

Our internal researchers procure vulnerability information for Windows Operating systems and other Microsoft products from Microsoft's official security guidance page, and for different Linux distros from the official security advisories of the respective vendors. For third-party products, we obtain the vulnerability data from NVD and CVE details, and the respective vendors' official security advisory pages.
Our internal researchers procure information regarding security misconfigurations from recommendations in STIG and CIS, and also from respective vendor websites.
All the CIS benchmarks that are used for Endpoint Central's audits are arrived at from the official CIS website.
Any of the Windows computers in your network with the requirements mentioned here can be hosted as your Central server.
Currently, if the operating systems meet any of the following criteria, we consider them as server machines:
We recommend purchasing server licenses for any Linux machine when deploying them as servers within the organization.
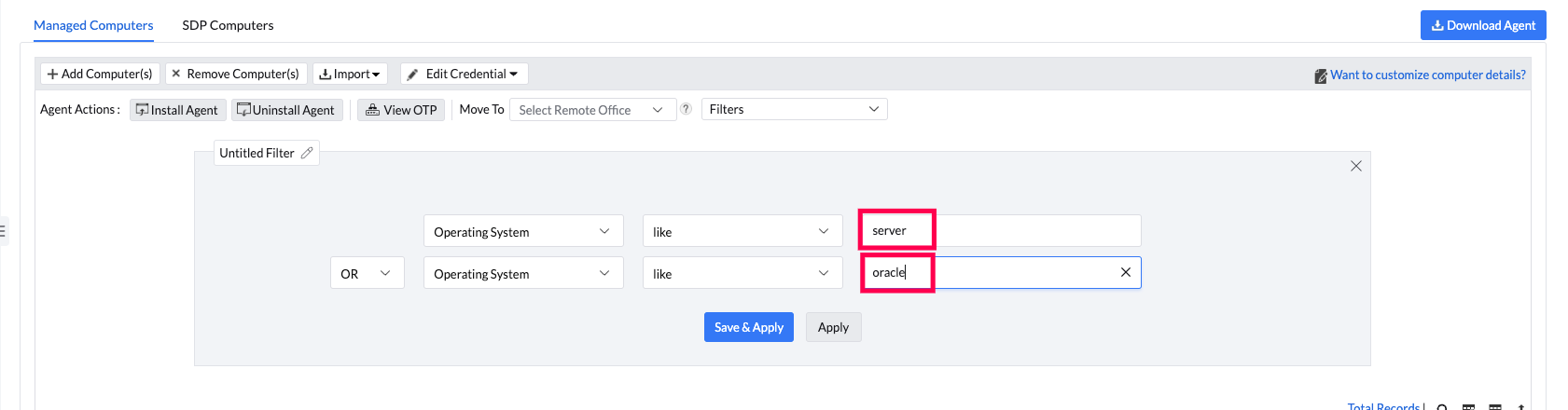
Navigate to Agent --> Computers in the console interface. Create a filter for Operating System with tags "server" and "Oracle". The Red Hat Enterprise Linux OS server machines cannot be identified using the web console as its subscription has to be checked.
The free edition allows management of any number of servers, as long as the total number of endpoints does not exceed 25.
The product performs a patch scan under the following conditions:
Note: The product does not support scheduling patch scans.
You can initiate a manual scan in local computer via Agent Tray icon -> Scan -> Initiate Patch Scan or via product console by navigating to Systems -> Scan Systems. Here choose the computers to be scanned and click Scan Systems. To scan all the systems, click Scan All. Please note that this option is limited to a maximum of 100 computers.
Endpoint Central does not support scanning network devices for vulnerabilities. This capability is available exclusively in the standalone Vulnerability Manager Plus product.
Under software vulnerabilities, patches are displayed as a resolution to fix a known threat or vulnerability.
Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS v3.0) is used to assess the severity of vulnerabilities based upon the ease of exploit and the approximated potential of impact. Scores range between 1 and 10 with 10 being most severe. Additionally patches can be looked up using their CVE ID
We detect web and database server vulnerabilities by scanning listening ports and identifying the application and its version. Vulnerabilities are identified by comparing the detected version to the vulnerability database. For further clarification on vulnerability applicability, please contact the vendor.
