Understanding the basics: How JMX works
Java Management Extensions (JMX) is a built-in framework that allows you to monitor and manage Java applications at runtime. It exposes critical JVM information like memory usage, garbage collection, thread counts, and class loading through Managed Beans (MBeans).
When connected to a monitoring tool such as Applications Manager, these MBeans become a continuous data source that helps you:
- Visualize performance metrics.
- Detect bottlenecks and anomalies.
- Trigger alerts and automated responses.
However, to collect this data securely and efficiently, JMX needs to be configured properly.
Step 1: Enabling JMX monitoring in your environment
Before you can start tracking JVM metrics, your Java application needs to have JMX enabled.
Most modern Java applications include a JMX agent by default. This agent exposes metrics that can be accessed by authorized tools like Applications Manager, over a network port.
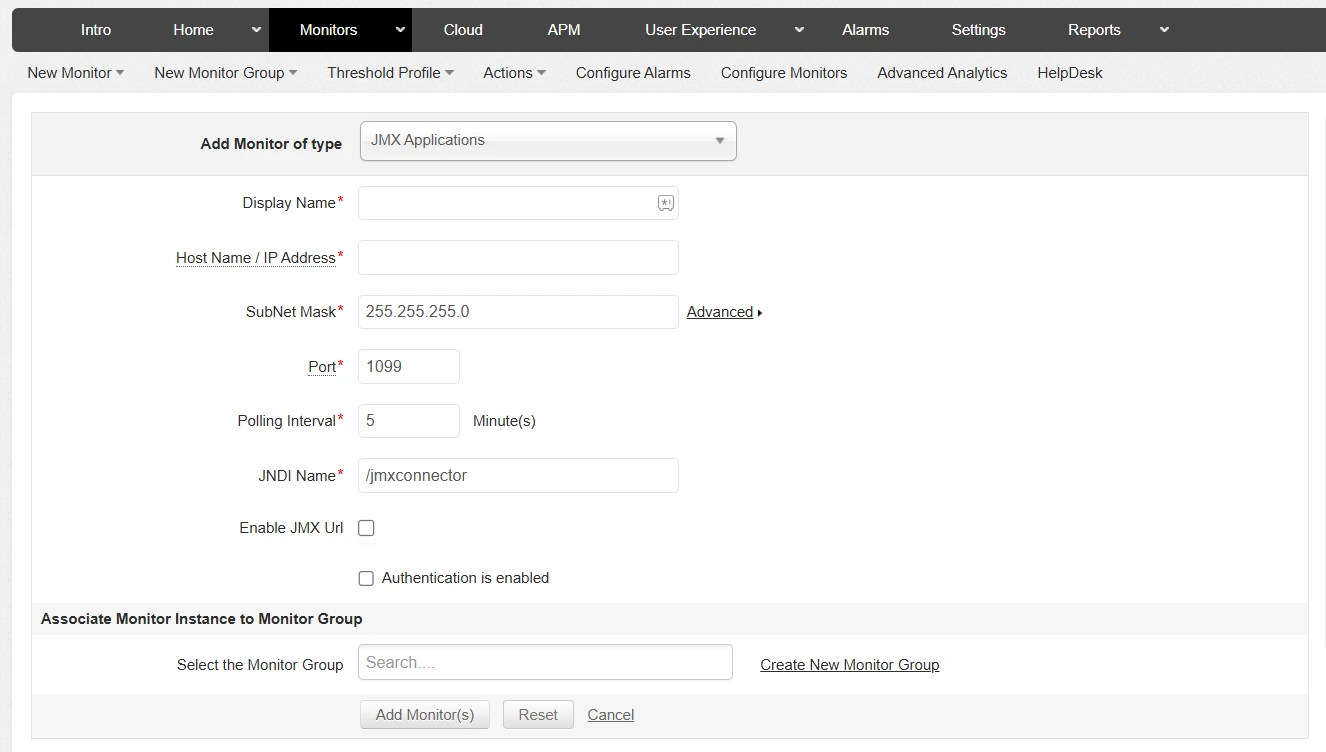
In Applications Manager, you simply need to add a new JMX monitor and specify the following:
- The host name or IP address of your Java application.
- The JMX port through which the JVM exposes its metrics.
- Optional authentication details if security is enabled.
Applications Manager then automatically connects to the JMX interface, fetches MBean attributes, and displays them as easy-to-read performance graphs and dashboards.
