- Free Edition
- What's New?
- Key Highlights
- Suggested Reading
- All Capabilities
-
Log Management
- Event Log Management
- Syslog Management
- Log Collection
- Agent-less Log Collection
- Agent Based Log collection
- Windows Log Analysis
- Event Log Auditing
- Remote Log Management
- Cloud Log Management
- Security Log Management
- Server Log Management
- Linux Auditing and Reporting
- Auditing Syslog Devices
- Windows Registry Auditing
- Privileged User Activity Auditing
-
Application Log Management
- Application Log Monitoring
- Web Server Auditing
- Database Activity Monitoring
- Database Auditing
- IIS Log Analyzer
- Apache Log Analyzer
- SQL Database Auditing
- VMware Log Analyzer
- Hyper V Event Log Auditing
- MySQL Log Analyzer
- DHCP Server Auditing
- Oracle Database Auditing
- SQL Database Auditing
- IIS FTP Log Analyzer
- IIS Web Log Analyzer
- IIS Viewer
- IIS Log Parser
- Apache Log Viewer
- Apache Log Parser
- Oracle Database Auditing
-
IT Compliance Auditing
- ISO 27001 Compliance
- HIPAA Compliance
- PCI DSS Compliance
- SOX Compliance
- GDPR Compliance
- FISMA Compliance Audit
- GLBA Compliance Audit
- CCPA Compliance Audit
- Cyber Essentials Compliance Audit
- GPG Compliance Audit
- ISLP Compliance Audit
- FERPA Compliance Audit
- NERC Compliance Audit Reports
- PDPA Compliance Audit reports
- CMMC Compliance Audit
- Reports for New Regulatory Compliance
- Customizing Compliance Reports
-
Security Monitoring
- Threat Intelligence
- STIX/TAXII Feed Processor
- Threat Whitelisting
- Real-Time Event Correlation
- Log Forensics
- Incident Management System
- Automated Incident Response
- Linux File Integrity Monitoring
- Detecting Threats in Windows
- External Threat Mitigation
- Malwarebytes Threat Reports
- FireEye Threat Intelligence
- Application Log Management
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- Real-Time Event Alerts
- Privileged User Activity Auditing
-
Network Device Monitoring
- Network Device Monitoring
- Router Log Auditing
- Switch Log Monitoring
- Firewall Log Analyzer
- Cisco Logs Analyzer
- VPN Log Analyzer
- IDS/IPS Log Monitoring
- Solaris Device Auditing
- Monitoring User Activity in Routers
- Monitoring Router Traffic
- Arista Switch Log Monitoring
- Firewall Traffic Monitoring
- Windows Firewall Auditing
- SonicWall Log Analyzer
- H3C Firewall Auditing
- Barracuda Device Auditing
- Palo Alto Networks Firewall Auditing
- Juniper Device Auditing
- Fortinet Device Auditing
- pfSense Firewall Log Analyzer
- NetScreen Log Analysis
- WatchGuard Traffic Monitoring
- Check Point Device Auditing
- Sophos Log Monitoring
- Huawei Device Monitoring
- HP Log Analysis
- F5 Logs Monitoring
- Fortinet Log Analyzer
- Endpoint Log Management
- System and User Monitoring Reports
-
Log Management
- Product Resources
- Related Products
- Log360 (On-Premise | Cloud) Comprehensive SIEM and UEBA
- ADManager Plus Active Directory Management & Reporting
- ADAudit Plus Real-time Active Directory Auditing and UBA
- ADSelfService Plus Identity security with MFA, SSO, and SSPR
- DataSecurity Plus File server auditing & data discovery
- Exchange Reporter Plus Exchange Server Auditing & Reporting
- M365 Manager Plus Microsoft 365 Management & Reporting Tool
- RecoveryManager Plus Enterprise backup and recovery tool
- SharePoint Manager Plus SharePoint Reporting and Auditing
- AD360 Integrated Identity & Access Management
- AD Free Tools Active Directory FREE Tools
Syslog management software
The System Logging Protocol (syslog) is a protocol that was designed to standardize the message format used by network devices to communicate with the log server. It provides a mechanism for collecting, parsing, analyzing, and storing the logs generated in a centralized manner for real-time analysis. It is supported by many network devices, such as routers, switches, firewalls, Unix/Linux, and MacOS servers, making it easier to manage the logs generated by these devices.
As organizations grow, so do the number of devices within their network. And the volume of logs generated by these devices is enormous. Syslog monitoring and management is important for every organization to reduce system downtime, enhance the performance of the network, and strengthen the security policies of the enterprise.
