Protocols used for syslog collection - TCP, UDP, RELP
Last updated on:In this page
Syslogs are the logs generated from Linux/Unix devices and other network devices like switches, routers and firewalls The syslogs can be centralized by aggregating them to a server called the syslog server, syslog daemon or syslogd. Transmission of syslogs from the devices to the syslog daemons happens with the help of TCP, UDP and RELP protocols.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
UDP is a connectionless and unreliable protocol. So, the syslog messages sent to the syslog daemon do not return any receipt acknowledgment. By default, the syslog transmission over UDP protocol happens through port 514. However, the user can always change this port number.
Generally it is not recommended to transmit using UDP, as syslog packets may not be properly received at the syslog server, and vital information could be lost.
You have to configure a server to act as a syslog daemon by enabling it to listen on UDP port 514.
- Open etc/syslog.conf file in your terminal.
- Identify the below statements and uncomment them.
- $ModLoad imudp
- $UDPServerRun 514
- Restart the machine and check if the changes are applied
Learn more about syslogs
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
TCP is a connection-oriented and reliable transmission protocol that can use the same port 514 to send syslog messages to syslog daemons. TCP is used by default for data transmission in syslog collecting tools like rsyslog and syslog-ng. The syslogd sends an acknowledgement for every syslog message received. This ensures all the sysog messages are stored in a single repository.
You can configure a server to act as a syslog daemon and enable it to listen on TCP port 514 using the below commands.
- Open etc/syslog.conf file in your terminal.
- Identify the below statements and uncomment them.
