What JMX monitoring enables
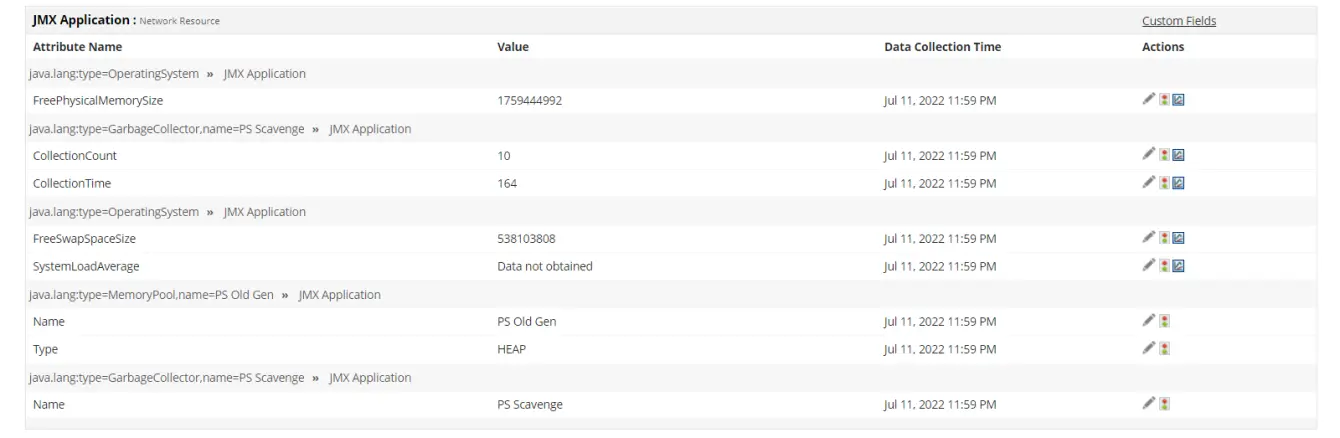
JMX is a built-in Java technology that allows developers and administrators to monitor and manage application components at runtime. Using Managed Beans (MBeans), it exposes performance data such as memory consumption, garbage collection, thread usage, and class loading.
When combined with a dedicated JMX monitoring tool like Applications Manager, these metrics become part of a continuous feedback system that supports proactive maintenance, automation, and optimization.
1. Real-time JVM visibility with JMX Monitoring
The biggest advantage of JMX monitoring is its ability to uncover what’s happening inside your JVM in real time. Rather than relying only on application-level metrics like request latency or error counts, you can monitor what drives those numbers internally.
With JMX monitoring, you can:
- Track heap and non-heap memory utilization.
- Observe garbage collection frequency and duration.
- Monitor thread counts, states, and contention points.
- Watch class loading and unloading activity.
This visibility helps teams spot trends such as growing heap usage or rising GC pause times early, allowing you to optimize JVM configurations before performance issues reach users.
2. Faster troubleshooting and root cause analysis
Every minute spent diagnosing an issue in production can cost valuable time and user trust. JMX monitoring streamlines troubleshooting by providing context-rich data that pinpoints the root cause faster.
- If response times spike, check thread activity or connection pool utilization instantly.
- If the system becomes unresponsive, analyze blocked threads or resource contention via MBeans.
- For recurring issues, use JMX data to spot leaks, misconfigured caches, or unoptimized GC settings.
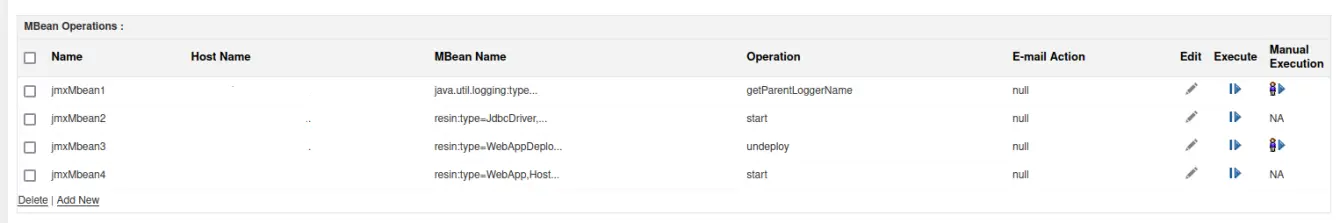
Applications Manager enhances this process by enabling MBean operations and automated recovery actions.
3. Aligning JVM metrics with business KPIs
JMX monitoring allows you to expose custom application or business-level metrics alongside JVM data. Developers can create custom MBeans that report KPIs such as:
- Active sessions and transaction throughput
- Cache hit ratios
- Message queue depth
- Failed login or payment attempts
This helps correlate technical performance with business outcomes and improve Java application reliability.
4. Long-term insights for capacity planning
Historical JMX metrics reveal memory allocation rates, GC trends, and thread growth patterns, which aid in accurate capacity forecasting and performance tuning.
- Anticipate when resources hit limits.
- Plan JVM scaling strategies.
- Optimize tuning parameters for sustained performance.
- Justify infrastructure upgrades with evidence-based metrics.
5. Automation and self-healing with JMX
Modern JMX monitoring solutions support automation. Using Applications Manager, you can set up workflows that react to anomalies:
- Restart thread pools when capacity is reached.
- Run cleanup scripts when heap usage exceeds thresholds.
- Trigger diagnostics automatically during anomalies.
6. Reliability and end-user experience
JMX monitoring improves user satisfaction by preventing JVM-level bottlenecks before they impact performance. Continuous observation reduces downtime and keeps applications responsive under load.
Key advantages include:
- Early detection of memory leaks and thread bottlenecks.
- Reduced downtime through proactive alerts.
- Optimized performance under high load conditions.
- Better user satisfaction due to consistent response times.
Reliable applications lead to stronger customer trust and lower operational costs. With JMX monitoring, you’re not just reacting to problems, you’re preventing them.
7. Scalable JMX Monitoring for cloud and microservices
JMX is ideal for hybrid and cloud environments. Applications Manager supports agentless data collection across multiple JVM instances, simplifying Java application performance monitoring in microservices architectures.
Benefits for scaling environments:
- Works across multiple JVM instances and services.
- Requires minimal reconfiguration as your system grows.
- Optimized performance under high load conditions.
- Integrates easily with centralized observability platforms.
Applications Manager offer agentless JMX data collection, letting you manage multiple JVMs from one unified dashboard, ideal for microservices or hybrid deployments.
8. Unified technical and business observability
JMX monitoring bridges infrastructure and business visibility. With both JVM and application-specific metrics accessible in one dashboard, developers, operations, and stakeholders can collaborate better.
Unified visibility means:
- Developers understand how JVM tuning affects throughput.
- Operations teams see which bottlenecks affect key transactions.
- Business stakeholders can view metrics that reflect customer experience.
This shared perspective leads to faster decisions and better collaboration between technical and non-technical teams.
Best practices for effective JMX monitoring
- Monitor key JVM metrics: memory, threads, GC.
- Expose relevant custom MBeans.
- Secure your JMX ports with SSL and authentication.
- Correlate JMX data with logs and traces.
- Set up anomaly detection and alerts.
These practices ensure that JMX monitoring evolves from basic metric tracking into a comprehensive performance management strategy.
ManageEngine Applications Manager offers all of this with intuitive dashboards and minimal setup effort.
Ready to see how it works? Download a free 30-day trial of ManageEngine Applications Manager now!