How are syslog messages collected?
Every syslog server contains three common components that help in the process of collection, storage, and analysis:
- Syslog listener: This is a crucial component that is responsible for receiving syslog messages transmitted over the network from various devices and applications. It primarily listens on a specific port (by default, port 514) for incoming messages.These messages are sent using User Datagram Protocol (UDP) or Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). The listener port gathers all the syslog messages it receives from all the network devices.
- Database: Since network devices generate a huge amount of data every second, the server should be capable of handling the high volume of syslog messages it receives. Therefore, efficient storage, organization, and retrieval mechanisms are essential. The database component of a syslog server is designed to handle a high volume of log data. It ensures that messages are stored securely and can be accessed quickly for analysis, reporting, and auditing purposes. The structured nature of databases allows for efficient querying, filtering, and analysis of log data.
- Filtering: When a large amount of logs are generated every minute, it can be hard to find specific logs. Syslog servers help with the filtering of logs as well.
Standard syslog servers provide basic analyzing capabilities such as viewing and filtering of log data. Therefore, to identify a single problem, administrators often have to invest many hours sifting through stacks of syslog messages. When it comes to securing larger networks, it is important to have a third component on top of the listener, database, and filtering modules to make syslog management easier.
A log management tool can help you automate many tasks that can't be automated when using a standard syslog server. You can also trigger alerts and notifications and automate processes in response to select messages so that administrators can take immediate action when a problem occurs.
Here's how EventLog Analyzer helps in managing syslog data
EventLog Analyzer is a syslog management tool that collects syslog events from various flavors of Unix operating systems such as RedHat, Debian, Open SUSE, OpenBSD, Ubuntu, Solaris, HP-UX, IBM AIX, and more. Once collected, the syslog messages are analyzed and insights on network activities are presented in concise reports displayed on dashboards.
EventLog Analyzer's syslog management capabilities include:
A real-time alerting system
With over 300 predefined alert criteria, EventLog Analyzer can quickly identify security incidents and send real-time SMS or email notifications to administrators.
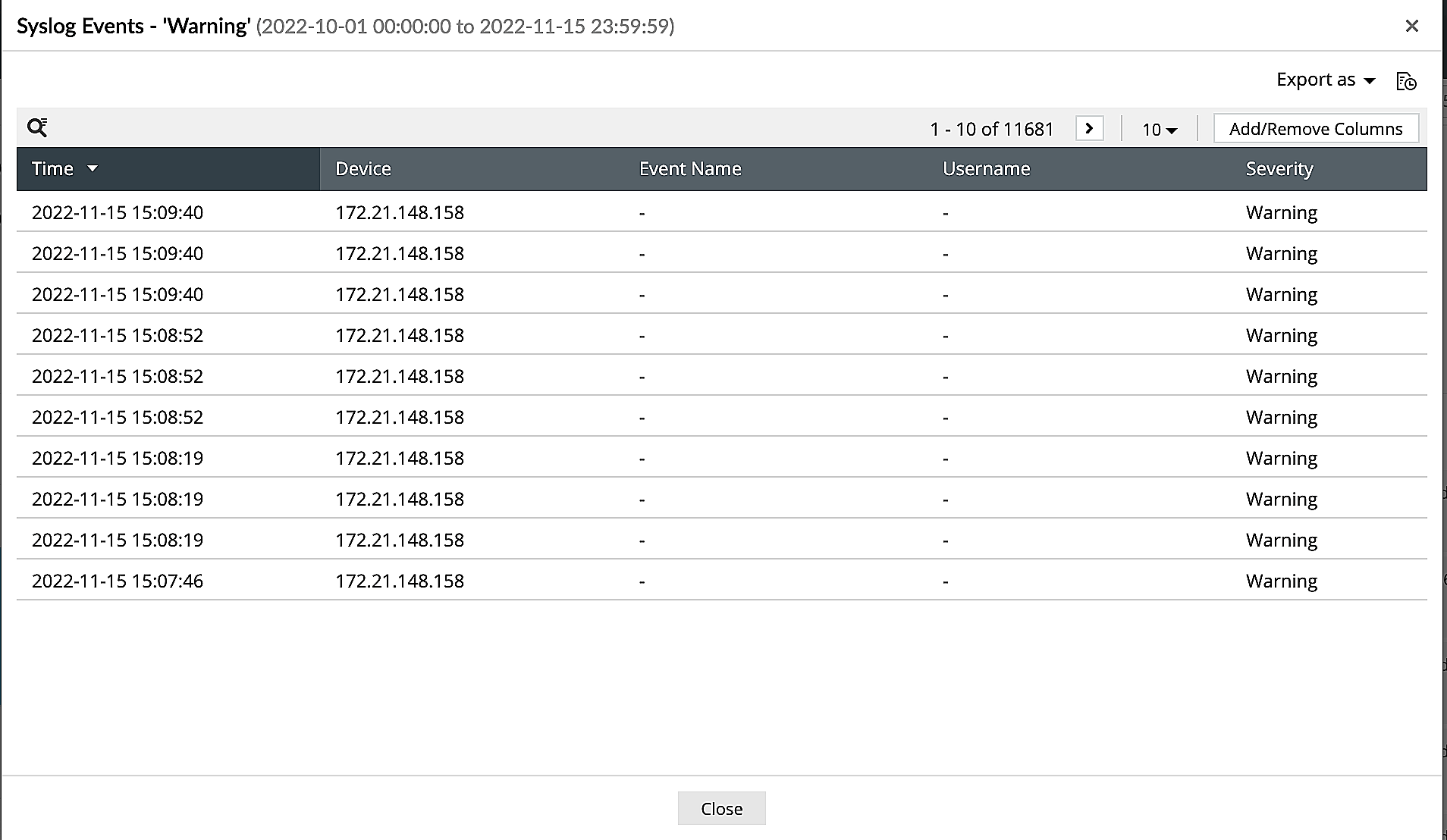
A powerful correlation engine
EventLog Analyzer provides rule-based correlation of incoming syslog messages that enables administrators to spot external attacks, analyze their patterns, and recognize network breaches.
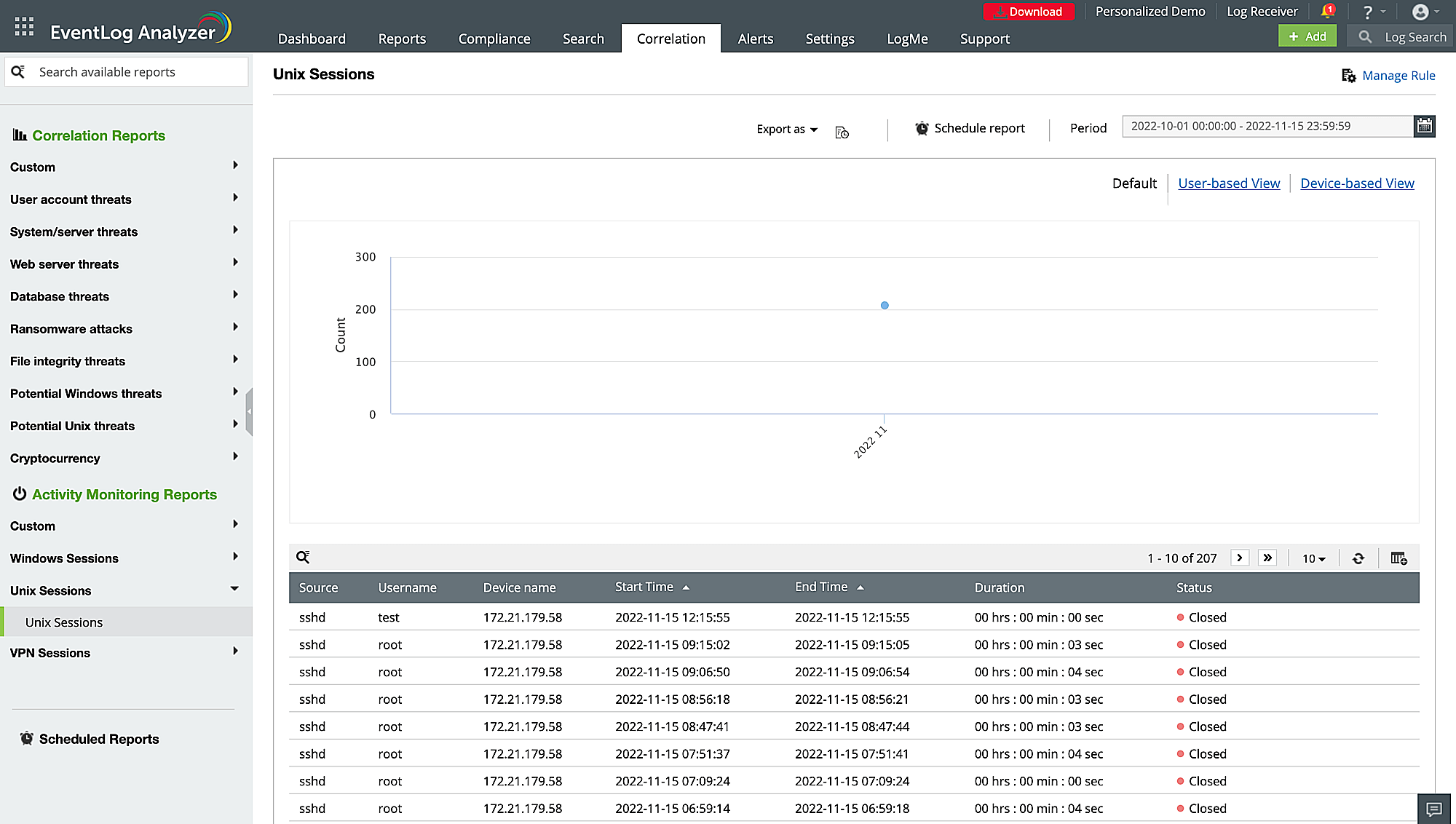
Log archiving
EventLog Analyzer automatically archives and securely stores all log data collected from different sources. This archived log data is not only useful for immediate analysis but also for future reference, compliance audits, and forensic investigations.
