- Free Edition
- Quick Links
- MFA
- Self-Service Password Management
- Single Sign-On
- Password Synchronizer
- Password Policy Enforcer
- Employee Self-Service
- Reporting and auditing
- Integrations
- Related Products
- ADManager Plus Active Directory Management & Reporting
- ADAudit Plus Real-time Active Directory Auditing and UBA
- Exchange Reporter Plus Exchange Server Auditing & Reporting
- EventLog Analyzer Real-time Log Analysis & Reporting
- M365 Manager Plus Microsoft 365 Management & Reporting Tool
- DataSecurity Plus File server auditing & data discovery
- RecoveryManager Plus Enterprise backup and recovery tool
- SharePoint Manager Plus SharePoint Reporting and Auditing
- AD360 Integrated Identity & Access Management
- Log360 (On-Premise | Cloud) Comprehensive SIEM and UEBA
- AD Free Tools Active Directory FREE Tools
Why is Active Directory MFA/2FA needed?
Active Directory remains the core of identity management for most organizations, and as cyberattacks grow more sophisticated, relying on legacy username and password-based authentication for Active Directory access is no longer sufficient. With 80% of breaches involving stolen or weak credentials, two-factor authentication (2FA), a subset of multi-factor authentication (MFA) can thwart credential-based attacks in your Active Directory environment. After all, just one compromised password could give attackers access to your entire network. Whether your system is hybrid or on-premises, Active Directory two-factor authentication is no longer a best practice—it’s a baseline requirement.
How does Active Directory multi-factor authentication on-premises work?
When an user tries to log in to their Windows, macOS, or Linux machine, here’s how they perform 2FA or MFA for Active Directory:
- The user enters their Active Directory username and password, which are verified using the domain controller or cached credentials.
- If the credentials are valid, the user is taken through the MFA steps configured by the admin.
- ADSelfService Plus checks the user’s enrollment and applicable policy, then prompts them with the required MFA authenticators from a list of over 20 supported options.
- Once MFA is successfully completed, the user gains access to their machine.
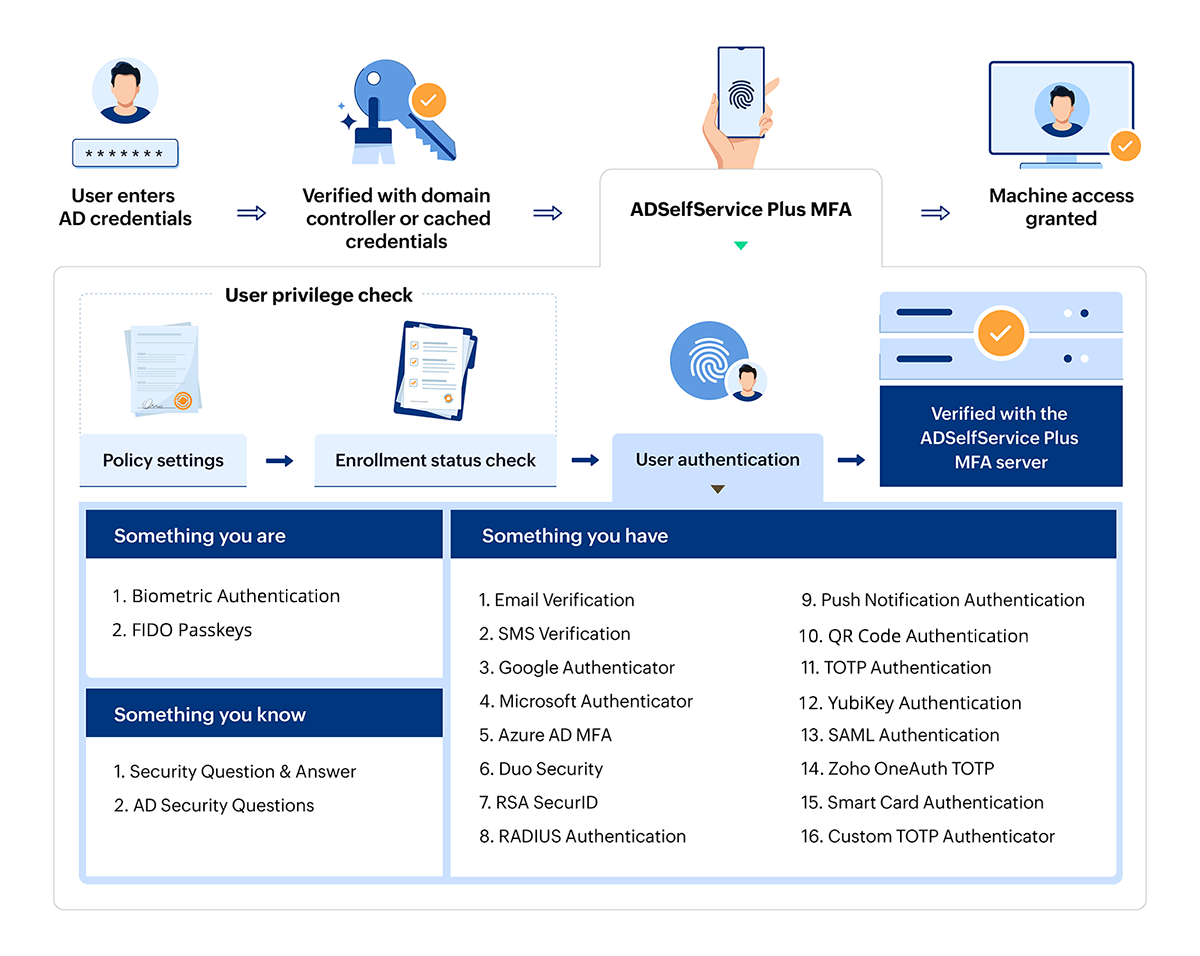
Comprehensive Active Directory multi-factor authentication system
ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus offers robust, holistic, on-prem MFA for Active Directory backed by modern authentication methods, seamless configuration and deployment, and full-spectrum identity security.
