Introduction to switch spoofing
Switch spoofing is the process of modifying the MAC address of a device to pose as a authorized switch port and gain access to the target network. Since MAC addresses are unique to a particular device, most networks use these MAC addresses to authenticate a device and communicate or establish a network connection with it. By spoofing an authorized device or, in simpler terms, a device the network recognizes as a "trusted device", a malicious agent can easily gain access to your network. Switch spoofing is also referred to as MAC address spoofing, and is one of the switch port management challenges most network admins face today.
In this page, we will be looking into,
Types of switch spoofing
To successfully carry out switch spoofing, the spoofing device should be able to emulate:
- Dynamic trunking protocol (DTP)
- Inter switch link (ISL) for CISCO switches
- 802.1Q signaling for virtual LAN trunking
This can be achieved by either:
- Using switch spoofing software: The easier method, this involves using software programs. With various free, open source options available on the internet, a attacker or network tester can download and install one of the software programs on the attacking device to modify the device's unique MAC address and carry out switch spoofing.
- Hardware configurations: This method requires sound technical knowledge of switch functioning, signaling, and configurations. A switch, or any network device's MAC address, is a 12-digit hexadecimal number that is assigned to the device's network interface card (NIC) at the time of manufacture. Using the spoofing device's firmware, the MAC address can be manually modified.
Switch spoofing: What is trunking and how does it enable switch spoofing?
Before we delve into how switch spoofing can affect your network, it is important to understand the basis of how a switch spoofing attack is carried out. Switch ports enable communication within and between different VLANs. Switch ports are associated with either access ports or trunk ports.
- Access port: Access ports are associated with and carry traffic from only a single preconfigured VLAN assigned to it. It does not add any identifying tags to the data packets passing through it since the port only facilitates traffic to and from one VLAN. If no VLAN is preconfigured, the access port by default only carries traffic to and from the network's default VLAN.
- Trunk port: Trunk ports are associated with and carry traffic from more than one VLAN. To differentiate and identify traffic coming from different VLANs, these ports add identifying tags using IEEE 802.1Q, or ISL in case of CISCO switches, to the data packets processed.
- Trunk links or switch trunking: To enable connection between two switch ports associated with different VLANs, the "trunking" configuration should be enabled on both switches connected in a link, and must be configured with the same tagging mechanism using IEEE 802.1Q or ISL.
Exploiting trunk links with switch spoofing
Switch spoofing cannot be carried out in switch ports that are configured as access ports. Configuring a switch port as an access port makes it a non-trunking port that does not negotiate with a neighboring switch port's DTP signals to convert it to a trunking port.
The most susceptible ports to a switch spoofing attack are ports that are configured as,
- Trunk ports: The switch port remains a trunk port until configured again to change its state. It does not convert into a non-trunking port even if its neighboring ports are non-trunking switch ports.
- Dynamic auto: These ports are not trunk ports by default, but can change into a trunk link if their neighboring ports are trunking ports, i.e., set to dynamic desirable or trunk ports.
- Dynamic desirable: These switch ports actively attempt to convert their links as trunk links using DTP signaling. They become trunk ports if their neighboring ports are set to dynamic auto or trunk ports.
Most switch ports in a modern network are configured as dynamic auto to avoid the hassle of manual intervention and to try to make the switch port more accessible and adaptable to the network traffic requirements.
However, setting the switch ports to these modes opens up the switches to a switch spoofing attack.
Attackers configure their spoofing device to emulate an authorized switch MAC address and to send DTP or ISL signaling to establish trunk links with ports set as "trunk", "dynamic desirable", or "dynamic auto".
Once trunk links are established, the attacker gains access to all the VLANs associated with the target switch port and its neighboring switches with established trunk links.
Rogue devices and switch spoofing attacks
Does your network support BYOD policies? Your network is now much more susceptible to a switch spoofing attack. Attackers can leverage a rogue switch port to establish a trunk link with a switch port associate with a critical VLAN to exploit your network. Also, rogue devices connecting directly to your network have much less hurdles to spoof as a authorized switch and establish trunk links with an internal switch, when compared to external devices trying to access your network.