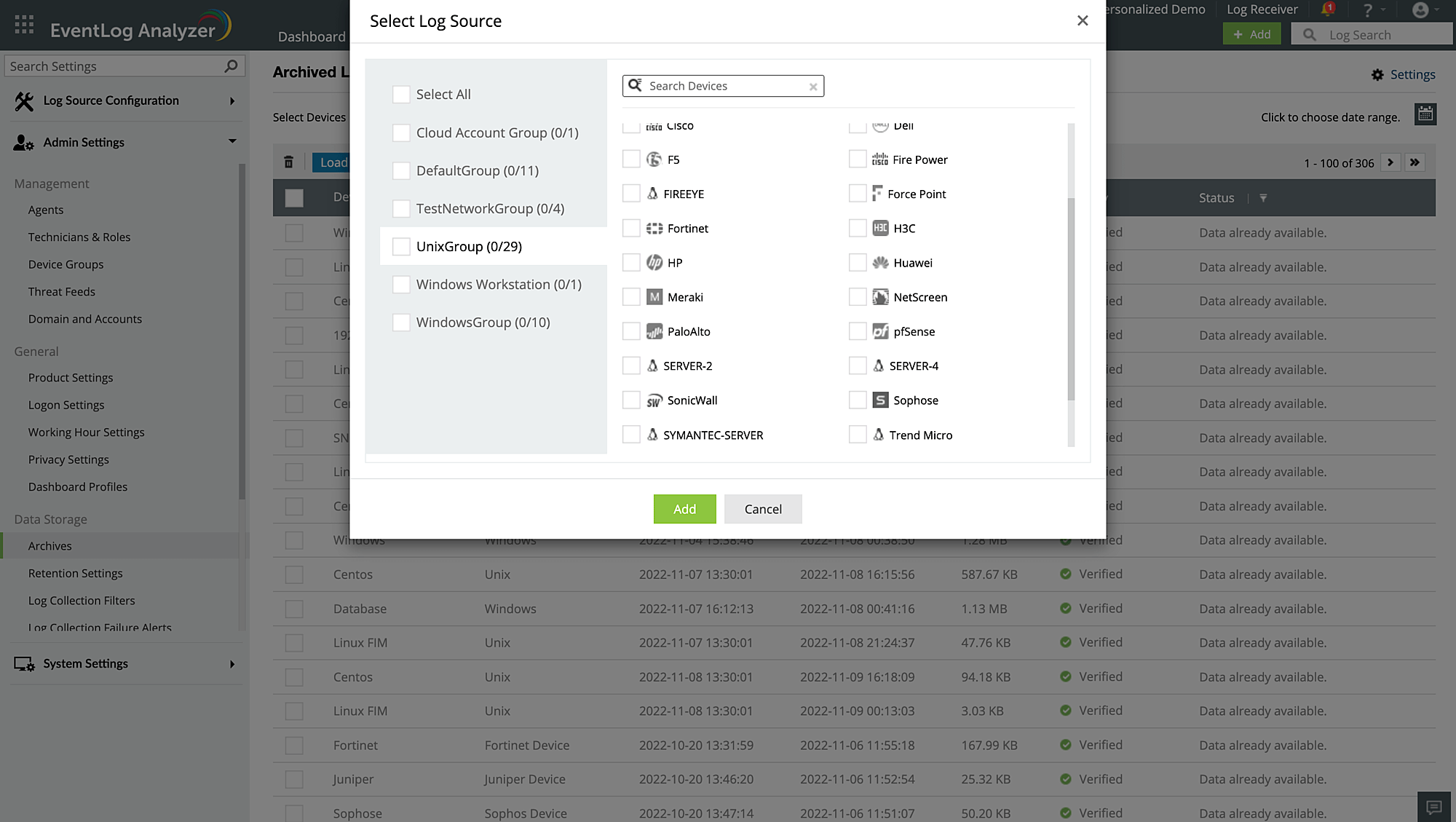
Out-of-the-box reports
EventLog Analyzer's exhaustive reporting package includes over 1,000 out-of-the-box reports. It also has a custom report builder that provides an option to build reports based on several criteria such as syslog event type, severity, source, and more.