MFA for machine access
Secure access to machine (Windows, macOS, and Linux OS) logins with MFA for Active Directory users.
MFA for VPNs
Allow users to securely access IT resources through a VPN after a stringent authentication flow with advanced enterprise authentication methods.
MFA for OWA
Ensure secure access to OWA accounts by deploying MFA for Active Directory accounts with strong authentication factors during OWA logins.
Offline MFA
Secure your offline remote users by enabling Active Directory MFA for offline Windows and macOS machine logons.
MFA for enterprise applications
Regulate enterprise application access via SSO using strong authenticators such as FIDO passkeys, YubiKey, and biometric authentication for Active Directory users.
MFA for SSPR
Enable users to perform Active Directory self-service password reset (SSPR) and self-service account unlock only after user identity verification using the MFA authentication types supported by SSPR.
Key benefits of implementing Active Directory MFA
Enabling AD MFA on-premises with ADSelfService Plus brings numerous advantages for your organization, directly addressing common IT security challenges:
- Unrivaled security: Drastically reduces the risk of all password-based attacks, including phishing, brute-force, and credential stuffing, by making compromised credentials useless without the second factor.
- Mitigate insider threats: Provides an essential layer of security against compromised internal accounts, accidental misconfigurations, or malicious insiders seeking to elevate privileges.
- Protect critical resources: Safeguards sensitive data, business-critical applications, and systems that are integrated with and reliant on your AD infrastructure.
- Flexible authentication methods: Offers support for a wide range of factors including biometrics, push notifications, Time-based One-Time Passwords (TOTP), security keys (e.g., YubiKey), and more.
- Adaptive security policies: Implement conditional access policies based on user location, device trustworthiness, or time of access, adding an intelligent layer of defense.
Best practices for Active Directory MFA deployment
- Enforce MFA for all admin accounts: Protect your Active Directory environment from privilege escalation attacks by implementing mandatory multi-factor authentication for domain administrators, enterprise admins, and other privileged users.
