- Free Edition
- Quick Links
- MFA
- Self-Service Password Management
- Single Sign-On
- Password Synchronizer
- Password Policy Enforcer
- Employee Self-Service
- Reporting and auditing
- Integrations
- Related Products
- ADManager Plus Active Directory Management & Reporting
- ADAudit Plus Real-time Active Directory Auditing and UBA
- Exchange Reporter Plus Exchange Server Auditing & Reporting
- EventLog Analyzer Real-time Log Analysis & Reporting
- M365 Manager Plus Microsoft 365 Management & Reporting Tool
- DataSecurity Plus File server auditing & data discovery
- RecoveryManager Plus Enterprise backup and recovery tool
- SharePoint Manager Plus SharePoint Reporting and Auditing
- AD360 Integrated Identity & Access Management
- Log360 (On-Premise | Cloud) Comprehensive SIEM and UEBA
- AD Free Tools Active Directory FREE Tools
Why cyber insurance companies now mandate MFA for policy approval
With cyber insurance companies now mandating MFA as a prerequisite for policy approval, organizations without comprehensive MFA implementation may face coverage rejection or higher premiums. Insurance underwriters have identified MFA as one of the most critical controls, given that stolen credentials remain the number one initial access vector and are involved in 88% of basic web application attacks, according to Verizon's 2025 Data Breach Investigations Report.
What cyber insurers mandate for MFA compliance
Cyber insurance underwriters now require comprehensive MFA implementation across specific access points and systems. Satisfying these technical requirements is essential for policy approval and claims coverage.
Core MFA mandates that cyber insurers verify
- Privileged account protection: MFA must be enabled for all administrative accounts, service accounts, and users with elevated permissions across your organization. This includes domain admins, database admins, cloud platform admins, and any accounts with the ability to modify security settings or access sensitive data. Cyber insurers specifically audit these high-value targets because compromised privileged accounts often lead to the most devastating breaches.
- Remote access coverage: All VPN connections, cloud application access, and webmail systems must enforce MFA without exception. This requirement extends beyond traditional VPN clients to include browser-based SSL VPNs, remote desktop connections, and cloud-native authentication flows. Cyber insurers pay particular attention to remote access vectors because they represent the primary entry point for external attackers. Your implementation must cover both corporate-managed devices and personal devices accessing company resources through any remote connection method.
- Endpoint security: MFA is required for Windows, macOS, and Linux workstation logins, especially for remote workers. This mandate covers initial device authentication, screen unlocks after idle periods, and access to locally stored sensitive data. Insurers recognize that compromised endpoints often serve as launching points for lateral movement within networks.
- Complete user enrollment: Cyber insurers expect 100% user adoption with documented proof of active MFA usage across your organization. This means every user account that can access company resources must have MFA configured and actively in use, not just enabled as an option. Insurers will request enrollment reports, usage statistics, and evidence that MFA cannot be bypassed or disabled by the end users.
Technical implementation standards that insurers expect
- Support for multiple authentication factors meeting NIST guidelines: Your MFA solution must offer diverse authentication methods that align with NIST Special Publication 800-63B standards, allowing you to implement layered security approaches. These methods include time-based one-time passwords through apps like Microsoft Authenticator or Google Authenticator, hardware security keys such as YubiKeys for phishing-resistant authentication, and biometric verification like fingerprint and facial recognition. Insurers evaluate whether your implementation supports an array of different authentication factors because different threat scenarios require different defensive approaches, and a single authentication method creates vulnerabilities that sophisticated attackers can exploit.
- Backup authentication methods to prevent business disruptions during primary factor failures: Your MFA system must include redundant authentication pathways that maintain security while ensuring business continuity when primary methods fail. These backup methods include backup codes for situations where mobile devices are lost or damaged, alternative authenticator device registration for users traveling internationally, and administrative override procedures with proper audit trails for emergency access scenarios. Insurers specifically examine these backup procedures because inadequate fallback methods often force organizations to disable MFA temporarily during critical situations, creating security gaps that void coverage during the most vulnerable periods.
- Session timeout policies that automatically require reauthentication for sensitive operations: Your implementation must enforce granular session management that balances user productivity with security requirements through intelligent timeout mechanisms. This includes configuring shorter session durations for high-risk activities like financial transactions or administrative changes, implementing step-up authentication for privilege escalation within existing sessions, and automatically terminating sessions based on user behavior anomalies or location changes. Insurers evaluate these policies because extended session durations without reauthentication create windows where compromised accounts can cause extensive damage even after the initial breach is contained.
- Integration with your existing directory services to ensure centralized policy enforcement: Your MFA solution must seamlessly connect with Active Directory (AD), LDAP, or cloud identity providers to maintain consistent security policies across your entire technology ecosystem. This requires proper attribute mapping (to ensure user roles and permissions correctly trigger appropriate authentication requirements), automated policy propagation when organizational changes occur, and real-time synchronization between identity systems to prevent security gaps during user life cycle management. Insurers scrutinize this integration because fragmented identity management often creates policy inconsistencies that attackers exploit to move between systems with varying security controls.
Documentation requirements for policy approval
- Real-time MFA coverage reports showing protection across all critical systems
- User enrollment metrics demonstrating organization-wide MFA adoption
- Authentication audit logs proving active usage and successful implementation
- Incident response procedures specifically addressing MFA bypass attempts and failures
Ensuring cyber insurance compliance with ADSelfService Plus
ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus, an identity security solution, helps you meet all cyber insurance MFA requirements while ensuring comprehensive protection across every access point that underwriters verify. ADSelfService Plus empowers you to enable MFA for:
- Windows, macOS, and Linux endpoints.
- VPNs from providers like Fortinet, Cisco AnyConnect, and Ivanti.
- Systems supporting RADIUS authentication, such as Citrix Gateway, Omnissa Horizon (formerly VMware Horizon), and Microsoft Remote Desktop Gateway (RDP).
- Cloud applications, including Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and Salesforce.
In addition to the above, ADSelfService Plus provides offline MFA for machines without internet connectivity, ensuring complete coverage that satisfies insurance requirements for remote workers in any scenario.
How it works
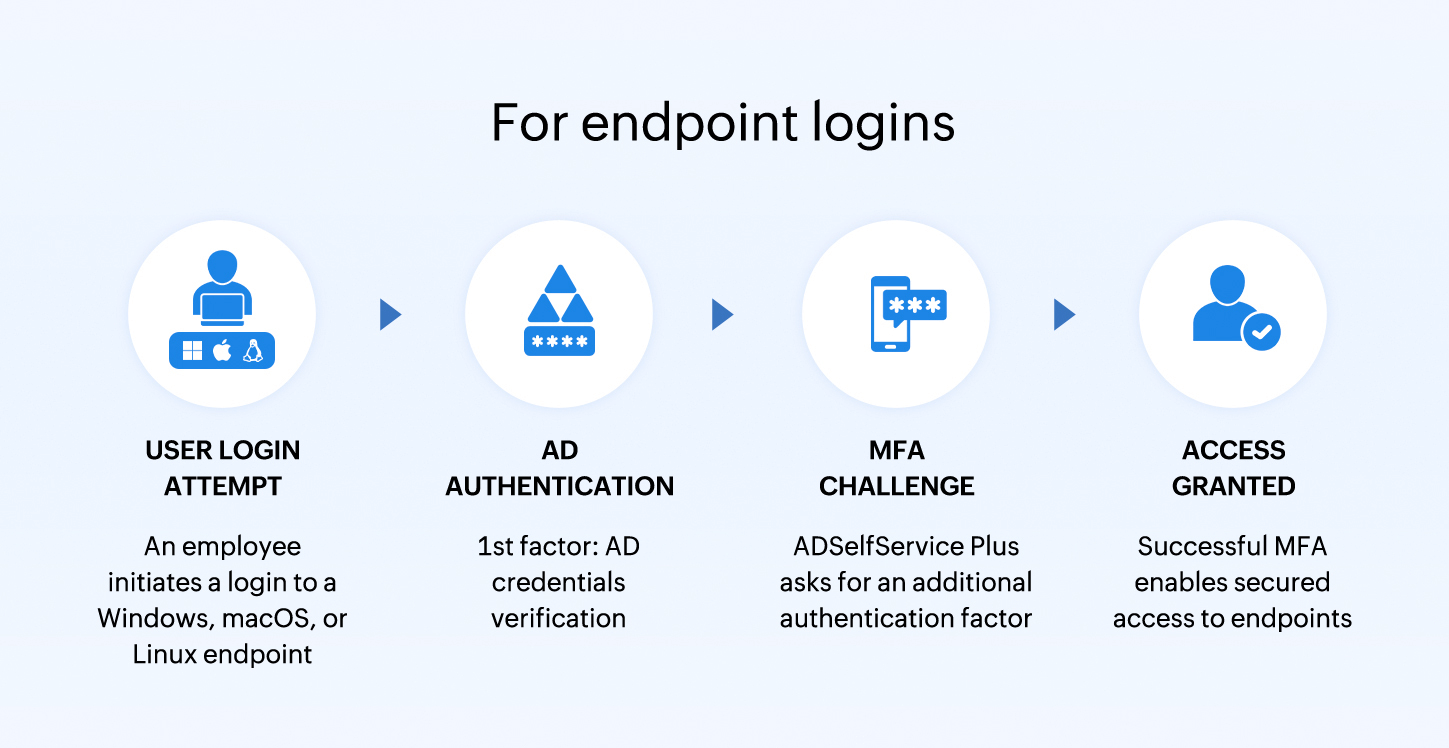
For endpoint logins
- A user initiates a login to a Windows, macOS, or Linux endpoint with their AD credentials.
- ADSelfService Plus prompts the user for additional authentication using the configured MFA methods based on insurance requirements.
- Only after successful multi-factor verification can the user access their workstation and connected systems.
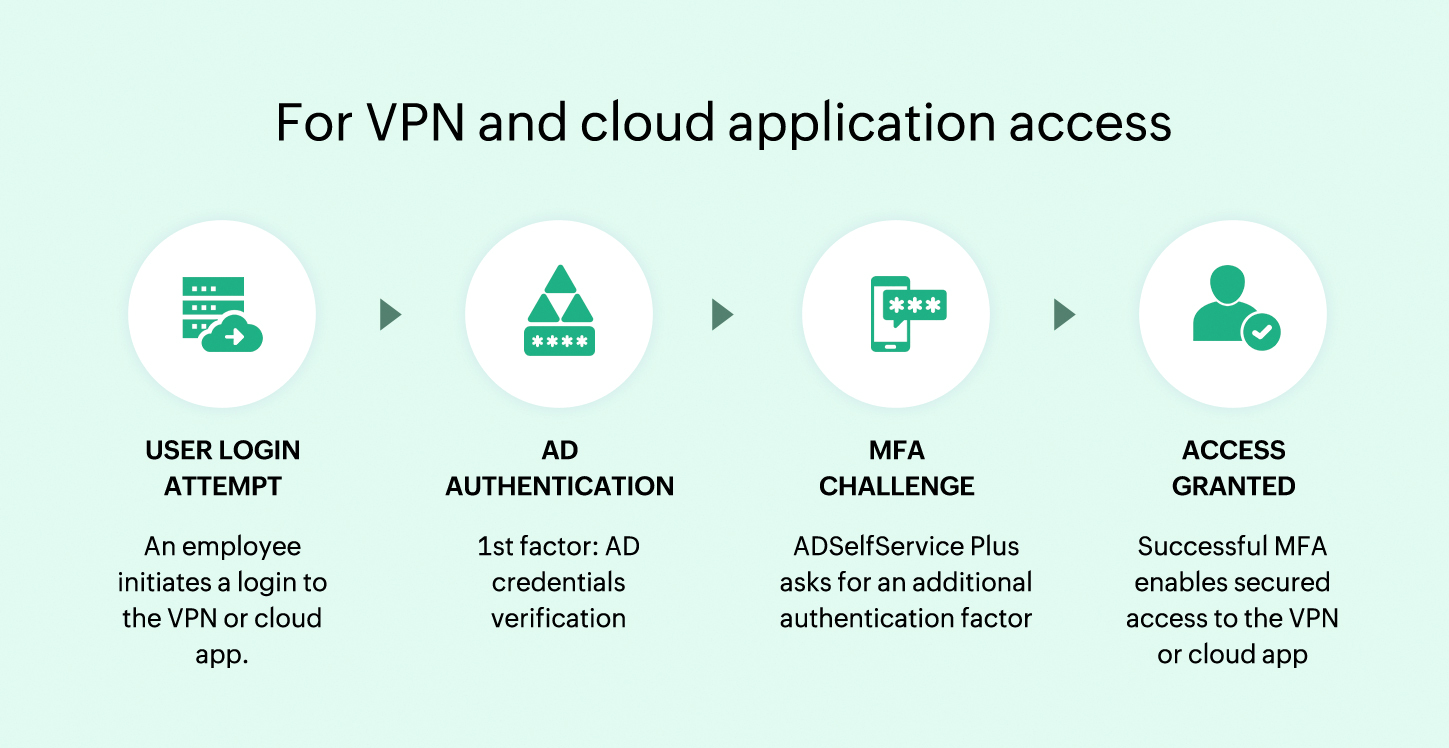
For VPN and cloud application access
- When a user attempts to access a VPN connection or cloud application, they are redirected to ADSelfService Plus for identity verification.
- The user authenticates with their AD credentials, followed by additional factors configured for their risk profile.
- Successful authentication grants access, while failed attempts are blocked and logged for security analysis.
Supported authentication methods
ADSelfService Plus provides 20 authenticators for MFA and gives you flexibility in configuration based on your organization's particular requirements. Here are some of the supported methods:
- Biometric authentication (fingerprint and facial recognition)
- FIDO2 passkeys
