What is a CASB?
A cloud access security broker or CASB is an on-premises or cloud-hosted security software or solution that acts as a gatekeeper and monitors the interaction between users and cloud applications. Gartner® defines a CASB as "on-premises or cloud-based security policy enforcement points, placed between cloud service consumers and cloud service providers to combine and interject enterprise security policies as the cloud-based resources are accessed."
Figure 1: A CASB solution monitoring user activity in the cloud, including file uploads
The increasing use of cloud technology in business operations poses risks such as reduced visibility, increased complexity in ensuring security, and the use of unsanctioned cloud applications by users. A CASB-integrated SIEM solution helps mitigate these security risks. CASBs allow you to gain visibility into user activities on the cloud. They also allow enterprises to control access by enforcing policies and extending their on-premises security policies to the cloud.
Why do you need a cloud access security broker?
Organizations require CASBs for the following reasons:
- Regulate user access: Since cloud services are hosted outside the perimeter of organizations, exercising control over user activities becomes difficult. CASB solutions enable organizations to enforce security policies and regulate users' access to data stored on the cloud.
- Protect sensitive data: CASB technology can be used to monitor sensitive data in-transit and protect the contents of the data through encryption.
- Stop data exfiltration:CASB helps identify and restrict unauthorized attempts to access and transmit data to and from the cloud, thus preventing data exfiltration attacks.
- Monitor and prevent shadow IT: CASB keeps a close eye on unsanctioned cloud applications or "shadow IT" applications being accessed by users.
- Ensure compliance: Using CASB technology, organizations can meet the data security and access requirements of various IT compliance mandates.
- Stop app duplication: CASB audits the usage of cloud services for budgeting purposes. CASB identifies users utilizing third-party applications for convenience of work while the organization has paid subscriptions for similar software.
- Secure collaboration: CASB ensures resource sharing platforms are not exploited.
Use cases of cloud access security broker
CASBs are frequently used to prevent the problem of shadow IT and malicious data exfiltration.
Monitoring shadow IT applications: Shadow IT, the use of unsanctioned cloud applications, reduces visibility and leads to increased security risks and compliance violations. When employees use unauthorized software or cloud services, IT admins have no way of ensuring if a user accessing a particular resource is authorized to do so, or if the organization's data security policies are being adhered to. This may inadvertently expose sensitive company data to security threats such as data breaches, malware, and cyberattacks. To avoid these issues, you need a CASB solution that can discover shadow apps, the requesting user, when they made the request, and their activities.
Log360, a comprehensive CASB-integrated SIEM solution by ManageEngine, discovers shadow applications and provides information regarding the domain name, actor or user, time an event was generated, app category, app reputation, URL, and upload size. The reputation score is obtained from Log360's threat feeds. With this, administrators can ban applications in their network and enforce policies.
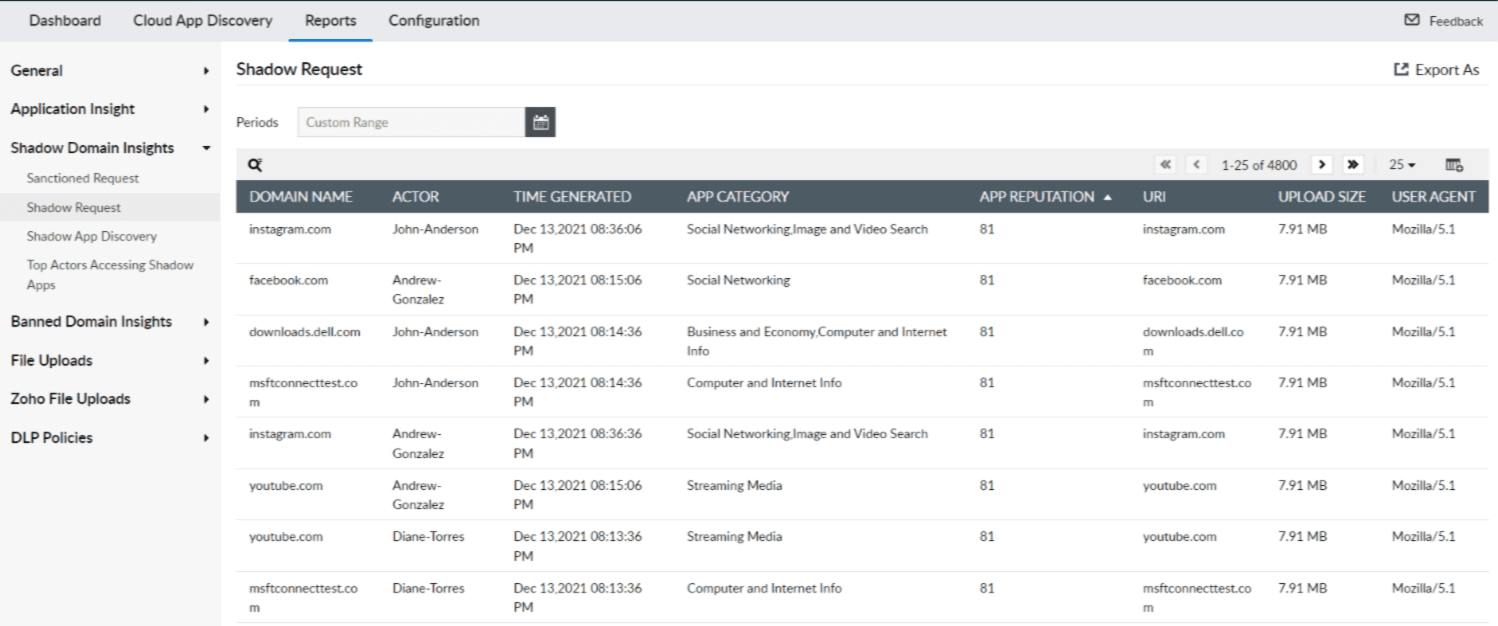
Figure 2: Log360 reports offering insights into shadow app requests
Monitoring sensitive data uploads: Organizations should protect against data exfiltration or data theft attempts, which involve an unauthorized transfer of business-critical data from inside the organization to an external network. A CASB solution can monitor the data leaving the network and detect suspicious activities that are indicative of data exfiltration.