However, most modern networks allow their end users to connect their own devices to their network and enable network communication through switch ports. While this offers a hassle free networking experience for end users, leaving the new devices connecting to your network unmonitored might lead to untoward consequences.
As a best practice, it is advisable to deploy appropriate rogue device monitoring and management strategies in your network. To thwart rogue switch spoofing attacks, network admins need to constantly monitor all new devices connecting to their network, authorize trusted and guest devices, and filter out and block rogue devices from accessing the network.
Switch spoofing: Is it just for attackers?
Switch spoofing is undoubtedly a nefarious activity that offers attackers uninterrupted access into your network's critical resource. But is it only for malicious purposes? The answer is no. There are several legitimate use cases for network admins to leverage switch spoofing as a part of their network testing, diagnosis, and monitoring activities.
- Network diagnosis with switch spoofing: Switch spoofing plays a helpful part in troubleshooting several switch specific issues in the network. For instance, by spoofing the MAC address of a switch or its connected end device, a network admin can test whether a problem is caused by a specific device or is a general network issue.
- Enhancing network security: A network security team can carry out switch spoofing attacks on their network to identify, test, and reduce their network's security risk vectors and vulnerabilities.
However, it is worth noting that to reduce the nefarious use of switch spoofing, many countries have cybersecurity laws making the use of switch spoofing illegal. It is important to consider the legal implications of switch spoofing in your region before proceeding to attempting it.
Best practices to avert switch spoofing attacks
Network administrators can safeguard their network from the threats of switch spoofing by deploying various security measures including,
- MAC address filtering: By setting up MAC address filtering capabilities, network admins configure their networks to allow only specific MAC addresses to connect to it. This restricts unauthorized devices from accessing the network. However, this can be difficult and ineffective to implement in devices that allow BYOD policies since it is impractical to collect, configure, and filter devices every time based on user provided MAC details.
- Network access controls (NAC): For networks implementing BYOD policies, NAC offers an effective and efficient alternative to MAC address filtering. NAC uses various methods of device authentication to identify, record, and authorize devices entering your network including username and password authentication, and certificate-based authentication.
- Appropriate firewall configurations: Firewalls play a vital role in network security. Configuring firewalls to block unauthorized devices entering your network enables a strong defense against switch spoofing.
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems: These systems ensure network admins are aware of any intrusions into the network as and when they occur. This helps network admins tackle switch spoofing attempts before they establish a successful trunk link with an authorized switch.
Securing your network switch ports with OpUtils
ManageEngine OpUtils is a comprehensive switch port monitoring software that provides advanced network port scanning, end-to-end switch port mapping, and management. Built to tackle modern networks of all sizes and complexities, OpUtils' effective switch port monitoring capabilities enable network admins to tackle and resolve several switch port related issues in the network.
To hinder switch spoofing and ensure optimal use of their switch port resources, network admins can leverage OpUtils capabilities including,
- Holistic switch port mapping: View the switch port utilization, port status, interface details, and nature of connection. OpUtils also identifies and displays for you ports that have multiple MAC addresses, stacked ports, and ports connected to virtual IPs.
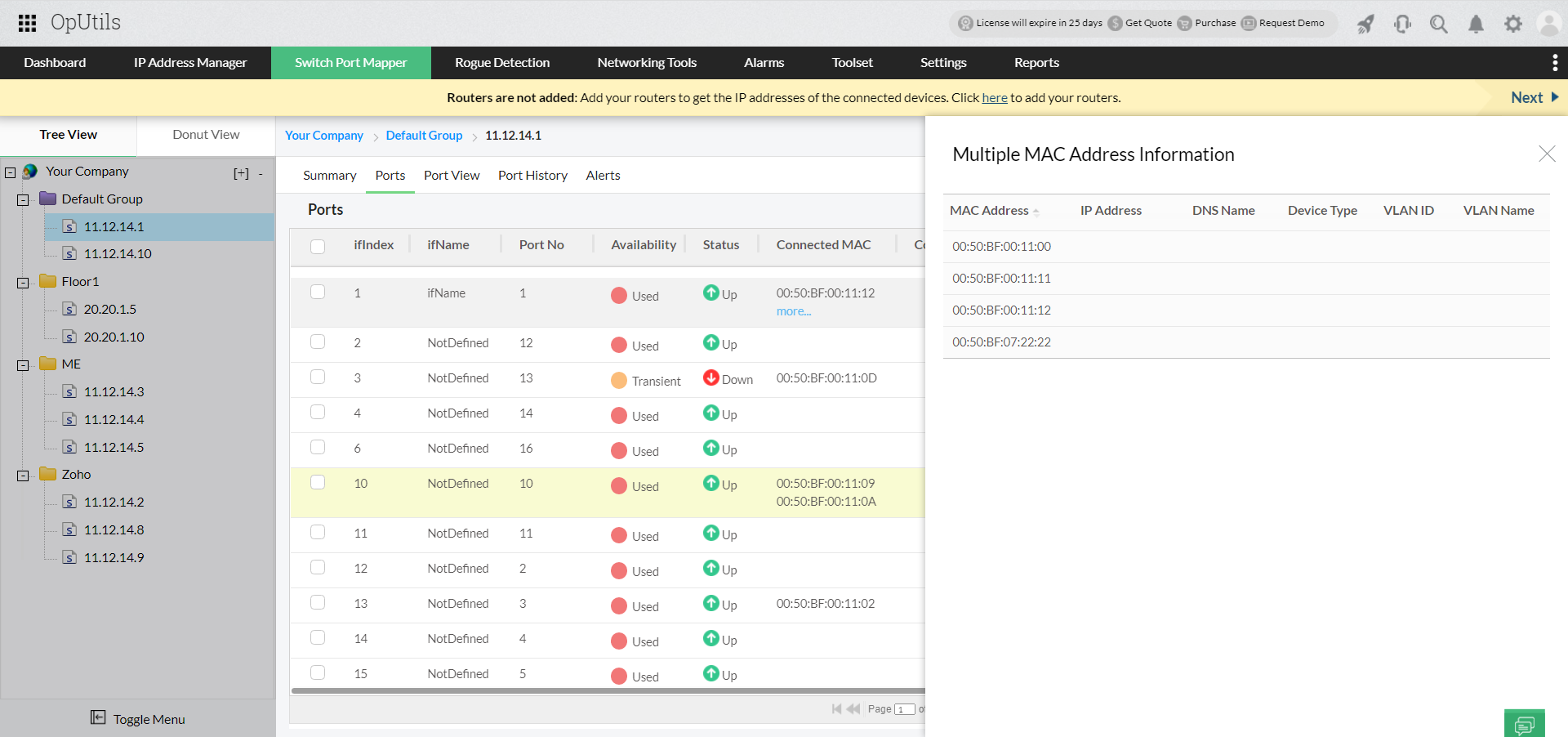
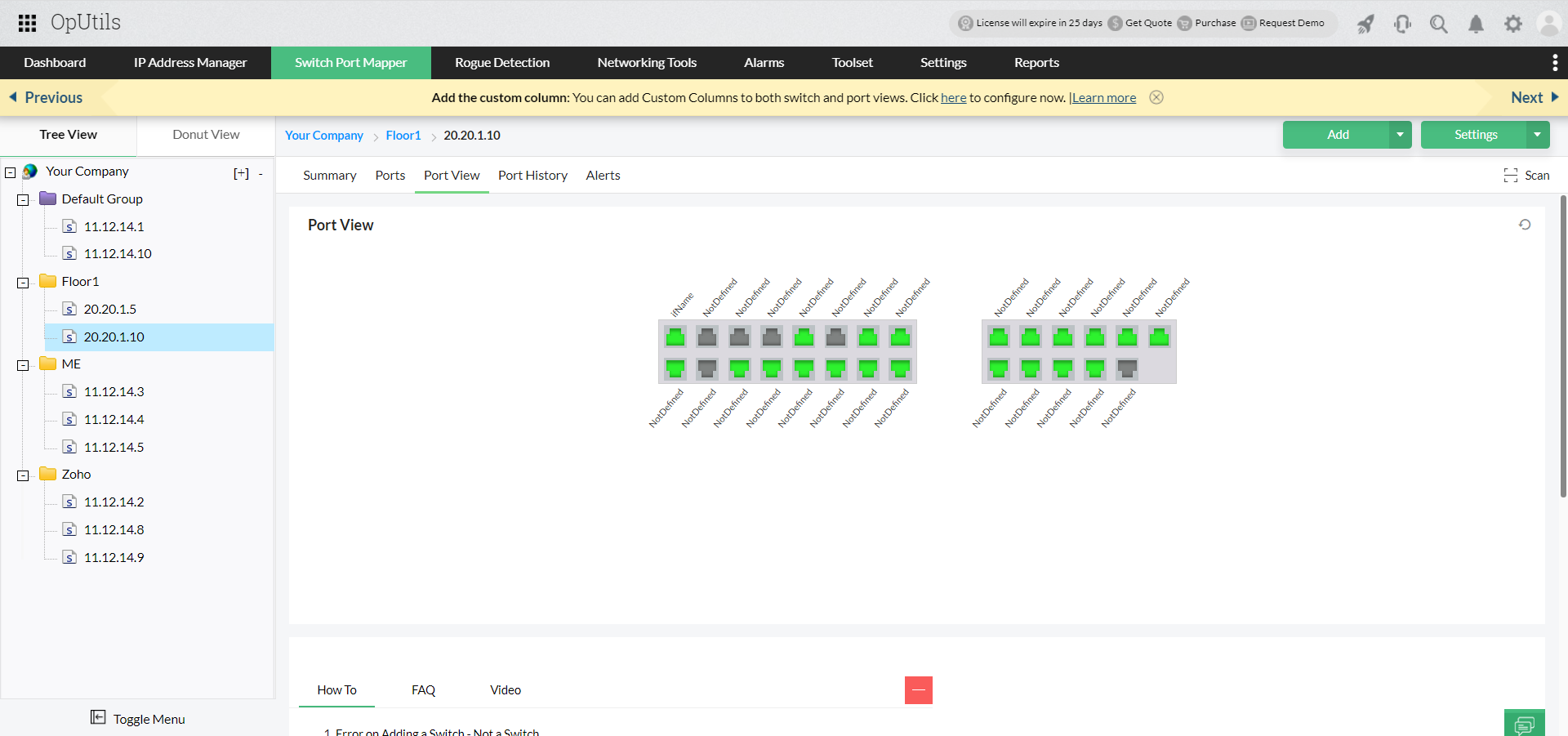
- Switch end device details: Dive into the details of switch port connections. View end device details, their MAC and IP address details. Simplify switch port management with OpUtils' Port View that provides a visual representation of the switch port connectivity and utilization in your network.
- Rogue device detection: As discussed earlier, rogue devices not only pose resource exhaustion threats but can also enable attacks on your network, including switch spoofing. Stay in the know about all the devices entering your network with OpUtils' rogue detection and prevention module that continually scans your entire network to detect new devices. In the list of new devices displayed by OpUtils, mark authorized devices as trusted or guest with a validity period. You can also mark suspicious devices as rogue to differentiate and track the device activity in your network.