- $ModLoad imudp
- $UDPServerRun 514
- Restart the machine and check if the changes are applied
Reliable Event Logging Protocol (RELP)
RELP, originally developed for rsyslog-rsyslog communication, is a networking protocol which helps in reliable transmission of event messages to the destinations. RELP uses TCP for transmission of syslogs. However, it provides the additional functionality of identifying the messages that are properly received at the syslog daemon using a backchannel. Backchannels can view the syslog messages that are sent from devices and simultaneously listen to them at the receiver end.
If there is a sudden connection termination during syslog transmission, RELP solves the ambiguity of whether the message that was in transmission was received at the syslog server or not. It conveys a message back to the sender about the syslogs processed by the syslog server.
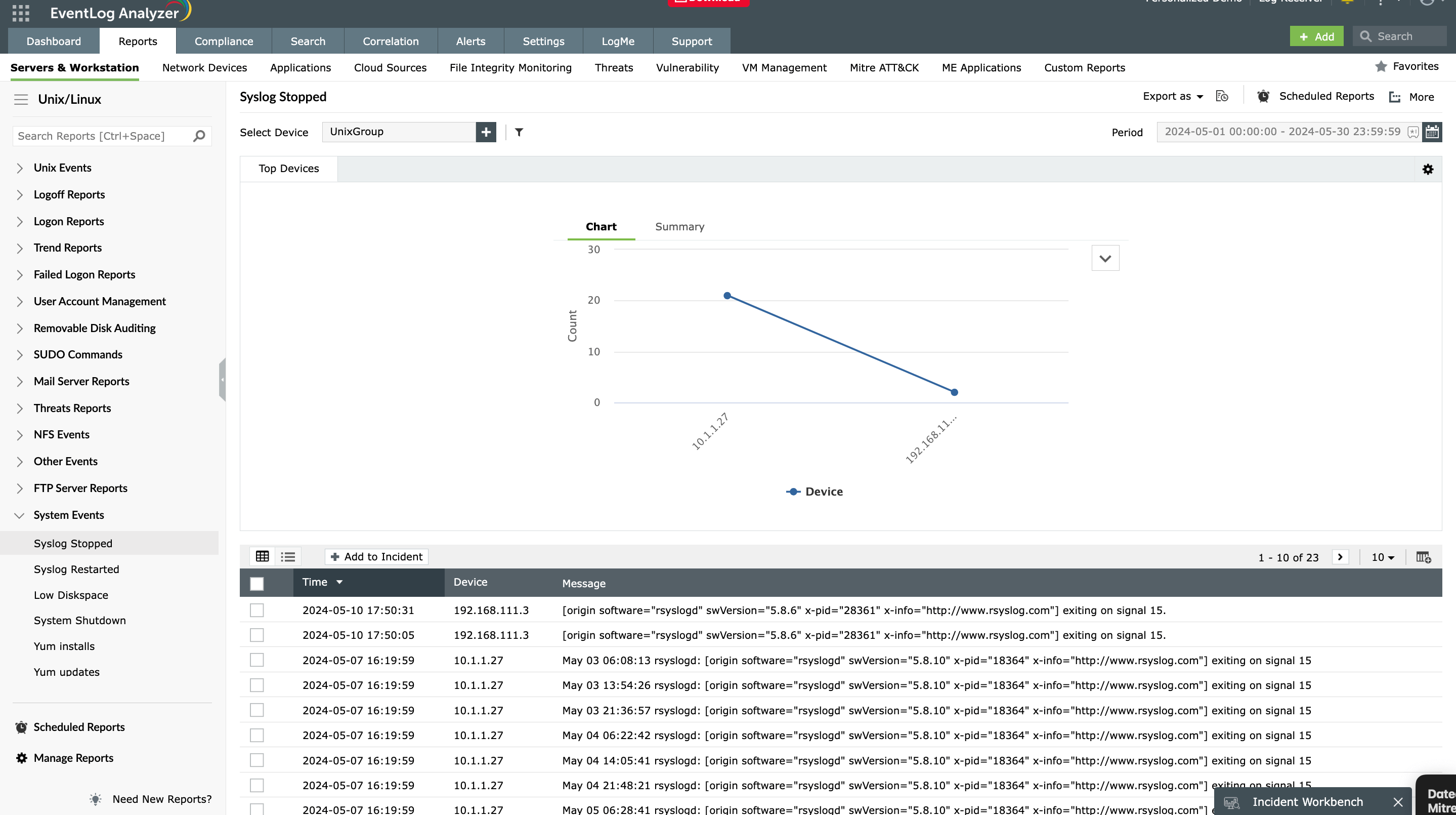
Monitoring syslogs using EventLog Analyzer
Whether your devices transmit logs over UDP for speed, TCP for reliability, or TLS for security, effective syslog monitoring requires more than just receiving packets. Manually collecting and parsing these logs using command-line tools like grep is inefficient, error-prone, and slow, especially in large, distributed environments.
Centralized and automated syslog collection
EventLog Analyzer simplifies syslog management by acting as an automated, centralized syslog listener and analyzer. It ensures that every syslog generated across network devices is securely transmitted, stored, parsed, and analyzed without manual intervention.
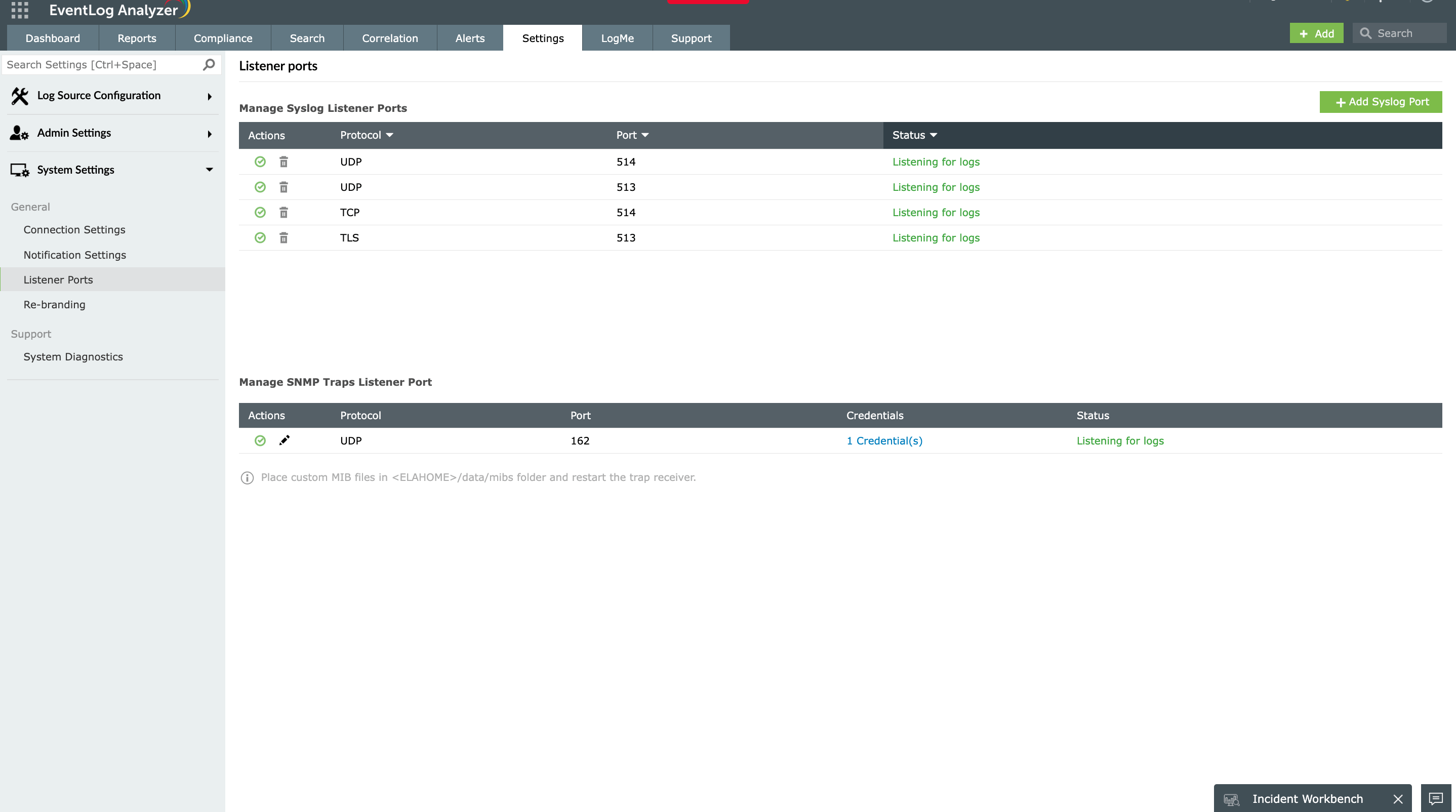
Protocol-agnostic syslog collection
EventLog Analyzer comes with a built-in syslog listener supporting all major transport protocols:
- UDP 514: High-speed collection for firewalls, routers, and high-volume devices
