 Learn more about OpManager's features & functions Network topology, or network architecture, refers to the layout or organization of a network. Mapping and understanding the network topography is a critical part of network administration, monitoring, and management. It can help network administrators in the following ways:
Learn more about OpManager's features & functions Network topology, or network architecture, refers to the layout or organization of a network. Mapping and understanding the network topography is a critical part of network administration, monitoring, and management. It can help network administrators in the following ways:Without a topology view, IT teams don’t truly know what is connected to what. Devices, interfaces, and links exist in isolation, leading to blind spots that can result in unknown or rogue devices and unused or misconfigured connections. In virtualized environments, this challenge is amplified by VM sprawl—virtual machines are frequently created, cloned, moved, or retired without corresponding updates to network documentation. As a result, teams lose visibility into orphaned or inactive VMs consuming resources, VM-to-VM dependencies, east–west traffic flows, and how virtual networks map to the underlying physical infrastructure. This lack of end-to-end visibility across physical and virtual layers increases operational risk and makes networks harder to manage as they scale.
When issues occur without a topology view, teams rely on logs, alerts, and manual checks—reactive approaches that slow down troubleshooting. Network engineers often spend valuable time figuring out where to start, significantly increasing mean time to resolution (MTTR). What should take minutes can stretch into hours. A comprehensive topology view provides an at-a-glance understanding of affected devices, interfaces, or locations, enabling teams to act quickly and resolve issues faster.
A single core device failure can trigger dozens or even hundreds of alerts from dependent devices. Without topology intelligence, these alerts are treated as separate incidents, making it difficult to identify the root cause. Critical issues often get buried under alert noise, leading to alert fatigue and missed priorities that delay response and recovery.
Without clear visibility into network dependencies, even basic impact assessment during an outage becomes challenging. IT teams struggle to quickly determine which applications are affected, which users or business services are at risk, and whether the issue is localized or widespread. This lack of clarity delays prioritization and results in vague, reactive communication with business stakeholders, reducing confidence in IT operations.
In the absence of a shared visual reference, collaboration between NOC teams, network engineers, and application owners becomes fragmented. Each team views the environment through different tools and perspectives, leading to slower handovers, longer escalations, and increased confusion during incidents. A shared topology map provides a common context that improves coordination and speeds up resolution.
