Account compromises—that can result in unauthorized access to sensitive information, identity theft, financial loss, and reputational damage—have become a prominent threat in today's digital landscape.
Microsoft says MFA blocks 99.9% of account compromises. Despite this, only 28% of users use MFA during login. To mitigate unnecessary risks and enhance security measures, individuals and organizations should implement MFA.
With ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus, you can implement various MFA options in your authentication process. Here are some use cases highlighting how ADSelfService Plus' MFA can protect you from cyberattacks.
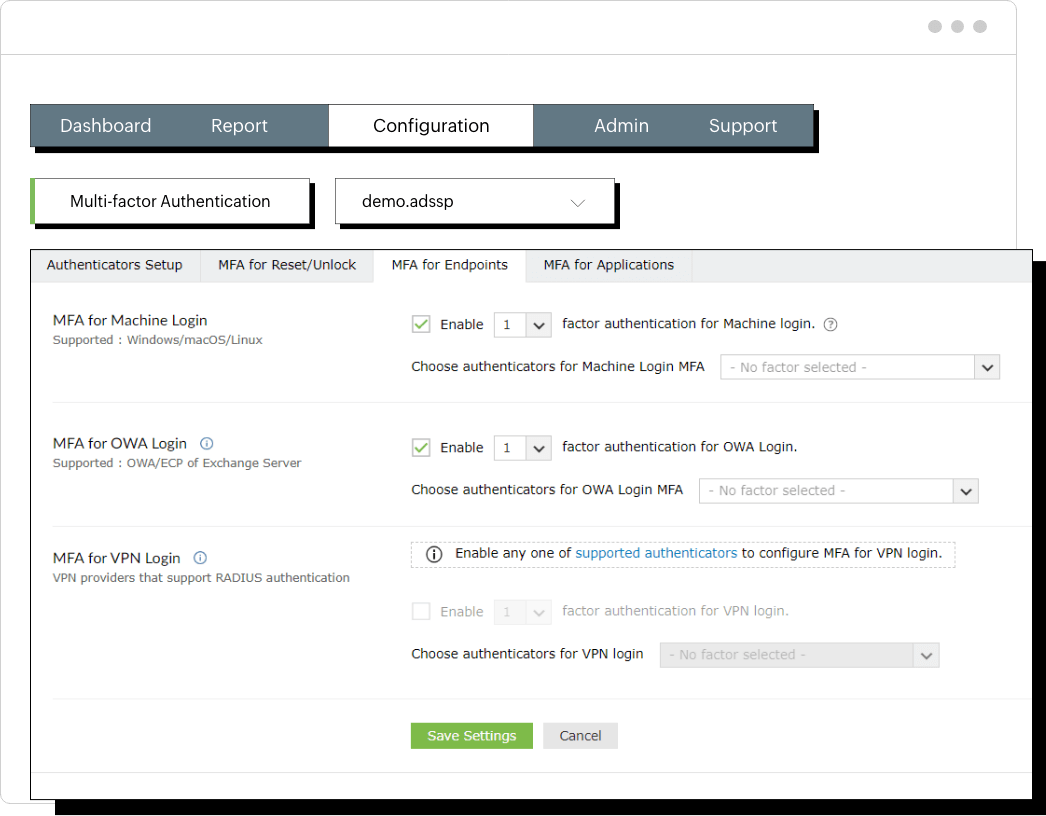
Most organizations use directory services like AD to verify usernames and password combinations to authorize account access. The same password is used for multiple accounts by 68% of users. If an attacker gains access to a user's single password, they can potentially access resources across various accounts. To prevent credential-based attacks, it is essential to implement MFA. Even if the attacker compromises the user's credentials, they cannot gain access to resources without the additional authentication factor.