Log360 can control access to your data and applications in the cloud, and perform deep packet inspection during file uploads into the cloud in real time by leveraging its CASB capabilities. The File Uploads report in Log360 lists all upload requests with contextual information such as file name, upload request size, domain name, actor, and more.
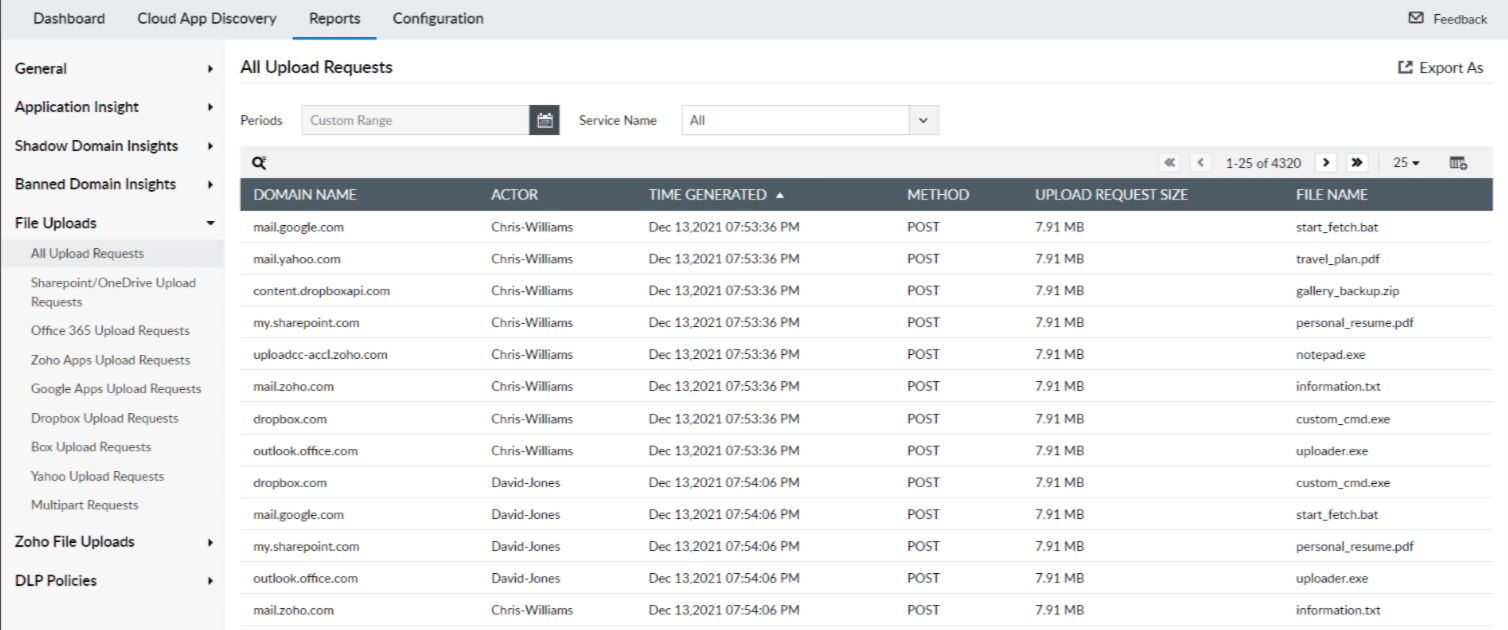
Figure 3: Log360 reports offering insights into all file uploads
User risk tracking: CASB provides contextual insights such as the top user accessing banned applications, all of the user's download activity, upload activity, and cloud application requests, as shown in the banned applications dashboard in Log360.
