How to view and access Windows error logs
Last updated on:In this page
What are Windows error logs?
Windows error logs primarily record significant events, such as critical system errors that indicate potential issues with the operating system or installed software. These logs serve as a valuable resource for diagnosing and resolving system problems, as they provide detailed information about the error conditions and the state of the system at the time of the failure.
How to view and access Windows error logs
In Windows 11, update logs can be accessed through various methods:
Method 1: Using Event Viewer
Windows Event Viewer provides a comprehensive view of system, application, and security logs.
- Open Event Viewer
- Press Win + S, type Event Viewer, and select it from the search results.
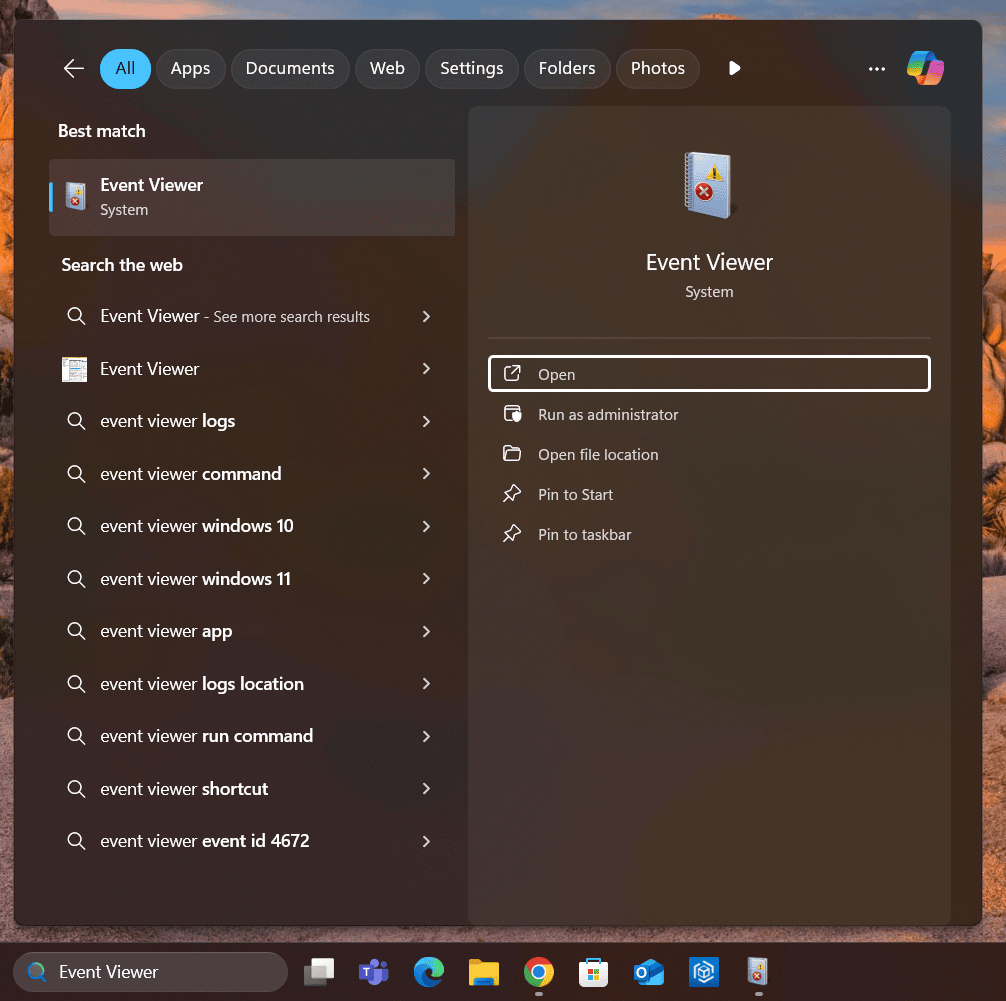
- Alternatively, you can press Win + X and choose Event Viewer from the menu.
- Press Win + S, type Event Viewer, and select it from the search results.
- Navigate to error logs
- In the Event Viewer window:
- Expand Windows Logs in the left pane.
- Select Application or System depending on where you expect the error to be logged.