ADSelfService Plus' Endpoint MFA secures access to:
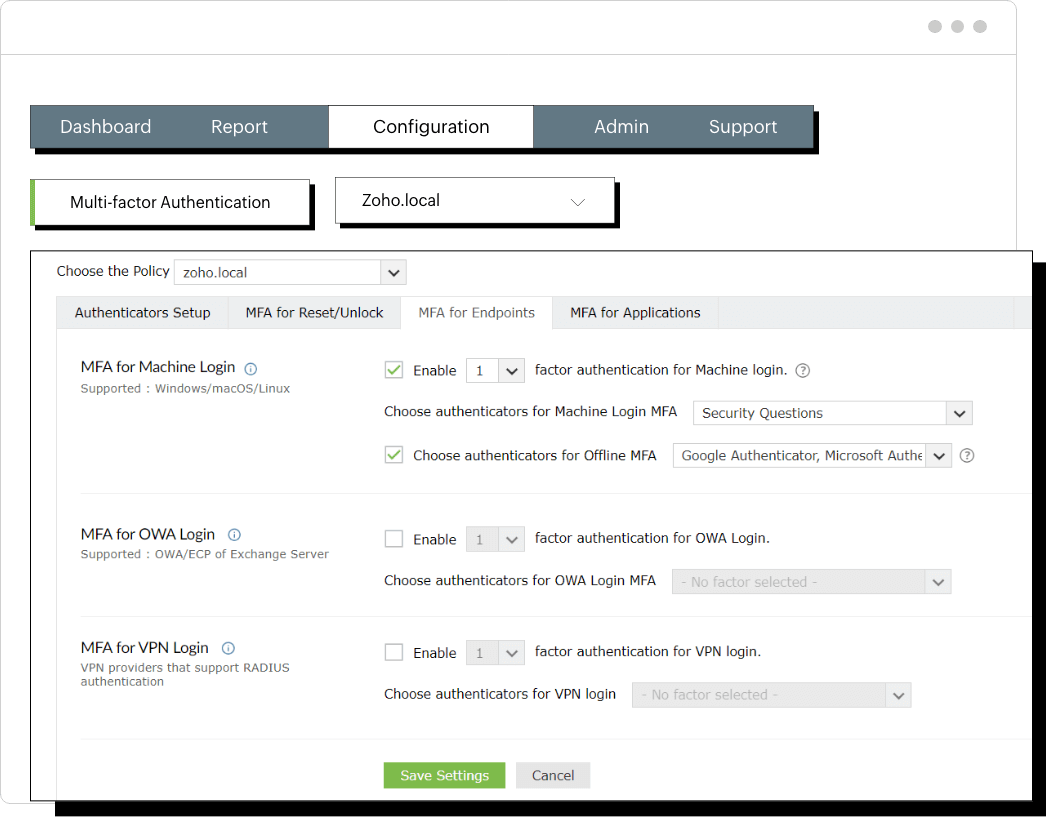
MFA isn't possible when an authentication server is offline or inaccessible. In such cases, offline MFA plays a crucial role in hardening endpoint and network security.
For instance, your laptop is stolen and your network connectivity is disabled. If offline MFA is enabled, both the initial login credentials and the offline authentication factor must be bypassed. The attacker would need multiple factors for authentication, which significantly increases the difficulty.
ADSelfService Plus' Offline MFA enables remote users to securely authenticate via MFA even if,
ADSelfService Plus supports offline MFA for Windows, RDP, and UAC logons.
Organizations ensure that each user is given access appropriate to their job function and privileges.