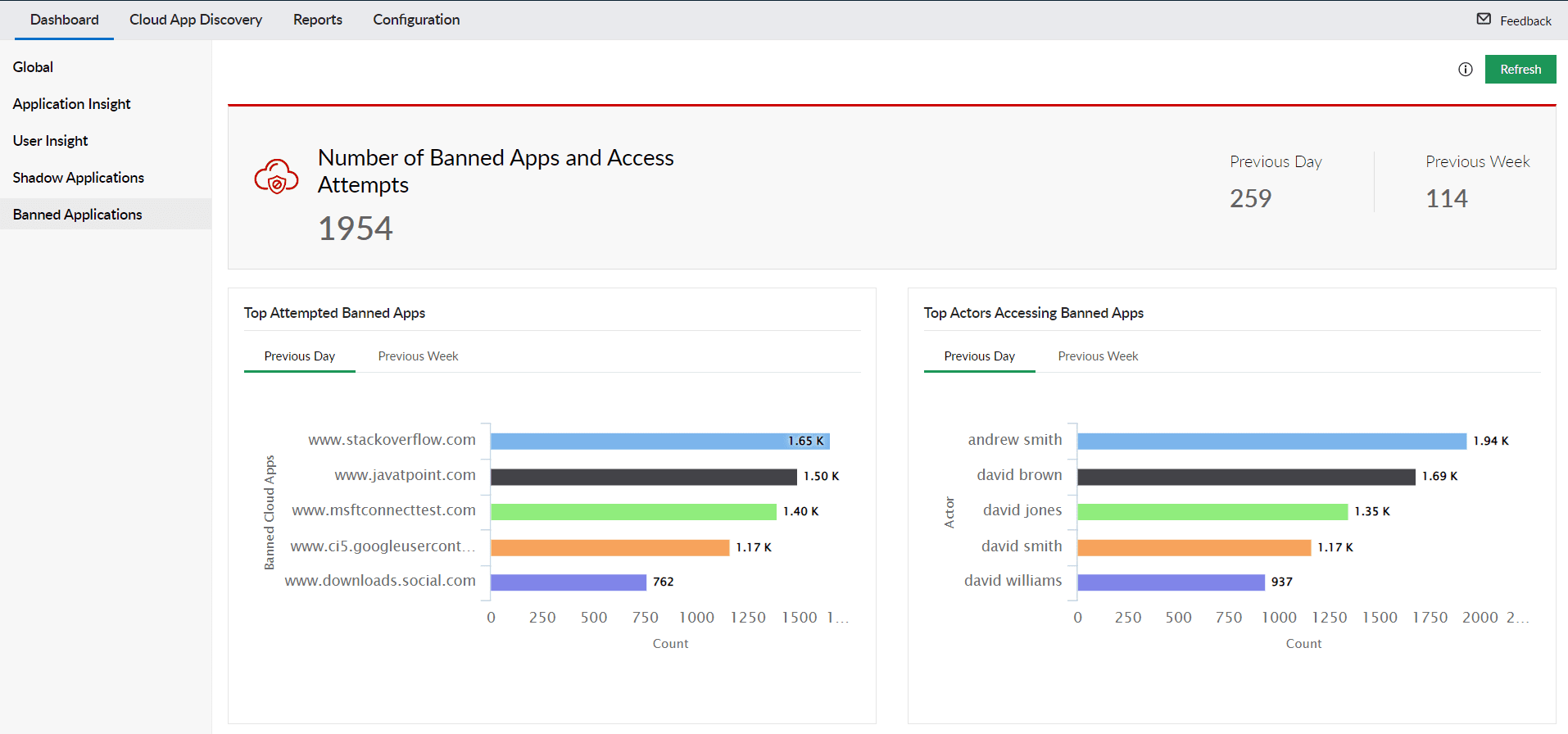
Figure 4: Log360 dashboard displaying the number of banned applications and their access attempts by users
ManageEngine Log360 helps you detect; investigate; and respond to threats, while meeting compliance requirements.
Pillars of cloud access security broker
Gartner has defined four core features or components that a CASB solution should have, and these components are termed as pillars. The four pillars of CASB in cybersecurity are: visibility, data security, compliance, and threat detection.

Visibility: Most cloud security providers (CSPs) offer very little in terms of audit and logging capabilities. CASB tools overcome these limitations by providing details about the traffic of data being moved between the organization and cloud providers. This helps organizations better understand what sanctioned and unsanctioned cloud services are being utilized by users, and guides them to safer alternatives. User, location, device, application, and quantity of data are some of the metrics that can be extracted to monitor the usage of cloud services by users.
Data security: While the cloud has made sharing data with people easier than ever, it has also put traditional data leak prevention tools into jeopardy because cloud services do not fall under their purview. CASB security solutions can inspect sensitive data being moved to and from the cloud, between cloud services, and within the cloud. These observations help organizations identify and stop attempts to leak sensitive information.
Compliance: It's important to consider compliance when switching to cloud-based services. Regulations such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR and others ensure that organizations have proper security systems in place to store and handle sensitive data. CASBs provide you with a range of options to identify and control the flow of personal data, monitor high-risk activities, and detect shadow IT applications to ensure adherence to privacy regulations and compliance mandates.
Threat detection: Organizations need to regulate the access of critical data from cloud services. Businesses also need to detect the exfiltration of data by malicious actors with stolen credentials or negligent users accessing sensitive information. CASBs can observe and register patterns of usage exhibited by users and form a baseline, using user entity and behavior analysis (UEBA). Any deviation from the baseline gets flagged as an anomaly, helping organizations spot and mitigate threats earlier.
Clearly, CASBs elevate your organization's cloud security. But, do you know what will take your security to a higher level? A CASB-integrated SIEM solution. To learn why CASBs should be a part of your SIEM solution, read this resource. To see how a unified SIEM solution with integrated CASB capabilities like ManageEngine Log360 has incorporated the four pillars of CASB, visit this page.
How does a cloud access security broker work?
There are three main deployment modes in CASB, namely: forward proxy, reverse proxy, and API scanning.
Forward Proxy: All traffic from the assets within your organizational network is channeled through the CASB before reaching cloud applications, acting as a gateway server at the organization's perimeter. The CASB controls access, and allows or blocks uploads deep packet inspection (DPI) and DLP, and provides real-time analysis of HTTPS traffic during file uploads, including file name, type, and size, aiding in identifying potential threats and policy violations. Learn more about the different deployment modes and the real file use cases of forward CASB from this resource.
Log360 offers forward proxy CASB to monitor traffic from on-prem environments. The gateway server and policies can be configured from the Log360 console.