When traffic paths and interconnections are not visible, capacity planning becomes reactive. Bottlenecks remain hidden until performance degrades, while redundant links stay underutilized. Infrastructure decisions are often based on assumptions rather than data, leading to higher costs, inefficient resource usage, and inconsistent network performance over time.
In hybrid and distributed environments, the absence of topology visibility results in fragmented monitoring across on-premises, cloud, and remote locations. Tracing end-to-end traffic paths becomes difficult, especially when applications span multiple environments. This increases the risk of misconfigurations, delays troubleshooting, and raises the likelihood of outages. As networks grow more distributed, operating without a unified topology view becomes increasingly complex and risky.
ManageEngine OpManager is robust, real-time network topology tool with topography mapping capabilities trusted by more than one million network administrators across the globe. Its most prominent network topology features include:
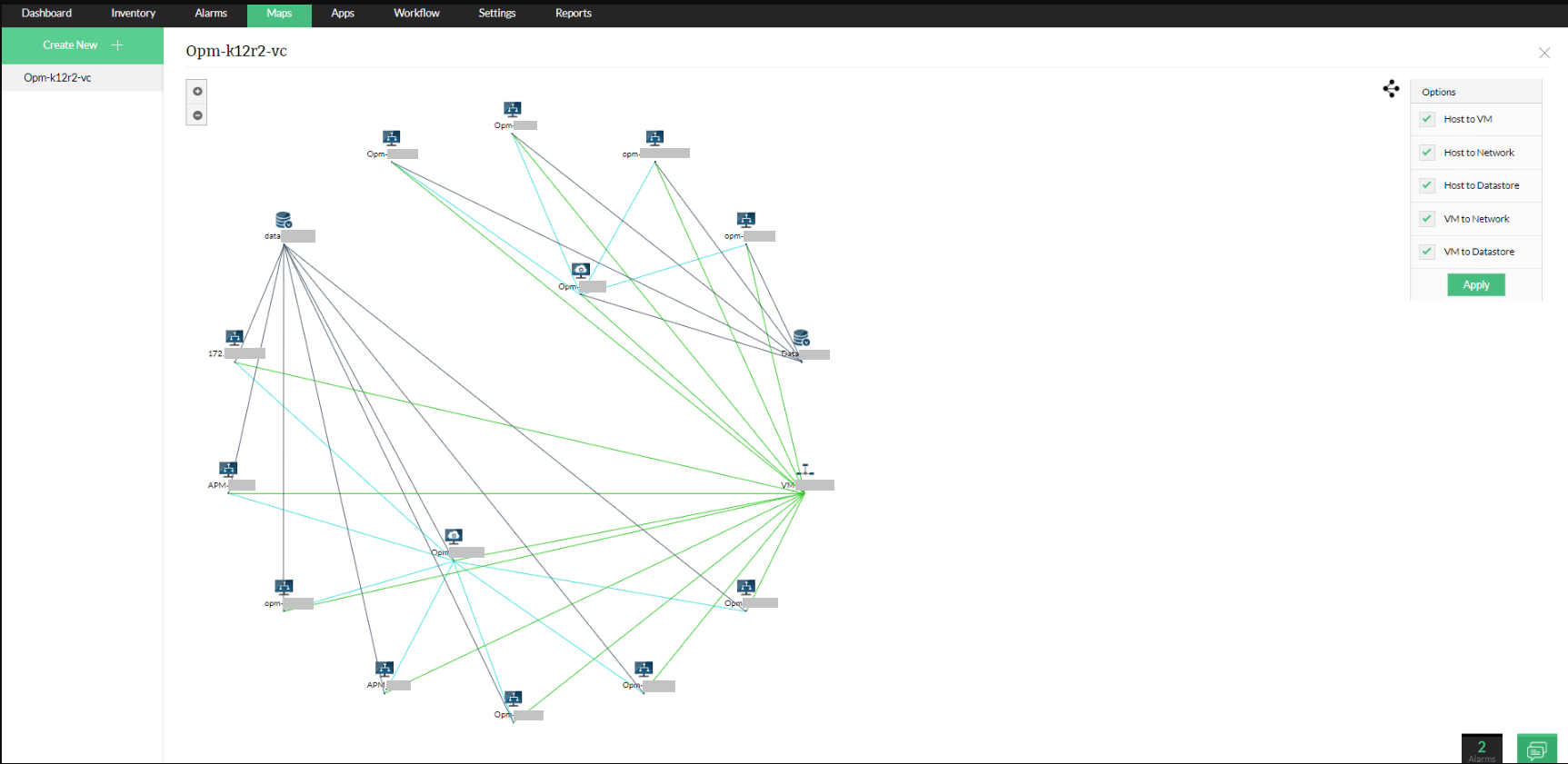
As a network topology diagram software, OpManager's network topology capabilities aren't just limited to physical topology mapping—they can also provide a visual map of the organization of your virtual infrastructure including VMware, hypervisors, Xen and Nutanix devices. OpManager's network diagram software also allows network administrators to selectively view host to VM, host to network, host to datastore, VM to network, and VM to datastore connections.
Effective network visualization is fundamental to reliable IT operations, and OpManager’s Organization Maps are designed to provide that through a single, real-time view of your entire IT ecosystem. OpManager’s Organization Maps provide a holistic, real-time view of your entire network topology, enabling IT teams to instantly understand how devices, servers, and applications are interconnected and detect issues faster. By visually mapping real-world dependencies across network, server, and application layers, teams no longer need to trace relationships during performance issues manually.
For example, in a data center hosting mission-critical applications like ERP or CRM, Organization Maps visually group each application with its backend servers, switches, firewalls, and storage in the exact order they interact. When performance degrades or a component fails, the affected device is immediately highlighted on the map using color-coded alerts, allowing teams to pinpoint the precise layer causing the issue within seconds. This end-to-end visibility eliminates dashboard hopping, reduces dependency blind spots, accelerates root-cause analysis, and significantly cuts down resolution time, helping enterprises prevent prolonged outages.