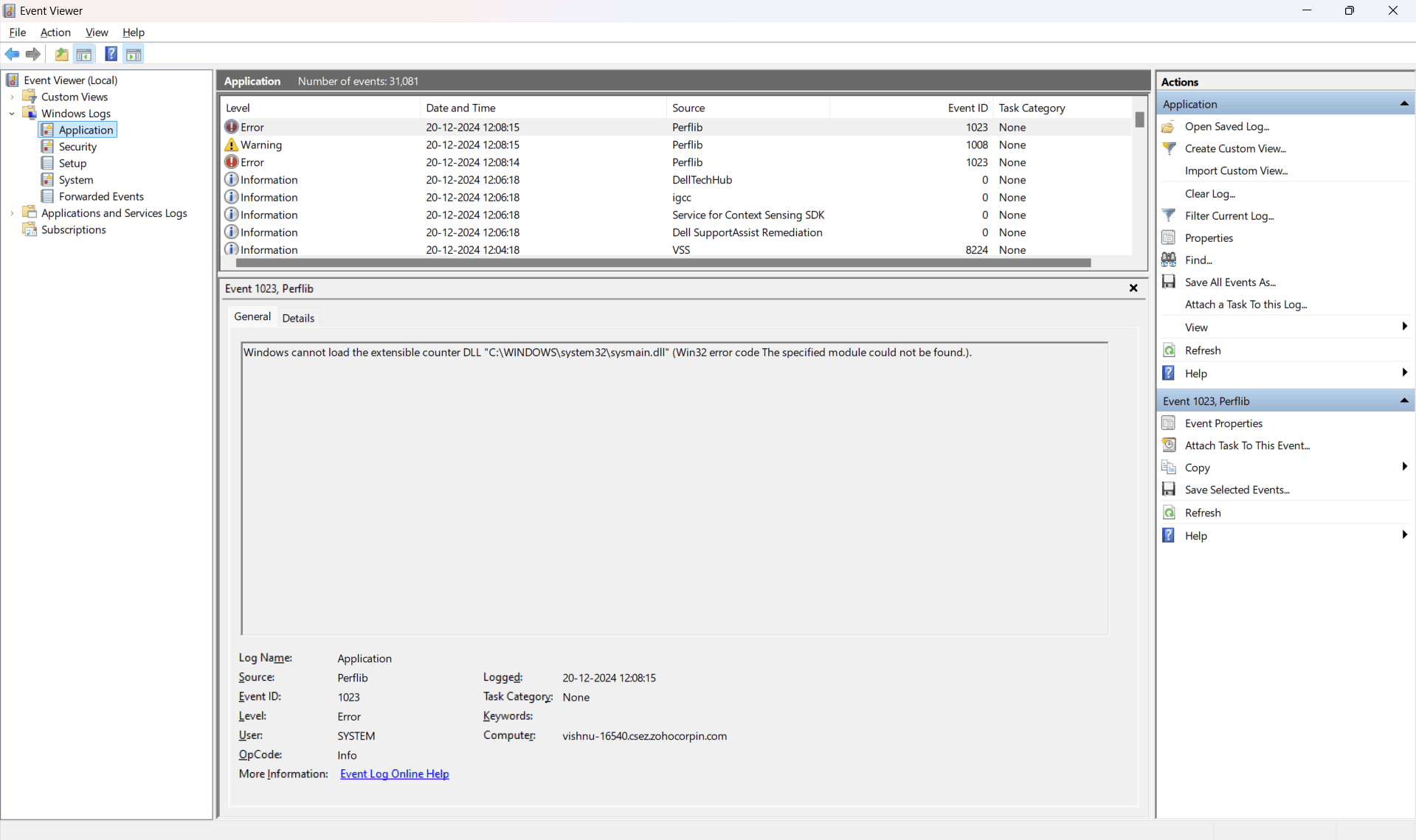
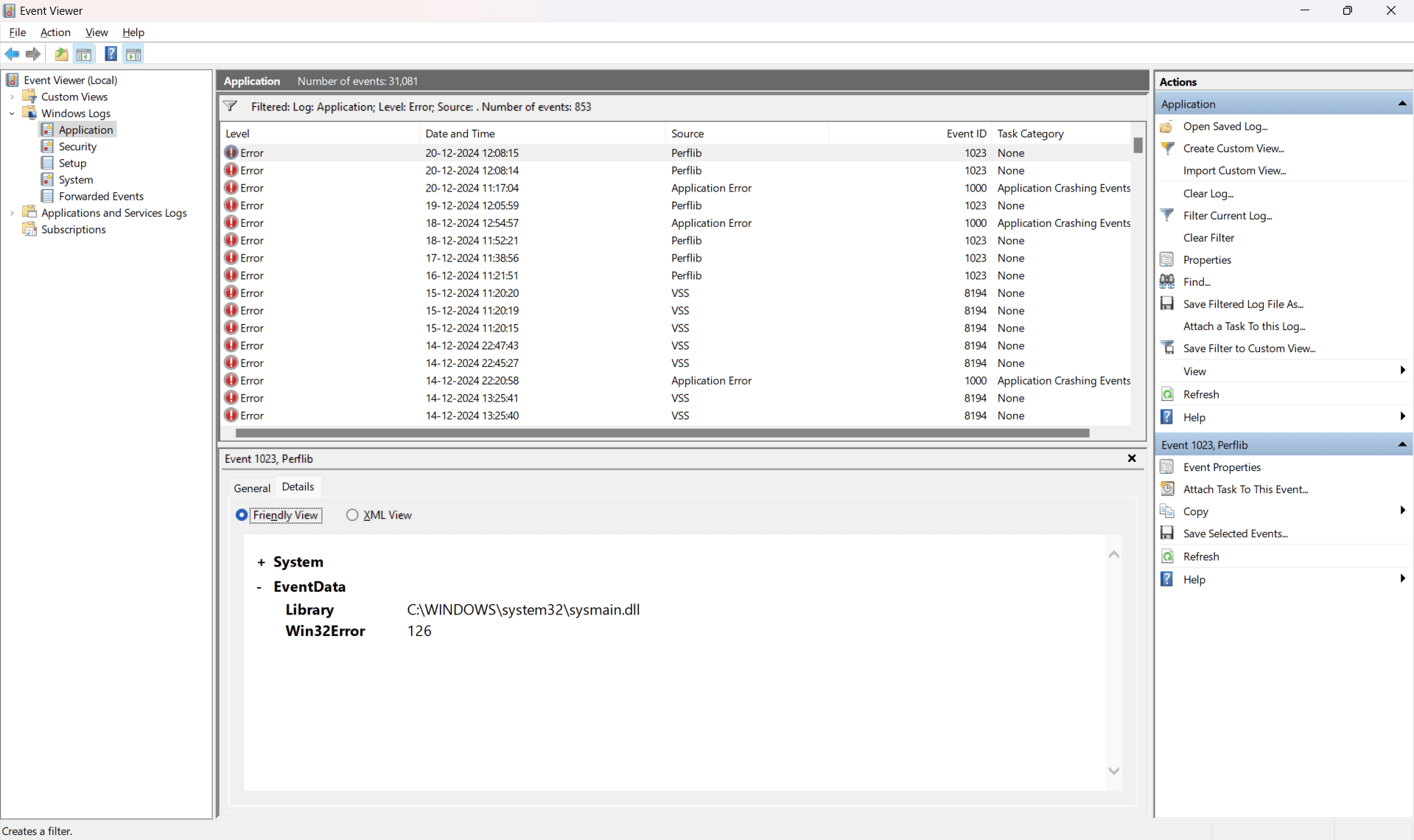
- In the Event Viewer window:
- Filter logs for errors
- Right-click Application or System, and select Filter Current Log.
- Under Event Level, check Error and click OK.

- Review the logs for entries marked as errors.
- View log details
- Click an error log entry to view its details in the lower pane.