- TCP 514: Reliable delivery with acknowledgment for servers and critical applications
- TLS 6514: Encrypted transmission for sensitive environments and compliance requirements
This flexibility allows seamless integration with your existing network infrastructure. Devices can be configured to forward syslogs directly to EventLog Analyzer using whichever protocol suits their security requirements—no protocol conversion or additional middleware needed.
Which protocol should you use with EventLog Analyzer?
- UDP 514: Best for high-volume devices (firewalls, routers) where occasional log loss is acceptable
- TCP 514: Recommended for servers and applications where every log must be delivered
- TLS 6514: Required for sensitive environments, compliance mandates, or logs crossing untrusted networks
EventLog Analyzer supports all three simultaneously to ensure users configure each device based on its security requirements.
Unified analysis across protocols
Once logs arrive, EventLog Analyzer normalizes them into a consistent format for analysis. UDP-delivered firewall logs, TCP-transmitted server events, and TLS-encrypted application logs all appear in unified dashboards and reports.
The correlation engine cross-analyzes syslogs with other log sources to detect unauthorized access, suspicious behavior, and security breaches. Predefined alert profiles notify administrators instantly, enabling faster incident response.
Built-in compliance support
Regulations like the PCI DSS and HIPAA require encrypted transmission for logs containing sensitive data. EventLog Analyzer's TLS listener (port 6514) satisfies these requirements while secure archival ensures audit-ready log retention.
By supporting UDP, TCP, and TLS within a single platform, EventLog Analyzer lets you balance performance, reliability, and security based on each device's requirements.