- Configure multiple authentication methods: Ensure user accessibility and provide backup options by deploying a combination of push notifications, SMS codes, hardware tokens, biometric authentication, and FIDO2 security keys to accommodate different user preferences and scenarios.
- Use conditional access policies: Enhance user convenience by automating Active Directory 2FA flows based on risk assessment and contextual factors.
- Monitor sign-in logs: Continuously track and analyze MFA events across your Active Directory infrastructure, including successful authentications, failed attempts, unusual access patterns, and potential bypass attempts.
- Educate users: Proactively inform end-users about the critical benefits of Active Directory multi-factor authentication and provide comprehensive training on proper usage.
Why choose ADSelfService Plus as your on-prem AD MFA solution?
Granular Active Directory 2FA configuration
Admins can enforce different authenticators for different sets of users, based on their OUs, domains, and group memberships.
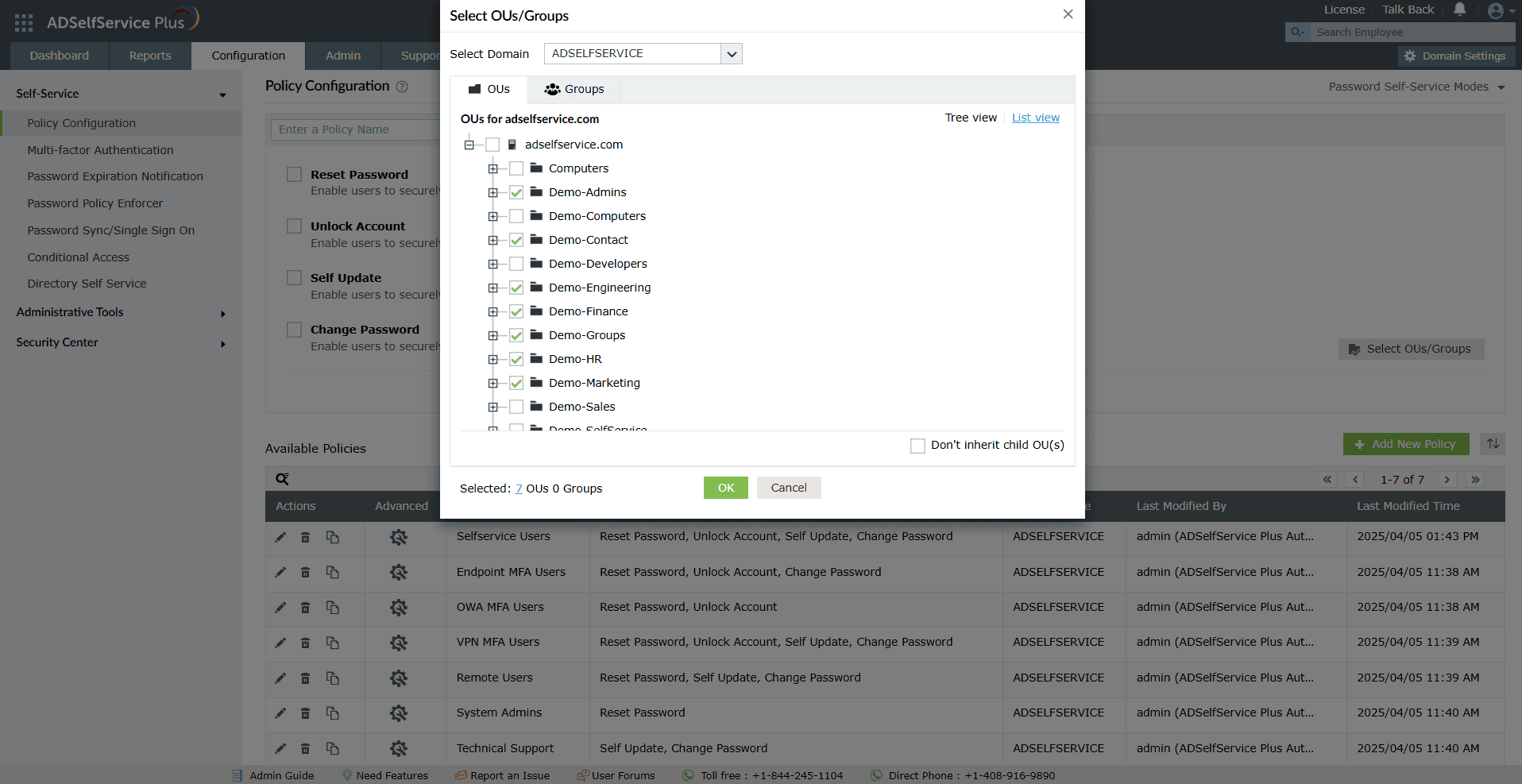
Granularly enforce MFA based on domains, OUs, or groups.
Enabled Active Directory MFA for multiple domains from a single console.
Seamless MFA enrollment
Automatically prompt users to enroll for Active Directory MFA during login or enforce mandatory enrollment policies to ensure complete coverage without manual intervention or delays.
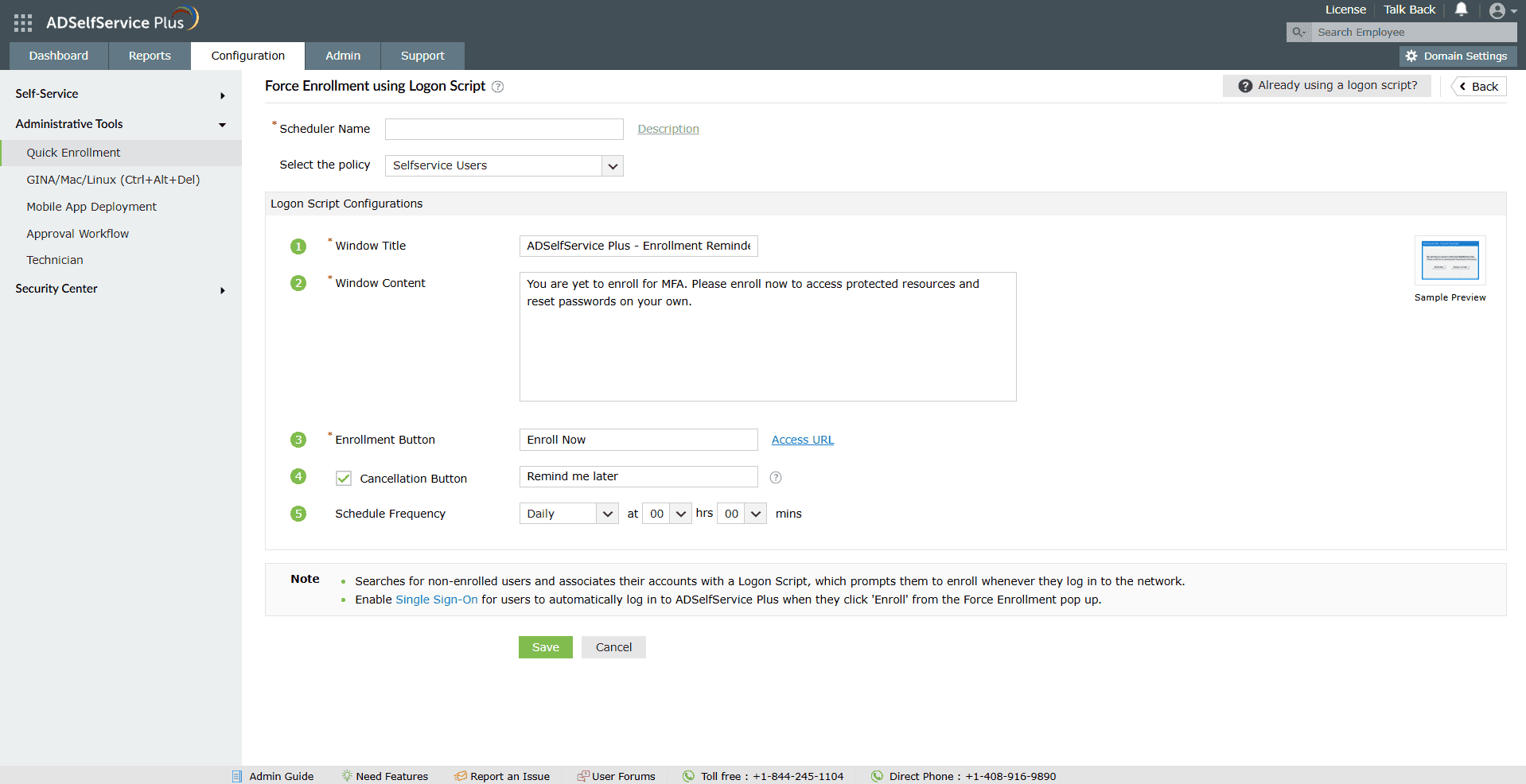
Draft a compelling message for the login script to be displayed every time a non-enrolled user logs in to their machine.
