compliance reporting: Verify that the SIEM solution can generate audit-ready reports and conduct audit trails to meet compliance requirements of mandates such as the GDPR, PCI DSS, HIPAA, and SOX.
- Scalability and performance: Ensure the solution can scale to meet your organization's growing data volumes and security needs.
- Total cost of ownership: Consider not only the initial licensing costs but also the ongoing costs of implementation, maintenance, and staffing.
Want to explore ManageEngine SIEM?
Looking to implement or replace your existing SIEM solution? Connect with our experts for a complete walkthrough, exclusive onboarding and onsite implementation, and premium support.
FAQs
What is the difference between SIEM and XDR?
SIEM focuses on aggregating and analyzing security data from across the entire IT environment for broad visibility, compliance, and long-term security posture. XDR focuses on detection and response, collecting and correlating data primarily from endpoint, network, and cloud environments. SIEM provides a wider view of an organization's security, while XDR is more focused on immediate threat mitigation.
How does AI enhance SIEM capabilities?
AI enhances SIEM by automating threat detection, reducing false positives, providing actionable insights, and enabling predictive analytics. AI-powered SIEMs can identify complex patterns and anomalies, learn from data, and adapt to evolving threats more effectively than traditional rule-based systems.
What are the benefits of a cloud-native SIEM?
Cloud-native SIEM solutions offer scalability, flexibility, reduced infrastructure costs, and easier deployment and management. They are designed to leverage the advantages of cloud computing, making them well-suited for modern, distributed IT environments.
Check out the cloud-based SIEM solution from ManageEngineHow does SIEM help with Zero Trust?
SIEM plays a crucial role in Zero Trust by providing the visibility and analytics needed to monitor and enforce Zero Trust policies. It helps ensure that all access to resources is strictly controlled, logged, and analyzed, and that any deviations from established baselines are detected and addressed.
- SIEM solutions as the central hub: From compliance to customization
- Security-as-data: How AI and Zero Trust adoption extend SIEM’s reach
- Evolving core capabilities of SIEM in 2025
- Buyer's guide: SIEM adoption in 2025
- FAQs