For example, in an educational institution, there are user groups with specific roles and access privileges. For instance,
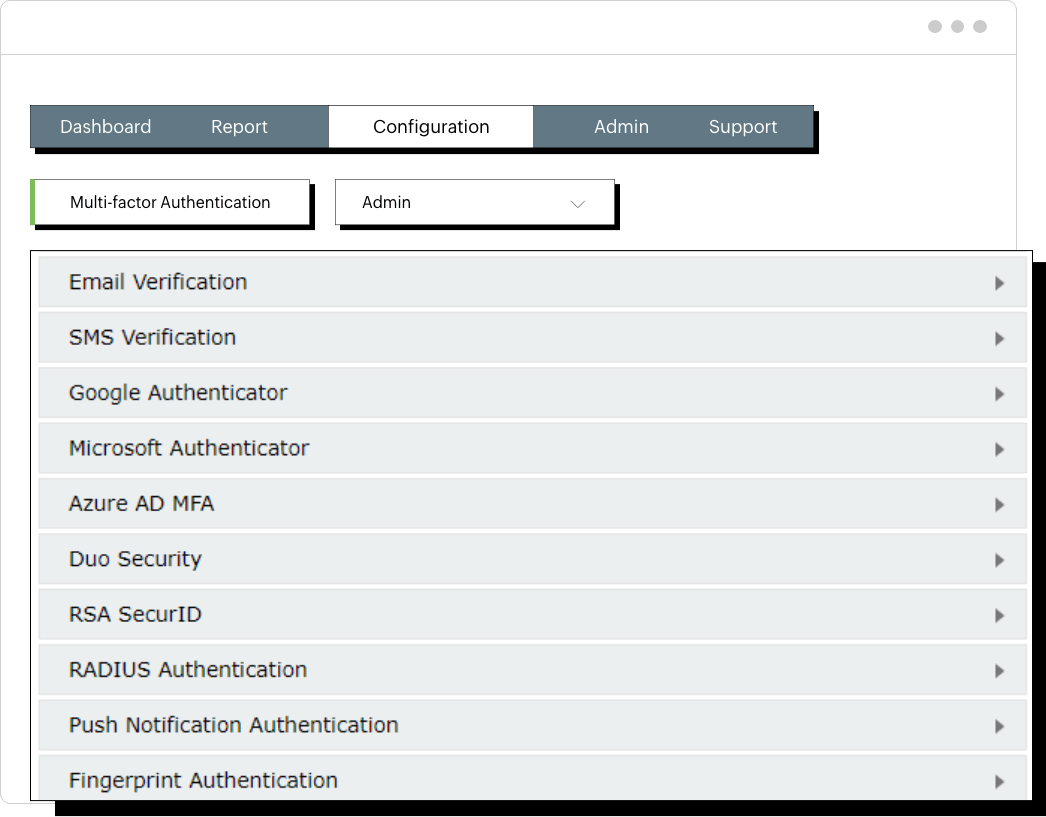
With ADSelfService Plus' MFA, admins can select a self-service policy and configure authentication methods. It can be applied to all users or only to users in specific OUs or groups within the selected domain.
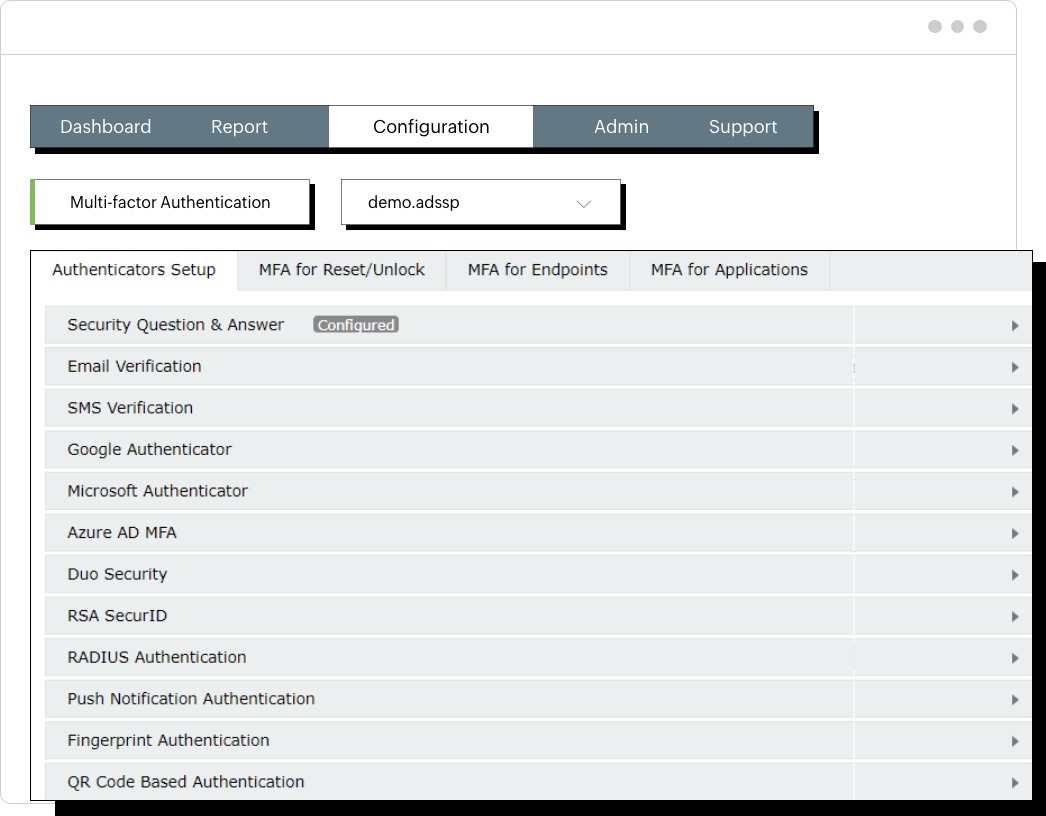
It supports 19 authentication methods, including SMS verification, email verification, push notifications, DUO security, Google Authenticator, and Microsoft Authenticator.