- For additional details, click Details in the log entry.
Method 2: Using PowerShell
PowerShell provides a quicker way to fetch error logs.
- Open PowerShell
- Press Win + X and choose Windows Terminal (Admin) or PowerShell (Admin).
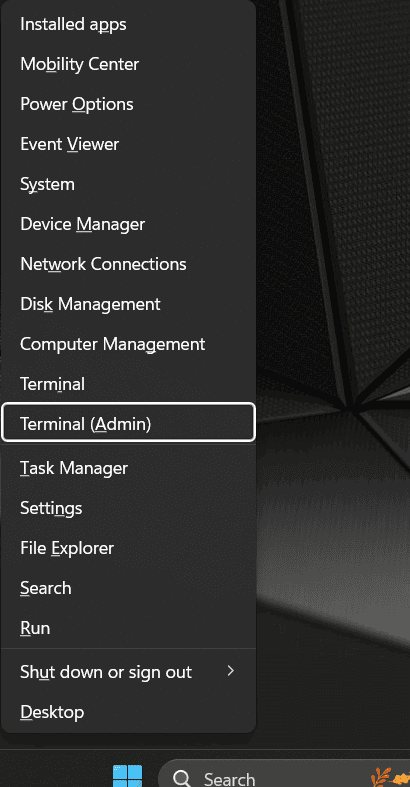
- Press Win + X and choose Windows Terminal (Admin) or PowerShell (Admin).