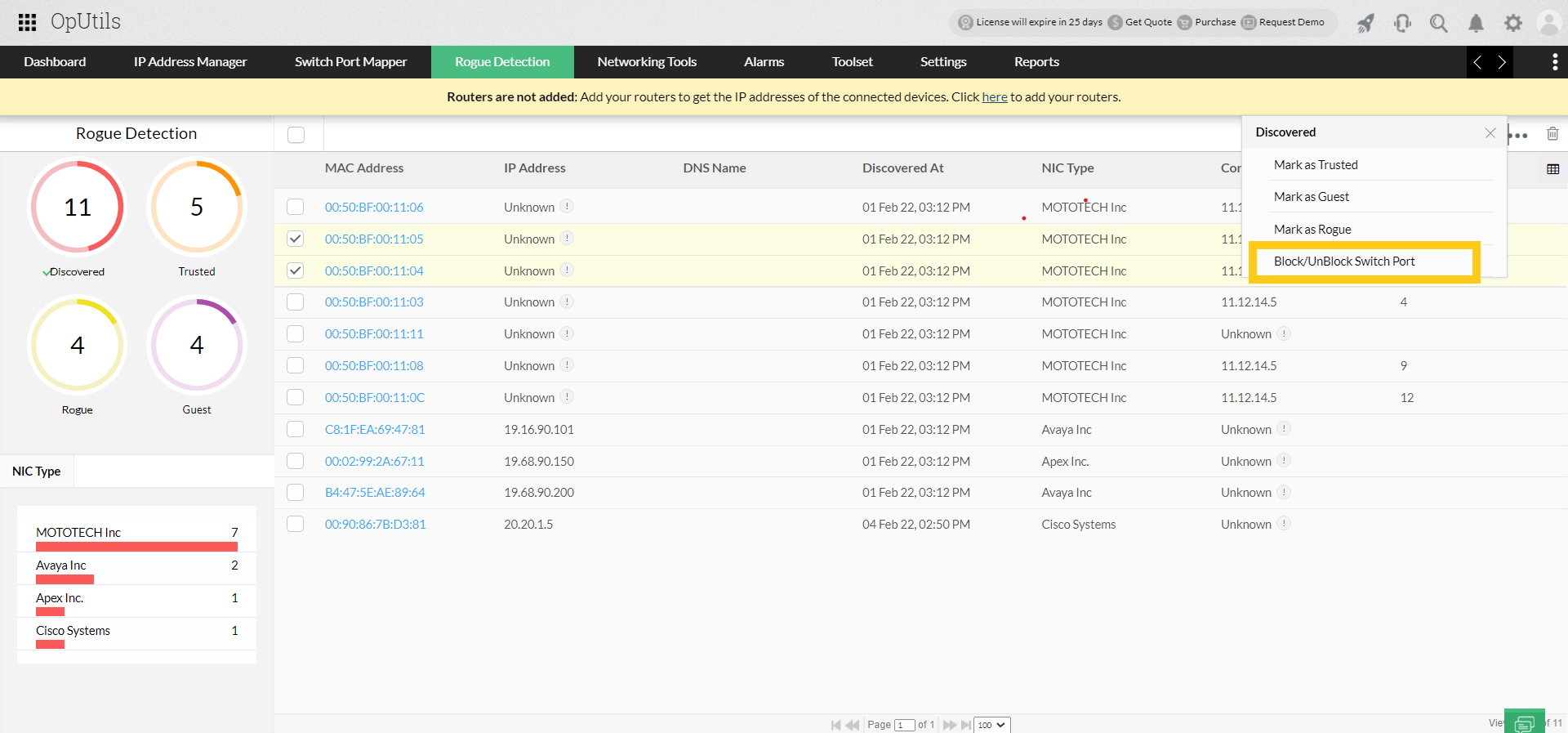
- Remote switch port blocking: OpUtils also enables you to block identified rogue devices from accessing your network. You can view the switch port facilitating network access to the rogue device and block that switch port remotely from OpUtils' console.
- MAC address inspection: With OpUtils' advanced IP address management module and it's diverse network tool set, identifying, scanning, and inspecting MAC addresses becomes hassle free. View the IP details of a MAC address, resolve MAC addresses, scan it's system details, and other insights right from your IP address management console.
New to ManageEngine OpUtils? Get started for free today with our free 30-day trial or get in touch with our product expert who can help you explore the product hands on, by scheduling a free personalized demo.


