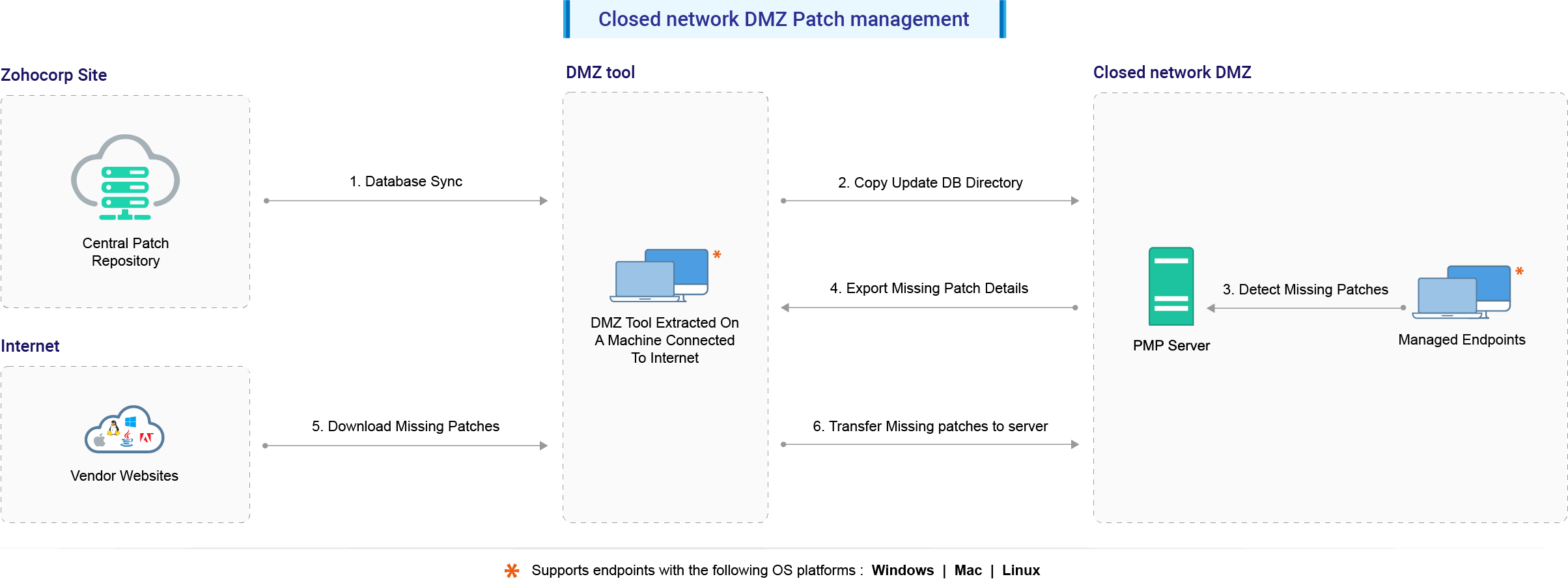
If the Patch Manager Plus Server is installed in a closed network, like Demilitarized Zone (DMZ), where the Server has no internet connection, the patch synchronization and automatic update are not possible. The following steps will help you to manually download all the missing patches and update them to the required computers.
|
You have successfully configured the tool and it is ready to be used. Configuring Proxy and setting up the tool are one time operations, whereas Updating the Patch Database and Downloading the required patches need to be done every time you wanted to deploy the latest missing patches.
Execute the command: patchsync.bat -c updatedb -i linux
This will update the latest patch information available at Zohocorp website and the metadata files available at respective Linux vendor sites to the local computer. The update will take some time and after completion, the necessary information will be updated in the updatedb directory.
Copy the updatedb directory to the Patch Manager Plus Server to <Install Directory>/conf/CRSData directory.
From the Patch Manager Plus Web Console, click the Patch Mgmt tab and click Update Now button. This will copy the necessary information from the updatedb directory to the database. Now, the local database in the server will have the latest patch information to detect missing patches and the metadata files to check for patch dependencies.
Now, scan the computers in the network to identify the missing patches and patch dependencies.
|
The next step is to download the missing patches and dependencies from the computer with internet connection and copy it back to the server.
To download the patches, you would first require the details of missing patches and dependencies. To get this, go to the Missing Patches view and click Export Missing Patches button. This will export the details of the missing patches along with the dependencies which should be downloaded as downloadUrlJson.txt
Copy this file to the directory in the computer where you had extracted the downloadmanager.7z
Open a command prompt and execute the command: patchsync.bat -c dwnpatch -f downloadUrlJson.txt
This will download all the missing patches and the dependencies to the store directory. Once all the files are downloaded, copy the contents of the store directory and copy it to the Patch Manager Plus Server to <Install_Dir>/webapps/DesktopCentral/Store directory (this is the default location; if this has been changed copy it to the appropriate location)
You should then update this information to the database so that all these patches are shown in the Downloaded Patches view. To do this, open the Downloaded Patches view and click Update Downloaded Patches button
All the manually downloaded patches will appear in the view from where you can deploy them to the required computers.
You have successfully configured the patch management process in a closed network.