Application performance management (APM) is an important process that involves monitoring, measuring, and optimizing application performance to ensure desired service quality and user satisfaction. This involves constant tracking of applications for their performance as well as effectively addressing any issues that may arise for enhanced business operations.
The APM acronym also stands for application performance monitoring, which again is a part of application performance management. While application performance monitoring focuses on proactive monitoring and detecting performance issues, application performance management takes a more comprehensive approach to managing and optimizing an application's performance from start to finish to achieve successful business results. In short, monitoring is a subset of management when it comes to tracking application performance.
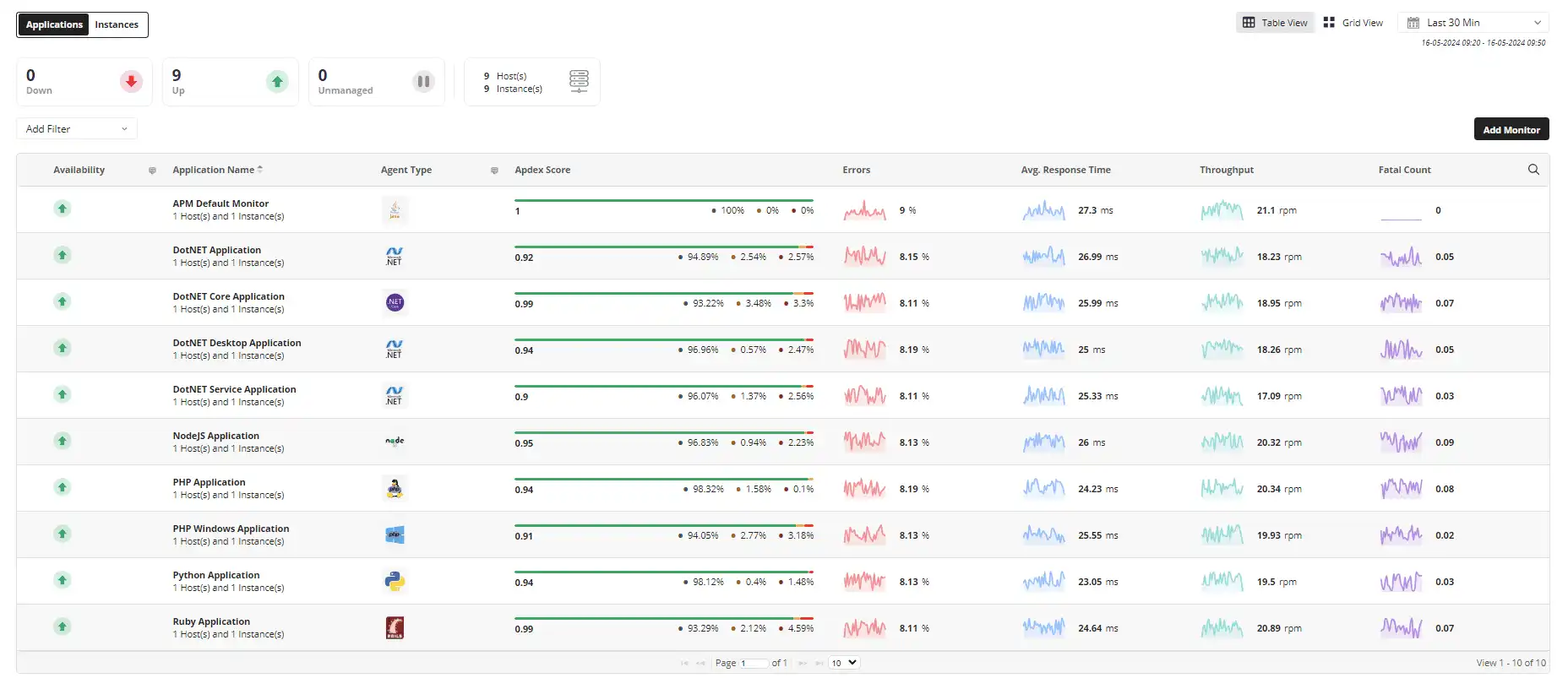
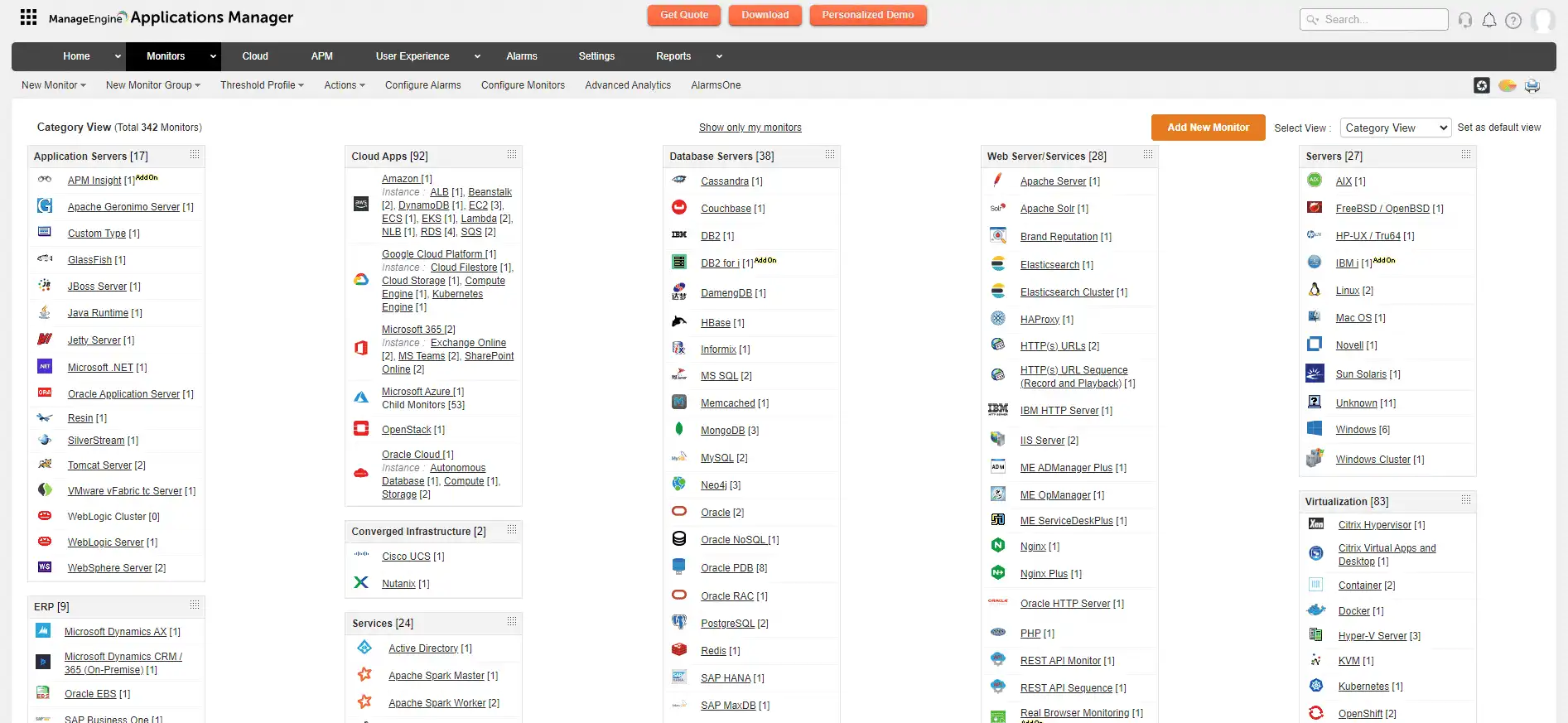
To effectively manage application performance, it is crucial to have a comprehensive view of your application's performance from start to finish. This means monitoring and analyzing every aspect of the application, from the user interface to the backend infrastructure. By having a holistic understanding of your application's performance, you can identify and address any issues that may arise, optimize performance, and ultimately provide a better experience for your users. Here are some of the core components involved in APM:
Evaluating the efficiency of your application is crucial for optimizing its performance and enhancing business operations. Post application development and deployment, continuous performance monitoring is necessary to swiftly detect and address any issues that may arise. Real-time information about the application's internal functioning can significantly improve the precision of business outcomes. Tracking individual transactions, database calls, thread profiles, and error reports can help identify and fix any slowdowns. Analyzing the connections between various application components with the help of automated service maps can also greatly facilitate problem-solving and issue resolution before they impact business operations.