- Run the command
-
Use the following command to display error logs:
Get-EventLog -LogName Application -EntryType Error -Newest 20
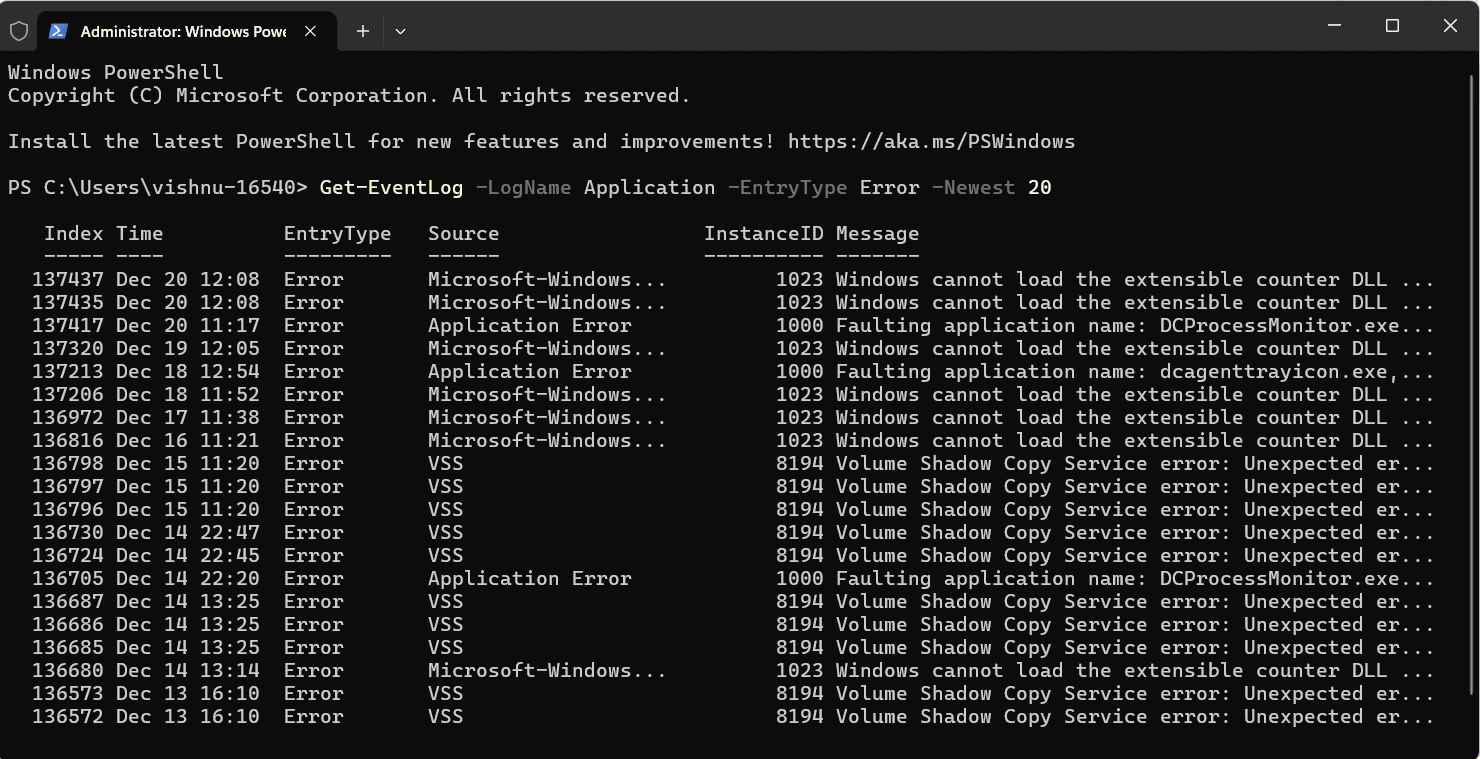
- Replace Application with System for system-related errors and adjust -Newest to specify the number of logs you want.
-
How to analyze Windows error log entries
Windows error log entries typically include the following information:
- Event ID: A unique identifier for the error event.
- Source: The component or application that generated the error.
- Level: The severity of the error (e.g., Error, Warning, Information).
- Task category: The category of the error event.
- Keywords: Additional metadata associated with the error.
- User: The user account under which the error occurred.
- Computer: The name of the computer where the error was logged.
- Description: A detailed explanation of the error and its potential causes .
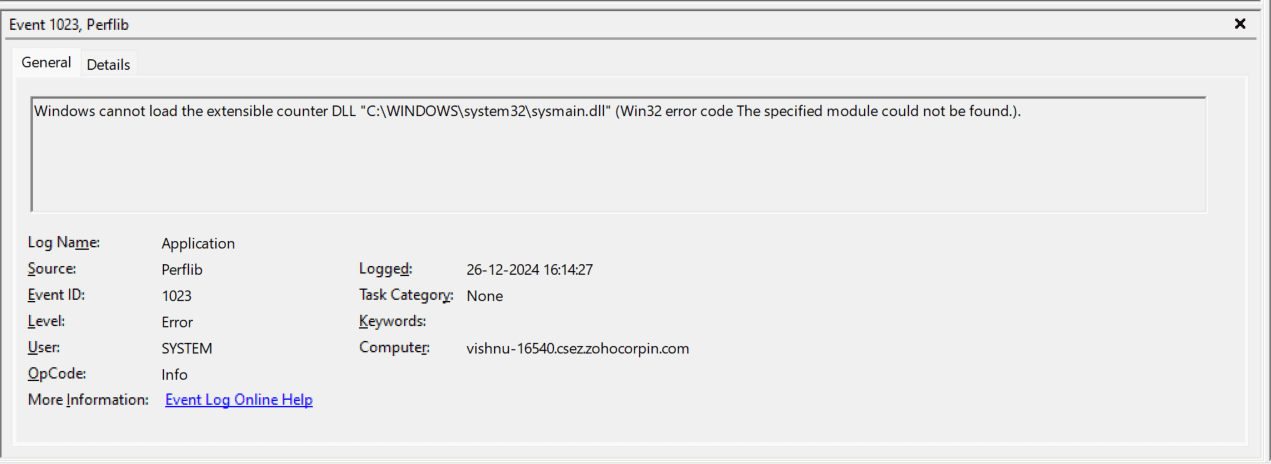
By understanding the meaning of these fields and the specific error codes, you can better interpret the error logs and identify the root cause of the problem.