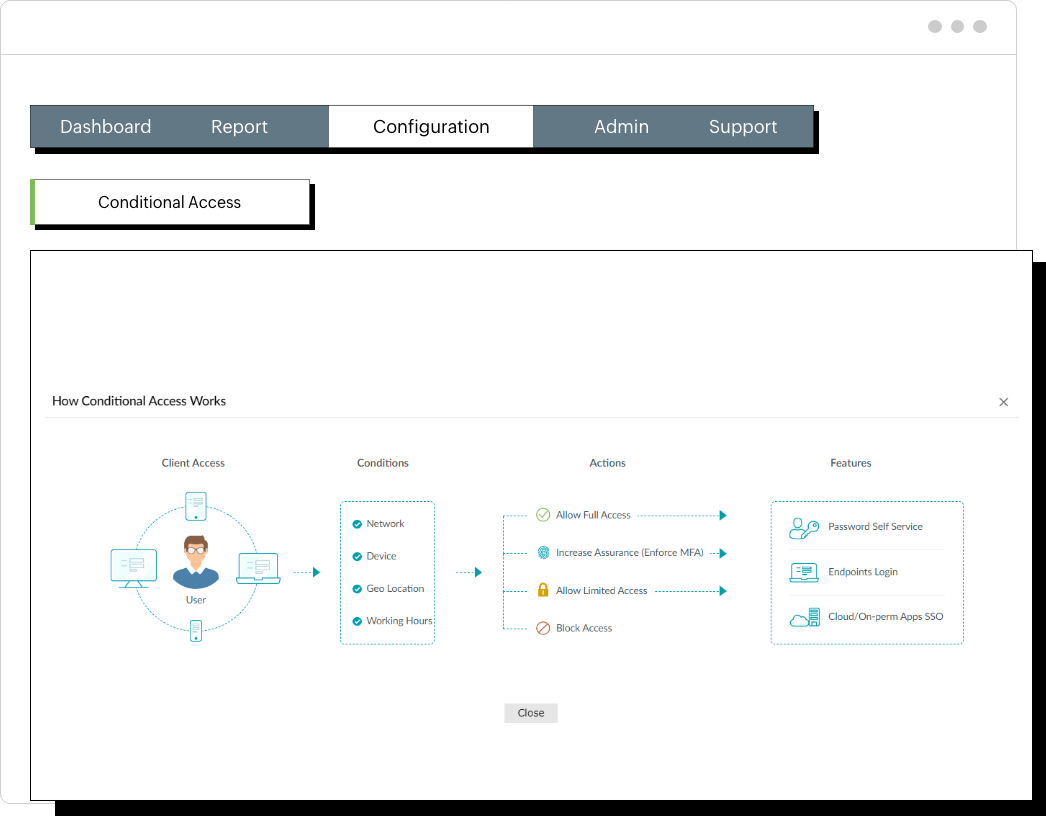
Remote users are more vulnerable to cyberattacks because they might access corporate resources through public networks, use personal devices with potentially weaker security measures, and expose themselves to a wider range of potential threats.
To enhance security, admins should enforce MFA for remote users. Conditional access policies empower admins to manage access effectively by allowing complete and unrestricted access, limited access, or no access to resources.
