

Active Directory (AD) is a directory service developed by Microsoft that provides centralized management of network resources such as users, computers, printers, and security groups within a domain-based network. It is designed to help IT administrators efficiently manage and secure an organization's network infrastructure by controlling user access, enforcing policies, and maintaining resource integrity.
At its core, AD acts as a centralized database where all information about network resources is stored, allowing administrators to organize access efficiently, and manage these resources through a single interface, streamlining IT operations across the enterprise.
With an AD integration, onboarding and offboarding of domain-based devices in UEMS becomes much easier. Once a domain is configured, you can import and manage all AD-linked devices from a centralized console. Also, UEMS can adjust its management scope automatically to reflect these changes as computers are added or removed from Active Directory.
AD integration also supports automatic creation of custom groups (Logical Structure Groups) based on AD Organizational Units (OUs) or other criteria. This simplifies the process of categorizing and managing domain-based devices dynamically to deploy the tasks as well as to provide them as scope for technicians.
AD integration also supports AD user-based login to UEMS Server console. This allows the technicians to use a single password to access both AD resources and the UEMS server.
AD integration also supports generating insights on AD components such as OU, Group, Domain, users, computers, and GPOs.
The AD integration also allows technicians to use the same credentials to deploy tasks such as agent deployment, custom scripts, or software to the computers.
For optimal functionality, the Endpoint Central service account requires specific permissions within Active Directory:
After the credential has been setup, we can confirm whether all the objects, OU can be retrieved by using the Basic LDP tool analysis.
set L in Command Prompt to get the Domain Controller name (Logonserver = Domain Controller Name).set U to retrieve the Domain Name and AD Domain Name (Userdomain = Domain Name, Userdnsdomain = AD Domain Name)set L and set U commands) in the appropriate fields.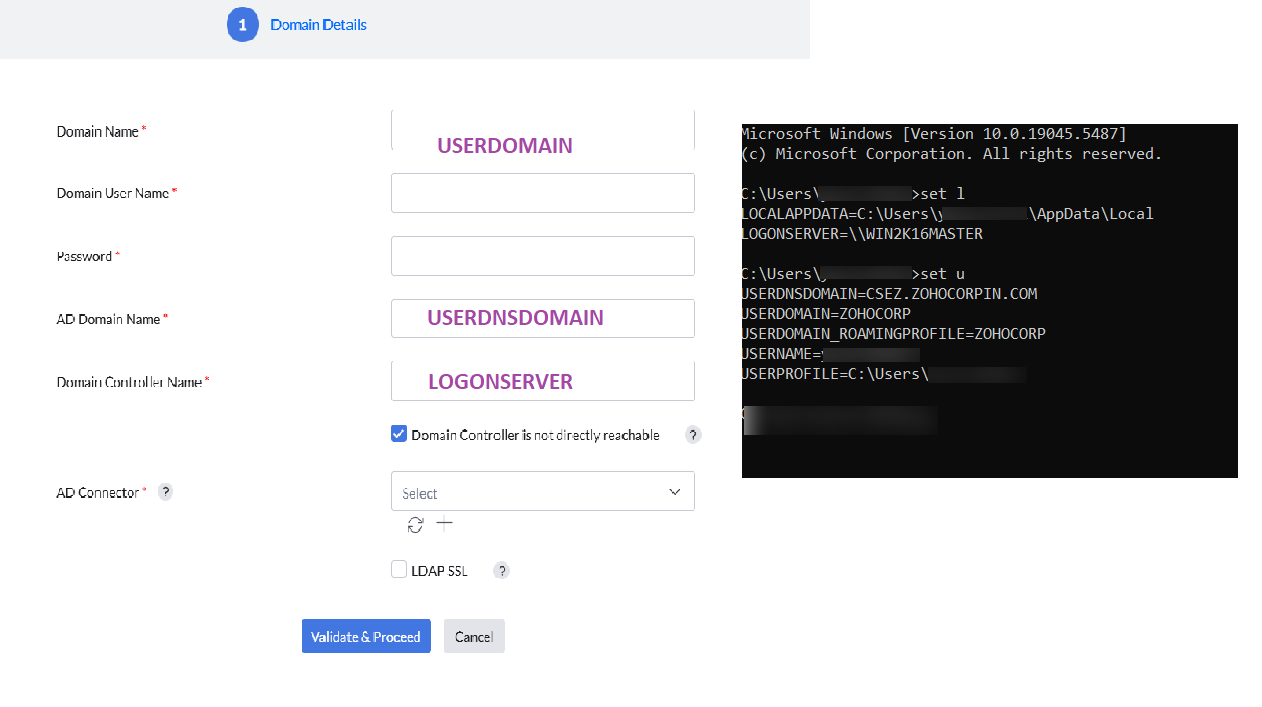
AD resource information is synced according to a pre-configured schedule. Changes in sync frequency will affect Domain, Auto Discovery - Active Directory Sync and Custom group functionalities.