How can Windows error logs help with troubleshooting system issues?
Windows error logs can be used to troubleshoot various system issues, such as:
- Identifying issues: Windows error logs help administrators and users identify issues by recording error codes, failure details, and timestamps, which provide insights into the nature of the error.
- Tracking application errors: Some errors, such as application malfunctions, are recorded, helping pinpoint issues in specific software programs.
- Monitoring system failures: Logs capture system-level problems like hardware failures, driver issues, and resource conflicts, offering a pathway to resolving critical system errors.
- Offering security insights: Error logs also track security-related incidents, such as failed login attempts, unauthorized access, or changes to system settings that may indicate security breaches.
By analyzing the error logs and correlating them with other system information like performance counters or event traces, you can effectively diagnose and resolve complex system problems.
Suggested reading: Check out our troubleshooting guide on Windows error logs, such as application errors.
What are the best practices to manage Windows error logs?
Managing Windows error logs effectively is crucial for ensuring system reliability, security, and troubleshooting efficiency.
Here are some of the best practices for Windows error log management:
- Centralized log management: Centralizing error logs into a single platform simplifies monitoring and troubleshooting. Log management tools like EventLog Analyzer aggregate logs from multiple sources, providing a unified view. This approach reduces the risk of missing critical errors and ensures faster diagnostics, especially in complex IT environments.
- Automate collection and monitoring: Automating error log collection using tools or scripts ensures no critical data is missed. Pair this with real-time monitoring and alerting to instantly detect issues like application failures or security breaches. This proactive approach helps address problems before they escalate into significant disruptions.
- Define retention policies: Set clear retention policies for logs based on compliance requirements and business needs. Retain logs long enough to analyze trends and support forensic investigations, but also archive or delete older logs to optimize storage and maintain system performance.
- Analyze logs regularly: Periodic analysis of error logs helps identify recurring issues, enabling preventive measures. By integrating error logs with analytics tools, you can uncover patterns, trends, and root causes. This continuous review process fosters improved system stability and reliability.
- Secure log data: Protecting error logs is essential to prevent unauthorized access or tampering. Encrypt log files and restrict access to authorized personnel only. This ensures log integrity, especially when logs are used for compliance or legal purposes.
These practices form the foundation for effective error log management, ensuring smoother operations, compliance readiness, and improved incident response.
How ManageEngine EventLog Analyzer monitors Windows error logs
ManageEngine EventLog Analyzer is a log management and IT compliance tool that centralizes and analyzes event logs from Windows infrastructure. It provides a comprehensive platform to track, manage, and troubleshoot error logs, ensuring seamless system performance and security.
EventLog Analyzer simplifies error log analysis by automatically collecting logs from all Windows devices and categorizing them based on severity and type. It offers predefined reports for various error events, enabling administrators to identify, diagnose, and mitigate issues promptly.
- Predefined reports: Provides detailed insights through reports such as failed software installations and security logs cleared.
- Raw log access: Offers the ability to drill down into raw logs for comprehensive root cause analysis.
- Audit trail analysis: Use the audit trail reports to understand user and system actions leading up to an error.
- Real-time alerts: Automate the detection of significant events such as failed updates or application crashes.
- Integrated search: Use the advanced search feature to pinpoint error events across logs quickly.
- Dashboards and analytics: Gain insights into error patterns through visual dashboards, helping prioritize resolutions.
