Virtualization is the act of creating a virtual version of a physical IT resource, like a server or a desktop. A virtual machine (VM) is created on a physical host device. The VM behaves exactly like a physical device would and can run different OSs from the host. VMs are also named guest machines. Multiple guest VMs can run on a host device.
For instance, you can create a virtual server running on Windows on a physical device that runs on Linux. The VM is a fully functional Windows server that utilizes host resources. On the same host server, you can run more Windows servers, Linux servers, and so on.
Virtualization as a practice started as early as the 1960s on mainframe computers as a way of provisioning system resources. Nowadays, it's widely adopted in IT, and there's a trend of consolidating or converging bulky physical devices into neat virtual counterparts.
Going further, we'll discuss:
Virtualization works by partitioning the host device's resources between VMs. This partitioning is performed by software known as a hypervisor. There are two kinds of hypervisors: bare-metal ones that are installed directly on the host hardware and hosted ones that need some kind of OS to run on the host.
A hypervisor acts as the intermediary between the VMs and the host device. When a VM is created, or spun up, the hypervisor allocates some host resources, like the CPU and memory, to it. If the VM needs more resources while operating, the hypervisor allocates more host resources.
Similarly, the disk storage of the host device is simulated as virtual storage on the VM. When the VM tries to locate any files in its virtual storage, the hypervisor translates this request to locate the files in the actual physical storage of the host.
A hypervisor can manage multiple VMs like this, distributing host resources ad hoc. VMs can be spun up or taken down easily. They can also be migrated from one host to another and operate as before.
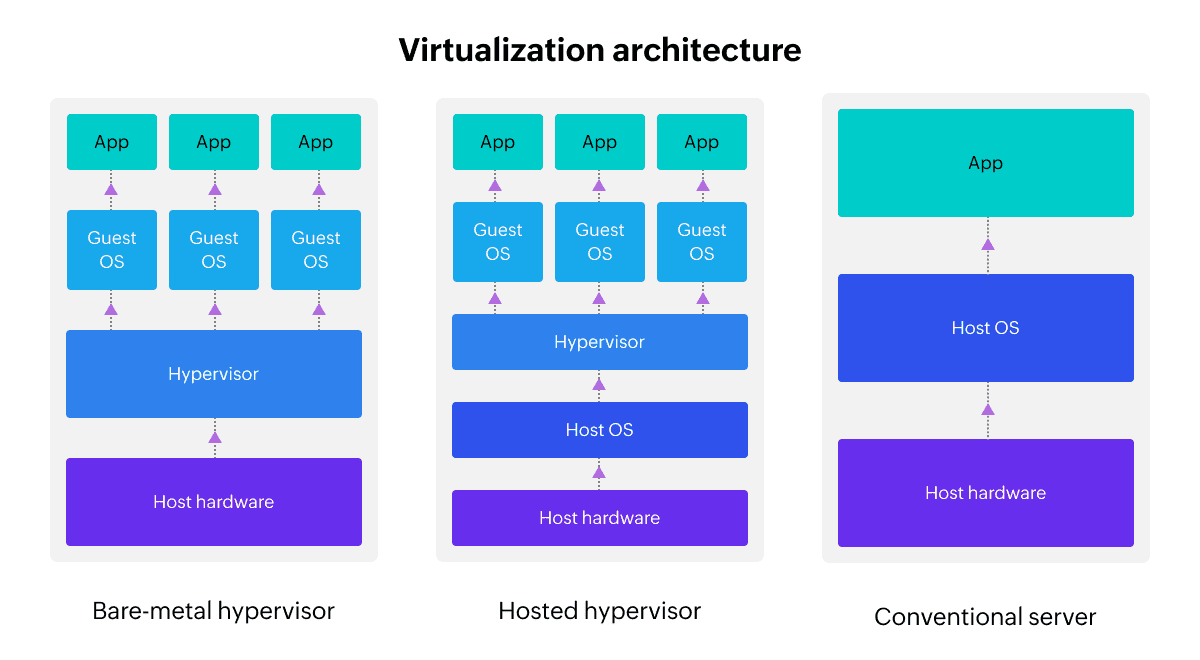
At the base of virtualization architecture is the host hardware. This includes system resources like the CPU, memory, and disk space. In the case of bare-metal virtualization, the hypervisor doesn't need any host OS and can operate directly on top of the host hardware. In the case of hosted hypervisors, the hypervisor operates on top of a host OS.
The hypervisor pulls resources from the layers below and partitions them into virtual instances. For this reason, the hypervisor is also known as the virtualization layer. Guest OSs operate on top of the hypervisor. Often, the guest OSs aren't aware of themselves and behave like independent devices. Applications are hosted on each guest OS on a VM. This layer is known as the application layer.
In the case of nested virtualization, the guest OSs have another set of hypervisors running above them, and so on.
Virtualized devices are more versatile and efficient compared to their traditional physical counterparts. They are also convenient to spin up, move, and take down as you please. Some of the advantages of virtualization are:
Virtualization can be classified based on the extent of virtualization and the functionality offered by the VM. Virtualization can be performed to provide services or simulate hardware, data, system resources, etc. Let's see what the most important kinds of virtualization are.
We can classify three types of virtualization based on the extent:
Virtualization can be classified into hardware virtualization, server virtualization, network virtualization, storage virtualization, application virtualization, data virtualization, desktop virtualization, and more based on the functionality provided. These are discussed in detail below.