Step 2: Understanding agents and their role
You might often hear the term agent in the context of JMX. Simply put, the agent is what enables your Java application to be “visible” to monitoring tools.
There are two main types of JMX agents:
- Local agent: Runs inside the JVM and collects metrics locally. Ideal for monitoring on the same host.
- Remote agent: Allows monitoring tools (like Applications Manager) to connect from a different host using a TCP/IP port.
Applications Manager can work with either approach. When you add a new JMX monitor, the tool communicates with the agent to:
- Discover all available MBeans.
- Retrieve JVM and application-level metrics.
- Display them on performance dashboards.
- Trigger alerts when thresholds are breached.
You don’t have to manually install or configure separate agents when using Applications Manager. The built-in support for JMX makes the setup quick and straightforward.
Step 3: Configuring JMX ports
Every JMX-enabled JVM listens on one or more ports for incoming connections. Think of the port as a “doorway” through which Applications Manager accesses the performance data.
Why ports matter
When you configure a JMX monitor, you’ll need to specify the correct port so Applications Manager can establish communication with the JVM. By default, Java assigns a random RMI (Remote Method Invocation) port for JMX communication, but in production environments, using fixed ports is always better.
Best practices for port configuration
- Use a fixed JMX port: This makes firewall configuration easier and avoids conflicts when multiple JVMs run on the same host.
- Keep ports unique: Assign a different JMX port for each JVM instance.
- Restrict access: Ensure only your Applications Manager server can connect to the JMX port.
In containerized or cloud setups, make sure these ports are exposed through secure internal networks rather than the public internet.
Step 4: Securing JMX connections
Since JMX gives access to sensitive runtime information and, in some cases, allows administrative operations, security is non-negotiable.
Here are three key aspects of securing your JMX setup:
1. Authentication
Enable authentication to ensure that only authorized users or tools can connect to your JMX interface. Applications Manager supports secure connections by allowing you to configure username and password credentials when creating a JMX monitor. This ensures that even if the port is open, only authenticated requests from trusted tools can access metrics.
2. Encryption
To prevent data interception, it’s a good practice to encrypt communication between your JVM and Applications Manager. This is usually done by enabling SSL (Secure Socket Layer) on your JMX connection. With SSL enabled, all data such as metric values or credentials, travels securely over the network. If your organization already uses encrypted communications, your network or application teams can help you configure JMX SSL settings to align with existing security policies.
3. Network-level restrictions
Limiting who can connect to the JMX port adds another layer of security. You can:
- Allow access only from the Applications Manager host.
- Restrict JMX access to internal IPs or subnets.
- Use firewalls, VPNs, or private network routes instead of exposing the port publicly.
Step 5: Verifying and testing the configuration
Once JMX monitoring is configured, testing your setup ensures everything is working correctly.
In Applications Manager:
- Navigate to Add Monitor → Java/JMX Monitor.
- Enter the hostname, JMX port, and credentials (if applicable).
- Click Test Credentials.
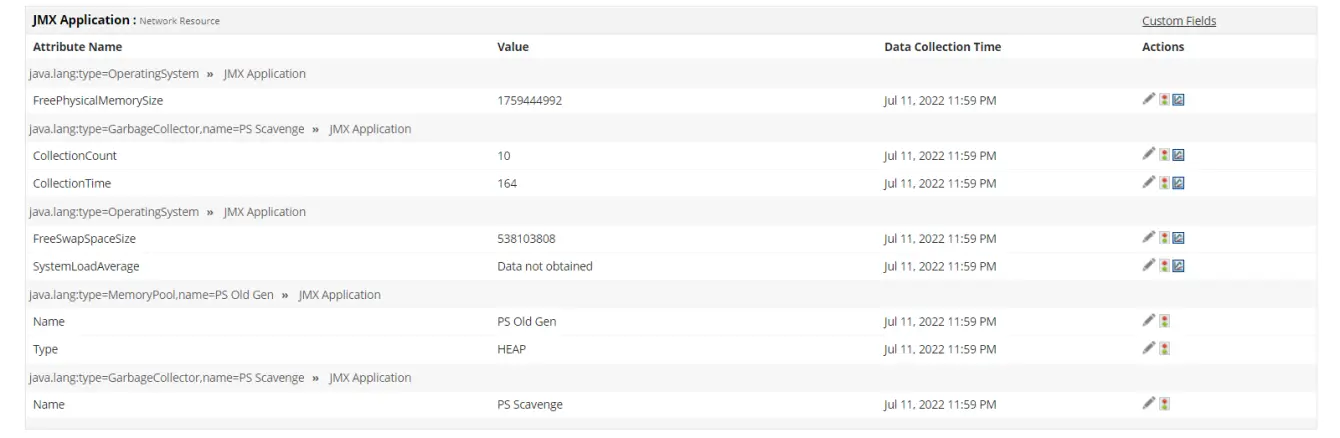
If the connection succeeds, Applications Manager automatically discovers all available MBeans and begins polling metrics. You’ll soon see dashboards with JVM performance graphs, including:
- Heap and non-heap memory usage
- Garbage collection activity
- Thread statistics
- Class loading details
- Custom MBeans if your application exposes them
If the test fails, double-check that:
- The JMX port is open and reachable from the Applications Manager server.