Specific Windows device reports relevant to error logs include:
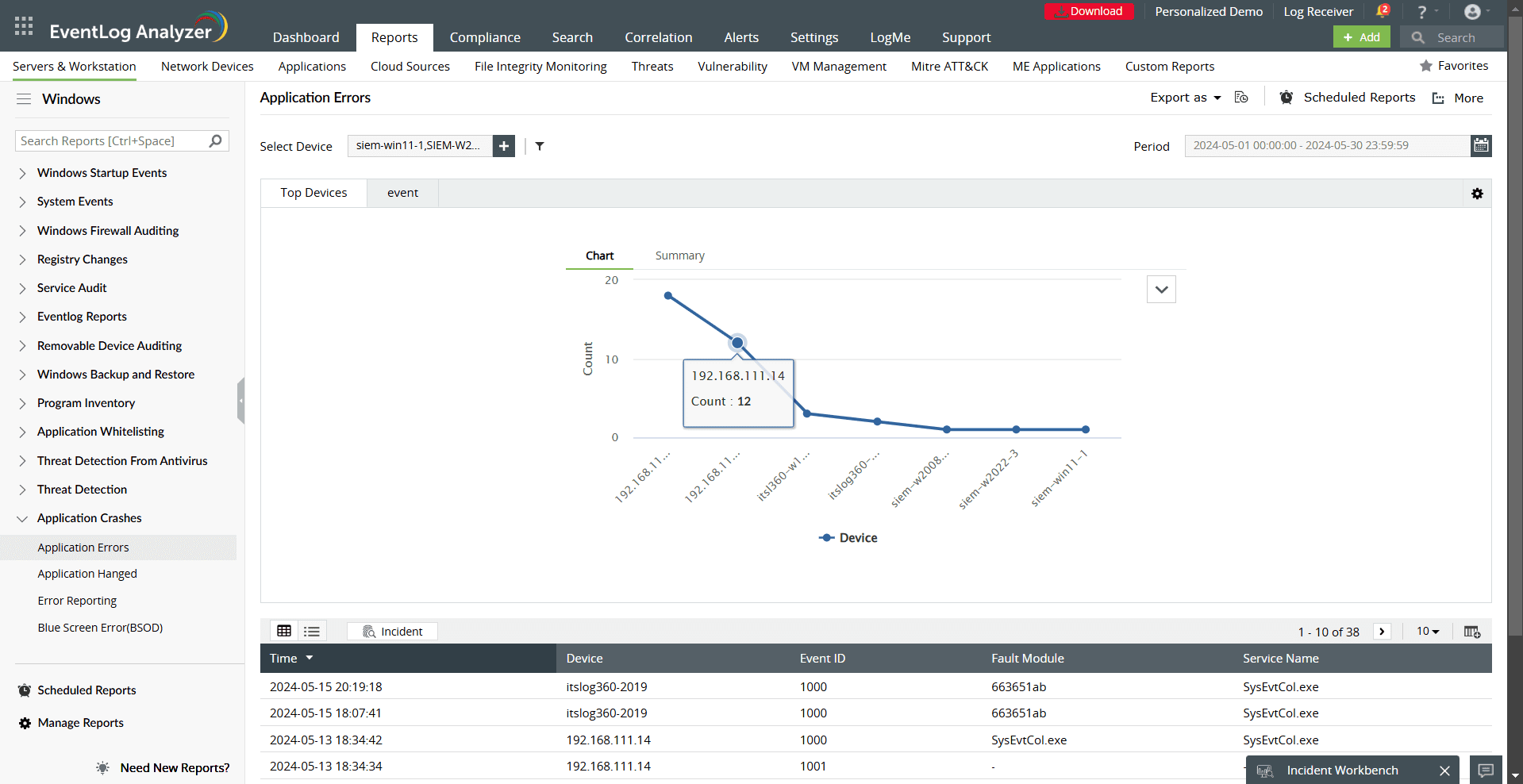
- Application Errors: Tracks issues like crashes, hangs, or execution failures of installed applications.
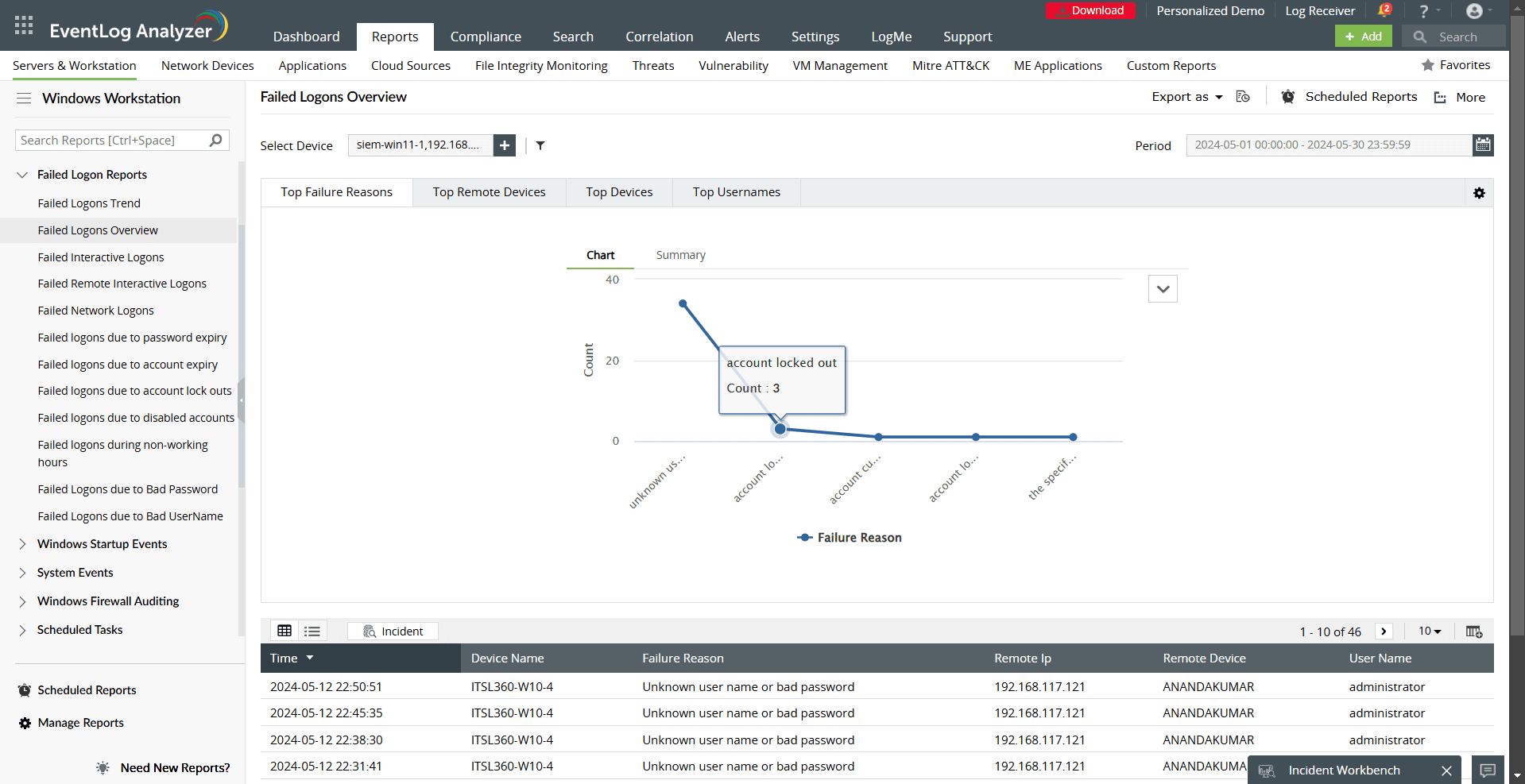