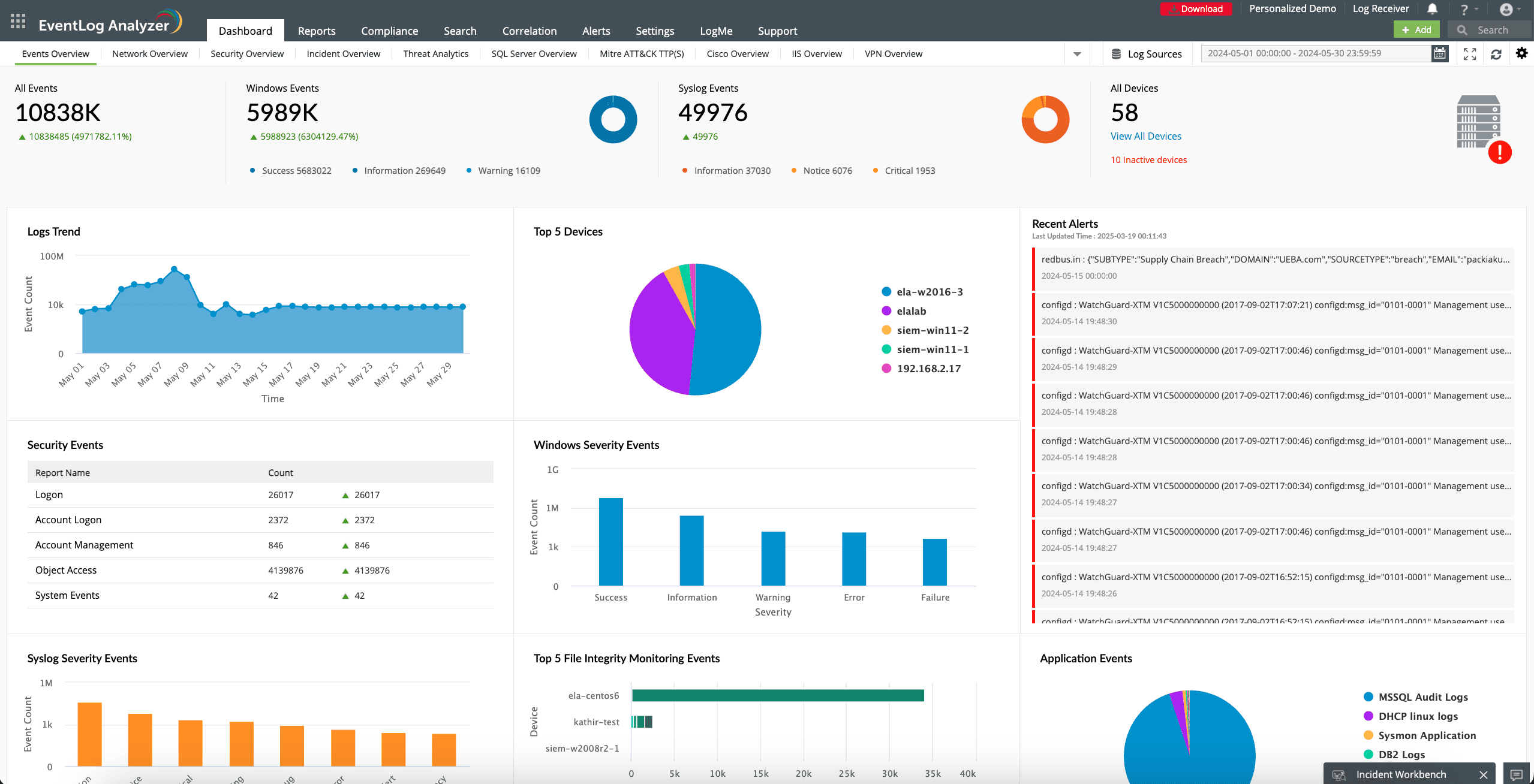
Incident and response management
EventLog Analyzer provides comprehensive incident response and management functions for syslog messages. The solution offers search and filtering capabilities to quickly investigate specific incidents, trace back events, and analyze root causes. You can also create automated workflows that go into immediate effect when an alert is triggered.