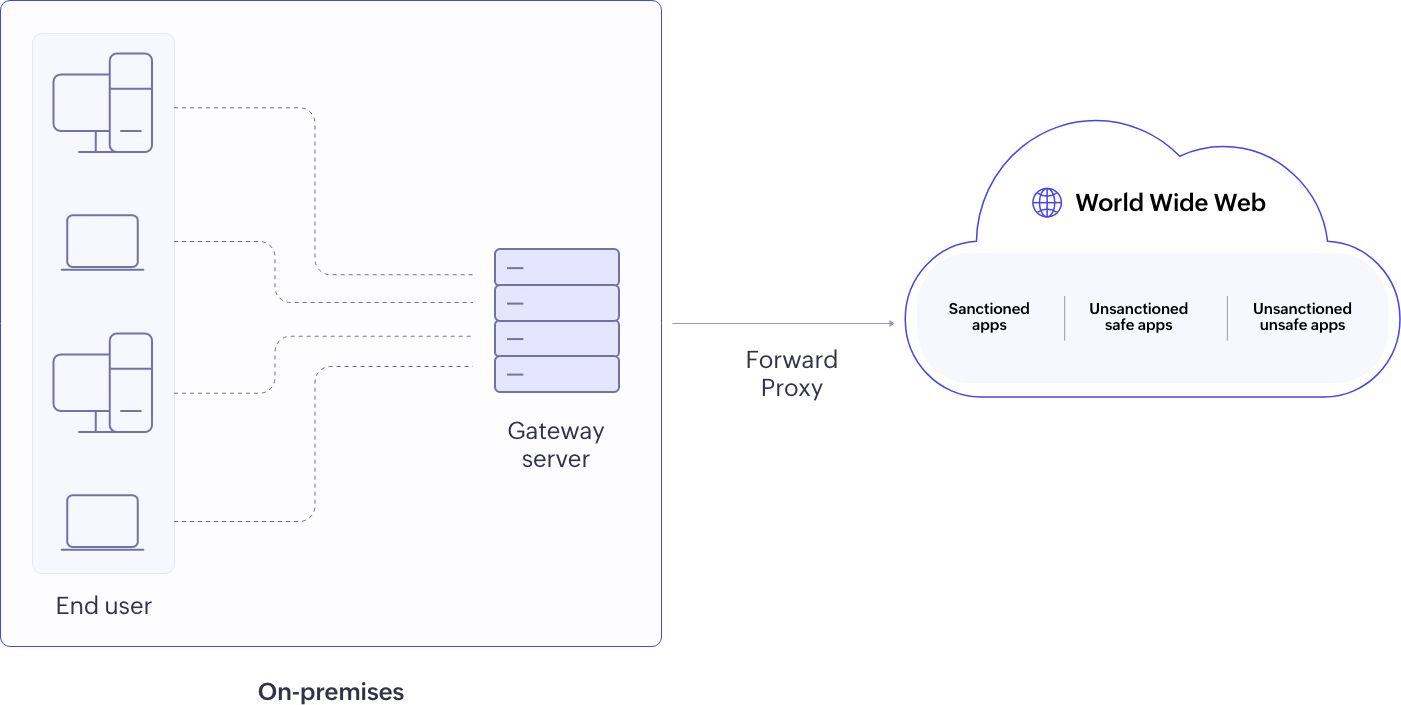
Figure 5: Forward proxy CASB deployment
Reverse Proxy: Cloud applications redirect user requests to the CASB for validation via user identity using Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) and grants access. This is particularly beneficial for sanctioned/approved applications and BYOD scenarios. It offers enterprises control over uploads or downloads from unmanaged devices accessing cloud apps from any network (home or work). Read this resource to learn more about proxy-based CASBs.
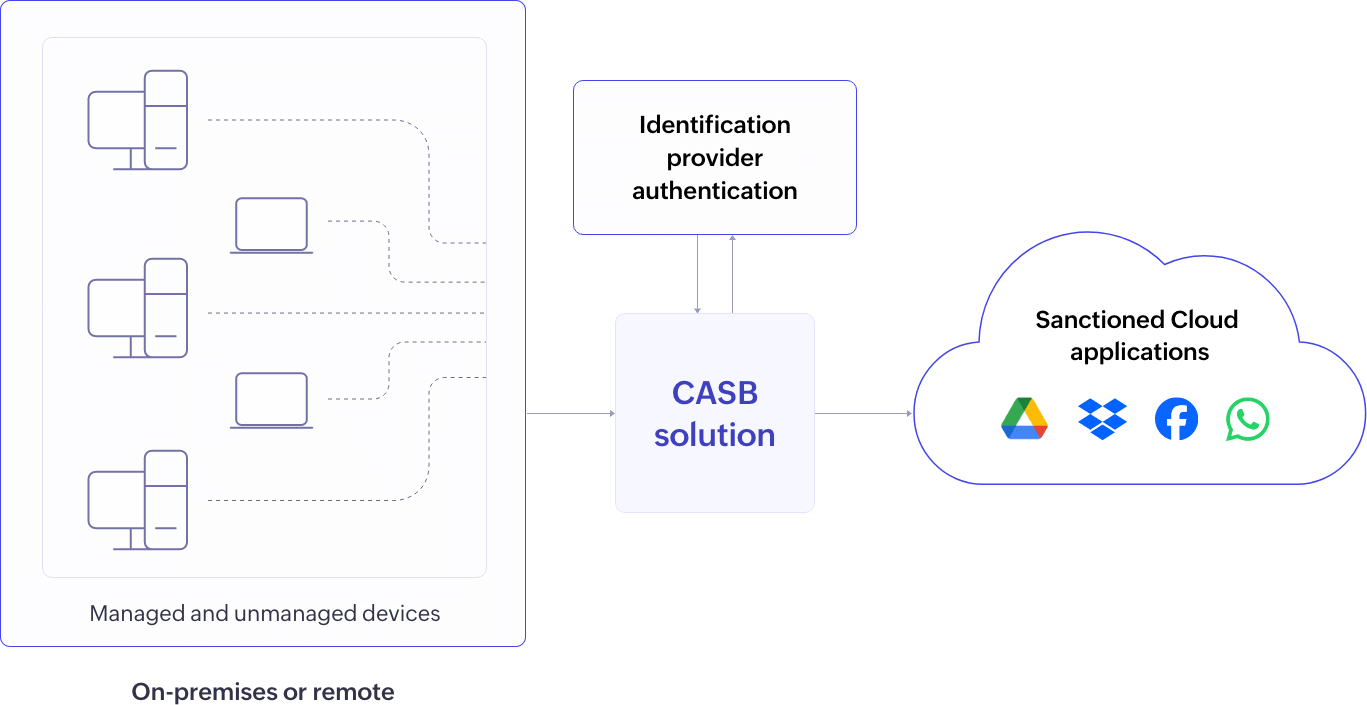
Figure 6: Reverse proxy CASB deployment
API Scanning: CASBs directly connect with cloud apps to scan data at rest, quarantining or revoking access upon policy breaches, providing effective protection for data stored in sanctioned applications, although it may not control user access or offer real-time protection.
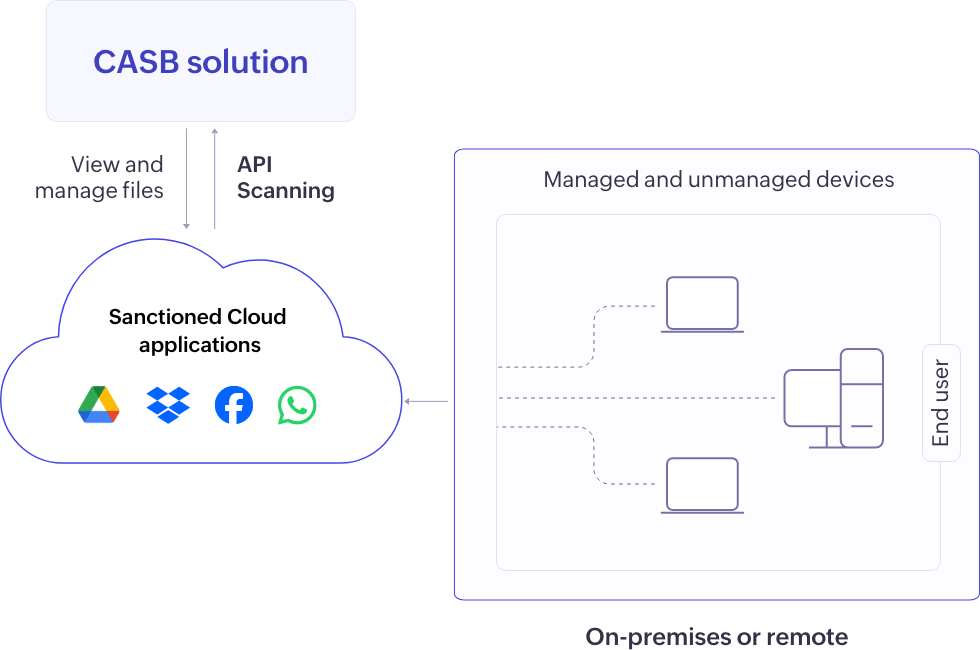
Figure 7: API scanning CASB deployment
Architecture of cloud access security broker
The architecture of CASB varies based on the deployment modes.
Forward proxy architecture
The forward proxy CASB architecture relies on a gateway server positioned on the client's premises. This server intercepts outbound traffic, conducts DPI to analyze HTTPS packets, manages SSL/TLS certificates for decryption and re-encryption, and enforces security policies such as URL filtering, application controls, and DLP.
The gateway server is configured and managed through Log360, facilitating periodic configuration syncing and audit data collection.
Reverse proxy architecture
In the reverse proxy CASB architecture, a proxy server is positioned in front of cloud applications. These cloud applications are sanctioned or official applications that the organization has configured reverse proxy for. When clients initiate requests to access these cloud applications, these requests are rerouted to the CASB reverse proxy server (CRPS). This rerouting process is facilitated through SSO, ensuring that all client interactions—whether from managed or unmanaged devices and on-premises or remote—with sanctioned applications are channeled through the reverse proxy server. The CRPS acts as an intermediary between clients and service providers, executing core CASB functionalities such as policy enforcement and audit logging. Organization administrators utilize the CASB application to configure control policies, supply policy settings, and metadata to the CRPS.
API scanning
In an API scanning CASB architecture, the CASB integrates with cloud service providers' APIs to monitor and secure data interactions between an organization's users and cloud applications. This involves continuous monitoring of API calls to inspect files and data at rest, ensuring the content of requests and responses is free from security threats, policy violations, or sensitive data. The CASB enforces security measures such as access controls, encryption, and DLP on API traffic. In simple terms, API scanning keeps an eye on the files and data that are stored and accessed in the cloud. If it spots security issues or sensitive info being shared, it steps in to lock it down using access controls and encryption.