Customize the login script to provide users with a choice to enroll for MFA later or mandate immediate enrollment.
Improved user experience and security
Balance security and convenience with 20 different authentication methods—including biometrics and TOTPs—allowing users to choose from familiar, convenient, and secure MFA options.
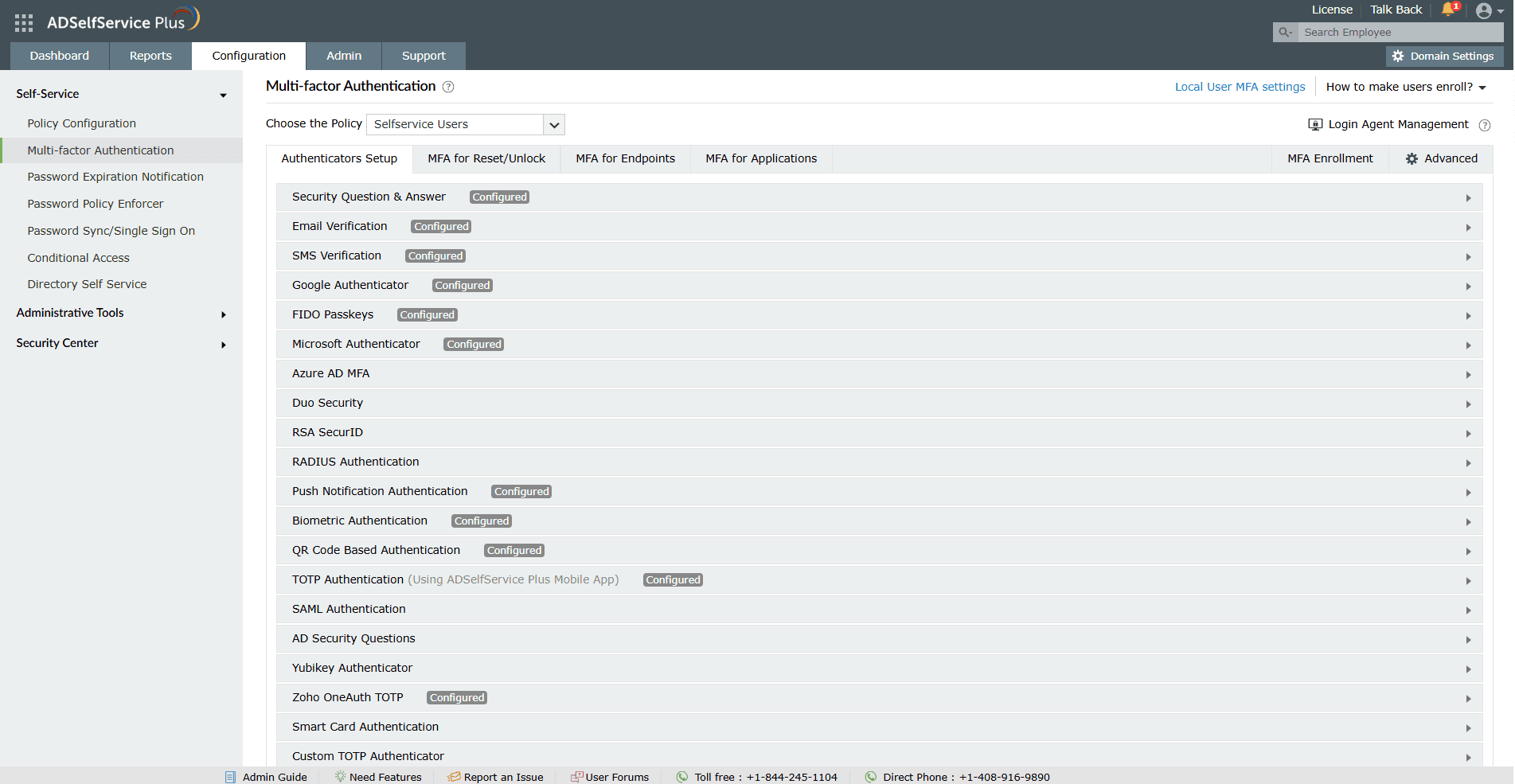
Apply specific authentication methods to different user policies.