- Authentication details are correct.
- Firewall rules allow communication.
Step 6: Applying security best practices
Beyond initial setup, maintaining a secure and reliable JMX environment requires ongoing attention. Here are some key recommendations:
- Rotate credentials periodically to prevent unauthorized access.
- Limit permissions by giving read-only access wherever possible.
- Monitor JMX access logs for unusual connection attempts.
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) in Applications Manager to ensure only authorized administrators can add or modify JMX monitors.
- Regularly review port configurations and remove unused or unnecessary open ports.
Following these guidelines helps maintain a healthy balance between visibility and security.
Step 7: Monitoring JVM health and business metrics together
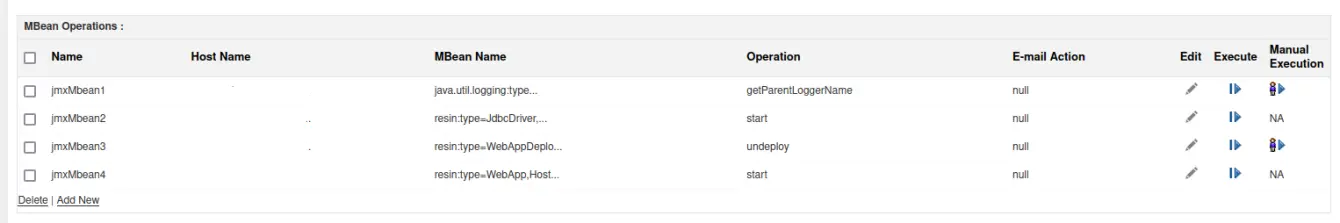
One of the unique advantages of using Applications Manager is that it not only tracks JVM metrics but also helps you monitor custom MBeans.
Your development team can expose application-specific metrics, such as transaction counts, queue sizes, or active sessions through custom MBeans. Applications Manager automatically detects and visualizes these metrics alongside JVM data, offering a complete view of both system and business performance.
Step 8: Automating alerts and actions
After configuration, the next step is automation. In Applications Manager, you can set up threshold-based alerts to receive notifications whenever key JVM parameters like memory usage or thread counts, cross critical limits.
Additionally, you can configure automated corrective actions, such as restarting a service or clearing cache, to respond to issues without manual intervention.
This automation layer turns JMX monitoring from a passive data source into an active performance management tool that helps maintain uptime and reliability.
Common configuration scenarios
Here are a few examples of real-world JMX monitoring setups in Applications Manager:
| Scenario | Setup | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring a local Java app | Use default JMX agent and local host connection | Simple and fast setup |
| Monitoring a remote JVM | Configure a fixed JMX port and connect over network | Secure with authentication |
| Monitoring multiple JVMs | Assign distinct JMX ports for each instance | Avoid port conflicts |
| Cloud or containerized app | Use internal service networking | Restrict external exposure |
| Secure enterprise setup | Enable SSL and firewall restrictions | Recommended for production |
Configure in minutes!
Setting up JMX monitoring doesn’t have to be complicated. With the right configuration and a robust tool like Applications Manager, you can monitor your Java applications with precision, security, and confidence.
By correctly configuring agents, ports, and security settings, you ensure that your JMX monitoring environment remains reliable, scalable, and secure, giving you actionable insights into JVM performance and business operations.
Ready to see how it works? Download a free 30-day trial of ManageEngine Applications Manager now!