Learn more about CASB architecture: CASB Architecture: Understanding forward proxy,reverse proxy, and API scanning
How to evaluate or choose a CASB solution
Every CASB security solution vendor will offer different functionalities. These functionalities can range from shadow IT monitoring to encryption to web content filtering. Here are a few CASB prerequisites you should consider while evaluating or choosing a CASB solution:
- Assess your security needs and goals to find the CASB solution that best fits your requirements.
- Check if the CASB vendor has designed the solution keeping in mind the four pillars of CASB.
- Identify if the solution provides complete visibility into the shadow applications used in your organization.
- Check if the CASB will improve the cloud security posture of your organization by providing activity analytics insights, such as tracking applications used in the cloud, sensitive file uploads made by users, or compliance policy violations at a granular level.
- Ascertain the solution's scalability. A good CASB solution will be able to keep up with the growing cloud usage without compromising on security.
- Check if the CASB software can provide actionable data in the form of dashboards and reports, and can satisfy your requirements at a reasonable cost.
For more insights into choosing CASBs for multi-cloud, read this resource.
CASB solution by ManageEngine
Log360, ManageEngine's unified SIEM solution, comes with integrated DLP and CASB capabilities. Log360 has the four pillars of CASB integrated into it, thereby allowing you to leverage CASB for:
- Enhanced visibility into cloud events
- Facilitating identity monitoring in the cloud
- Compliance management in the cloud
- Threat protection in the cloud
With Log360's integrated CASB capabilities, you can discover and ban the use of shadow applications in your network, safeguard cloud accounts from unauthorized access, ensure the security of cloud-based resources, prevent web-based attacks, and malicious data exfiltration attempts.
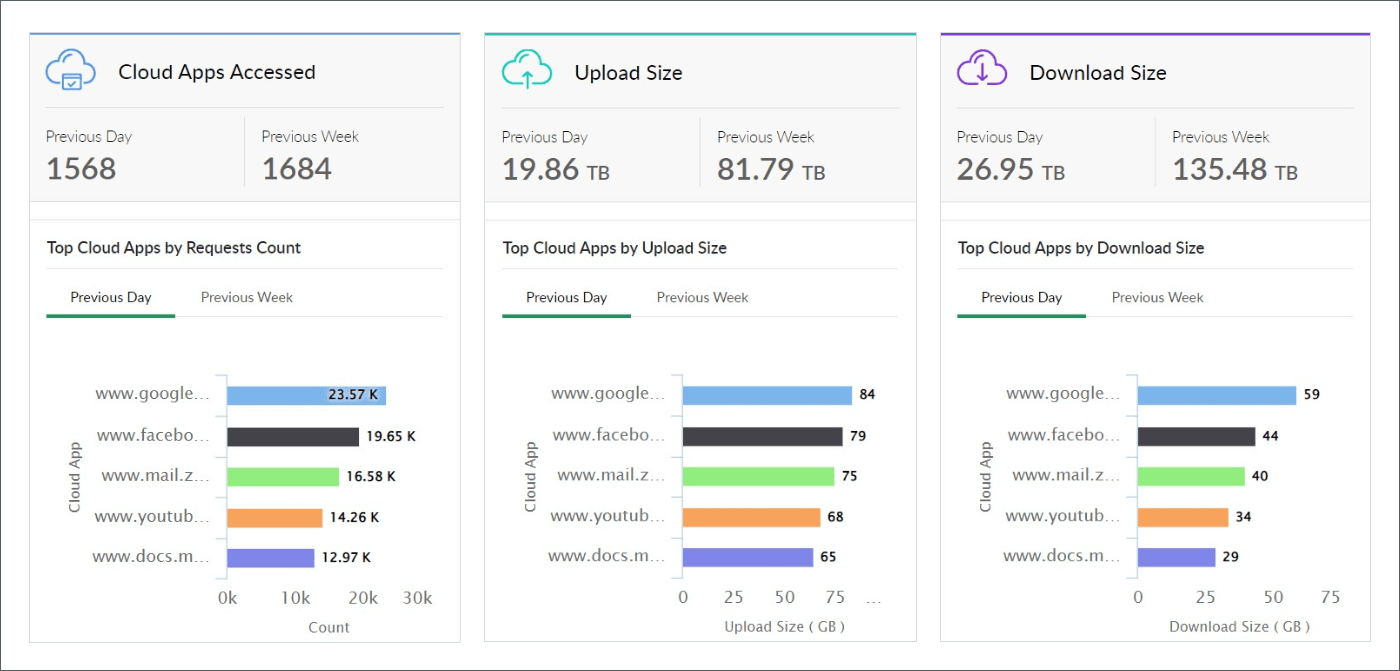
Figure 6: Log360 dashboard showing Top Cloud Apps by accesses, upload, and download size
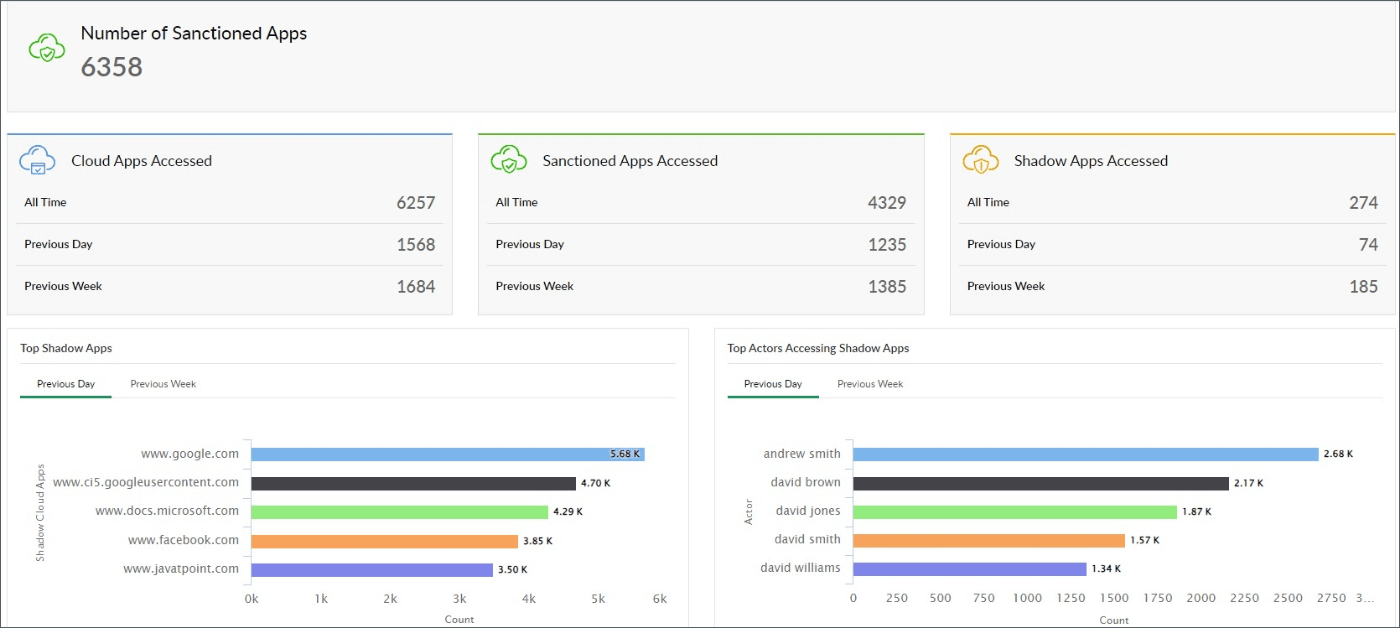
Figure 6: Log360 dashboard offering insights into sanctioned apps and shadow app access.
Role of CASB in healthcare
Healthcare organizations are like fortresses protecting valuable treasures—the personal health information of patients. CASBs act as the vigilant guards of these fortresses, constantly monitoring and controlling access to cloud-based applications and data. They serve as the gatekeepers, ensuring that only authorized personnel—doctors, nurses, and staff—can access patient records and sensitive medical information. In this way, CASBs help healthcare organizations mitigate security risks such as data exfiltration, protect sensitive patient data, achieve compliance with regulatory requirements, and enable secure collaboration and remote access in today's cloud-centric healthcare environment.
To learn more,explore how CASBs can help improve cloud security in healthcare.
Role of CASB in banking and finance
The role of CASB in banking institutions lies in its critical ability in safeguarding highly sensitive financial data and complying with rigorous regulatory standards.
CASBs allow banks to apply tailored access controls based on factors like the user's role, device, and location, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access confidential, cloud-stored data. Banks handle sensitive customer information such as financial records and personal data, and must comply with strict regulatory standards such as PCI DSS, GLBA, and GDPR, which vary depending on their location and operations.
Suggested read: Cloud access security brokers (CASBs): How to leverage one in banking and finance
Role of CASB in the education sector
Educational institutions enforce stringent internet access policies, driven by the understanding that their users primarily consist of students. This necessity arises due to the varied user groups present, encompassing students, faculty, staff, and researchers, requiring tailored approaches to user management and data security. Additionally, the prevalence of shadow IT, where unauthorized cloud applications are adopted without oversight, poses a significant concern. BYOD policies are common, which allow students and faculty to utilize personal devices for educational purposes. Cloud-based collaboration tools such as learning management systems (LMS) and email services play a pivotal role in facilitating remote learning and productivity.
Zero Trust and CASB
Both CASB and Zero Trust are cybersecurity measures that aim to enhance security in cloud environments and adopt a proactive, risk-based approach to security. While CASB focuses primarily on securing access to cloud services and data, Zero Trust extends this concept to all network resources, including on-premises infrastructure, remote users, and third-party connections.
CASBs can play a crucial role in implementing Zero Trust principles by providing visibility into cloud usage, enforcing security policies based on user behavior and context, and integrating with SIEM solutions. By leveraging a CASB-integrated SIEM solution within a Zero Trust framework, organizations can achieve granular control, visibility, and security across their cloud environments while mitigating the risks associated with unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance violations.
FAQ
- What is shadow IT?
-
Shadow IT refers to applications or services used by employees or departments outside the official approval of the IT department in an organization. These are cloud applications used by employees that the IT team is not aware of, i.e, applications that are neither sanctioned nor unsanctioned. The flexibility and familiarity offered by cloud-based SaaS applications over the years is one of the main factors in the growth of shadow IT.
- What is data exfiltration?
-
Data exfiltration, also known as data theft, is a stealth cyberattack that involves the unauthorized transfer of business-critical data from inside the organization to an external network. It can be caused by insider threats, phishing emails, and other external attacks.
- What is data visibility?