- Failed Logon Reports: Includes events like bad passwords or account lockouts, which may indicate security misconfigurations.
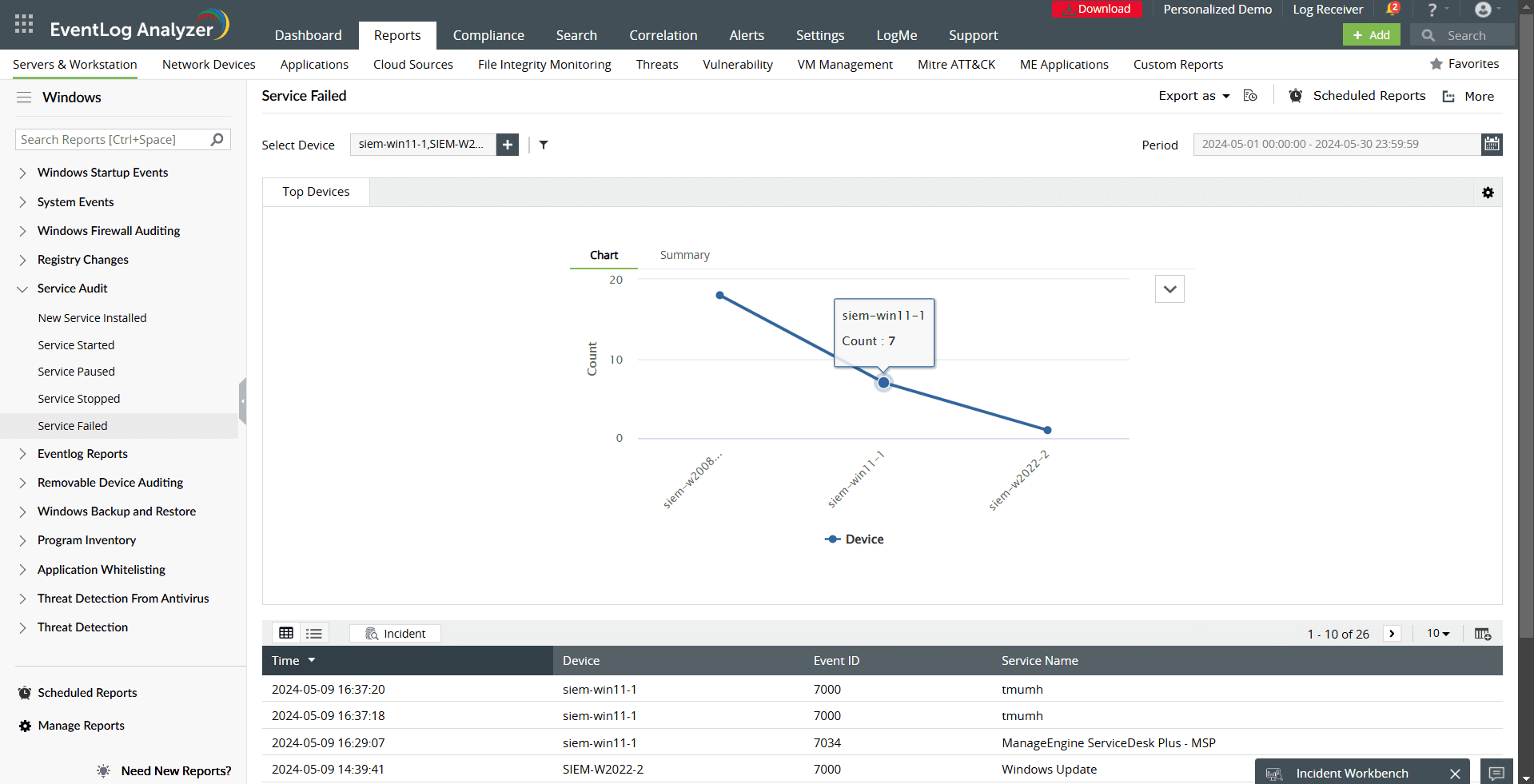
- Service Failed: Tracks errors in service startups or stops, offering critical insights into system health.