NOTE: Web/database servers will be detected only when they are actively running.Endpoint Central does not currently support patching or remediation for cURL-related vulnerabilities as of now. If you wish to see this supported as a part of future release, kindly fill out the feature request form.
To add patches for applications that aren't supported by the product, please fill out the feature request form. This will allow us to understand your needs and potentially incorporate support for those applications in future updates. Your feedback is valuable in helping us enhance our offerings to better serve your needs.
For Endpoint Central and other ManageEngine products, we use CVE analysis data from our internal security experts to exclude non-applicable vulnerabilities and display only applicable ones. In the initial days after a CVE is released, vulnerabilities may be detected, but if our analysis determines they are not applicable, they will be removed in subsequent scans after a database sync.
Endpoint Central and Vulnerability Manager Plus are two distinct products from ManageEngine designed for different IT management needs. Endpoint Central is a unified endpoint management (UEM) solution focused on managing and maintaining endpoints throughout their lifecycle. It offers features such as patch management, software deployment, asset tracking, remote troubleshooting, configuration management, and mobile device management. It is ideal for IT teams looking to centrally manage a large number of diverse devices. On the other hand, Vulnerability Manager Plus is a security-focused solution that specializes in identifying, prioritizing, and remediating vulnerabilities across the network. It provides advanced vulnerability scanning, risk-based prioritization using CVSS scores and threat intelligence, exploit detection, configuration audits, and compliance reporting. While both products include patch and vulnerability management capabilities, Endpoint Central also provide more endpoint administration features, whereas Vulnerability Manager Plus only focusses on vulnerability detection and risk mitigation.
Yes it support Windows updates too. Patches that need to be installed are directly downloaded from the respective vendors' web sites and stored in the Endpoint Central server before deploying them to computers in the network. The agents copy the required patch binaries from this server.
You can track the status of deployed security configurations from Deployments> Security configurations and re-deploy the failed deployments from here.
You can filter the Security Misconfigurations on the basis of:
1. Misconfigurations: Misconfiguration Name, Category, Severity, Remediation Availability and Post Deployment Issue.
2. Systems: Computer Name, Platform, Domain Name, Branch Office, Custom Group, Operating System, Language and Agent Live Status.
You can filter the Web Server Misconfigurations on the basis of:
1. Misconfigurations: Misconfiguration Name, Category, Severity, Web Server Name and DB Server Name.
2. Systems: Computer Name, Platform, Domain Name, Branch Office, Custom Group, Operating System, Language and Agent Live Status.
The product currently supports security configuration management only for systems running on Windows OS
To revert the misconfiguration fixes applied through our product, create a Manual Deployment task using a dummy patch, say Disable Updates Patches. You can search and select them from the Supported Patches view. Then, configure a deployment policy where the necessary custom script to revert the configuration is added as a pre- or post-deployment activity. Select this policy in the manual deployment task to deploy that dummy patch.
When a system is quarantined, it is isolated from the network to prevent potential security risks. Users will be notified, and administrators can take necessary actions to remediate compliance issues.
Yes, once the compliance issues are addressed, administrators can lift the quarantine, allowing the system to resume normal operations.
Yes, compliance scans are different Patch and Vulnerability scans. Compliance scans can be scheduled via the product console to custom groups while Patch and Vulnerability scan happens during the below mentioned scenarios:
Regular audits are recommended, with the frequency determined by organizational policies. Monthly or quarterly audits are common, but more frequent daily checks may be necessary for highly dynamic environments.
Absolutely! The policy is highly customizable to accommodate the unique requirements of your organization. Administrators can define rules tailored to specific compliance standards and security policies.
You can track the status of high-risk software uninstallation from Deployments> Software uninstallation.
By navigating to Report -> Scheduled Report, you can schedule a specific vulnerability report. Alternatively, an export option is available in the top right corner of each specific table, allowing you to export the table data.
In the Detailed Software Vulnerabilities view, you can use Advanced Filters to filter machine vulnerabilities by the 'Patch Availability' criteria set to 'Not Available,' and then export the report.
Static group exclusion happens immediately, whereas for Dynamic groups, it reflects after the next scan.
The below-mentioned features will be released with future updates. If you have other feature requests other than the ones mentioned below, please fill out this form.