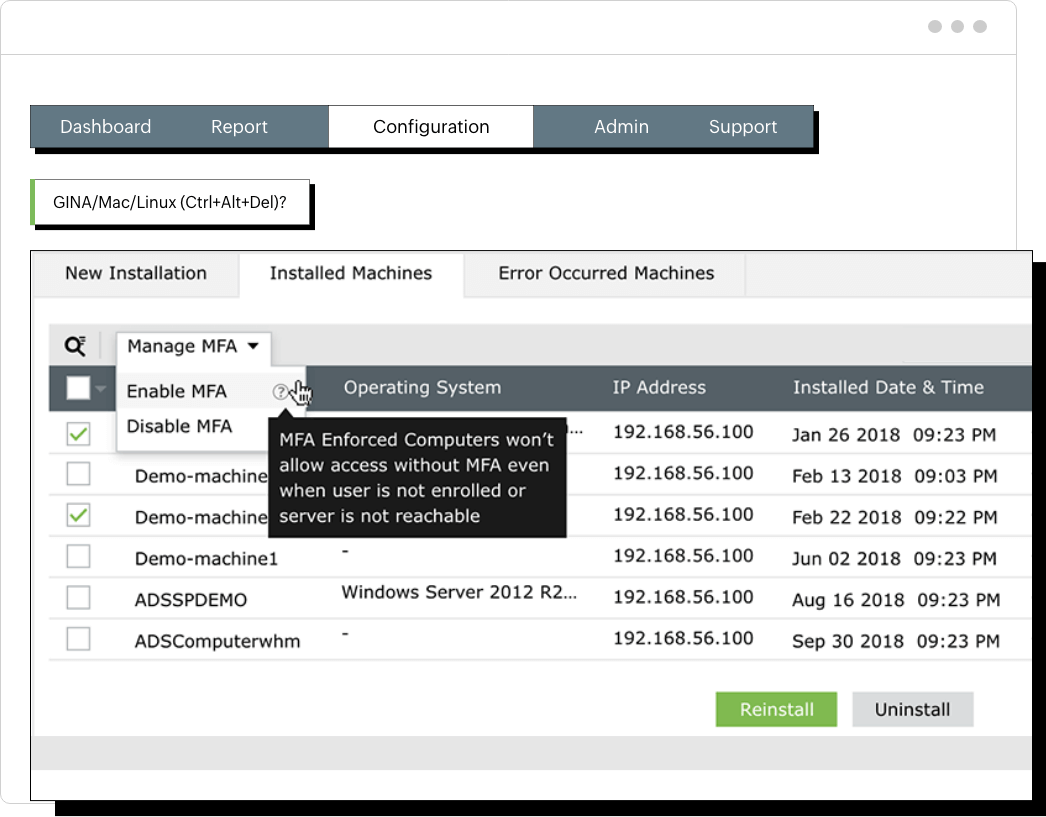
Machine-based MFA provides device-level security for servers and devices, regardless of user login. It ensures the authenticity of the device by registering it, collecting and validating authentication factors, and granting access only if the factors match the device profile. This provides security for critical machines, supports a variety of authenticators, and benefits RDP users.
ADSelfService Plus machine-based MFA supports the following :
When this feature is enabled, all users logging on to a particular machine must prove their identities using MFA. The authenticators prompted to the user will be based on the authenticators configured for them in the machine logon MFA.
To protect sensitive data, organizations must adhere to various compliance rules and regulations, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, the GDPR and more.
For example, PCI DSS 8.3 requires MFA whenever a third party or portable computer accesses the network remotely, while NIST's SP 800-63B recommends to use 2FA or MFA methods such as TOTPs, Google Authenticator, or RADIUS.
ADSelfService Plus helps organizations meet compliance standards such as NIST SP 800-63B, GDPR, HIPAA, SOC, FFIEC, PCI DSS and more. It enables MFA for application access in cloud and on-premises environments, as well as for endpoints, supporting 19 authentication factors like biometrics, Duo Security, TOTPs, Google Authenticator, YubiKey, and smart cards.
Implementing MFA can provide significant cost savings for organizations by decreasing the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks.
Regulations such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, the GDPR, and more prioritize the protection of sensitive data and reduce compliance fines.
Many insurance agencies require organizations to have MFA to qualify for cyber insurance coverage.