In this page:
Log360 Cloud offers multiple storage tiers for efficient managing, flexible retention, and cost reduction. This multi-tiered storage option lets you apply different retention policies across the collected data. Each storage tier lets you specify what type of logs can be stored and how they need to be cleaned up. Each tier can be customized with its own retention period, log types, sources, and filtering criteria, making it possible to retain important logs for longer durations while minimizing the storage of less relevant or high-volume logs.
This approach helps organizations control storage consumption and prioritize critical logs without compromising on cost or performance. Log360 Cloud also offers you detailed statistical analysis of log trends across tiers.
The following capabilities form the core of the storage management system in Log360 Cloud:
Storage Tiers allow you to define separate log retention strategies for different types of logs. Instead of applying a single policy across all data, you can create up to twenty custom tiers, each with its own configuration for log types, sources, retention periods, and optional filters, such as log severity levels, host IP, and device name.
Each tier supports two types of retention:
Log360 Cloud includes the following built-in tiers:
You can address this by:
Storage Tiers can be edited, disabled, cleaned, or deleted (except built-in ones). Any changes apply only to newly collected logs. If a tier is disabled, logs are routed to the next matching tier or the default tier. Existing logs within a disabled tier are retained until their retention period ends.
Storage Tiers help you retain important logs for longer durations and purge high-volume or less relevant logs early, resulting in better control over storage.
To help visualize how storage is consumed across different tiers, Log360 Cloud offers detailed usage insights through the Stats Analysis view. You can track storage trends over time, identify high-volume log sources, and analyze which log types are contributing most to overall storage usage.
Statistics can be filtered by storage tier, log type, and log source. The visual graphs display both log size and log count, based on the time logs were received rather than the original timestamp of the log event.
You can filter using a custom date range, with a maximum limit of 365 days. For Default and Custom Storage Tiers, Top Log Sources and Top Log Types tabs help identify the devices or event categories contributing most to storage consumption. For Alerts and Correlation Storage Tiers, the respective Top Profiles and Top Rules tabs highlight alert profiles or correlation rules generating the most log volume. This visibility allows administrators to adjust retention policies, apply filters, or reassign logs to more appropriate tiers for better storage optimization.
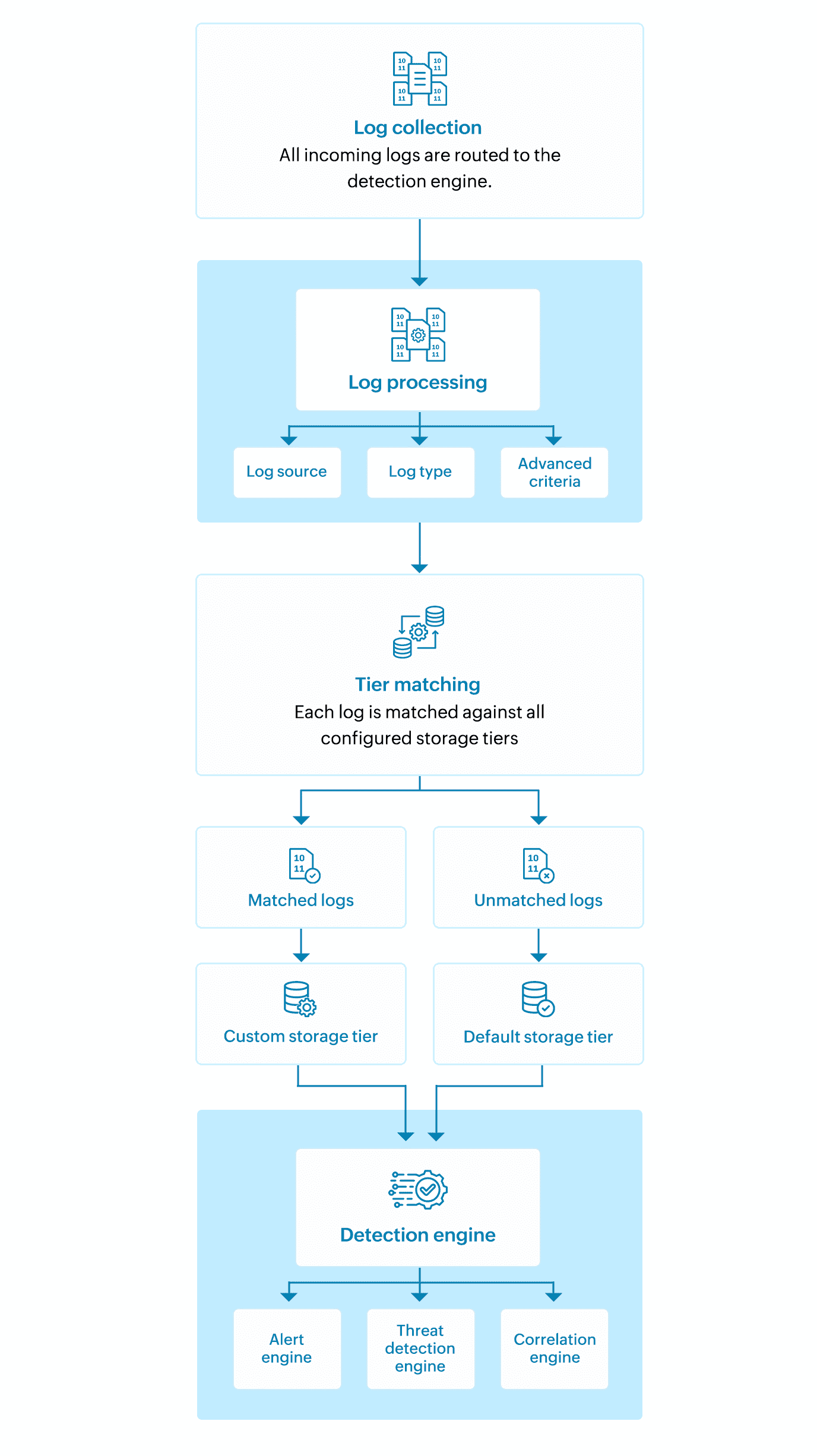
The workflow starts with the collection of incoming logs, which are then analyzed by the detection engine and assigned to storage tiers based on specific criteria to ensure efficient storage and processing.
Log360 Cloud's storage tiering capabilities enable IT and security teams to manage log data intelligently, control retention at scale, and reduce overall storage overhead without compromising on visibility or compliance. These capabilities help teams:
Read also
This document detailed the key features and operational benefits of Storage Tiers in Log360 Cloud. To learn how to configure and manage these capabilities in your environment, refer to the following articles: