RedHat (RHEL) Patch Management
Patch Management for Red Hat Enterprise Linux enables administrators to manage all security and non-security patches that are released by the Red Hat Security Advisory (RHSA), for Red Hat subscribed machines and servers. It allows to identify, install, and audit Red Hat package updates, helping enterprises maintain a high level of security across Linux endpoints.
How to configure Red Hat Linux settings to perform Red Hat Patching?
Note: For patching Red Hat, it is recommended that all the managed endpoints have Standard subscriptions for Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
This how to document provides prerequisites to patch Red Hat systems and instructions to configure Red Hat settings.
Prerequisites to patch Red Hat Linux server and machines:
- Ensure that the nominated Red Hat machine has a Standard Red Hat Enterprise Linux subscription that points to Red Hat's CDN
- Configure proxy settings in YUM and ensure https://cdn.redhat.com/ is accessible from the nominated system.
- Ensure that https://access.redhat.com/ is accessible from the central server.
- Ensure our External Download ToolThe patch download in a Red Hat Linux environment is triggered through an external download tool. You can locate this tool under Server Installed Directory -> Lib -> Download Tool is available on the Central Server.
- Install agents on the RHEL systems to be patched.
- Allow your proxy to download .jar, .rpm files.
- Verify if you have purchased sufficient licenses for your patching requirements.
- Ensure that the Red Hat machines have at-least 20GB of space in the /var/cache directory for the offline meta sync.
Note: In order to attach/register the license to Red Hat, all managed Red Hat machines must connect to the Internet "at least" once and authenticate with the Red Hat Subscription Management system. Only then we will be able to validate the machine's subscription status successfully. Apart from this instance, machines (other than the nominated machine) don't require an active Internet connection.
System Nomination steps for RHEL Patch Management
1. Provide Red Hat account information
- Provide the credentials using which you have purchased the Red Hat subscription. This information is required to validate and download all the .rpm packages for your network.
- Ensure this credential has permissions to download packages from https://access.redhat.com/downloads/ to the server machines.
2. System Nomination
System Nomination is a process of hand-picking one computer each for these categories - Server, Desktop and Workstation in your network. The selected systems will be used to download meta files required by YUM tool for patching.
Red Hat Linux uses the YUM (Yellow dog Updater Modified) as its package management solution. The YUM provides all dependencies required to deploy a patch.
Prerequisites to nominate a computer:
- Verify if the UEMS agent is installed in the computer.
- Check if the nominated system has an active Red Hat subscription.
- Configure proxy in YUM such that https://cdn.redhat.com/ is accessible from the nominated system.
- Ensure that it has an active internet connection without any firewall restrictions. Only the nominated machine requires an active Internet connection.
- Ensure that there is at least 20GB free space for cache directory (default location: /var).
- Ensure that the machine has minimal down-time.
- The nominated machine should have the following specifications
- RAM size : 4 GB or higher.
- Processor : Intel Core i3 (2 Core / 4 Thread) 2.0 GHz or higher
Steps to follow for system nomination:
- Provide the name of the computer nominated for Server category.
- Provide the name of the computer nominated for Desktop category.
- Provide the name of the computer nominated for Workstation category.
3. Whitelist domains
The following domains need to be whitelisted for the Red Hat packages to be downloaded:
- https://access.redhat.com
- https://cdn.datatables.net
- https://sso.redhat.com
- https://access.cdn.redhat.com
- https://static.redhat.com
- https://www.redhat.com
- https://cdn.jsdelivr.net
- https://code.jquery.com/
Architecture and process of Red Hat Patching:
This section explains the processes involved in patching Red Hat systems with the help of architecture diagrams.
1. Cache creation
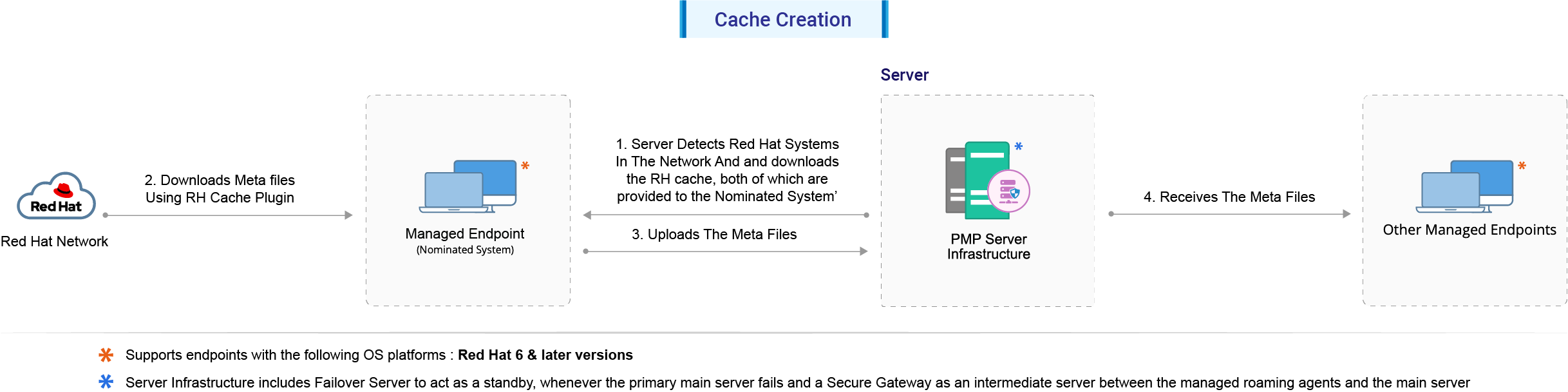
Steps involved in the process of Cache creation:
- The Patch server detects the available Red Hat versions and architecture in all the systems in your network.