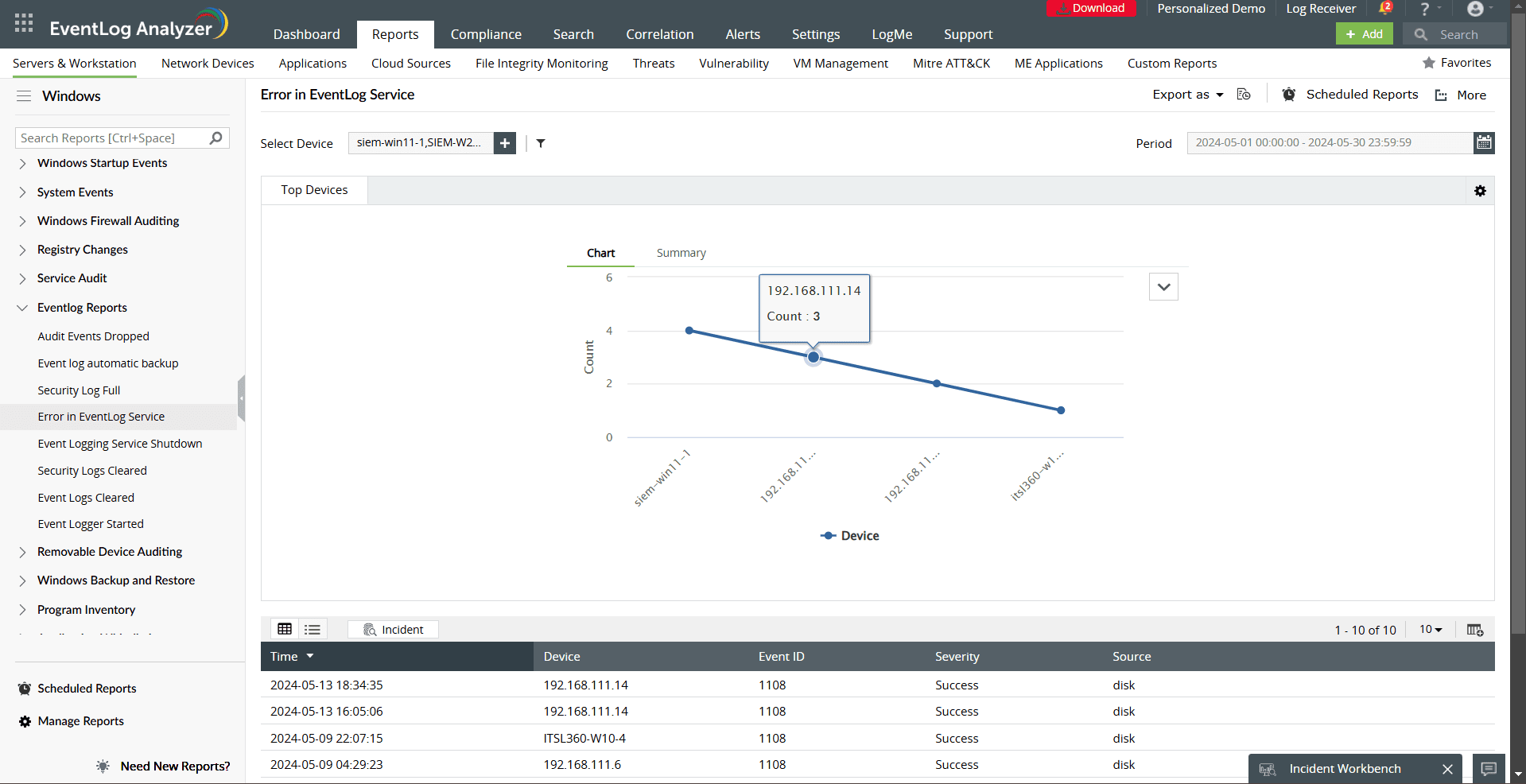
- Error in EventLog Service: Identifies failures in the event logging service, ensuring uninterrupted log generation.
By monitoring Windows error logs, IT teams can quickly detect and address system failures, enhancing security, reliability, and performance.