Server virtualization is a widely adopted type of virtualization where a full-fledged server is simulated for use on a host device. Virtual servers perform the same roles as physical servers. They host websites and applications, work as databases, perform computations, and do even more. Multiple virtual servers run on one physical server and share the system resources. Servers can also be implemented as a load-balanced array where the VMs are shared between different host devices.
Server virtualization is offered by vendors like VMware, Nutanix, Xen, and Hyper-V. Organizations can consolidate their server architectures by replacing multiple physical servers with a virtualized cluster. A typical virtualized environment contains a host server, many virtual servers, and virtual data stores.
Virtual sprawl
Virtual sprawl is a situation where the virtual servers are using up too much of the host resources. The hypervisor can't allocate enough resources to all the VMs, and the other virtual servers experience performance issues because of resource scarcity. VM sprawl can occur because of the sheer number of virtual servers running on a host. It's easy to spin up VMs, but if you lose track of them, they'll keep on running in anonymity and drain your resources. Eliminating virtual sprawl ensures efficient performance.
In network virtualization, the functionalities of a network (routing, switching, and data transfers) are virtualized using hardware and software components. There are two types of network virtualization: external and internal.
External network virtualization
In this type, the same physical network is partitioned to form multiple virtual networks. An example of this is a virtual local area network (VLAN). Multiple VLANs share the same network devices, switches, routers, controllers, and access points. But they are virtually separated and act as different networks.
Another example of this type is a virtual private network (VPN). A VPN provides access to private local area networks (LANs) over the internet using tunneling and encryption protocols. In this case, the same LAN exists across network devices from multiple locations.
Internal network virtualization
Internal network virtualization simulates a network within a single host device using software. This server might contain multiple containers and other virtual instances. The network connections between them are simulated to form a virtual network. Virtual versions of hardware network devices like routers and switches are created.
Software-defined networking
Software-defined networking (SDN) is another application of network virtualization that is designed to make network operations faster and more efficient. In a traditional physical network, the network devices, like the routers and switches, individually perform control operations as well as data operations.
Control operations involve making the routing table, updating the topology, shaping traffic, etc. Data operations include receiving and transmitting data packets. In an SDN system, an SDN controller takes over the control operations, while the network devices are concerned with data transfers alone. Admins can use the controller to shape traffic according to their requirements.
Storage virtualization involves simulating logical storage units above physical storage. In storage virtualization, the individual storage units, like disks, are often pooled to form a storage network. This network is then managed using software. From a storage network, it's possible to create virtual storage units. Virtualization makes storage systems faster, more resilient, and more reliable.
Storage virtualization has multiple advantages over conventional storage systems. As the physical storage systems are pooled together, data can be migrated from one location to another while the virtual data unit remains the same. This means that data migration won't affect normal operations.
Similar to server virtualization, storage virtualization results in efficient storage usage as all the storage capacity is pooled together. Idle storage per disk is minimized. When storage is about to run out, you can add more heterogeneous storage devices to increase capacity. Instead of dealing with multiple storage devices with different capacities placed in different locations, IT admins handle uniform, neatly classified virtual storage units.
RAID
A redundant array of independent disks (RAID) is a storage virtualization technology where disks are combined to form a virtual storage unit. Multiple levels of RAIDs are available with varying levels of speed, capacity, fault tolerance, and reliability.
Storage area networks
A storage area network (SAN) is a dedicated network that connects storage devices, servers, and network devices together. A SAN is not connected to a LAN but has its own set of SAN switches to connect storage devices. SANs are accessed through a server that's known as the host layer.
A unified computing system (UCS) is a converged data center architecture that combines server virtualization, network virtualization, and storage virtualization. A UCS usually has a powered chassis with a cooling unit and slots to connect blade servers and rack servers. Virtual hosts can be connected to the server slots and interconnected with a virtualized network. A UCS can be connected to a SAN to provide virtualized storage capabilities.
A UCS allows data centers to be highly converged and efficient with massive reductions in cabling and space utilization. Cisco introduced the first UCS back in 2009, and it's the most popular UCS vendor in the market. UCSs have management software that can monitor and manage their operations.
Virtualization is a popular technology that has been adopted in multiple different ways to simulate different network components and services. Most network infrastructures worldwide have one or more kinds of virtualization technology. This is where virtualization monitoring becomes relevant.
Virtualization has some disadvantages that can cause problems for IT teams. Chief among them are the complexity of virtual systems and a lack of visibility over virtual components. Unlike physical devices that can be checked individually, VMs are logical units that have no physical distinction.
There's no way to monitor VMs without network monitoring software. Most virtualization vendors offer management software dedicated to their virtualization offering, but handling multiple virtual monitoring tools for all the components can be tedious. Unified virtualization monitoring software that can monitor virtual components just as well as physical components is exemplary.
ManageEngine OpManager is network monitoring software that is specialized for monitoring virtualized environments, whether servers, networks, storage units, or other virtualized components like UCSs. OpManager discovers virtual environments, collects performance metrics, analyzes them, and presents them to you in graphs and reports on a single, powerful console.
Let's discuss some of OpManager's virtualization monitoring capabilities:
OpManager provides visibility into virtualized infrastructure by discovering virtual hosts, VMs, data stores, and more and by listing them in a neatly classified inventory. By setting alerts, you can remain aware of events, issues, and performance declines in your systems.