- Microsoft Authenticator
- Google Authenticator
- YubiKey authentication
- Email verification
- SMS verification
Benefits of implementing MFA using ADSelfService Plus for cyber insurance
- Comprehensive coverage: Implement MFA across all systems that insurance underwriters verify (endpoints, applications, VPN connections, and administrative access) using centralized policies.
- Policy flexibility: Configure different authentication methods for different user groups while maintaining comprehensive coverage.
- Automated compliance documentation: Generate detailed reports and audit trails that insurance underwriters require without manual effort.
- Complete enrollment: Automate user enrollment and force MFA adoption using login scripts, ensuring there are no coverage gaps that could jeopardize insurance policies.
- Conditional access: Deploy conditional access to automatically adjust authentication requirements based on the location, device, and user behavior.
Highlights of ADSelfService Plus
Password self-service
Eliminate lengthy help desk calls for AD users by empowering them with self-service password reset and account unlock capabilities.
1 identity with single sign-on
Gain seamless one-click access to more than 100 cloud applications. With enterprise single sign-on, users can access all their cloud applications using their AD credentials.
Password synchronization
Synchronize AD user passwords and account changes automatically across multiple systems, including Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and IBM i.
MFA
Enable context-based MFA with 20 different authentication factors for endpoint, application, VPN, Outlook on the web, and RDP logins.
Password and account expiration notifications
Notify AD users of impending password and account expirations via email and SMS notifications.
Password Policy Enforcer
Strong passwords resist various hacking threats. Require AD users to adhere to strong password standards by displaying password complexity requirements.