Comprehensive reporting and auditing
Monitor MFA enrollment status, authentication attempts, and failures with over 14, detailed, audit-ready reports to gain visibility into user activity and compliance across your Active Directory environment.
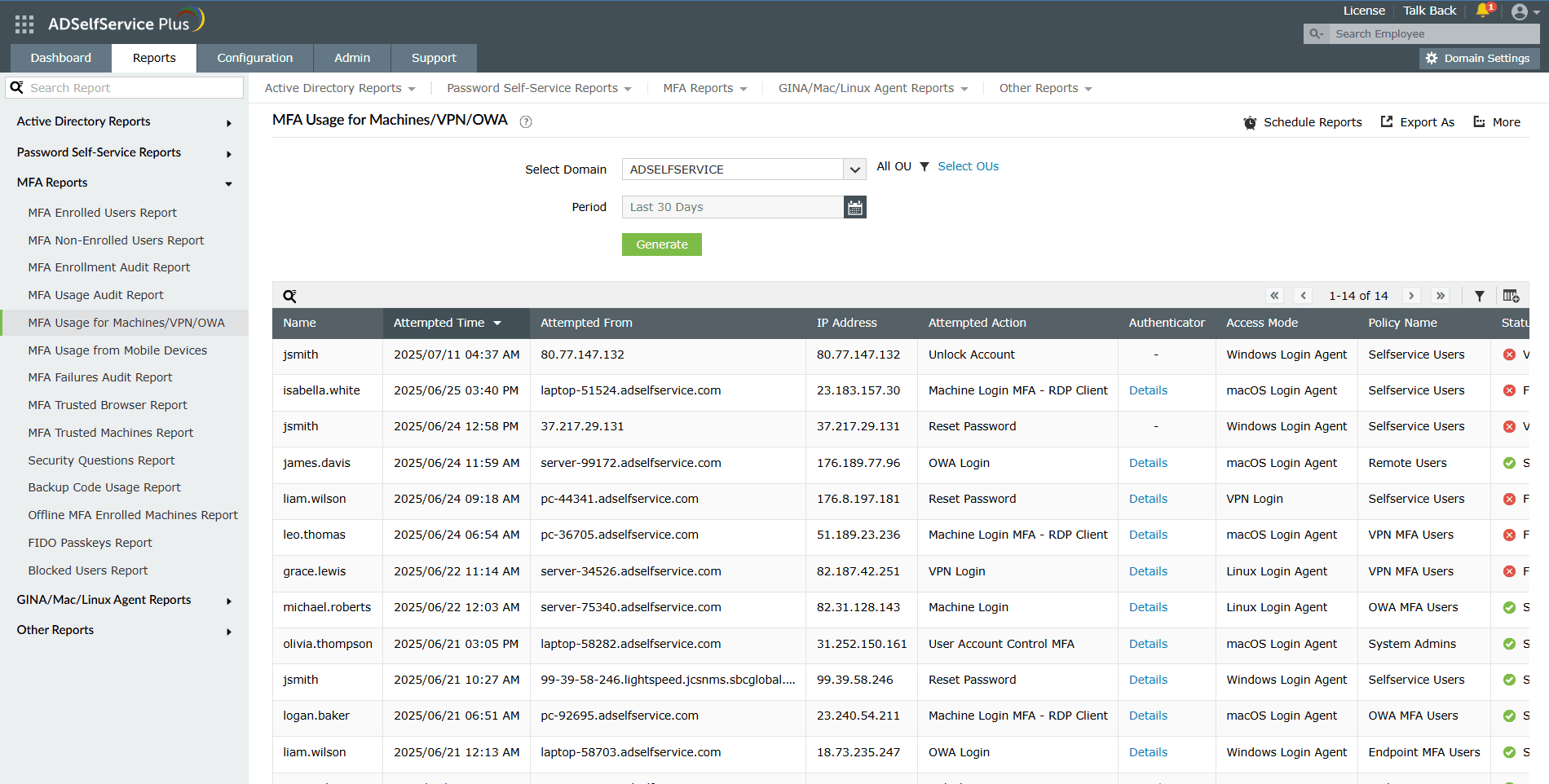
Schedule Active Directory MFA reports to be periodically generated and stored in the server or mailed to specific email addresses.
Filter out specific log entries from the entire report.
Active Directory multi-factor authentication and compliance
Active Directory MFA directly addresses compliance requirements mandated by industry regulations. Standards like NIST, PCI DSS, GDPR, and HIPAA explicitly require multi-factor authentication.
| Industry | Compliance | Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Government | NIST |
NIST SP 800-171 Rev. 2 - Protecting Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) Control 3.5.3 - Identification and Authentication specifically mandates MFA for both privileged and non-privileged accounts. NIST 800-171 control 3.5.3 specifically requires MFA for both privileged and non-privileged accounts. This means that all users, regardless of their access level, must go through the MFA process to gain access to the system or data. |
| Healthcare | HIPAA | Section § 164.308(a)(3)(i): Standard: Workforce security. Implement policies and procedures to ensure that all members of its workforce have appropriate access to electronic protected health information and to prevent those workforce members who do not have access from obtaining access to electronic protected health information. |
| Finance | PCI DSS | Section 8.4.2: MFA must be implemented to secure access to the cardholder data environment (CDE). |
| IT | GDPR | The GDPR does not require MFA. However, organizations seeking comprehensive GDPR compliance are encouraged to adopt MFA as a best practice for data security. |
