In this page
This page outlines the prerequisites for using UEBA in Log360 Cloud and explains how its machine learning models detect different types of anomalies. It also includes the conditions required for the activation of this feature and how time-based, count-based, and pattern-based anomaly detection models are trained and applied.
Please note that the UEBA capability of Log360 Cloud is available only for the Professional plan, Zoho One and MSSP users. If you are not using either of these plans, upgrade your instance to these plans.
ManageEngine Log360 Cloud's UEBA uses unsupervised learning to detect anomalies. The training details for each type of anomaly detection method are as follows:
Time-based anomalies are unusual data points that deviate significantly from the expected behavior. These anomalies are identified by analyzing data collected over time and looking for deviations from the established trends or other temporal patterns.
Here's a breakdown:
Anomalies that can be detected based on this method:
Unusual login time, for instance. A user who usually logs in at 8 am suddenly logs in at 10 pm. Such deviations are flagged and notified as anomalies.
Count-based anomalies, also known as frequency-based anomalies, are anomalous data points that occur with an unusual frequency of events compared to the expected or normal count.
Here's a breakdown:
Anomalies that can be detected based on this method:
Logon Failures, for instance. The usual amount of logon failures faced by a host may be 5-10. A sudden spike in this number could hint at anomalous behavior, eventually surfacing as an attack like Brute Force attack.
Pattern-based anomalies are deviations from established sequences of event occurrences.
Unlike time and count anomalies which are focused on finding the anomalous data points based on the number of events that fall into a particular data point range, pattern-based anomalies involve a series of subsequent actions, as a whole.
Here's a breakdown:
Anomalies that can be detected based on this method:
Usual devices for logins, for instance. A user usually logs in with specific machine- Host1, Host2, Host3 for example. If the same user deviates from this usual pattern of behavior and logs in into Host4 machine, this will be detected as a pattern anomaly since the usual sequence of his actions have been disrupted. Anomaly is detected in case of a sudden spike in usage of device(s)/machine(s) too. Example, if Host3 is usually a lesser used machine and all of a sudden its usage increases noticeably, then that will be detected as an anomaly as well.
NOTE:
In the cases of time and count anomaly detection there lies a limitation associated with the older logs. For instance, a scheduled job runs every hour to process events. If the job runs at 10:00 AM, it will fetch and process logs from the 8:00 AM to 9:00 AM window. Logs that arrive late (after processing for their corresponding time window has already started or completed) will be skipped and not processed. This will be seen in cases like:
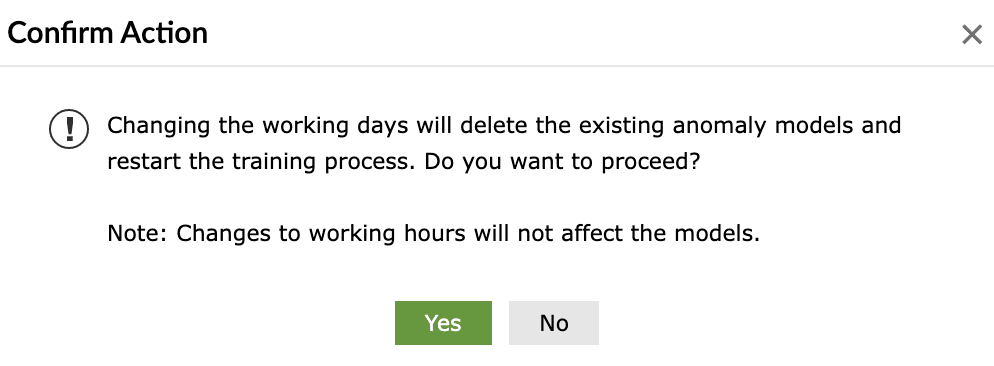
Limitation with working days configurations:
If a user changes the working days configuration in the product with the UEBA feature already active, then all the previously trained models will be deleted by the ML model and the training has to be restarted again, post configuration. An error message pops-up like the below when such configuration changes are attempted:
Read also
This document elaborated the pre-requisites and the training phase of the anomaly models of Log360 Cloud's UEBA. For leveraging the capabilities of UEBA, refer the below articles: