

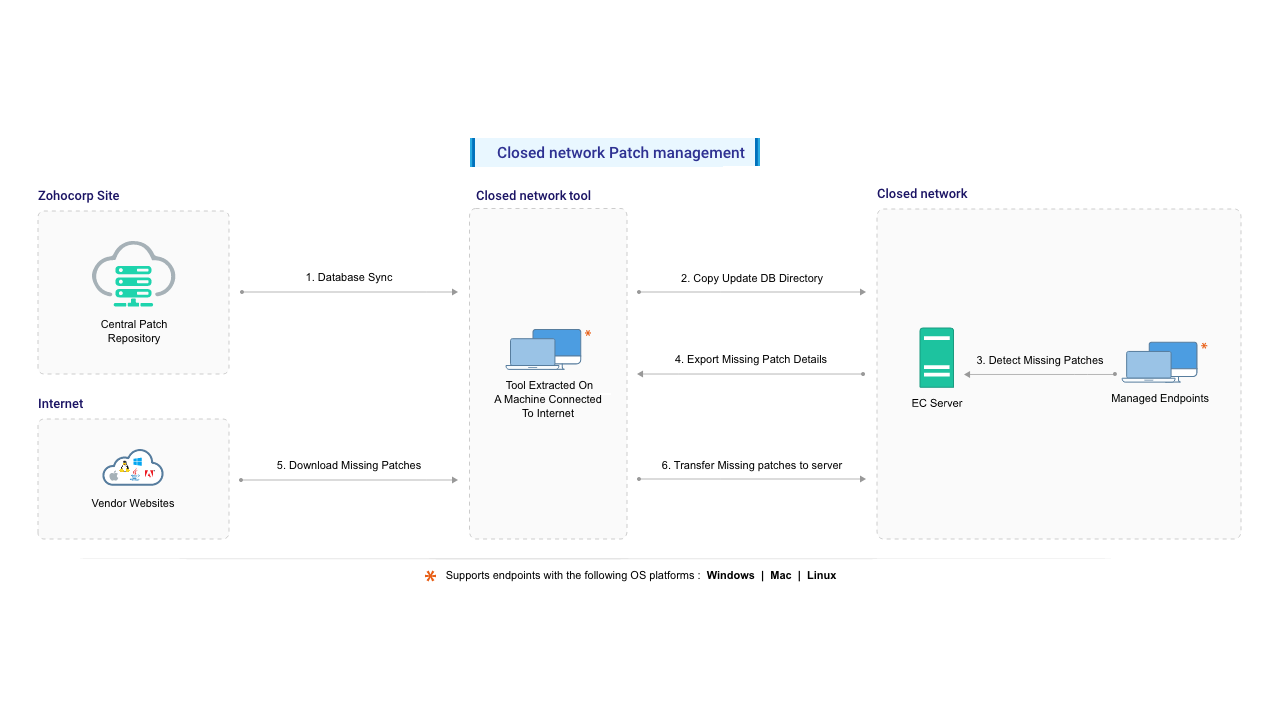
Note: In this document, the term Closed Network is used to describe any environment where the Endpoint Central server does not have direct Internet access. This includes secured internal networks, DMZ, and fully air-gapped environments. The patch management workflow described here is determined by Internet connectivity restrictions, not by network placement or topology.
When the Endpoint Central server is deployed in an environment without direct Internet access, core patching functions—such as vulnerability database synchronization, automatic patch downloads, and vendor update retrieval—cannot be performed online.
This limitation applies to closed networks, where outbound Internet connectivity is intentionally blocked, irrespective of where the server is placed. A Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) is one such placement scenario. A DMZ is a segmented network zone positioned between an internal network and external or untrusted networks, designed to host systems that require strict access control and isolation. While DMZs can allow tightly controlled Internet access, they are frequently configured without outbound connectivity in high-security environments, effectively operating as closed networks.
In more restrictive setups, such as air-gapped networks, the Endpoint Central server is fully isolated, with no physical or logical connectivity to external networks.
Although these environments differ in network topology and isolation level, they share a common constraint: the Endpoint Central server cannot communicate directly with external update sources. As a result, patching and vulnerability remediation must be performed using offline or manual workflows. The following steps explain how to manually synchronize vulnerability data, download required patches using an Internet-connected system, and deploy them to the target computers within the restricted environment.
The steps given below will guide you to configure the proxy settings:
To configure the patch database settings, follow the steps below:
This prevents the DB sync from being initiated without the necessary data in the <installdirectory>/conf/CRSData directory because the updatedb folder in the above-mentioned directory will get erased after a successful sync. So, the upcoming DB sync will get failed if the required folder is expunged.
Follow the steps below to download and set up the Closed Network tool:
If the computer does not have direct internet connection, open the downloadMgr.propfile available within the extracted location and provide the details of the proxy server, port and authentication details.
Note: If you are running a TAA-compliant Endpoint Central Server, download the Closed Network tool from this link.
Follow the steps below to update the vulnerability database:
You can find the build number by clicking on your profile located in the top-right corner of the Endpoint Central console.
Note : Before copying, if the updatedb folder already exists in the <Installation Directory>/conf/CRSData directory, delete it and then replace it with the latest version.
The CRSData folder must remain intact. Deleting its contents may disrupt patch management in closed networks.
You will not be able to view all the missing patches unless scanning is completed for all the computers. Ensure that all the computers are scanned, before manually downloading the missing patches.
The next step is to download the missing patches from the computer with internet connection and copy it back to this computer.
Now, you can successfully manage vulnerabilities and have configured the patch management process in a closed network.
Follow the below pre-requisite steps:
JAVA_HOME="/usr/lib/jvm/jre_1_8_0_192"
JAVA_HOME="/usr/lib/jvm/java-11-openjdk-amd64"
For further steps to run the tool in Linux set-up, follow from the Download and Setup the Closed Network Tool.
If you have any further questions, please refer to our Frequently Asked Questions section for more information.