Many companies use a variety of systems to support their applications, such as servers, databases, networks, application servers, and more. As businesses embrace the onset of cloud and latest technology platforms, infrastructure monitoring now encompasses a collection of virtualized environments, cloud infrastructure, microservices, and containers. Gaining deep understanding of the workings of these components helps ensure the application's performance needs are met and problems can be identified and resolved promptly, leading to improved performance, capacity planning, and cost control.
Ensuring a positive user experience is essential for business application success. Monitoring the frontend, alongside understanding the backend, ensures a seamless experience. Neglecting the frontend can lead to frustrated users, lower satisfaction, and reduced retention. By monitoring a web application's real user experience and back-end performance (by simulating user actions, tracking page URLs, monitoring APIs, etc.), businesses can gain real-time insights into user engagement from various locations, improve customer loyalty, reduce costs, and increase revenue.
In a fast-changing business environment, efficient application performance management requires understanding the interdependencies between infrastructure elements. This involves gaining a comprehensive view of how resources and infrastructure elements are interconnected within an application. By consistently discovering applications, creating dependency maps, and updating them with newly-discovered resources, organizations can ensure a seamless user experience by proactively identifying and resolving potential issues before they escalate, minimizing downtime.
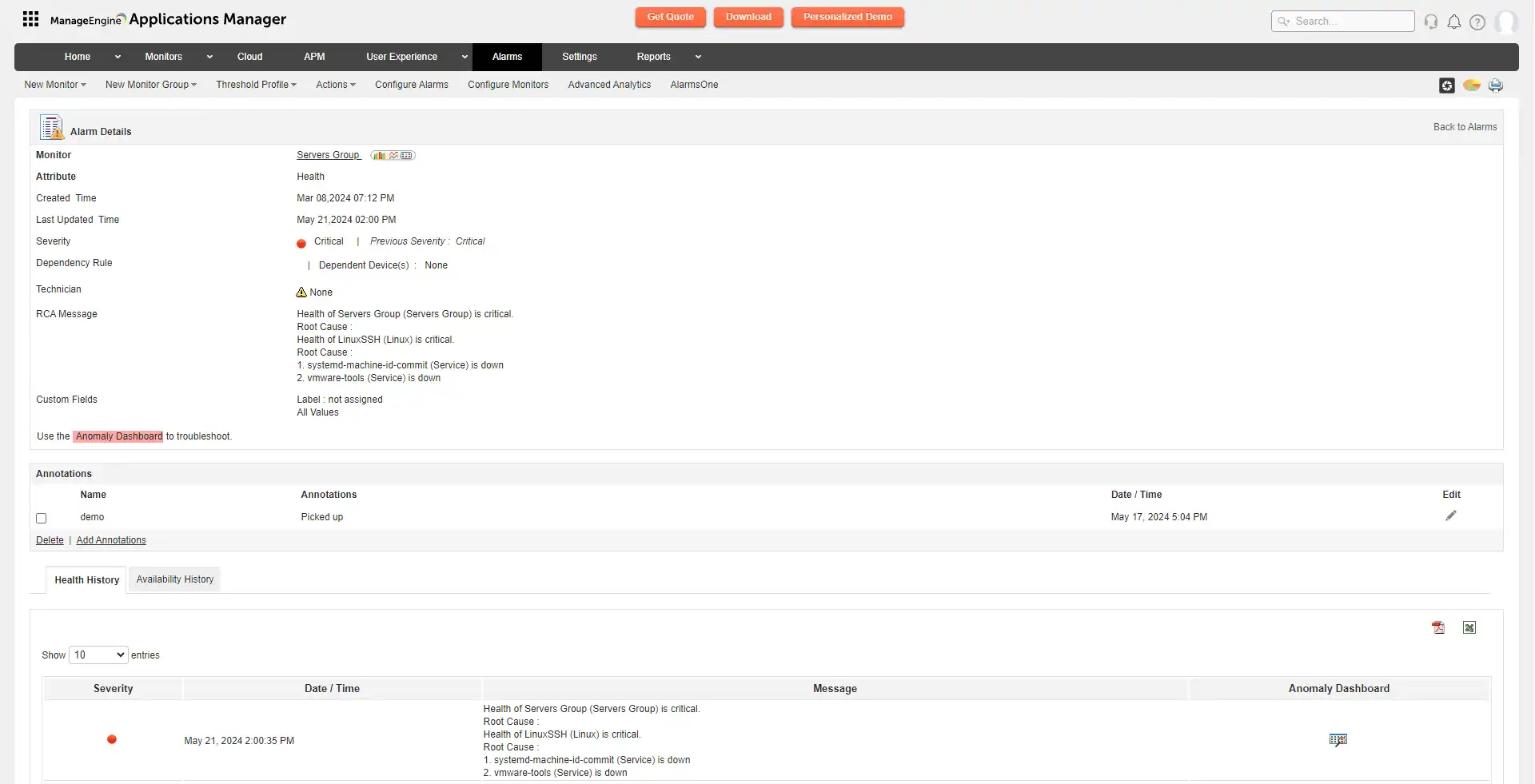
Obtaining real-time alerts is a crucial requirement of APM to detect performance issues and application downtime. These alerts should have configurable thresholds for individual metrics and the overall application at the granular level. Receiving notifications via multiple channels such as email, SMS, Slack messages, along with ITSM tool integrations like ServiceNow, ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus enables admins for quick issue troubleshooting. Additionally, they should have the ability to perform pre-configured, automated actions like running scripts, restarting virtual machines, or executing MBean operations, which can facilitate faster troubleshooting and resolution of any issues that may arise.
Obtaining in-depth performance analytics of your application infrastructure is crucial to enable you to track and measure the performance of your applications over time. While monitoring your entire application stack can help you a lot in performance tracking, gaining deep insights into how your application is performing with respect to different application components can provide a complete understanding on how your application infrastructure is actually performing, especially when your application operates in a hybrid or microservices architecture. This can help you identify potential areas of improvement, forecast application performance, and detect complex issues right on time.