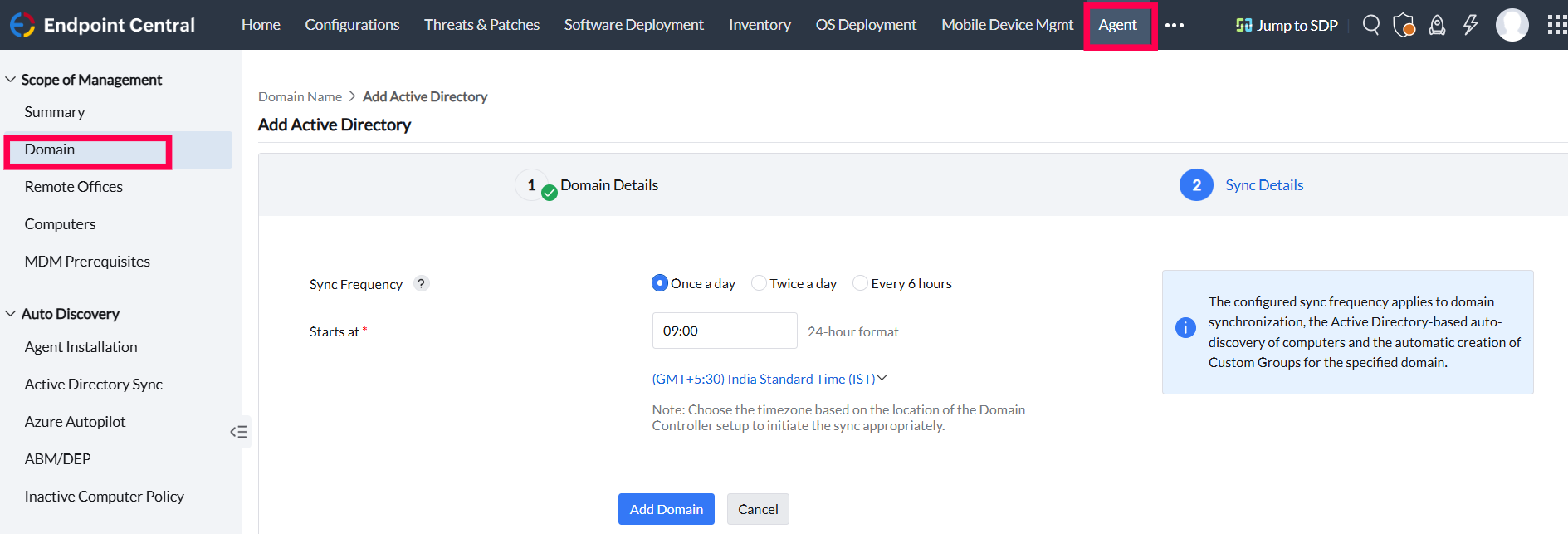
Once the domain is validated, the sync frequency can be configured for that particular domain.
Users can choose how often the domain syncs with the server:
Once a domain is added, you can manage it through the Actions menu.
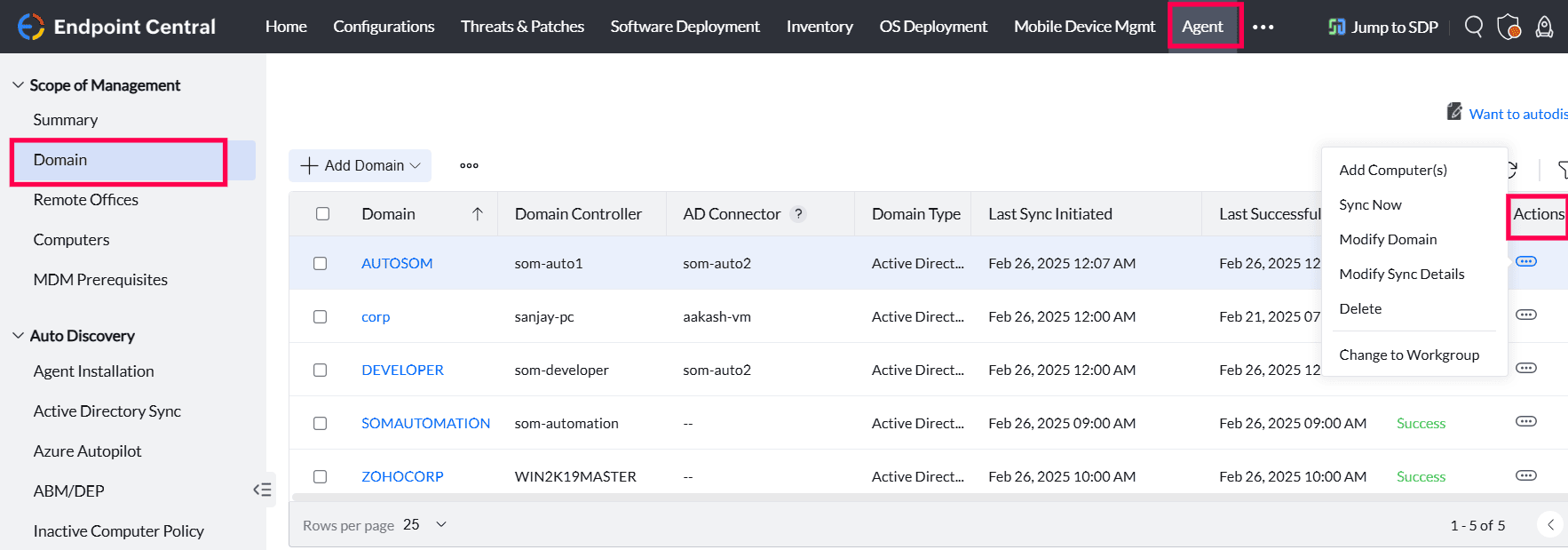
ipconfig /all in the command prompt and locate the data corresponding to Primary DNS Suffix.For any issues during domain setup or synchronization, review your administrative credentials, access rights, and AD object permissions. Ensure proper configuration of sync frequency and domain connectivity to avoid disruptions.