FAQs
No, Active Directory MFA requires additional tools like Azure MFA, NPS extension, or third-party solutions.
Yes, using ADSelfService Plus, Active Directory 2FA can be enabled for on-premise and remote logins.
Yes, ADSelfService Plus integrates with on-premises Active Directory for MFA.
It’s a security measure that requires users to verify their identity through multiple factors before logging into AD-connected systems.
Yes. Both terms refer to adding additional authentication layers to Active Directory logins. While AD two-factor authentication is a subset of AD MFA requiring an extra layer os authentication apart from username and password, AD MFA can involve two or more layers of authentication.
Yes, ADSelfService Plus supports multi-factor authentication on both local and remote logins.
Highlights of ADSelfService Plus
Password self-service
Unburden Windows AD users from lengthy help desk calls by empowering them with self-service password reset and account unlock capabilities.
Multi-factor authentication
Enable context-based MFA with 20 different authentication factors for endpoint, application, VPN, OWA, and RDP logins.
One identity with single sign-on
Get seamless one-click access to more than 100 cloud applications. With enterprise single sign-on (SSO), users can access all their cloud applications using their Windows AD credentials.
Password and account expiry notifications
Notify Windows AD users of their impending password and account expiry via email and SMS notifications.
Password synchronization
Synchronize Windows AD user passwords and account changes across multiple systems automatically, including Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, IBM iSeries, and more.
Password policy enforcer
Strong passwords resist various hacking threats. Enforce Windows AD users to adhere to compliant passwords by displaying password complexity requirements.