-
A key function of CASB technology, data visibility, offers insights into sensitive data residing in different sources across the network for effective monitoring, analysis, and management. Security monitoring is incredibly difficult to perform when there is no or minimal data visibility. Maximum data visibility helps enterprises enforce the right security policies, quickly troubleshoot operational failures, and protect the network from cyberattacks.
- What is SaaS?
-
SaaS refers to a software delivery model where software is hosted in the cloud and accessed by users over the internet, typically on a subscription basis. This model allows businesses to access and use software applications without the need for infrastructure or maintenance, as the software provider handles all updates and technical support. Some popular examples of SaaS include Microsoft 365, Google Workplace, and Zoho One.
- What is SSPM?
-
SaaS security posture management (SSPM) refers to the tools that continuously monitor SaaS environments or assess their security posture. SSPM employs SaaS application monitoring techniques to spot and fix misconfigurations, detect risks, and minimize data leaks.
- What is CSPM?
-
Cloud security posture management (CSPM) solutions help enterprises secure their entire cloud infrastructure by spotting misconfigurations, security loopholes, risks, and compliance violations in the cloud. CSPM tools automate cloud security management through identification and remediation of risks across diverse infrastructures, including:
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- What is identity service provider?
-
An identity service provider (IdP) is a trusted entity that manages and verifies digital identities, and provides authentication and authorization services to users. IdPs play a crucial role in ensuring the security and privacy of online transactions and data exchange by verifying the identity of users and granting access to authorized resources or services. Identity service providers also offer single sign-on solutions, allowing organizational users to access multiple applications or cloud services with a single set of credentials.
- What is access control?
-
Access control refers to the ability to define and enforce policies that determine which users or devices have access to specific cloud applications and data. This includes setting guidelines for who can access certain resources, what actions they are allowed to perform, and under what circumstances access will be granted or denied.
- What is a gateway server?
-
A CASB can be deployed as a gateway server (proxy server) at the organization's network perimeter to intercept and control traffic between users and cloud services. By acting as a gateway, a CASB can enforce access control, session control, and encryption policies directly on the traffic passing through it. The gateway server receives and enforces security policies defined within the CASB solution instantaneously. It sends logs and reports of all traffic and policy enforcement actions to the CASB. This data is used for auditing, compliance, and further analysis.
- What is application programming interface?
-
An application programming interface (API) is a set of rules and protocols that allows different software applications to communicate with each other. APIs define the methods and data formats that developers can use to interact with a software application, allowing them to access and utilize its functionality without needing to understand its internal workings. APIs are commonly used to enable integration between different systems, automate tasks, and extend the functionality of software applications.
- What is deep packet inspection?
-
Deep packet inspection (DPI) is a technology used to inspect and analyze the contents of data packets as they pass through a network. This technology allows network administrators to monitor, filter, and control network traffic based on the content of the packets rather than just the source or destination. CASB solutions with DPI are able to read the contents of HTTPS traffic to provide contextual information such as the type, size, and name of files being uploaded or downloaded.
- What is data loss prevention?
-
Data loss prevention (DLP) is a strategy used to ensure that sensitive data is not lost, stolen, or accessed by unauthorized users. DLP technologies are designed to prevent accidental or intentional data leaks by monitoring, detecting, and blocking sensitive data from leaving the organization's network. This can include monitoring data in motion, data at rest, or data in use, and applying policies to prevent unauthorized access or transmission of sensitive information.
- What is the difference between DLP and cloud access security broker?
-
A CASB solution primarily focuses on securing cloud-based services and applications. It provides visibility into cloud usage, controls access to cloud resources, and enforces security policies to protect data stored in the cloud. A DLP solution on the other hand, focuses on preventing the unauthorized disclosure of sensitive data. It monitors data in motion, at rest, and in use across various endpoints, network gateways, email servers, and cloud storage platforms to enforce data security policies and prevent data breaches and leaks. Organizations will benefit from having both DLP as well as CASB capabilities as a part of their security infrastructure.
- What is SASE?
-
Secure access service edge (SASE) is a cloud-based IT model that brings together wide area networking and network security services in a single platform. This convergence proves efficient to meet the growing challenges of security and access control. SASE enables employees to authenticate and safely connect to the internal resources of an organization while also ensuring improved control and visibility of traffic and data.
- What is the difference between CASB and SASE?
-
CASB focuses on securing cloud applications and enforcing cloud usage policies to ensure data protection and compliance. SASE, on the other hand, integrates multiple networking and security functions into a single framework, resulting in a more holistic approach to secure access. CASB can be a component within the broader SASE framework. SASE can incorporate CASB functionality to manage and secure cloud access, alongside other network and security services like firewall-as-a-service, secure web gateways, and zero-trust network access.
- Are CASBs and firewalls the same?
-
No. While both CASBs and firewalls can help monitor data traffic and control users' access to resources, CASBs go a step further in providing complete visibility into user activities in cloud environments, enforcing DLP policies, achieving compliance, and in preventing data exfiltration and data loss. Organizations should use both firewalls and CASBs to improve their cybersecurity posture.
- Are CASB and SIEM the same?
-
No. CASBs are available as a standalone security solution. However, modern SIEM solutions have CASB capabilities built into them. Organizations will benefit from using a SIEM solution with integrated CASB capabilities.
- Can SIEM solutions help monitor shadow IT or prevent data exfiltration?
-
Yes. A unified SIEM solution like ManageEngine Log360 that comes with integrated CASB and DLP capabilities can help in monitoring shadow IT, enforcing DLP policies, and in preventing data loss and data theft. To learn more, sign up for a personalized demo.

Click here to download this content in PDF format