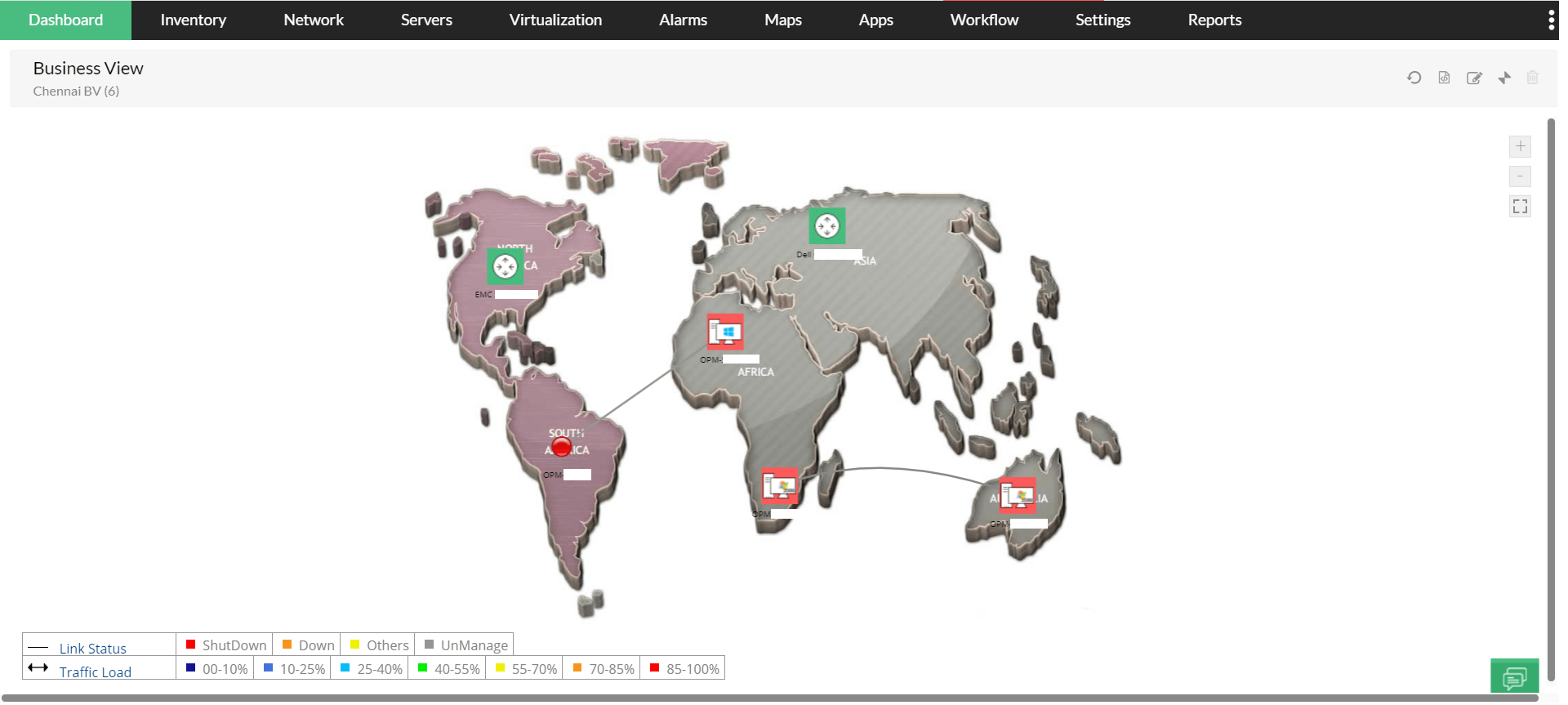
OpManager's Business Views is a powerful topology visualization feature that enables network administrators to easily categorize, visualize, and manage devices based on business needs; understand the larger impact whenever devices run into downtime; and isolate, prioritize, and troubleshoot faults based on business criticality of the devices affected.With Business Views, network administrators can view the real-time status of a device and its interfaces that are connected to the other devices, and also set custom backgrounds for different views.
An additional capability enables network admins to place Business views within Business Views. With this advanced feature, they can gain a more detailed view of the network topography, and understand why a network device in a custom topography runs into issues.
Want to learn how OpManager's network mapping capabilities can help simplify network management in your organization? Request a free demo now.