- The Nominated System (for the category of Servers) downloads the RH Cache Plugin from the server. The Plugin will reside on the Nominated System.
- The RH Cache Plugin in the Nominated System downloads required meta files for all the other systems in the network ( that belong to the category of 'servers') from the Red Hat portal, using the YUM tool.
- The downloaded files are then uploaded to the server.
- All the other systems residing in the network receive the data from the server. Each system uses the meta data to detect it's missing patches and dependencies.
Note: The above steps refer to the category of Servers. The same steps are applicable to the category of Workstations and Desktops as well.
2. Scan and Deployment
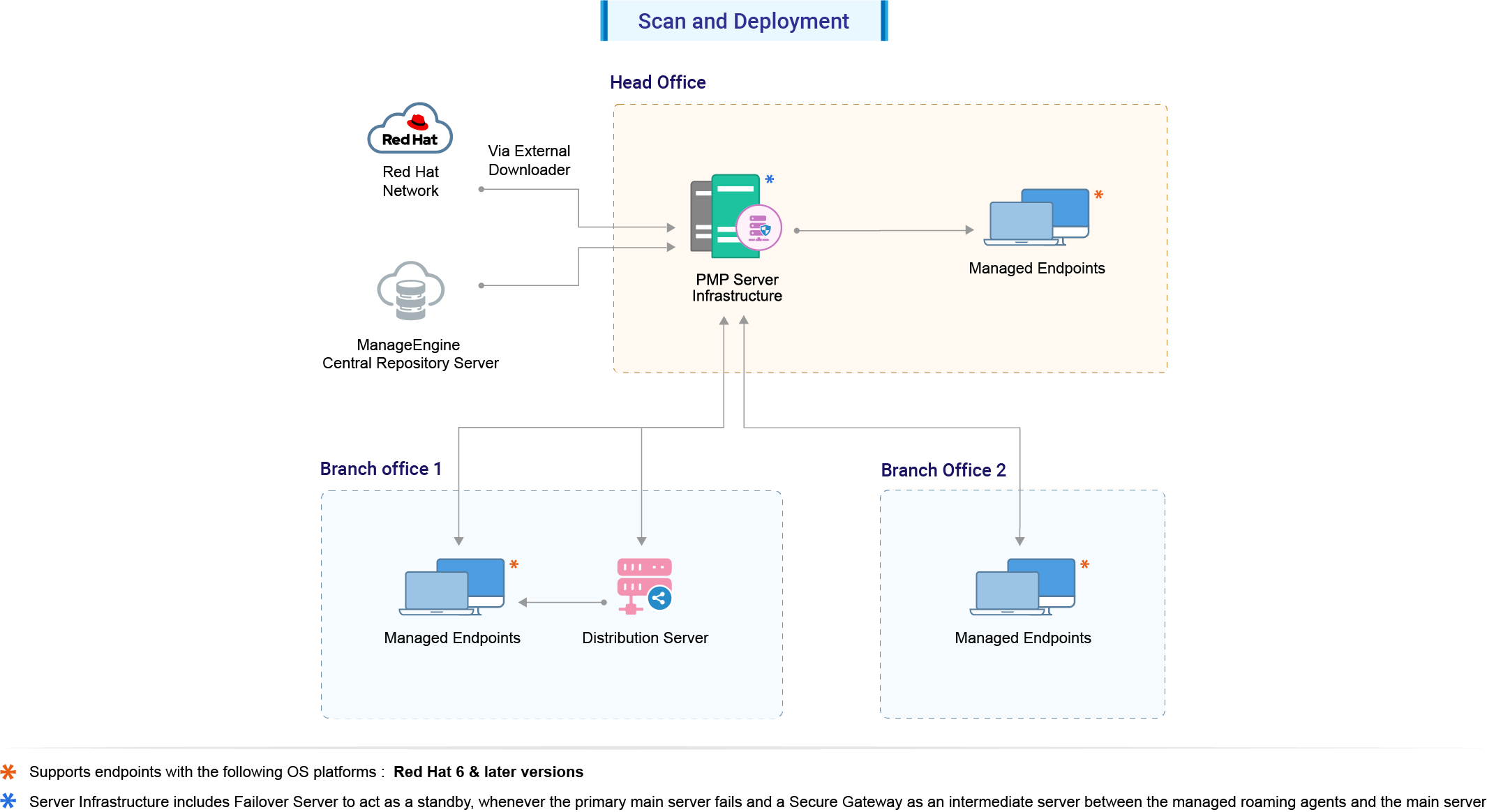
Steps involved in the process of scanning and patch deployment:
- The central server syncs the External Download Tool and supported patches information from ManageEngine's central Patch Repository.
- The server initiates the scan on all the Red Hat systems and detects the missing patches.
- The External Download Tool downloads the patches and dependencies from the Red Hat portal using the account credentials provided.
- a) The downloaded files are replicated from the Central server to the Distribution Server(s). The remote office agents download the files from the Distribution Server.
b)Other agents download the files from the Central Server.
- Once patches are downloaded and available, deployment is carried out.