At first glance, APM and observability may seem alike since they both involve gathering data from multiple sources and offering performance insights. However, APM focuses primarily on debugging of applications, whereas observability delivers an understanding of applications.
APM monitors what is happening within a specific application and its backend system calls, but lacks the broader context of the entire system. Observability provides a broader context and understanding of how different components and services interact. In addition, observability provides a comprehensive understanding of the technical elements impacting application performance. By analyzing and correlating logs, metrics, and traces, it identifies the underlying cause of performance issues and helps troubleshoot complex problems in dynamic system environments.
ManageEngine Applications Manager serves as the robust tool for monitoring your business infrastructure by providing the following capabilities:
An APM solution offers valuable insights into application performance, empowering IT and DevOps administrators to effectively manage the availability, performance, and end-user interactions. By swiftly pinpointing any potential problems, APM tools effectively minimize downtime, resulting in a smooth and efficient software experience for end-users.
APM has two expansions and they are:
As technology advances and customer expectations grow, businesses are adopting microservices and cloud-native architectures to enhance application performance and stay competitive. This approach involves building application components as microservices and using distributed infrastructure like containers, VMs, serverless, or cloud applications. This allows for independent scaling and reduces the impact of technology interruptions on daily business activities, revenue, and brand reputation.
To ensure high performance for applications, it's crucial to have deep visibility into their components, from the frontend to the backend. This real-time observability helps in identifying and addressing issues before they impact end-users, providing a seamless digital experience. Since modern applications have a complex and dynamic structure, APM is crucial to keep your applications running and functioning at their best. It is critical since applications typically represent the brand. Without an APM tool, it might be strenuous to locate issues and resolve them which rises the likelihood of a poor end user experience. It can also reduce operational costs, and increase revenue and sales.
Following are some of the challenges observed in APM:

It allows us to track crucial metrics such as response times, resource utilization, error rates, and transaction performance. The real-time monitoring alerts promptly notify us of any issues or anomalies, enabling us to take immediate action.
Reviewer Role: Research and Development
Trusted by over 6000+ businesses globally