Compliance support
Generate reports for regulatory mandates such as PCI DSS, FISMA, the GDPR etc. with EventLog Analyzer's predefined and custom report templates.
Frequently asked questions
Here are some of the benefits of using syslog:
- Standardization: Syslog is a standardized protocol. This means that devices from different manufacturers and applications from various developers can send their log messages in a universal format.
- Centralized logging: Syslog servers allow you to centralize the logging data from various systems and applications in one location. This helps speed up and simplify the log management process, fostering quicker troubleshooting and decision-making. The logs can also be stored for an extended period, provide an audit trail, and enable historical analysis of incidents.
- Forensic analysis and security: Logs are crucial for maintaining network security. They can help determine the nature of an attack, the affected systems, and the potential data breach's scope. Centralized logs ensure that even if an attacker compromises a particular system and tries to delete its logs, copies are safely stored elsewhere.
Syslog messages follow a standardized structure defined by RFC 5424 when communicating within the network. The syslog format is as follows:
- Header: The header includes details such as the priority, version, timestamp, hostname, application, process ID, and message ID.
- Structured data: This is a way to include machine-readable data within syslog messages to add additional information in a way that's structured and can easily be parsed. It’s encapsulated within square brackets and comprises a series of key-value pairs.
- Message: This contains the actual log content, including details about the event, error, or system condition.
This is an example of what a syslog message would look like:
<165>1 2023-10-03T14:32:12Z myserver.example.com myapp - - [exampleSDID@32473 iut="3" eventSource="Application" eventID="1011" errorCode="E404" detail="File not found"]Syslog messages are categorized based on their severity. These levels help administrators quickly identify and address the most critical issues in their systems. There are eight priority levels, ranging from zero (most severe) to seven (least severe). Here are the standard syslog priority levels as defined in the syslog protocol:
- Emergency (0): The system is unusable. This is the highest priority and typically indicates a complete system crash or a severe failure.
- Alert (1): Immediate action is required. Something has occurred that needs urgent attention. For example, a data storage volume might be running out of space, and without immediate intervention, the system might crash.
- Critical (2): Critical conditions might not require immediate intervention but represent situations that could lead to more severe problems if not addressed promptly. Examples include significant system components failing or unexpected behavior that might soon lead to a system crash.
- Error (3): Error conditions that aren't as critical as the levels above but still represent anomalies or issues in the system—for example, a software module failing to load or a network connection dropping unexpectedly.
- Warning (4): Warning messages represent situations that aren't errors but are of interest, because they might indicate potential problems—for instance, configuration settings that are not optimized or transient issues that might resolve themselves but are worth noting.
- Notice (5): These messages notify about normal but significant conditions that don't indicate error conditions but are flagged because they represent significant events in the system's operation—for example, a user changing their password or a new device connecting to the network.
- Informational (6): These messages are purely for informational purposes and don't indicate error or warning conditions. Examples might include routine system status updates or logs of normal but noteworthy activities.
- Debug (7): Debug-level messages are used primarily for troubleshooting and debugging purposes and provide detailed insights into system operations. They often produce very verbose logging information and are typically enabled when diagnosing specific issues.
| Syslog | Event log | |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Syslog is a protocol that was initially developed for Unix-like operating systems but was later adopted by other operating systems and network devices over the years. | Event logs are specific to Windows operating systems |
| Format | Syslog messages follow a standardized format, which makes it easier to integrate and analyze logs from different sources. | Event logs contain information about the system, applications, and security in a structure that's unique to Windows. |
| Flexibility | Syslog is supported by many log management and SIEM solutions and can be easily configured to suit the requirements of the environment. | Event logs offer less flexibility in comparison to syslog messages, as event log configurations are bound by the Windows environment. |
| Detail | The detail in syslog messages is a little simpler. These details focus on giving essential information efficiently. | Event logs contain detailed information that provides visibility and in-depth insight into each event. |












